
by Adam Hartung | Jul 11, 2018 | Computing, Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Software
The last few quarters sales growth has not been as good for Apple as it once was. The iPhone X didn’t sell as fast as they hoped, and while the Apple Watch outsells the entire Swiss watch industry it does not generate the volumes of an iPhone. And other new products like Apple Pay and iBeacon just have not taken off.
Amidst this slowness, the big winner has been “Apple Services” revenue. This is largely sales of music, videos and apps from iTunes and the App store. In Q2, 2018 revenues reached $9.2B, 15% of total revenues and second only to iPhone sales. Although Apple does not have a majority of smartphone users, the user base it has spends a lot of money on things for Apple devices. A lot of money.
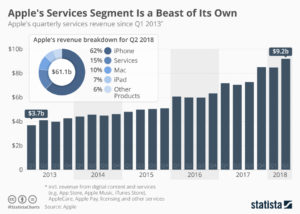 In a bit of “get them the razor so they will buy the razor blades” CEO Tim Cook’s Apple is increasingly relying upon farming the “installed base” of users to drive additional revenues. Leveraging the “installed base” of users is now THE primary theme for growing Apple sales. And even old-tech guys like Warren Buffett at Berkshire Hathaway love it, as they gobble up Apple shares. As do many analysts, and investors. Apple has paid out over $100B to developers for its services, and generated over $40B in revenues for itself – and with such a large base willing to buy things developers are likely to keep providing more products and working to grow sales.
In a bit of “get them the razor so they will buy the razor blades” CEO Tim Cook’s Apple is increasingly relying upon farming the “installed base” of users to drive additional revenues. Leveraging the “installed base” of users is now THE primary theme for growing Apple sales. And even old-tech guys like Warren Buffett at Berkshire Hathaway love it, as they gobble up Apple shares. As do many analysts, and investors. Apple has paid out over $100B to developers for its services, and generated over $40B in revenues for itself – and with such a large base willing to buy things developers are likely to keep providing more products and working to grow sales.
But the risks here should not be taken lightly. At one time Apple’s Macintosh was the #1 selling PC. But it was “closed” and required users buy their applications from Apple. Microsoft offered its “open architecture” and suddenly lots of new applications were available for PCs, which were also cheaper than Macs. Over a few years that “installed base” strategy backfired for Apple as PC sales exploded and Mac sales shrank until it became a niche product with under 10% market share.
Today, Android phones are the #1 smartphone market share platform, and Android devices (like the PC) are much cheaper. Even cheaper are Chinese made products. Although there are problems, the risk exists that someday apps, etc for Android and/or other platforms could become more standard and the larger Android base could “flip” the market.
The history of companies relying on an installed base to grow their company has not gone well. Going back 30 years, AM Multigraphics an ABDick sold small printing presses to schools, government agencies and businesses. After the equipment sale these companies made most of their growth on the printing supplies these presses used. But competitors whacked away at those sales, and eventually new technologies displaced the small presses. The installed base shrank, and both companies disappeared.
Xerox would literally give companies a copier if they would just pay a “per click” charge for service on the machine, and use Xerox toner. Xerox grew like the proverbial weed. Their service and toner revenue built the company. But then people started using much cheaper copiers they could buy, and supply with cheaper consumables. And desktop publishing solutions caused copier use to decline. So much for Xerox growth – and the company rapidly lost relevance. Now Xerox is on the verge of disappearing into Fuji.
HP loved to sell customers cheap ink-jet printer so they bought the ink. But now images are mostly transferred as .jpg, .png or .pdf files and not printed at all. The installed base of HP printers drove growth, until the need for any printing started disappearing.
The point? It is very risky to rely on your installed platform base for your growth. Why? Because competitors with cheaper platforms can come along and offer cheaper consumables, making your expensive platform hard to keep forefront in the market. That’s the classic “innovator’s dilemma” – someone comes along with a less-good solution but it’s cheaper and people say “that’s good enough” thus switching to the cheaper platform. This leaves the innovator stuck trying to defend their expensive platform and aftermarket sales as the market switches to ever better, cheaper solutions.
It’s great that Apple is milking its installed base. That’s smart. But it is not a viable long-term strategy. That base will, someday, be overtaken by a competitor or a new technology. Like, maybe, smart speakers. They are becoming ubiquitous. Yes, today Siri is the #1 voice assistant. But as Echo and Google speaker sales proliferate, can they do to smartphones what smartphones did to PCs? What if one of these companies cooperates with Microsoft to incorporate Cortana, and link everything on the network into the Windows infrastructure? If these scenarios prevail, Apple could/will be in big trouble.
I pointed out in October, 2016 that Apple hit a Growth Stall. When that happens, maintaining 2% growth long-term happens only 7% of the time. I warned investors to be wary of Apple. Why? Because a Growth Stall is an early indicator of an innovation gap developing between the company’s products and emerging products. In this case, it could be a gap between ever enhanced (beyond user needs) mobile devices and really cheap voice activated assistant devices in homes, cars, offices, everywhere. Apple can milk that installed base for a goodly while, but eventually it needs “the next big thing” if it is going to continue being a long-term winner.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 27, 2018 | In the Swamp, Innovation, Investing, Manufacturing, Transportation, Trends
On Monday, Harley Davidson, America’s leading manufacturer of motorcycles, announced it was going to open a plant in Europe.
Ostensibly this is to counter tariffs the EU will be imposing on its products if imported from the USA. President Trump reacted vociferously on Tuesday, threatening much bigger taxes on Harley if it brings to the USA any parts or motorcycles from its offshore plants in Brazil, Australia, India or Thailand. He also intimated that Harley Davidson was likely to collapse.
Lots of heat, not much light. The issues for Harley Davidson are far worse than an EU tariff.
