
by Adam Hartung | Jun 27, 2018 | In the Swamp, Innovation, Investing, Manufacturing, Transportation, Trends
On Monday, Harley Davidson, America’s leading manufacturer of motorcycles, announced it was going to open a plant in Europe.
Ostensibly this is to counter tariffs the EU will be imposing on its products if imported from the USA. President Trump reacted vociferously on Tuesday, threatening much bigger taxes on Harley if it brings to the USA any parts or motorcycles from its offshore plants in Brazil, Australia, India or Thailand. He also intimated that Harley Davidson was likely to collapse.
Lots of heat, not much light. The issues for Harley Davidson are far worse than an EU tariff.
Harley Davidson has about 1/3 of the US motorcycle market. But in “heavy motorcycles,” those big bikes that are heavier and generally considered for longer riding, Harley has half the market. Which sounds great, until you realize that until the 1970s, Harley had 100% of that market. Ever since then, Harley has been losing share – to imports and to its domestic competitor Polaris.
It was 2006 when I first wrote about Harley Davidson’s big demographic problem. Basically, its customers were all aging. Younger people were buying other motorcycles, so the “core” Harley customer was getting older every year. From mid-30s in the 1980s, by the year 2000 the average buyer was well into their mid-40s. In 2007, I pointed out that Harley had made a stab at changing this dynamic by introducing a new motorcycle with an engine made by Porsche, and a far more modern design (the V-Rod.) But Harley wasn’t committed to building a new customer base, so when dealers complained that the V-Rod “wasn’t really a Harley” the company backed off the marketing and went back to all its old ways of doing business.
Simultaneously, Harley Davidson motorcycle prices were rising faster than inflation, while Japanese manufacturers were not. Thus, as I also pointed out in 2007, it was struggling to maintain market share. Slower sales caused a lay-off that year, and despite the brand driving huge sales of after-market products like jackets and T-shirts, which had grown as big as bike sales, it was unclear how Harley would slow the aging of its customer base and find new, younger buyers. Harley simply eschewed the trend toward selling smaller, lighter, cheaper bikes that had more appeal to more people – and in more markets.
Globally, the situation is far more bleak than the USA. America has one of the lowest motorcycle ridership percentages on the globe. Americans love cars. But in more congested countries like across Europe or Japan and China, and in much poorer countries like India, Korea, and across South America motorcycles are more popular than automobiles. And in those countries Harley has done poorly. Because Harley doesn’t even have the smaller 100cc,200cc, 400cc and 600cc bikes that dominate the market. For example, in 2006 (I know, old, but best data I could find) Harley Davidson sold 349,200 bikes globally. Honda sold 10.3 million. Yamaha sold 4.4 million. Even Suzuki sold 3.1 million – or 10 times Harley’s production.
But, being as fair as possible, let’s focus on Europe – where the new Harley plant is to be built. And let’s look exclusively at “heavy motorcycles” (thus excluding the huge market in which Harley has no products.) In 2006, Harley was 6th in market share. BMW 16%, Honda 15%, Yamaha 15%, Suzuki 15%, Kawasaki 11% and Harley Davidson 9%. Wow, that is simply terrible.
Clearly, Harley has already become marginalized globally. Outside the USA, Harley isn’t even relevant. The Japanese and Germans have been much more successful everywhere outside the USA, and every one of those other markets is bigger than the USA. Harley was simply relying on its core product (big bikes) in its core market (USA) and seriously failing everywhere else.
Oh, but even that story isn’t as good as it sounds. Because in the USA sales of Harley motorcycles has been declining for a decade! Experts estimate that every year which passes, Harley’s customer base ages by 6 months. The average rider age is now well into their 50s. Since Q3, 2014 Harley’s sales growth has been negative! In Q2 and Q3 2017 sales declines were almost 10%/quarter!
As its customer demographic keeps working against it, new customers for big bikes are buying BMWs from Germany – and Victory and Indian motorcycles made by Polaris, out of Minnesota (Polaris discontinued the Victory brand end of 2017.) BMW sales have increased for 7 straight quarters, and their European sales are growing stronger than ever – directly in opposition to Harley’s sales problems. Every quarter Indian is growing at 16-20%, taking all of its sales out of Harley Davidson USA share.
Going back to my 2016 column, when I predicted Harley was in for a hard time. Shares hit an all-time high in 2006 of $75. They have never regained that valuation. They plummeted during the Great Recession, but bailout funds from Berkshire Hathaway and the US government saved Harley from bankruptcy. Shares made it back to $70 by 2014, but fell back to $40 by 2016. Now they are trading around $40. Simply put, as much as people love to talk about the Harley brand, the company is rapidly becoming irrelevant. It is losing share in all markets, and struggling to find new customers for a product that is out-of-date, and sells almost exclusively in one market. Its move to manufacture in Europe is primarily a Hail-Mary pass to find new sales, paid for by corporate tax cuts in the USA and tariff tax avoidance in Europe.
But it won’t likely matter. Like I said in 2006, Harley Davidson is a no-growth story, and that’s not a story where anyone should invest.

by Adam Hartung | Mar 6, 2018 | In the Swamp, Investing, Retail, Scenario Planning
On February 20, 2018 Walmart’s stock had its biggest price drop ever. And the second biggest percentage decline ever. Even though same store sales improved, investors sold off the stock in droves. And after a pretty healthy recent valuation run-up.
What happened? Simply put, Walmart said its on-line sales slowed and its cost of operations rose, slowing growth and cramping margins. In other words, even though it bought Jet.com Walmart is still a long, long way from coming close to matching the customer relationship and growth of Amazon.com. And (surprise, surprise) margins in on-line aren’t an easy thing — as Amazon’s thin margins for 15 years have demonstrated.
In other words, this was completely to be expected. Walmart is a behemoth with no adaptability. For decades the company has been focused on how to operate its warehouses and stores, and beat up its suppliers. Management had to be drug, kicking and screaming, into e-commerce. And failing regularly it finally made an acquisition. But to think that Jet.com was going to change WalMart’s business model into a growing, high profit operation any time soon was foolish. Management still wants people in the store, first and foremost, and really doesn’t understand how to do anything else.
All the way back in 2005, I wrote that Walmart was too big to learn, and was unwilling to create white space teams to really explore growing e-commerce (hence the belated Jet-com acquisition.) In 2007, I wrote that calling Walmart a “mature” competitor with huge advantages was the wrong way to view the company already under attack by all the e-commerce players. In July, 2015 Amazon’s market cap exceeded Walmart’s, showing the importance of retail transformation on investor expectations. By February, 2016 there were 10 telltale signs Walmart was in big trouble by a changing retail market. And by October, 2017 it was clear the Waltons were cashing out of Walmart, questioning why any investor should remain holding the stock.
It really is possible to watch trends and predict future markets. And that can lead to good predictions about the fates of companies. The signs were all there that Walmart shouldn’t be going up in value. Hope had too many investors thinking that Walmart was too big to stumble – or fail. But hope is not how you should invest. Not for your portfolio, and not for your business. Walmart should have dedicated huge sums to e-commerce 15 years ago, now it is playing catch up with Amazon.com, and that’s a race it simply won’t win. Are you making the right investment decisions for your business early enough? Or will you stumble like Walmart?