Harley Davidson has about 1/3 of the US motorcycle market. But in “heavy motorcycles,” those big bikes that are heavier and generally considered for longer riding, Harley has half the market. Which sounds great, until you realize that until the 1970s, Harley had 100% of that market. Ever since then, Harley has been losing share – to imports and to its domestic competitor Polaris.
It was 2006 when I first wrote about Harley Davidson’s big demographic problem. Basically, its customers were all aging. Younger people were buying other motorcycles, so the “core” Harley customer was getting older every year. From mid-30s in the 1980s, by the year 2000 the average buyer was well into their mid-40s. In 2007, I pointed out that Harley had made a stab at changing this dynamic by introducing a new motorcycle with an engine made by Porsche, and a far more modern design (the V-Rod.) But Harley wasn’t committed to building a new customer base, so when dealers complained that the V-Rod “wasn’t really a Harley” the company backed off the marketing and went back to all its old ways of doing business.
Simultaneously, Harley Davidson motorcycle prices were rising faster than inflation, while Japanese manufacturers were not. Thus, as I also pointed out in 2007, it was struggling to maintain market share. Slower sales caused a lay-off that year, and despite the brand driving huge sales of after-market products like jackets and T-shirts, which had grown as big as bike sales, it was unclear how Harley would slow the aging of its customer base and find new, younger buyers. Harley simply eschewed the trend toward selling smaller, lighter, cheaper bikes that had more appeal to more people – and in more markets.
Globally, the situation is far more bleak than the USA. America has one of the lowest motorcycle ridership percentages on the globe. Americans love cars. But in more congested countries like across Europe or Japan and China, and in much poorer countries like India, Korea, and across South America motorcycles are more popular than automobiles. And in those countries Harley has done poorly. Because Harley doesn’t even have the smaller 100cc,200cc, 400cc and 600cc bikes that dominate the market. For example, in 2006 (I know, old, but best data I could find) Harley Davidson sold 349,200 bikes globally. Honda sold 10.3 million. Yamaha sold 4.4 million. Even Suzuki sold 3.1 million – or 10 times Harley’s production.
But, being as fair as possible, let’s focus on Europe – where the new Harley plant is to be built. And let’s look exclusively at “heavy motorcycles” (thus excluding the huge market in which Harley has no products.) In 2006, Harley was 6th in market share. BMW 16%, Honda 15%, Yamaha 15%, Suzuki 15%, Kawasaki 11% and Harley Davidson 9%. Wow, that is simply terrible.
Clearly, Harley has already become marginalized globally. Outside the USA, Harley isn’t even relevant. The Japanese and Germans have been much more successful everywhere outside the USA, and every one of those other markets is bigger than the USA. Harley was simply relying on its core product (big bikes) in its core market (USA) and seriously failing everywhere else.
Oh, but even that story isn’t as good as it sounds. Because in the USA sales of Harley motorcycles has been declining for a decade! Experts estimate that every year which passes, Harley’s customer base ages by 6 months. The average rider age is now well into their 50s. Since Q3, 2014 Harley’s sales growth has been negative! In Q2 and Q3 2017 sales declines were almost 10%/quarter!
As its customer demographic keeps working against it, new customers for big bikes are buying BMWs from Germany – and Victory and Indian motorcycles made by Polaris, out of Minnesota (Polaris discontinued the Victory brand end of 2017.) BMW sales have increased for 7 straight quarters, and their European sales are growing stronger than ever – directly in opposition to Harley’s sales problems. Every quarter Indian is growing at 16-20%, taking all of its sales out of Harley Davidson USA share.
Going back to my 2016 column, when I predicted Harley was in for a hard time. Shares hit an all-time high in 2006 of $75. They have never regained that valuation. They plummeted during the Great Recession, but bailout funds from Berkshire Hathaway and the US government saved Harley from bankruptcy. Shares made it back to $70 by 2014, but fell back to $40 by 2016. Now they are trading around $40. Simply put, as much as people love to talk about the Harley brand, the company is rapidly becoming irrelevant. It is losing share in all markets, and struggling to find new customers for a product that is out-of-date, and sells almost exclusively in one market. Its move to manufacture in Europe is primarily a Hail-Mary pass to find new sales, paid for by corporate tax cuts in the USA and tariff tax avoidance in Europe.
But it won’t likely matter. Like I said in 2006, Harley Davidson is a no-growth story, and that’s not a story where anyone should invest.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 20, 2018 | Boards of Directors, Growth Stall, Investing, Manufacturing, Strategy
An American epoch has ended. General Electric was part of the first ever Dow Jones Index in 1896. When the Dow Jones Industrial Average was formed in 1907 GE was a participant. GE has been the only company to remain on the index. All other original companies long ago completely disappeared.
GE did so well because its leadership had been able to constantly change the company to keep it relevant, and growing. During the century prior to hiring Jeff Immelt as CEO GE went from light bulbs to generating electricity and making all kinds of electrical infrastructure equipment, electric locomotives, mainframe computers, medical equipment, computer services, financial services, entertainment…. The list is very long.
Although not all GE CEOs were great, the Board was able to place CEOs in office who could sense market shifts and make good decisions. GE leadership thoughtfully analyzed markets, and made investment decisions to sell businesses that were not growing. And they made investment decisions to invest in trends which created growth. One of the best of these was Jack Welch, who developed the nickname “Neutron Jack” for his willingness to jettison businesses that were not growing and leading their industry, while willingly investing in entirely new growth markets where trends showed high rates of return like financial services and entertainment – wildly “non-industrial” markets.
But CEO Immelt was completely tone-deaf to the outside world. He was wholly unable to understand how to lead a team that could make good investments. Instead under Immelt’s leadership GE over-invested in historical products where they were losing advantage but trying to “keep up.” Selling businesses that were growing but faced stiff competition, rather than investing in growth. And refusing to invest in new external growth opportunities that could keep revenues increasing – and drive a higher GE market capitalization.
All the way back in 2009 I pointed out that GE was in a Growth Stall, and had only a 7% chance of consistently growing at 2%. I warned investors. At the time I said GE had to go all-out on a growth strategy, or things would turn ugly. But a lot of investors, employees – and apparently the Board of Directors – were ready to blame the Growth Stall on the economy. And blame it on Welch, who had been gone for 8 years. And say GE was lucky Immelt saved the company from bankruptcy with a loan from Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway.
Say what? Saved the company? Why did Immelt, and the Board, let GE get into such terrible shape? It was time to replace the CEO, not double down on his failed strategy.
Six years ago, May, 2012, I published in Forbes “5 CEOs that Should Have Already Been Fired.” At the time I said Immelt was the 4th worst CEO in America. I cited the 2009 column, and pointed out things really weren’t any better in 2012 than in 2009. That column had well over 1million reads. There was no way GE’s board was not aware of the column, and the realization that Immelt was a horrible CEO.
The Board of #3 (Walmart) fired Mike Duke. And the Board of #1 (Microsoft) fired Steve Ballmer. There is no real board at #2 Sears (which will file bankruptcy soon enough) because the CEO is also the largest shareholder (via his hedge fund) and he controls all board decisions. He should have fired himself, but had too much ego. But the board of GE – well it did nothing. Even though GE almost went bankrupt under Immelt, and its value was being destroyed quarter after quarter it left him in place.
I revisited the performance of these five CEOs and their companies in August, 2014 and reminded hundreds of thousands of readers – which I’m sure included GE’s Board of Directors – that company revenues had declined every year since 2009. And this string of failures had caused the company’s value to decline by 2/3. Yet, the board did nothing to replace this horrific CEO.
By March, 2017 I was so exasperated I finally titled my column “GE Needs a New Strategy and a New CEO.” Again, I detailed all the things that went wrong. It took 7 more months before the Board pushed Immelt out. But the new CEO failed to offer a better strategy, continuing to promote the notion of selling businesses to raise cash to “fix” the broken businesses – without identifying any growth strategy at all.
The only thing that can “fix” GE – save it from being dismembered and sold off – is a growth strategy. I offered how the new CEO could undertake this effort in October, 2017. But the Board, still wholly incompetent, still isn’t listening. Nobody should be surprised that GE is now removed from the Dow, and the new CEO is clearly without a clue how to find a path back to relevancy.
Too bad for investors, employees, suppliers, customers and the communities where the GE businesses reside. This didn’t have to happen. But due to an incompetent Board of Directors, which did nothing to properly govern an incompetent CEO, it did. And there’s little doubt it won’t be long before GE meets the same end as DuPont.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 5, 2018 | Investing, Retail, Strategy, Trends, Web/Tech
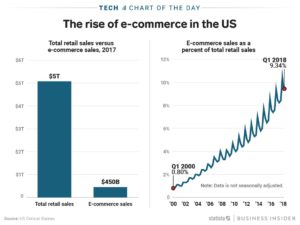
The US e-commerce market is just under 10% the size of entire retail market. On the face of it this would indicate that the game is far from over for big traditional retail. After all, how could such a small segment kill profits for such a huge industry based on enormous traditional players?
Yet, Sears – once a Dow Jones component and the world’s most powerful retailer – has announced it will close 100 more stores. The Kmart/Sears chain is now only 894 stores – down from thousands at its peak and 1,275 just last year. Revenue dropped 30% versus a year ago, and quarterly losses of $424M were almost 15% of revenues.
But, that ignores marginal economics. It often doesn’t take a monster change in one factor to have a huge impact on the business model. Let’s say Sales are $100. Less Cost of Goods sold of $75. That leaves a Gross Margin of $25. Selling, General and Administrative costs are 20%, so Operating Income is only $5. The Net Margin before Interest and Taxes is 5%. (BTW, these are the actual percentages of Walmart from 1/31/18.)
Now, in comes a new competitor – like Amazon.com. They have no stores, no store clerks, and minimal inventory due to “e-storefront” selling. So, they are able to lower prices by 5%. That seems pretty small – just a 5% discount compared to typical sales of 20%, 30% even 50% (BOGO) in retail stores. Amazon’s 5% price reduction seems like no big deal to established firms.
But, Walmart has to lower prices by 5% in response, which lowers revenues to $95. But the stores, clerks, inventory, distribution centers and trucks all largely remain. With Cost of Goods Sold still $75, Gross Margin falls to $20. Fixed headquarters costs, general and administrative costs don’t change, so they remain at $20. This leaves Operating Income of …$0.
(For more detailed analysis see “Bigger is Not Always Better – Why Amazon is Worth More than Walmart” from July, 2015.)
How can Walmart survive with no profits? It can’t. To get some margin back, Walmart has to start shutting stores, selling assets, cutting pay, using automation to cut headcount, beating on vendors to offer them better prices. This earns praise as “a low cost operation.” When in fact, this makes Walmart a less competitive company, because it’s footprint and service levels decline, which encourages people to do more shopping on-line. A vicious circle begins of trying to recapture lost profitability, while sales are declining rather than growing.
Walmart was (and is) huge. Even Sears was much bigger than Amazon.com at the beginning. But to compete with Amazon.com both had to lower prices on ALL of their products in ALL of their stores. So the hit to Walmart’s, and Sears’, revenue is a huge number. Though Amazon.com was a much, much smaller company, its impact explodes on the larger competitor P&L’s.
This disruption is felt across the entire industry: ALL traditional retailers are forced to match Amazon and other e-commerce companies, even though there is no way they can cut costs enough to compete. Thus, Toys-R-Us, Radio Shack, Claire’s and Bon-Ton have declared bankruptcy in 2018, and the once great, dominant Sears is on the precipice of extinction.