by Adam Hartung | Oct 21, 2017 | In the Swamp, Investing, Leadership
In other words, CEO Flannery continues the strategy of making GE smaller, and a less hospitable workplace, that his predecessor Immelt started implementing 16 years ago. That’s the strategy that has seen GE lose ~45% of its value since Immelt took the top job, and lose over 60% of its value since peaking at $60 in 2000. So far, GE just keeps shrinking in size, and value, and leadership gives no indication it has a plan to grow GE revenues and profits in future markets building on major market trends.
What’s most surprising is that people seem surprised by the horrible current performance, and surprised that GE is in such terrible condition. All the way back in
December, 2010 this column highlighted selections for CEO of the year, and CEO of the decade, and in doing so pointed out that GE’s Immelt was on nobody’s list. Even though his predecessor, Jack Welch, was widely lauded.
Immelt inherited one of America’s strongest, fastest growing and most valuable companies. But in the first few years of his leadership the company completely failed to maintain Welch’s gains, and under Immelt’s mismanagement nearly went bankrupt by not preparing for the near-collapse of financial services in the Great Recession. It was obvious then that Immelt was trying to be a “caretaker” of GE, a “steward” of its history. But he was not an effective leader with plans for a growing future, and competitors were beating up GE in all markets. Even upstarts like Facebook, and its CEO Mark Zuckerberg, were far outperforming the stagnating, declining GE.
By May, 2012 it was impossible to miss the mismanagement at GE.
This column selected CEO Immelt as the 4th worst CEO of all publicly traded American companies (beaten in badness by Mike Duke of WalMart who was pushed out during allegations of international bribery and fraud, Ed Lampert of Sears who has now completely destroyed the once great retailer, and Steve Ballmer of Microsoft who over-invested in Windows and Office while missing every major tech development of the last 15 years before being forced out by the board.) By 2012 it was time for the Board of Directors to take action and replace Immelt. But few investors amplified this column’s cries for change, and quiet complacency set in as people simply expected GE to perform better. Just because it was GE, it appeared, as there were no signs the company understood market trends and how to ignite growth.
Of course, performance did not improve at GE. By April, 2015 GE was the victim of a total leadership failure. The company was not developing any major new trends, and Immelt’s focus was on unraveling old businesses, mostly via sales to external parties, in order to increase cash. And the cash was used for share buybacks and dividends, rather than investing in growth. A slow, and badly implemented, liquidation of one of America’s oldest, and greatest, companies was underway.
Which made GE a target for activist investors, and Trian Funds took up the challenge, investing $1.5B in GE stock and taking a seat on the GE board. Finally, it was time for action. Immelt was pushed out and Flannery was put in, and dramatic cuts and re-organizations led the discussions. Current appearances indicate GE will be significantly dismantled, assets will be sold, and in short order GE will look nothing like the great company it once was.
But, the question remains, why did things have to become so bad before the board took action? Why were people surprised? Why didn’t Jim Cramer scream for a leadership housecleaning 7, 5 or 3 years ago? Why didn’t shareholders vote against CEO compensation plans on the “say-on-pay” measures, exerting their voice to change a lackluster board that was allowing an incompetent CEO to remain in the job? Why wasn’t the pension fund, constantly whittling away at retiree benefits, forcing change? Why were so many people, so many leaders, so quiet about what was an obvious business failure? A failure that needed to be addressed, first and foremost, by replacing the CEO?
So GE’s stock value has taken a big hit of late. And now people seem surprised by the admission of how bad things really are. What’s really surprising is that people are surprised. This was not hard to see coming.
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.

by Adam Hartung | Oct 17, 2017 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Investing, Leadership, Retail
The Waltons Are Cashing Out Of Walmart — And You Should Be, Too
Employees restock shelves of school supplies at a Walmart Stores Inc. location in Burbank, CA. Bloomberg
Last week there was a lot of stock market excitement regarding WalMart. After a “favorable” earnings report analysts turned bullish and the stock jumped 4% in one day, WMT’s biggest rally in over a year, making it a big short-term winner. But the leadership signals indicate WalMart is probably not the best place to put your money.
WalMart has limited growth plans
WalMart is growing about 3%/year. But leadership acknowledged it was not growing its traditional business in the USA, and only has plans to open 25 stores in the next year. It hopes to add about 225 internationally, predominantly in Mexico and China, but unfortunately those markets have been tough places for WalMart to grow share and make profits. And the company has been plagued with bribery scandals, particularly in Mexico.
And, while WalMart touts its 40%+ growth rate on-line, margins online (including the free delivery offer) are even lower than in the traditional Wal-Mart stores, causing the company’s gross margin percentage to decline. The $11.5 billion on-line revenue projection for next year is up, but it is 2.5% of Walmart’s total, and a mere 7-8% of Amazon’s retail sales. Amazon remains the clear leader, with 62% of U.S. households having visited the company in the second quarter. And it is not a good sign that WalMart’s greatest on-line growth is in groceries, which amount to 26% of on-line salesalready. WalMart is investing in 1,000 additional at-store curb-side grocery pick-uplocations, but this effort to defend traditional store sales is in the products where margins are clearly the lowest, and possibly nonexistent.
It is not clear that WalMart has a strategy for competing in a shrinking traditional brick-and-mortar market where Costco, Target, Dollar General, et.al. are fighting for every dollar. And it is not clear WalMart can make much difference in Amazon’s giant on-line market lead. Meanwhile, Amazon continues to grow in valuation with very low profits, even as it grows its presence in groceries with the Whole Foods acquisition. In the 17 months from May 10, 2016 through October 10, 2017 WalMart’s market cap grew by $24 billion (10%,) while Amazon’s grew by $174 billion (57%.)
Even after recent gains for WalMart, its market capitalization remains only 53% of its much smaller on-line competitor. This creates a very difficult pricing problem for WalMart if it has to make traditional margins in order to keep analysts, and investors, happy.
Leadership is not investing to compete, but rather cashing out the business
To understand just how bad this growth problem is, investors should take a look at where WalMart has been spending its cash. It has not been investing in growing stores, growing sales per store, nor really even growing the on-line business. From 2007-2016 WalMart spent a whopping $67.3 billion in share buybacks. That is over 20 times what it spent on Jet.com. And it was 45% of total profits during that timeframe. Additionally WalMart paid out $51.2 billion in dividends, which amounted to 34% of profits. Altogether that is $118.5 billion returned to shareholders in the last decade. And a staggering 79% of profits. It shows that WalMart is really not investing in its future, but rather cashing out the company by returning money to shareholders.
So very large investors, who control huge voting blocks, recognize that things are not going well at WalMart. But, because of the enormity of the share buybacks, the Walton family now controls over half of WalMart stock. That makes it tough for an activist to threaten shaking up the company, and lets the Waltons determine the company’s future.
There will be marginal enhancements. But the vast majority of the money is being returned to them, via $20 billion in share repurchases and $1.5 billion in cash dividends annually.
Amazon spends nothing on share repurchases. Nor does it distribute cash to shareholders via dividends. Amazon’s largest shareholder, Jeff Bezos, invests all the company money in new growth opportunities. These nearly cover the retail landscape, and increasingly are in other growth markets like cloud services, software-as-a-service and entertainment. Comparing the owners of these companies, quite clearly Bezos has faith in Amazon’s ability to invest money for profitable future growth. But the Waltons are far less certain about the future success of WalMart, so they are pulling their money off the table, allowing investors to put their money in ventures outside WalMart.
Investing your money, do you think it is better to invest where the owner believes in the future of his company?
Or where the owners are cashing out?
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.
by Adam Hartung | Nov 17, 2016 | Food and Drink, In the Swamp, Innovation, Marketing, Trends
(PAUL J. RICHARDS/AFP/Getty Images)
McDonald’s has been trying for years to re-ignite growth. But, unfortunately for customers and investors alike, leadership keeps going about it the wrong way. Rather than building on new trends to create a new McDonald’s, they keep trying to defend extend the worn out old strategy with new tactics.
Recently McDonald’s leadership tested a new version of the Big Mac,first launched in 1967. They replaced the “special sauce” with Sriracha sauce in order to make the sandwich a bit spicier. They are now rolling it out to a full test market in central Ohio with 128 stores. If this goes well – a term not yet defined – the sandwich could roll out nationally.
This is a classic sustaining innovation. Take something that exists, make a minor change, and offer it as a new version. The hope is that current customers keep buying the original version, and the new version attracts new customers. Great idea, if it works. But most of the time it doesn’t.
Unfortunately, most people who buy a product like it the way it is. Slower Big Mac sales aren’t due to making bad sandwiches. They’re due to people changing their buying habits to new trends. Fifty years ago a Big Mac from McDonald’s was something people really wanted. Famously, in the 1970s a character on the TV series Good Times used to become very excited about going to eat his weekly Big Mac.
People who are still eating Big Macs know exactly what they want. And it’s the old Big Mac, not a new one. Thus the initial test results were “mixed” – with many customers registering disgust at the new product. Just like the failure of New Coke, a New Big Mac isn’t what customers are seeking.
After 50 years, times and trends have changed. Fewer people are going to McDonald’s, and fewer are eating Big Macs. Many new competitors have emerged, and people are eating at Panera, Panda Express, Zaxby’s, Five Guys and even beleaguered Chipotle. Customers are looking for a very different dining experience, and different food. While a version two of the Big Mac might have driven incremental sales in 1977, in 2017 the product has grown tired and out of step with too many people and there are too many alternative choices.
Similarly, McDonald’s CEO’s effort to revitalize the brand by adding ordering kiosks and table service in stores, in a new format labeled the “Experience of the Future,” will not make much difference. Due to the dramatic reconfiguration, only about 500 stores will be changed – roughly 3.5% of the 14,500 McDonald’s. It is an incremental effort to make a small change when competitors are offering substantially different products and experiences.
When a business, brand or product line is growing it is on a trend. Like McDonald’s was in the 1960s and 1970s, offering quality food, fast and at a consistent price nationwide at a time when customers could not count on those factors across independent cafes. At that time, offering new products – like a Big Mac – that are variations on the theme that is riding the trend is a good way to expand sales.
But over time trends change, and adding new features has less and less impact. These sustaining innovations, as Clayton Christensen of Harvard calls them, have “diminishing marginal returns.” That’s an academic’s fancy way of saying that you have to spend ever greater amounts to create the variations, but their benefits keep having less and less impact on growing, or even maintaining, sales. Yet, most leaders keep right on trying to defend & extend the old business by investing in these sustaining measures, even as returns keep falling.
Over time a re-invention gap is created between the customer and the company. Customers want something new and different, which would require the business re-invent itself. But the business keeps trying to tweak the old model. And thus the gap. The longer this goes on, the bigger the re-invention gap. Eventually customers give up, and the product, or company, disappears.
Think about portable hand held AM radios. If someone gave you the best one in the world you wouldn’t care. Same for a really good portable cassette tape player. Now you listen to your portable music on a phone. Companies like Zenith were destroyed, and Sony made far less profitable, as the market shifted from radios and cathode-ray televisions to more portable, smarter, better products.
Motorola, one of the radio pioneers, survived this decline by undertaking a “strategic pivot.” Motorola invested in cell phone technology and transformed itself into something entirely new and different – from a radio maker into a pioneer in mobile phones. (Of course leadership missed the transition to apps and smart phones, and now Motorola Solutions is a ghost of the former company.)
McDonald’s could have re-invented itself a decade ago when it owned Chipotle’s. Leadership could have stopped investing in McDonald’s and poured money into Chipotle’s, aiding the cannibalization of the old while simultaneously capturing a strong position on the new trend. But instead of pivoting, leadership sold Chipotle’s and used the money to defend & extend the already tiring McDonald’s brand.
Strategic pivots are hard. Just look at Netflix, which pivoted from sending videos in the mail to streaming, and is pivoting again into original content. But, they are a necessity if you want to keep growing. Because eventually all strategies become out of step with changing trends, and sustaining innovations fail to keep customers.
McDonald’s needs a very different strategy. It has hit a growth stall, and has a very low probability of ever growing consistently at even 2%. The company needs a lot more than sriracha sauce on a Big Mac if it is to spice up revenue and profit growth.

by Adam Hartung | Aug 26, 2016 | In the Swamp, Investing, Retail, Trends
Photographer: Luke Sharrett/Bloomberg
Walmart is in more trouble than its leadership wants to acknowledge. Investors
need to realize that it is up to Jet.com to turn around the ailing giant. And
that is a big task for the under $1 billion company.
Relevancy Is Hard To Keep – Look At Sears
Nobody likes to think their business can disappear. What CEO wants to tell his investors or employees “we’re no longer relevant, and it looks like our customers are all going somewhere else for their solutions”? Unfortunately, most leadership teams become entrenched in the business model and deny serious threats to longevity, thus leading to inevitable failure as customers switch.
Gallery: “Walmart Goes Small”
In early September the Howard Johnson’s in Bangor, Maine will close. This will leave just one remaining HoJo in the USA. What was once an iconic brand with hundreds of outlets strung along the fast growing interstate highway system is now nearly dead. People still drive the interstate, but trends changed, fast food became a good substitute, and unable to update its business model this once great brand died.

AP Photo/Elise Amendola
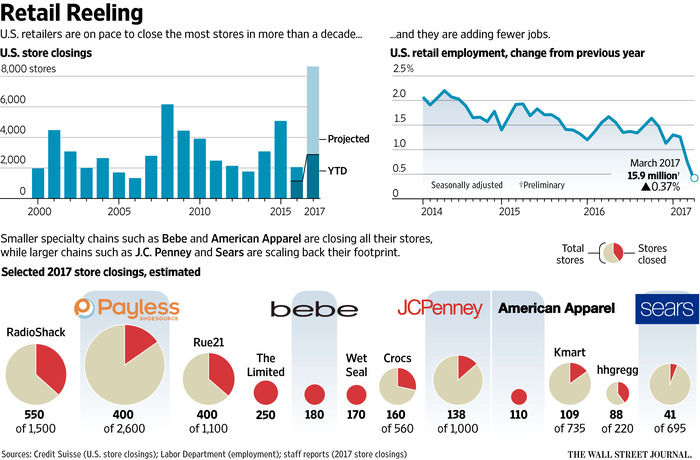
Sears announced another $350 million quarterly loss this week. That makes $9 billion in accumulated losses the last several quarters. Since Chairman and CEO Ed Lampert took over, Sears and Kmart have seen same store sales decline every single quarter except one. Unable to keep its customers Mr. Lampert has been closing stores and selling assets to stem the cash drain. But to keep the company afloat his hedge fund, ESL, is loaning Sears Holdings SHLD -2.94% another $300 million. On top of the $500 million the company borrowed last quarter. That the once iconic company, and Dow Jones Industrial Average component, is going to fail is a foregone conclusion.