All of which is good news for Amazon.com investors. Amazon.com has 40% market share of the entire e-commerce business. The fact that e-commerce is only 10% of all retail is great news for Amazon investors. That means there is still an enormously large market of traditional retail available to convert to on-line sales.
The shift to e-commerce will not be stopping, or even slowing. Since January, 2010 the future has been easily predictable for traditional retail’s decline. The next few years will see a transition of an additional $2.5 trillion on-line, which is 5X the size of the existing e-commerce market!
As stores close new competitors will emerge in the e-commerce market. But undoubtedly the big winner will be the company with 40% market share today – Amazon.com. So what will Amazon’s stock be worth when sales are 5x larger (or more) and Amazon can increase profits by making leveraging its infrastructure and slow future investments?
Twenty years ago, Amazon was a retail ant. And retail elephants ignored it. But that was foolish, because Amazon had a different business model with an entirely different cost of operations. And now the elephants are falling fast, due to their inability to adapt to new market conditions and maintain their growth.
_________________________________________________________________________
Author’s Note: In June, 2007 I was asked to predict WalMart’s future. Here are the predictions I made 11 years ago:
- “In 5 years (2012) Walmart would not have succeeded internationally” [True: Mexico, China, Germany all failed]
- “In 5 years (2012) Walmart would no new businesses, and its revenue will be stalled” [True]
- In 5 years (2012) Walmart would be spending more on stock repurchases then investing in its own stores or distribution” [True – and the Walton’s were moving money out of Walmart to other investments]
- “In 10 years (2017) Walmart would take a dramatic act, and make an acquisition” [True: Jet.com]
- “In 10 years (2017 Walmart’s value would not keep up with the stock market” [from 6/2007 to 6/2017 WMT went from $48 to $75 up 56.25%, DIA went from $134 to $180 up 34.3%, AMZN went from $70 to $1,000 up 1,330% or 13.3x]
- “In 30 years (2037) Walmart will only be known as “a once great company, like General Motors”

by Adam Hartung | May 22, 2018 | Innovation, Investing, Marketing, Software, Web/Tech
(Image: Troy Strange.)
Facebook’s CEO recently took a drubbing by America’s Congresspeople. And some thought it bode poorly for the internet giant. There were rumors of customer defections, and fears that privacy issues would sink the company. The stock dropped from a February high of $193 to a March low of $152 – down more than 20%.
But by mid-May Facebook had recovered to $186, and the concerns seemed largely ignored. As they should have been.
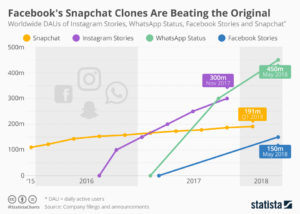
Facebook is much more than Facebook. As of January, 2018 Facebook had 2.1M monthly active users (MAUs,) 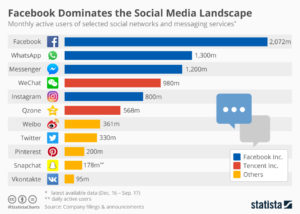 the most of all social media sites. But Facebook also owns the second most popular site WhatsApp with 1.3M MAUs, and the third most popular site Facebook Messenger with 1.2M MAUs, and the fifth most popular site Instagram with 800K MAUs. Instagram is 5 times larger than Snapchat. And Facebook Stories, which just started in 2017 is now almost as big as Snapchat and surely in the top 10. So, 5 of the top 10 social media sites are owned by Facebook, and they totally dominate the marketplace.
the most of all social media sites. But Facebook also owns the second most popular site WhatsApp with 1.3M MAUs, and the third most popular site Facebook Messenger with 1.2M MAUs, and the fifth most popular site Instagram with 800K MAUs. Instagram is 5 times larger than Snapchat. And Facebook Stories, which just started in 2017 is now almost as big as Snapchat and surely in the top 10. So, 5 of the top 10 social media sites are owned by Facebook, and they totally dominate the marketplace.
Facebook paid $1B for Instagram in 2012 though it had no revenues. Today, 1/3 of ALL USA mobile users use Instagram. 15 million businesses are registered on Instagram. In 2017 Instagram had $3.6B revenues, and projections for 2018 are $6.8B.
Facebook expands globally
Facebook paid $19B for WhatsApp in 2014, when it had just $15M in revenues. In 2015, WhatsApp had 1 billion users. It is the most used app on the planet – even though not a top app in the USA where mobile texting is generally free. Where texting is expensive, like India, over 90% of mobile users utilize WhatsApp, and users typically send over 1,000 messages/month. In 2017, WhatsApp revenue rose to $1B, and in 2018 it will cross over $2B.
 Facebook is smart at realizing new ways people can use the platform. It adds functionality constantly, exponentially growing the user base and time spent on its sites. It is untouchable in its social media market domination. And it has proven, more than any other platform (compare Snapchat and Twitter) that it can monetize users into revenues and profits. Facebook’s leadership is constantly in touch with trends and keeps making social media more relevant in the lives of every person.
Facebook is smart at realizing new ways people can use the platform. It adds functionality constantly, exponentially growing the user base and time spent on its sites. It is untouchable in its social media market domination. And it has proven, more than any other platform (compare Snapchat and Twitter) that it can monetize users into revenues and profits. Facebook’s leadership is constantly in touch with trends and keeps making social media more relevant in the lives of every person.
Unless you somehow think time will go backward, you have to recognize that social media – like all other personal technology – is constantly becoming more useful. It is gaining greater adoption, and more usage. And businesses are using social media to reach customers, thus paying for access, like they once did for newspapers, radio, television and then web sites.
Just the beginning…
Facebook is just getting started, sort of like Amazon did 20 years ago. That’s the Amazon that dominates on-line e-commerce sales. If you bought Amazon on the IPO 21 years ago (May, 2017) your investment would have risen from $18/share to $1,700 – a nearly 1,000-fold increase. Facebook’s IPO was 6 years ago (May, 2012) at $38 – 6 years later it is worth $185, almost a 5-fold increase. Not bad. But if Facebook performs like Amazon in the next 14 years it could rise to $3,600 – an almost 20x gain.
And that’s why you should ignore short–term blips like the Congressional investigation and realize that you, and everyone else, is a Facebook customer. And you want to share in that growth by being a Facebook shareholder.
(Featured image adapted from Troy Strange.)

by Adam Hartung | May 8, 2018 | Computing, Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Software, Trends, Web/Tech
One in five American homes with wifi now has an Amazon Alexa. And the acceptance rate is growing. To me that seems remarkable. I remember when we feared Google keeping all those searches we did. Then the fears people seemed to have about Facebook knowing our friends, families and what we talked about. Now it appears that people have no fear of “big brother” as they rapidly adopt a technology into their homes which can hear pretty near everything that is said, or that happens.
It goes to show that for most people, convenience is still incredibly important. Give us mobile phones and we let land-lines go, because mobile is so convenient – even if more expensive and lower quality. Give us laptops we let go of the traditional office, taking our work everywhere, even at a loss of work-life balance. Give us e-commerce and we start letting retailers keep our credit card information, even if it threatens our credit security. Give us digital documents via Kindle, or a smart device on the web grabbing short articles and pdf files, and we get rid of paper books and magazines. Give us streaming and we let go of physical entertainment platforms, choosing to download movies for one-time use, even though we once thought “owning” our entertainment was important.
With each new technology we make the trade-off between convenience and something we formerly thought was important. Such as quality, price, face-to-face communications, shopping in a store, owning a book or our entertainment – and even security and privacy. For all the hubbub that regulators, politicians and the “old guard” throws up about how important these things were, it did not take long for these factors to not matter as convenience outweighed what we used to think we wanted.
Now, voice activation is becoming radically important. With Google Assistant and Alexa we no longer have to bother with a keyboard interface (who wants to type?) or even a small keypad – we can just talk to our smart device. There is no doubt that is convenient. Especially when that device learns from what we say (using augmented intelligence) so it increasingly is able to accurately respond to our needs with minimal commands. Yes, this device is invading our homes, our workplaces and our lives – but it is increasingly clear that for the convenience offered we will make that trade-off. And thus what Alexa can do (measured in number of skills) has grown from zero to over 45,000 in just under 3 years.
And now, Amazon is going to explode the things Alexa can do for us. Historically Amazon controlled Alexa’s Skills market, allowing very few companies to make money off Alexa transactions. But going forward Amazon is monetizing Alexa, and developers can keep 70% of the in-skill purchase revenues customers make. Buy a product or service via Alexa and developers can now make a lot of money. And, simultaneously, Amazon is offering a “code-free” skills developer, expanding the group of people who can write skills in just minutes. In other words, Amazon is setting off a gold rush for Alexa skills development, while simultaneously making the products remarkably cheap to own.
This is horrible news for Apple. Apple’s revenue stagnated in 2016, declining year over year for 3 consecutive quarters. I warned folks then that this was a Growth Stall, which often implies a gap is developing between the company and the market. While Apple revenues have recovered, we can now see that gap. Apple still relies on iPhone and iPad sales, coupled with the stuff people buy from iTunes, for most of its revenue and growth. But many analysts think smartphone sales may have peaked. And while focusing on that core, Apple has NOT invested heavily in Siri, its voice platform. Today, Siri lags all other voice platforms in quality of recognition, quality of understanding, and number of services. And Apple’s smart speaker sales are a drop in the ocean of Amazon Echo and Echo Dot sales.
By all indications the market for a lot of what we use our mobile devices for is shifting to voice interactivity. And Apple is far behind the leader Amazon, and the strong #2 Google. Even Microsoft’s Cortana quality is considered significantly better than Siri. If this market moves as fast as the smartphone market grew it will rob sales of smartphones and iTunes, and Apple could be in a lot of trouble faster than most people think. Relevancy is a currency quickly lost in the competitive personal technology business.