But most people still think this fate cannot befall the nearly $500 billion revenue behemoth Walmart. It’s simply too big to fail in most people’s eyes.
Walmart’s Crime Problem Is Another Telltale Sign Of Problems In The Business Model
Yet, the primary news about Walmart is not good. Bloomberg this week broke the news that one of the most crime-ridden places in America is the local Walmart store. One store in Tulsa, Oklahoma has had 5,000 police visits in the last five years, and four local stores have had 2,000 visits in the last year alone. Across the system, there is one violent crime in a Walmart every day. By constantly promoting its low cost strategy Walmart has attracted a class of customer that simply is more prone to committing crime. And policies implemented to hang onto customers, like letting them camp out overnight in the parking lots, serve to increase the likelihood of poverty-induced crime.
But this outcome is also directly related to Walmart’s business model and strategy. To promote low prices Walmart has automated more operations, and cut employees like greeters. Thus leadership brags about a 23% increase in sales/employee the last decade. But that has happened as the employment shrank by 400,000. Fewer employees in the stores encourages more crime.
In a real way Walmart has “outsourced” its security to local police departments. Experts say the cost to eliminate this security problem are about $3.2 billion – or about 20% of Walmart’s total profitability. Ouch! In a world where Walmart’s net margin of 3% is fully one-third lower than Target’s 4.6% the money just isn’t there any longer for Walmart to invest in keeping its stores safe.
With each passing month Walmart is becoming the “retailer of last resort” for people who cannot shop online. People who lack credit cards, or even bank accounts. People without the means, or capability, of shopping by computer, or paying electronically. People who have nowhere else to go to shop, due to poverty and societal conditions. Not exactly the ideal customer base for building a growing, profitable business.
Competitors Relentlessly Pick Away At Walmart’s Sales And Profits
To maintain revenues the last several years Walmart has invested heavily in transitioning to superstores which offer a large grocery section. But now Kroger KR -0.5%, Walmart’s no. 1 grocery competitor, is taking aim at the giant retailer, slashing prices on 1,000 items. Just like competition from the “dollar stores” has been attacking Walmart’s general merchandise aisles. Thus putting even more pressure on thinning margins, and leaving less money available to beef up security or entice new customers to the stores.
And the pressure from e-commerce is relentless. As detailed in the Wall Street Journal, Walmart has been selling online for about 15 years, and has a $14 billion online sales presence. But this is only 3% of total sales. And growth has been decelerating for several quarters. Last quarter Walmart’s e-commerce sales grew 7%, while the overall market grew 15% and Amazon ($100 billion revenues) grew 31%. It is clear that Walmart.com simply is not attracting enough customers to grow a healthy replacement business for the struggling stores.
Thus the acquisition of Jet.com.
The hope is that this extremely unprofitable $1 billion online retailer will turn around Walmart’s fortunes. Imbue it with much higher growth, and enhanced profitability. But will Walmart make this transition. Is leadership ready to cannibalize the stores for higher electronic sales? Are they willing to make stores smaller, and close many more, to shift revenues online? Are they willing to suffer Amazon-like profits (or losses) to grow? Are they willing to change the Walmart brand to something different, while letting Jet.com replace Walmart as the dominant brand? Are they willing to give up on the past, and let new leadership guide the company forward?
If they do then Walmart could become something very different in the future. If they really realize that the market is shifting, and that an extreme change is necessary in strategy and tactics then Walmart could become something very different, and remain competitive in the highly segmented and largely online retail future. But if they don’t, Walmart will follow Sears into the whirlpool, and end up much like Howard Johnson’s.
by Adam Hartung | Jul 27, 2016 | Food and Drink, Growth Stall, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
Growth Stalls are deadly for valuation, and both Mcdonald’s and Apple are in one.
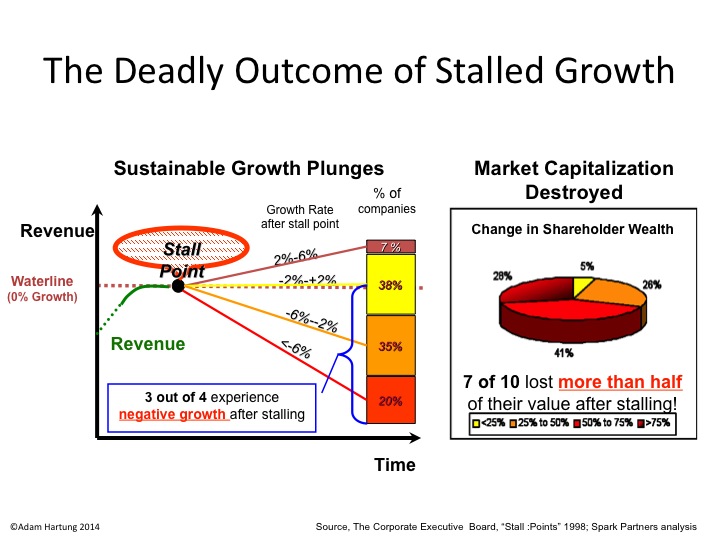
August, 2014 I wrote about McDonald’s Growth Stall. The company had 7 straight months of revenue declines, and leadership was predicting the trend would continue. Using data from several thousand companies across more than 3 decades, companies in a Growth Stall are unable to maintain a mere 2% growth rate 93% of the time. 55% fall into a consistent revenue decline of more than 2%. 20% drop into a negative 6%/year revenue slide. 69% of Growth Stalled companies will lose at least half their market capitalization in just a few years. 95% will lose more than 25% of their market value. So it is a long-term concern when any company hits a Growth Stall.
 A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also closed 700 stores in 2015, and 500 in 2016. And he announced the company would move its headquarters from suburban Oakbrook to downtown Chicago, IL. While doing something, none of these actions addressed the fundamental problem of customers switching to competitive options that meet modern consumer food trends far better than McDonald’s.
A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also closed 700 stores in 2015, and 500 in 2016. And he announced the company would move its headquarters from suburban Oakbrook to downtown Chicago, IL. While doing something, none of these actions addressed the fundamental problem of customers switching to competitive options that meet modern consumer food trends far better than McDonald’s.
McDonald’s stock languished around $94/share from 8/2014 through 8/2015 – but then broke out to $112 in 2 months on investor hopes for a turnaround. At the time I warned investors not to follow the herd, because there was nothing to indicate that trends had changed – and McDonald’s still had not altered its business in any meaningful way to address the new market realities.
Yet, hopes remained high and the stock peaked at $130 in May, 2016. But since then, the lack of incremental revenue growth has become obvious again. Customers are switching from lunch food to breakfast food, and often switching to lower priced items – but these are almost wholly existing customers. Not new, incremental customers. Thus, the company trumpets small gains in revenue per store (recall, the number of stores were cut) but the growth is less than the predicted 2%. The only incremental growth is in China and Russia, 2 markets known for unpredictable leadership. The stock has now fallen back to $120.