by Adam Hartung | Apr 25, 2018 | Entertainment, Film, Innovation, Investing, Retail
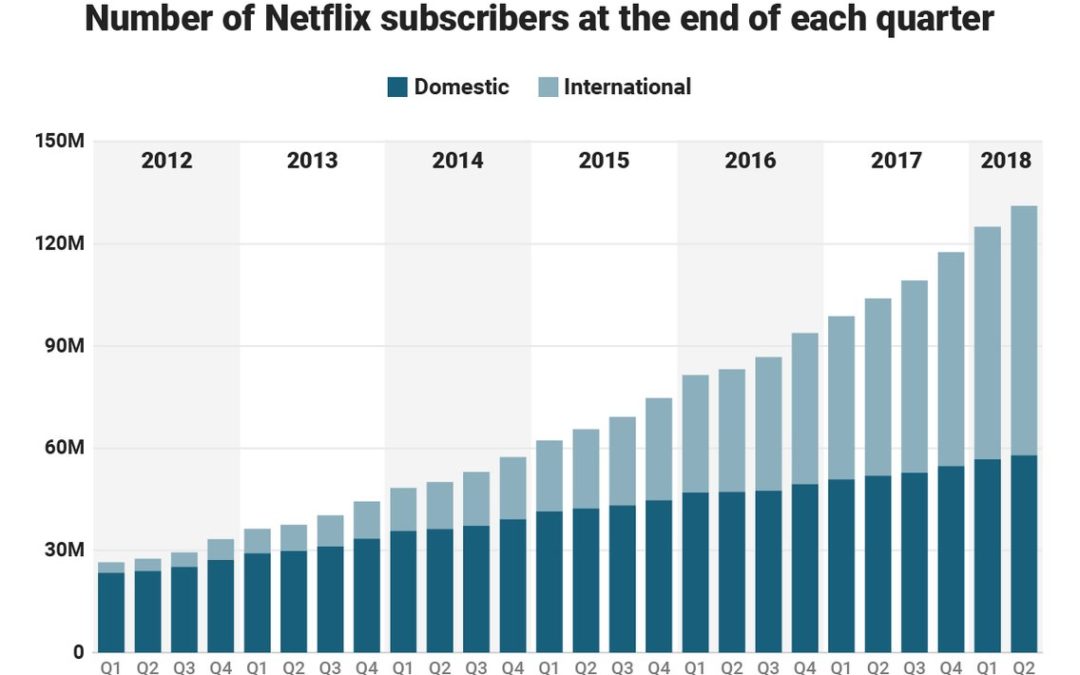
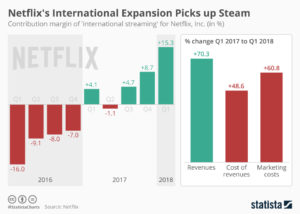
Netflix announced new subscriber numbers last week – and it exceeded expectations. Netflix now has over 130 million worldwide subscribers. This is up 480% in just the last 6 years – from under 30 million. Yes, the USA has grown substantially, more than doubling during this timeframe. But international growth has been spectacular, growing from almost nothing to 57% of total revenues. International growth the last year was 70%, and the contribution margin on international revenues has transitioned from negative in 2016 to over 15% – double the 4th quarter of 2017.
Accomplishing this is a remarkable story. Most companies grow by doing more of the same. Think of Walmart that kept adding stores. Then adding spin-off store brand Sam’s Club. Then adding groceries to the stores. Walmart never changed its strategy, leaders just did “more” with the old strategy. That’s how most people grow, by figuring out ways to make the Value Delivery System (in their case retail stores, warehouses and trucks) do more, better, faster, cheaper. Walmart never changed its strategy.
But Netflix is a very different story. The company started out distributing VHS tapes, and later DVDs, to homes via USPS, UPS and Fedex. It was competing with Blockbuster, Hollywood Video, Family Video and other traditional video stores. It won that battle, driving all of them to bankruptcy. But then to grow more Netflix invested far outside its “core” distribution skills and pioneered video streaming, competing with companies like DirecTV and Comcast. Eventually Netflix leaders raised prices on physical video distribution, cannibalizing that business, to raise money for investing in streaming technology. Streaming technology, however, was not enough to keep growing subscribers. Netflix leadership turned to creating its own content, competing with moviemakers, television and documentary producers, and broadcast television. The company now spends over $6B annually on content.
Think about those decisions. Netflix “pivoted” its strategy 3 times in one decade. Its “core” skill for growth changed from physical product distribution to network technology to content creation. From a “skills” perspective none of these have anything in common.
Could you do that? Would you do that?
How did Netflix do that? By focusing on its Value Proposition. By realizing that it’s Value Proposition was “delivering entertainment” Netflix realized it had to change its skill set 3 times to compete with market shifts. Had Netflix not done so, its physical distribution would have declined due to the emergence of Amazon.com, and eventually disappeared along with tapes and DVDs. Netflix would have followed Blockbuster into history. And as bandwidth expanded, and global networks grew, and dozens of providers emerged streaming purchased content profits would have become a bloodbath. Broadcasters who had vast libraries of content would sell to the cheapest streaming company, stripping Netflix of its growth. To continue growing, Netflix had to look at where markets were headed and redirect the company’s investments into its own content.
This is not how most companies do strategy. Most try to figure out one thing they are good at, then optimize it. They examine their Value Delivery System, focus all their attention on it, and entirely lose track of their Value Proposition. They keep optimizing the old Value Delivery System long after the market has shifted. For example, Walmart was the “low cost retailer.” But e-commerce allows competitors like Amazon.com to compete without stores, without advertising and frequently without inventory (using digital storefronts to other people’s inventory.) Walmart leaders were so focused on optimizing the Value Delivery System, and denying the potential impact of e-commerce, that they did not see how a different Value Delivery System could better fulfill the initial Walmart Value Proposition of “low cost.” The Walmart strategy never took a pivot – and now they are far, far behind the leader, and rapidly becoming obsolete.
Do you know your Value Proposition? Is it clear – written on the wall somewhere? Or long ago did you stop thinking about your Value Proposition in order to focus your intention on optimizing your Value Delivery System?
That fundamental strategy flaw is killing companies right and left – Radio Shack, Toys-R-Us and dozens of other retailers. Who needs maps when you have smartphone navigation? Smartphones put an end to Rand McNally. Who needs an expensive watch when your phone has time and so much more? Apple Watch sales in 2017 exceeded the entire Swiss watch industry. Who needs CDs when you can stream music? Sony sales and profits were gutted when iPods and iPhones changed the personal entertainment industry. (Anyone remember “boom boxes” and “Walkman”?)
I’ve been a huge fan of Netflix. In 2010, I predicted it was the next Apple or Google. When the company shifted strategy from delivering physical entertainment to streaming in 2011, and the stock tanked, I made the case for buying the stock. In 2015 when the company let investors know it was dumping billions into programming I again said it was strategically right, and recommended Netflix as a good investment. And I redoubled my praise for leadership when the “double pivot” to programming was picking up steam in 2016. You don’t have to be mystical to recognize a winner like Netflix, you just have to realize the company is using its strategy to deliver on its Value Proposition, and is willing to change its Value Delivery System because “core strength” isn’t important when its time to change in order to meet new market needs.

by Paul F | Apr 12, 2018 | E-Commerce, Ecommerce, Investing, Retail
President Trump has been bashing Amazon of late. And Amazon is down about 12.5% since peaking on March 12, 2018. Simultaneously the DJIA fell 10% from 1/26/18 thru 4/3/18, so it is hard to discern if Amazon’s pullback has more to do with market conditions and trade war fears or Presidential bashing. Amazon’s performance has been only slightly worse than the Dow. Anyway, one would think that if the President is right and Amazon plays unfairly, the future would bode well for Walmart.
That is very unlikely. Since peaking on January 29, just after the Dow, Walmart crashed 32% by April 3. Over the last month the stock has stabilized, but unfortunately the signs are not good for Walmart investors.
 Walmart leadership has never shown a keen understanding of e-commerce, nor a commitment to making Walmart a leading market competitor. You might counter that Walmart’s acquisition of Jet.com showed a strong commitment. But we now know that amidst the minimalistic hype, Walmart actually cheated when providing its e-commerce results. And when Walmart hired a former Tesco executive to lead Jet.com’s grocery sales effort, the news was not splashed front page. Rather it was hidden in an internal email discovered by Reuters and given almost no coverage. Like Walmart was afraid to let people know it was incompetent and hiring an outsider.
Walmart leadership has never shown a keen understanding of e-commerce, nor a commitment to making Walmart a leading market competitor. You might counter that Walmart’s acquisition of Jet.com showed a strong commitment. But we now know that amidst the minimalistic hype, Walmart actually cheated when providing its e-commerce results. And when Walmart hired a former Tesco executive to lead Jet.com’s grocery sales effort, the news was not splashed front page. Rather it was hidden in an internal email discovered by Reuters and given almost no coverage. Like Walmart was afraid to let people know it was incompetent and hiring an outsider.
Investors, and customers, need to admit that it is a LOT easier for Amazon to learn about traditional store operations by purchasing Whole Foods than it is for Walmart to learn how to succeed in e-commerce. Traditional grocery “excellence” is easy to come by, after all there are thousands of experienced grocery store executives. So Amazon can buy Whole Foods and gain what knowledge it needs overnight, while adapting Whole Foods to the tremendous e-commerce insight embedded in Amazon. But Walmart is struggling to add compete with Amazon in e-commerce, where knowledge is a lot, lot tougher to come by.
Telltale’s are strips of cloth used by sailors to provide early tips about wind direction and speed. Good sailors “read” the telltale strips to plot their sail use for maximum performance. We can read the “telltales” in business as well. The “telltales” at Walmart have long been bad signals for investors. After 3 years of recovery from a 2014 collision created by an overworked Walmart driver, comedian Tracy Morgan recently returned to television with a new show. The overworked driver was a worrisome telltale of how Walmart pressured its employees to attempt competing against much lower cost e-commerce. By February, 2016 there were 10 very obvious telltales of Walmart’s inability to cope with Amazon and the market shift to e-commerce.

Understanding e-commerce is worth a whole lot more than being good at running a tight retail operation. As I pointed out in May, 2016, knowing that trend is what makes Amazon worth so much more than the much bigger, and asset rich, Walmart. And the Walton family knows this, that’s why it became clear by October, 2017 that they were cashing out of the traditional Walmart business. As I’ve said before, if the Walton’s aren’t putting their money in Walmart (or shopping in the stores) why should you?

by Adam Hartung | Apr 3, 2018 | Computing, Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Mobile, Music
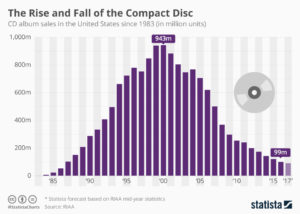
Do you still have a pile of compact discs? If so, why? When was the last time you listened to one? Like almost everyone else, you probably stream your music today. If you are just outdated, you listen to music you bought from iTunes or GooglePlay and store on your mobile device. But it would be considered prehistoric to tell people you carry around CDs for listening in your car – because you surely don’t own a portable CD player.
As the chart shows, CD sales exploded from nothing in 1983 to nearly 1B units in 2000. Now sales are less than 1/10th that number, due to the market shift expanded bandwidth allowed.
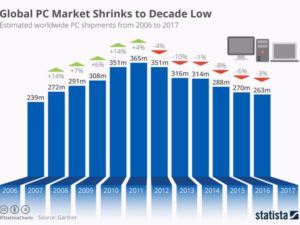
Do you still carry a laptop? If so, you are a dying minority. As PCs became more portable they became indispensable. Nobody left the office, or attended a meeting, without their laptop. That trend exploded until 2011, when PC sales peaked at 365M units. As the chart shows, in the 6 years since, PC sales have dropped by over 100M units, a 30% decline. The advent of mobile devices (smartphones and tablets) coupled with expanded connectivity and growing cloud services allowed mobility to reach entirely new levels – and people stopped carrying their PCs. And just like CDs are disappearing, so will PCs.
These charts dramatically show how quickly a new technology, or package of technologies, can change the way we behave. Simultaneously, they change the competitive landscape. Sony dominated the music industry, as a producer and supplier of hardware, when CDs dominated. But, as I wrote in 2012, the shift to more portable music caused Sony to fall into a rapid decline, and the company suffered 6 consecutive years (24 quarters) of falling sales and losses. The one-time giant was crippled by a technology shift they did not adopt. And they weren’t alone, as big box retailers such as Best Buy and Circuit City also faltered when these sales disappeared.
Once, Microsoft was synonymous with personal technology. Nobody maximized the value in PC growth more than Microsoft. But changing technology altered the competitive landscape, with Apple, Google, Samsung and Amazon emerging as the leaders. Microsoft, as the almost unnoticed launch of Windows 10 demonstrated, is struggling to maintain relevancy.