Given that the realization is growing as to the McDonald’s inability to fundamentally change its business competitively, the prognosis is not good that a turnaround will really happen. Instead, the common pattern emerges of investors hoping that the Growth Stall was a “blip,” and will be easily reversed. They think the business is fundamentally sound, and a little management “tweaking” will fix everything. Small changes will lead to the classic hockey-stick forecast of higher future growth. So the stock pops up on short-term news, only to fall back when reality sets in that the long-term doesn’t look so good.
Unfortunately, Apple’s Q3 2016 results (reported yesterday) clearly show the company is now in its own Growth Stall. Revenues were down 11% vs. last year (YOY or year-over-year,) and EPS (earnings per share) were down 23% YOY. 2 consecutive quarters of either defines a Growth Stall, and Apple hit both. Further evidence of a Growth Stall exists in iPhone unit sales declining 15% YOY, iPad unit sales off 9% YOY, Mac unit sales down 11% YOY and “other products” revenue down 16% YOY.
This was not unanticipated. Apple started communicating growth concerns in January, causing its stock to tank. And in April, revealing Q2 results, the company not only verified its first down quarter, but predicted Q3 would be soft. From its peak in May, 2015 of $132 to its low in May, 2016 of $90, Apple’s valuation fell a whopping 32%! One could say it met the valuation prediction of a Growth Stall already – and incredibly quickly!
But now analysts are ready to say “the worst is behind it” for Apple investors. They are cheering results that beat expectations, even though they are clearly very poor compared to last year. Analysts are hoping that a new, lower baseline is being set for investors that only look backward 52 weeks, and the stock price will move up on additional company share repurchases, a successful iPhone 7 launch, higher sales in emerging countries like India, and more app revenue as the installed base grows – all leading to a higher P/E (price/earnings) multiple. The stock improved 7% on the latest news.
So far, Apple still has not addressed its big problem. What will be the next product or solution that will replace “core” iPhone and iPad revenues? Increasingly competitors are making smartphones far cheaper that are “good enough,” especially in markets like China. And iPhone/iPad product improvements are no longer as powerful as before, causing new product releases to be less exciting. And products like Apple Watch, Apple Pay, Apple TV and IBeacon are not “moving the needle” on revenues nearly enough. And while experienced companies like HBO, Netflix and Amazon grow their expanding content creation, Apple has said it is growing its original content offerings by buying the exclusive rights to “Carpool Karaoke“ – yet this is very small compared to the revenue growth needs created by slowing “core” products.
Like McDonald’s stock, Apple’s stock is likely to move upward short-term. Investor hopes are hard to kill. Long-term investors will hold their stock, waiting to see if something good emerges. Traders will buy, based upon beating analyst expectations or technical analysis of price movements. Or just belief that the P/E will expand closer to tech industry norms. But long-term, unless the fundamental need for new products that fulfill customer trends – as the iPad, iPhone and iPod did for mobile – it is unclear how Apple’s valuation grows.
by Adam Hartung | May 15, 2016 | In the Swamp, Investing, real estate, Retail
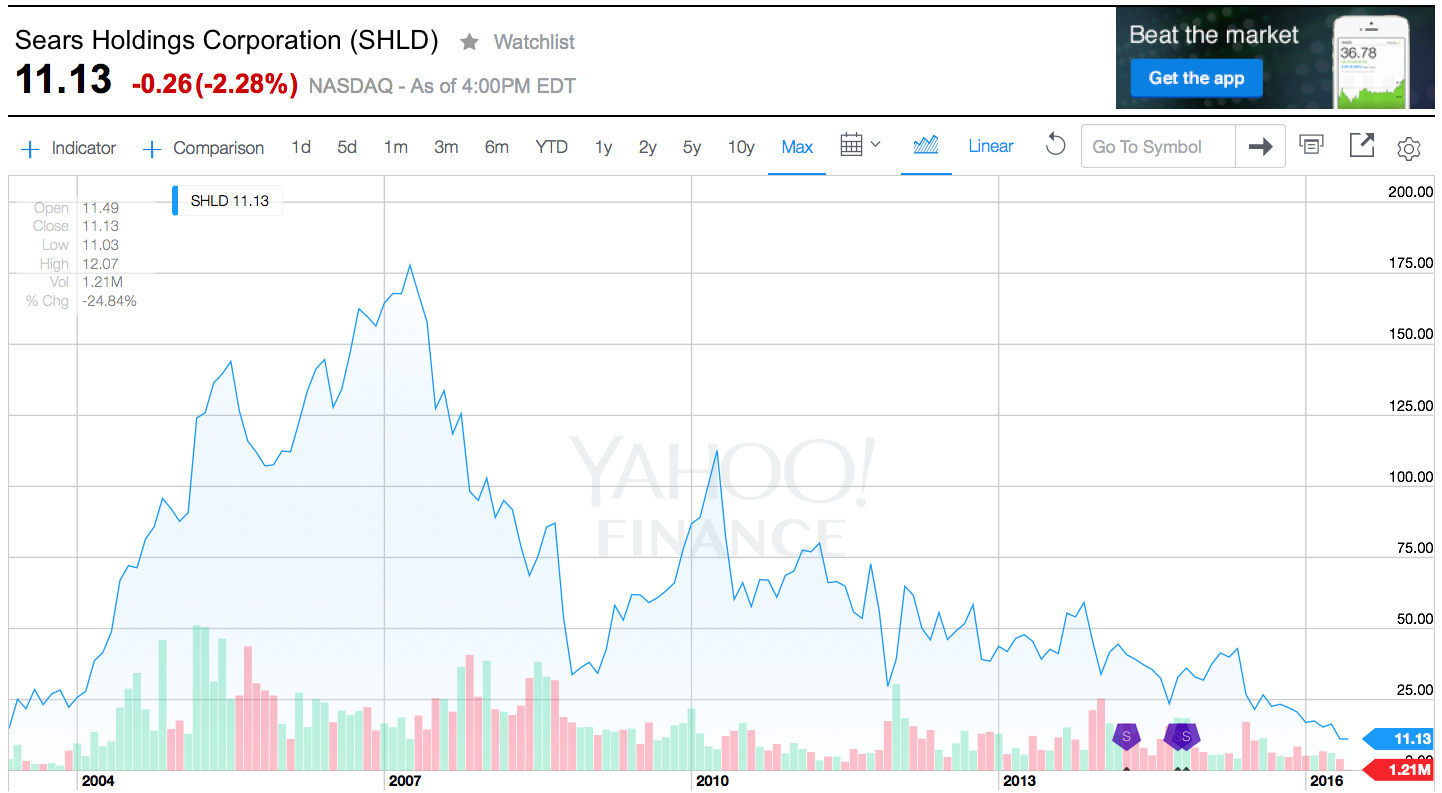
Last week Sears announced sales and earnings. And once again, the news was all bad. The stock closed at a record, all time low. One chart pretty much sums up the story, as investors are now realizing bankruptcy is the most likely outcome.
Chart Source: Yahoo Finance 5/13/16
Quick Rundown: In January, 2002 Kmart is headed for bankruptcy. Ed Lampert, CEO of hedge fund ESL, starts buying the bonds. He takes control of the company, makes himself Chairman, and rapidly moves through proceedings. On May 1, 2003, KMart begins trading again. The shares trade for just under $15 (for this column all prices are adjusted for any equity transactions, as reflected in the chart.)