Too often we discount trends. Like Sony and Microsoft we think historical growth will continue, unabated. We find ways to discount market shifts, saying the products are “niche” and denigrating their quality. We will express our view that the market has “hiccuped” and will return to growth again. By the time we admit the shift is permanent new competitors have overtaken the lead, and we risk becoming totally obsolete. Like Toys-R-Us, Radio Shack, Sears and Motorola.
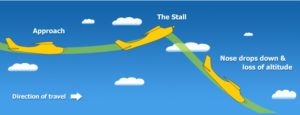
Aircraft stalls when not enough power to climb
The time for action is when the very first signs of shift happened. I’ve written a lot about “Growth Stalls” and they occur in just 2 quarters. 93% of the time a stalled company never again grows at a mere 2%/year. Look at how fast GE went from the best company in America to the worst. It is incredibly important that leadership react FAST when trends push customers toward new solutions, because it often takes very little time for the trend to make dying markets completely untenable.

by Adam Hartung | Mar 13, 2018 | Defend & Extend, Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Software
In February, Berkshire Hathaway revealed it had dumped its IBM position. Good riddance to a stock that has gone down for 5 years while the S&P went up! What did Buffett do with the money? He loaded up on Apple – making that high-flyer Berkshire’s #1 holding. So, isn’t the smart thing now to buy Apple?
First, don’t confuse your investing goals with Berkshire Hathaway’s. It may seem that everyone has the same objective, to buy stocks that go up. But Berkshire is a very special case. As I pointed out in 2014, we mere mortals can’t invest like Buffett, and shouldn’t try. Berkshire Hathaway has the opportunity to make investments in special situations with tremendous return potential that we don’t have. Berkshire’s investment strategy is to invest where it can create cash to prepare for special situations, or to park money where it can make a decent return, and hopefully generate cash while it waits.
Apple is the #1 most cash-rich company on the planet, and with the new tax laws it can repatriate that cash. This is an opportunity for a “special dividend” to investors, and that is the kind of thing that Buffett loves. He isn’t a venture capitalist looking for a 10x price appreciation. He wants a decent 5% rate of return, and hopefully dividends, so he can grow cash for his special situation opportunities. Apple, the most valuable company on any exchange, is exactly the kind of company where he can place a few billion dollars without driving up the price and let it sit making a solid 5-6%, collect dividends and maybe get a few kickers from things like the cash repatriation.
Second, let’s not forget that Buffett’s IBM buying spree lost money. If he was a great tech investor, he never would have bought IBM. He bought it for the same reason he’s buying Apple, only he was wrong about what was going to happen to IBM as it continued to lose relevancy.
I pointed out in May, 2016 that Apple was showing us all a lot of sustaining innovations, with new rev levels of existing products, but almost no new disruptive innovations. The company that once gave us iPods, iTunes, iPhones and iPads was increasingly relying on the next version of everything to drive sales. Lots of incremental improvement. But little discussion about any breakthrough products, like iBeacon, ApplePay or even the Apple Watch. In a real way, Apple was looking a lot more like the old Microsoft with its Windows and Office fascination than the old Apple.
By October, 2016 Apple hit a Growth Stall. While this may have seemed like “no big deal,” recall that only 7% of the time do companies maintain a 2% growth rate after stalling. Is Apple going to be in that 7%? With the launch of the less-than-overwhelming iPhone X, and the actual drop in iPhone sales in Q4, 2017 it looks increasingly like Apple is on the same road as all other stalled companies.
In the short term Apple has said it is milking its installed base. By constantly bringing out new apps it has raised iTunes sales to over $30B/quarter. And it has a dedicated cadre of developers making over $25B/year creating new apps. So Apple is doing its best to get as much revenue out of that installed base of iPhones as it can, even if device sales slow (or decline.) For Buffett, this is no big deal. After all, he’s parking cash and hoping to get dividends. Milking the base is a cash generation strategy he would love – like a railroad, or Coca-Cola.
But if you’re interested in maintaining high returns in your portfolio, be aware of what’s happening. Apple is changing. It’s not going to falter and fail any time soon. But don’t be lulled by Berkshire’s big purchases into thinking Apple in 2018 is anything like it was in 2012 – or through 2014. Instead, keep your eyes on game changers like Netflix, Tesla and Amazon.

 In a bit of “get them the razor so they will buy the razor blades” CEO Tim Cook’s Apple is increasingly relying upon farming the “installed base” of users to drive additional revenues. Leveraging the “installed base” of users is now THE primary theme for growing Apple sales. And even old-tech guys like Warren Buffett at Berkshire Hathaway love it, as they gobble up Apple shares. As do many analysts, and investors. Apple has paid out over $100B to developers for its services, and generated over $40B in revenues for itself – and with such a large base willing to buy things developers are likely to keep providing more products and working to grow sales.
In a bit of “get them the razor so they will buy the razor blades” CEO Tim Cook’s Apple is increasingly relying upon farming the “installed base” of users to drive additional revenues. Leveraging the “installed base” of users is now THE primary theme for growing Apple sales. And even old-tech guys like Warren Buffett at Berkshire Hathaway love it, as they gobble up Apple shares. As do many analysts, and investors. Apple has paid out over $100B to developers for its services, and generated over $40B in revenues for itself – and with such a large base willing to buy things developers are likely to keep providing more products and working to grow sales.











 Walmart leadership has never shown a keen understanding of e-commerce, nor a commitment to making Walmart a leading market competitor. You might counter that Walmart’s acquisition of Jet.com showed a strong commitment. But we now know that amidst the minimalistic hype,
Walmart leadership has never shown a keen understanding of e-commerce, nor a commitment to making Walmart a leading market competitor. You might counter that Walmart’s acquisition of Jet.com showed a strong commitment. But we now know that amidst the minimalistic hype, 