Lampert quickly starts hacking away costs and closing stores. Revenues tumble, but so do costs, and earnings rise. By November, 2004 the stock has risen to $90. Lampert owns 53% of Kmart, and 15% of Sears. Lampert hires a new CEO for Kmart, and quickly announces his intention to buy all of slow growing, financially troubled Sears.
In March, 2005 Sears shareholders approve the deal. The stock trades for $126. Analysts praise the deal, saying Lampert has “the Midas touch” for cutting costs. Pumped by most analysts, and none moreso than Jim Cramer of “Mad Money” fame (Lampert’s former roommate,) in 2 years the stock soars to $178 by April, 2007. So far Lampert has done nothing to create value but relentlessly cut costs via massive layoffs, big inventory reductions, delayed payments to suppliers and store closures.
Homebuilding falls off a cliff as real estate values tumble, and the Great Recession begins. Retailers are creamed by investors, and appliance sales dependent Sears crashes to $33.76 in 18 months. On hopes that a recovering economy will raise all boats, the stock recovers over the next 18 months to $113 by April, 2010. But sales per store keep declining, even as the number of stores shrinks. Revenues fall faster than costs, and the stock falls to $43.73 by January, 2013 when Lampert appoints himself CEO. In just under 2.5 years with Lampert as CEO and Chairman the company’s sales keep falling, more stores are closed or sold, and the stock finds an all-time low of $11.13 – 25% lower than when Lampert took KMart public almost exactly 13 years ago – and 94% off its highs.
What happened?
Sears became a retailing juggernaut via innovation. When general stores were small and often far between, and stocking inventory was precious, Sears invented mail order catalogues. Over time almost every home in America was receiving 1, or several, catalogues every year. They were a major source of purchases, especially by people living in non-urban communities. Then Sears realized it could open massive stores to sell all those things in its catalogue, and the company pioneered very large, well stocked stores where customers could buy everything from clothes to tools to appliances to guns. As malls came along, Sears was again a pioneer “anchoring” many malls and obtaining lower cost space due to the company’s ability to draw in customers for other retailers.
To help customers buy more Sears created customer installment loans. If a young couple couldn’t afford a stove for their new home they could buy it on terms, paying $10 or $15 a month, long before credit cards existed. The more people bought on their revolving credit line, and the more they paid Sears, the more Sears increased their credit limit. Sears was the “go to” place for cash strapped consumers. (Eventually, this became what we now call the Discover card.)
In 1930 Sears expanded the Allstate tire line to include selling auto insurance – and consumers could not only maintain their car at Sears they could insure it as well. As its customers grew older and more wealthy, many needed help with financia advice so in 1981 Sears bought Dean Witter and made it possible for customers to figure out a retirement plan while waiting for their tires to be replaced and their car insurance to update.
To put it mildly, Sears was the most innovative retailer of all time. Until the internet came along. Focused on its big stores, and its breadth of products and services, Sears kept trying to sell more stuff through those stores, and to those same customers. Internet retailing seemed insignificantly small, and unappealing. Heck, leadership had discontinued the famous catalogues in 1993 to stop store cannibalization and push people into locations where the company could promote more products and services. Focusing on its core customers shopping in its core retail locations, Sears leadership simply ignored upstarts like Amazon.com and figured its old success formula would last forever.
But they were wrong. The traditional Sears market was niched up across big box retailers like Best Buy, clothiers like Kohls, tool stores like Home Depot, parts retailers like AutoZone, and soft goods stores like Bed, Bath & Beyond. The original need for “one stop shopping” had been overtaken by specialty retailers with wider selection, and often better pricing. And customers now had credit cards that worked in all stores. Meanwhile, for those who wanted to shop for many things from home the internet had taken over where the catalogue once began. Leaving Sears’ market “hollowed out.” While KMart was simply overwhelmed by the vast expansion of WalMart.
What should Lampert have done?
There was no way a cost cutting strategy would save KMart or Sears. All the trends were going against the company. Sears was destined to keep losing customers, and sales, unless it moved onto trends. Lampert needed to innovate. He needed to rapidly adopt the trends. Instead, he kept cutting costs. But revenues fell even faster, and the result was huge paper losses and an outpouring of cash.
To gain more insight, take a look at Jeff Bezos. But rather than harp on Amazon.com’s growth, look instead at the leadership he has provided to The Washington Post since acquiring it just over 2 years ago. Mr. Bezos did not try to be a better newspaper operator. He didn’t involve himself in editorial decisions. Nor did he focus on how to drive more subscriptions, or sell more advertising to traditional customers. None of those initiatives had helped any newspaper the last decade, and they wouldn’t help The Washington Post to become a more relevant, viable and profitable company. Newspapers are a dying business, and Bezos could not change that fact.
Mr. Bezos focused on trends, and what was needed to make The Washington Post grow. Media is under change, and that change is being created by technology. Streaming content, live content, user generated content, 24×7 content posting (vs. deadlines,) user response tracking, readers interactivity, social media connectivity, mobile access and mobile content — these are the trends impacting media today. So that was where he had leadership focus. The Washington Post had to transition from a “newspaper” company to a “media and technology company.”
So Mr. Bezos pushed for hiring more engineers – a lot more engineers – to build apps and tools for readers to interact with the company. And the use of modern media tools like headline testing. As a result, in October, 2015 The Washington Post had more unique web visitors than the vaunted New York Times. And its lead is growing. And while other newspapers are cutting staff, or going out of business, the Post is adding writers, editors and engineers. In a declining newspaper market The Washington Post is growing because it is using trends to transform itself into a company readers (and advertisers) value.
CEO Lampert could have chosen to transform Sears Holdings. But he did not. He became a very, very active “hands on” manager. He micro-managed costs, with no sense of important trends in retail. He kept trying to take cash out, when he needed to invest in transformation. He should have sold the real estate very early, sensing that retail was moving on-line. He should have sold outdated brands under intense competitive pressure, such as Kenmore, to a segment supplier like Best Buy. He then should have invested that money in technology. Sears should have been a leader in shopping apps, supplier storefronts, and direct-to-customer distribution. Focused entirely on defending Sears’ core, Lampert missed the market shift and destroyed all the value which initially existed in the great retail merger he created.
Impact?
Every company must understand critical trends, and how they will apply to their business. Nobody can hope to succeed by just protecting the core business, as it can be made obsolete very, very quickly. And nobody can hope to change a trend. It is more important than ever that organizations spend far less time focused on what they did, and spend a lot more time thinking about what they need to do next. Planning needs to shift from deep numerical analysis of the past, and a lot more in-depth discussion about technology trends and how they will impact their business in the next 1, 3 and 5 years.
Sears Holdings was a 13 year ride. Investor hope that Lampert could cut costs enough to make Sears and KMart profitable again drove the stock very high. But the reality that this strategy was impossible finally drove the value lower than when the journey started. The debacle has ruined 2 companies, thousands of employees’ careers, many shopping mall operators, many suppliers, many communities, and since 2007 thousands of investor’s gains. Four years up, then 9 years down. It happened a lot faster than anyone would have imagined in 2003 or 2004. But it did.
And it could happen to you. Invert your strategic planning time. Spend 80% on trends and scenario planning, and 20% on historical analysis. It might save your business.
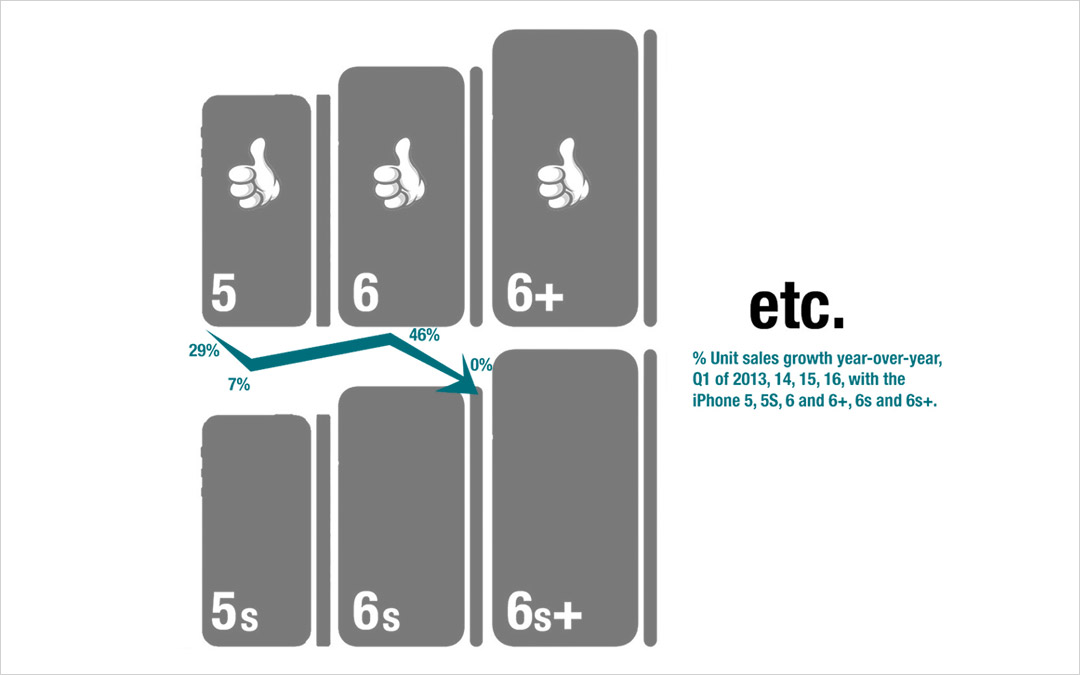
by Adam Hartung | May 10, 2016 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
My last column focused on growth, and the risks inherent in a Growth stall. As I mentioned then, Apple will enter a Growth Stall if its revenue declines year-over-year in the current quarter. This forecasts Apple has only a 7% probability of consistently growing just 2%/year in the future.
This usually happens when a company falls into Defend & Extend (D&E) management. D&E management is when the bulk of management attention, and resources, flow into protecting the “core” business by seeking ways to use sustaining innovations (rather than disruptive innovations) to defend current customers and extend into new markets. Unfortunately, this rarely leads to high growth rates, and more often leads to compressed margins as growth stalls. Instead of working on breakout performance products, efforts are focused on ways to make new versions of old products that are marginally better, faster or cheaper.
 Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
For example, Apple’s CEO has trumpeted the company’s installed base of 1B iPhones, and stated they will be a future money maker. He bragged about the 20% growth in “services,” which are iPhone users taking advantage of Apple Music, iCloud storage, Apps and iTunes. This shows management’s desire to extend sales to its “installed base” with sustaining software innovations. Unfortunately, this 20% growth was a whopping $1.2B last quarter, which was 2.4% of revenues. Not nearly enough to make up for the decline in “core” iPhone, iPad or Mac sales of approximately $9.5B.
Apple has also been talking a lot about selling in China and India. Unfortunately, plans for selling in India were at least delayed, if not thwarted, by a decision on the part of India’s regulators to not allow Apple to sell low cost refurbished iPhones in the country. Fearing this was a cheap way to dispose of e-waste they are pushing Apple to develop a low-cost new iPhone for their market. Either tactic, selling the refurbished products or creating a cheaper version, are efforts at extending the “core” product sales at lower margins, in an effort to defend the historical iPhone business. Neither creates a superior product with new features, functions or benefits – but rather sustains traditional product sales.
Of even greater note was last week’s announcement that Apple inked a partnership with SAP to develop uses for iPhones and iPads built on the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platform. This announcement revealed that SAP would ask developers on its platform to program in Swift in order to support iOS devices, rather than having a PC-first mentality.
This announcement builds on last year’s similar announcement with IBM. Now 2 very large enterprise players are building applications on iOS devices. This extends the iPhone, a product long thought of as great for consumers, deeply into enterprise sales. A market long dominated by Microsoft. With these partnerships Apple is growing its developer community, while circumventing Microsoft’s long-held domain, promoting sales to companies as well as individuals.
And Apple has shown a willingness to help grow this market by introducing the iPhone 6se which is smaller and cheaper in order to obtain more traction with corporate buyers and corporate employees who have been iPhone resistant. This is a classic market extension intended to sustain sales with more applications while making no significant improvements in the “core” product itself.
And Apple’s CEO has said he intends to make more acquisitions – which will surely be done to shore up weaknesses in existing products and extend into new markets. Although Apple has over $200M of cash it can use for acquisitions, unfortunately this tactic can be a very difficult way to actually find new growth. Each would be targeted at some sort of market extension, but like Beats the impact can be hard to find.
Remember, after all revenue gains and losses were summed, Apple’s revenue fell $7.6B last quarter. Let’s look at some favorite analyst acquisition targets to explain:
- Box could be a great acquisition to help bring more enterprise developers to Apple. Box is widely used by enterprises today, and would help grow where iCloud is weak. IBM has already partnered with Box, and is working on applications in areas like financial services. Box is valued at $1.45B, so easily affordable. But it also has only $300M of annual revenue. Clearly Apple would have to unleash an enormous development program to have Box make any meaningful impact in a company with over $500B of revenue. Something akin of Instagram’s growth for Facebook would be required. But where Instagram made Facebook a pic (versus words) site, it is unclear what major change Box would bring to Apple’s product lines.
- Fitbit is considered a good buy in order to put some glamour and growth onto iWatch. Of course, iWatch already had first year sales that exceeded iPhone sales in its first year. But Apple is now so big that all numbers have to be much bigger in order to make any difference. With a valuation of $3.7B Apple could easily afford FitBit. But FitBit has only $1.9B revenue. Given that they are different technologies, it is unclear how FitBit drives iWatch growth in any meaningful way – even if Apple converted 100% of Fitbit users to the iWatch. There would need to be a “killer app” in development at FitBit that would drive $10B-$20B additional annual revenue very quickly for it to have any meaningful impact on Apple.
- GoPro is seen as a way to kick up Apple’s photography capabilities in order to make the iPhone more valuable – or perhaps developing product extensions to drive greater revenue. At a $1.45B valuation, again easily affordable. But with only $1.6B revenue there’s just not much oomph to the Apple top line. Even maximum Apple Store distribution would probably not make an enormous impact. It would take finding some new markets in industry (enterprise) to build on things like IoT to make this a growth engine – but nobody has said GoPro or Apple have any innovations in that direction. And when Amazon tried to build on fancy photography capability with its FirePhone the product was a flop.
- Tesla is seen as the savior for the Apple Car – even though nobody really knows what the latter is supposed to be. Never mind the actual business proposition, some just think Elon Musk is the perfect replacement for the late Steve Jobs. After all the excitement for its products, Tesla is valued at only $28.4B, so again easily affordable by Apple. And the thinking is that Apple would have plenty of cash to invest in much faster growth — although Apple doesn’t invest in manufacturing and has been the king of outsourcing when it comes to actually making its products. But unfortunately, Tesla has only $4B revenue – so even a rapid doubling of Tesla shipments would yield a mere 1.6% increase in Apple’s revenues.
- In a spree, Apple could buy all 4 companies! Current market value is $35B, so even including a market premium $55B-$60B should bring in the lot. There would still be plenty of cash in the bank for growth. But, realize this would add only $8B of annual revenue to the current run rate – barely 25% of what was needed to cover the gap last quarter – and less than 2% incremental growth to the new lower run rate (that magic growth percentage to pull out of a Growth Stall mentioned earlier in this column.)
Such acquisitions would also be problematic because all have P/E (price/earnings) ratios far higher than Apple’s 10.4. FitBit is 24, GoPro is 43, and both Box and Tesla are infinite because they lose money. So all would have a negative impact on earnings per share, which theoretically should lower Apple’s P/E even more.
Acquisitions get the blood pumping for investment bankers and media folks alike – but, truthfully, it is very hard to see an acquisition path that solves Apple’s revenue problem.
All of Apple’s efforts big efforts today are around sustaining innovations to defend & extend current products. No longer do we hear about gee whiz innovations, nor do we hear about growth in market changing products like iBeacons or ApplePay. Today’s discussions are how to rejuvenate sales of products that are several versions old. This may work. Sales may recover via growth in India, or a big pick-up in enterprise as people leave their PCs behind. It could happen, and Apple could avoid its Growth Stall.
But investors have the right to be concerned. Apple can grow by defending and extending the iPhone market only so long. This strategy will certainly affect future margins as prices, on average, decline. In short, investors need to know what will be Apple’s next “big thing,” and when it is likely to emerge. It will take something quite significant for Apple to maintain it’s revenue, and profit, growth.
The good news is that Apple does sell for a lowly P/E of 10 today. That is incredibly low for a company as profitable as Apple, with such a large installed base and so many market extensions – even if its growth has stalled. Even if Apple is caught in the Innovator’s Dilemma (i.e. Clayton Christensen) and shifting its strategy to defending and extending, it is very lowly valued. So the stock could continue to perform well. It just may never reach the P/E of 15 or 20 that is common for its industry peers, and investors envisioned 2 or 3 years ago. Unless there is some new, disruptive innovation in the pipeline not yet revealed to investors.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 27, 2016 | Food and Drink, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Retail, Software, Web/Tech
Growth fixes a multitude of sins. If you grow revenues enough (you don’t even need profits, as Amazon has proven) investors will look past a lot of things. With revenue growth high enough, companies can offer employees free meals and massages. Executives and senior managers can fly around in private jets. Companies can build colossal buildings as testaments to their brand, or pay to have thier names on public buildings. R&D budgets can soar, and product launches can fail. Acquisitions are made with no concerns for price. Bonuses can be huge. All is accepted if revenues grow enough.
Just look at Facebook. Today Facebook announced today that for the quarter ended March, 2016 revenues jumped to $5.4B from $3.5B a year ago. Net income tripled to $1.5B from $500M. And the company is basically making all its revenue – 82% – from 1 product, mobile ads. In the last few years Facebook paid enormous premiums to buy WhatsApp and Instagram – but who cares when revenues grow this fast.
Anticipating good news, Facebook’s stock was up a touch today. But once the news came out, after-hours traders pumped the stock to over $118//share, a new all time high. That’s a price/earnings (p/e) multiple of something like 84. With growth like that Facebook’s leadership can do anything it wants.
But, when revenues slide it can become a veritable poop puddle. As Apple found out.
Rumors had swirled that Apple was going to say sales were down. And the stock had struggled to make gains from lows earlier in 2016. When the company’s CEO announced Tuesday that sales were down 13% versus a year ago the stock cratered after-hours, and opened this morning down 10%. Breaking a streak of 51 straight quarters of revenue growth (since 2003) really sent investors fleeing. From trading around $105/share the last 4 days, Apple closed today at ~$97. $40B of equity value was wiped out in 1 day, and the stock trades at a p/e multiple of 10.
The new iPhone 6se outsold projections, iPads beat expectations. First year Apple Watch sales exceeded first year iPhone sales. Mac sales remain much stronger than any other PC manufacturer. Apple iBeacons and Apple Pay continue their march as major technologies in the IoT (Internet of Things) market. And Apple TV keeps growing. There are about 13M users of Apple’s iMusic. There are 1.5M apps on the iTunes store. And the installed base keeps the iTunes store growing. Share buybacks will grow, and the dividend was increased yet again. But, none of that mattered when people heard sales growth had stopped. Now many investors don’t think Apple’s leadership can do anything right.
 Yet, that was just one quarter. Many companies bounce back from a bad quarter. There is no statistical evidence that one bad quarter is predictive of the next. But we do know that if sales decline versus a year ago for 2 consecutive quarters that is a Growth Stall. And companies that hit a Growth Stall rarely (93% of the time) find a consistent growth path ever again. Regardless of the explanations, Growth Stalls are remarkable predictors of companies that are developing a gap between their offerings, and the marketplace.
Yet, that was just one quarter. Many companies bounce back from a bad quarter. There is no statistical evidence that one bad quarter is predictive of the next. But we do know that if sales decline versus a year ago for 2 consecutive quarters that is a Growth Stall. And companies that hit a Growth Stall rarely (93% of the time) find a consistent growth path ever again. Regardless of the explanations, Growth Stalls are remarkable predictors of companies that are developing a gap between their offerings, and the marketplace.
Which leads us to Chipotle. Chipotle announced that same store sales fell almost 30% in Q1, 2016. That was after a 15% decline in Q4, 2015. And profits turned to losses for the quarter. That is a growth stall. Chipotle shares were $750/share back in early October. Now they are $417 – a drop of over 44%.
Customer illnesses have pointed to a company that grew fast, but apparently didn’t have its act together for safe sourcing of local ingredients, and safe food handling by employees. What seemed like a tactical problem has plagued the company, as more customers became ill in March.
Whether that is all that’s wrong at Chipotle is less clear, however. There is a lot more competition in the fast casual segment than 2 years ago when Chipotle seemed unable to do anything wrong. And although the company stresses healthy food, the calorie count on most portions would add pounds to anyone other than an athlete or construction worker – not exactly in line with current trends toward dieting. What frequently looks like a single problem when a company’s sales dip often turns out to have multiple origins, and regaining growth is nearly always a lot more difficult than leadership expects.
Growth is magical. It allows companies to invest in new products and services, and buoy’s a stock’s value enhancing acquisition ability. It allows for experimentation into new markets, and discovering other growth avenues. But lack of growth is a vital predictor of future performance. Companies without growth find themselves cost cutting and taking actions which often cause valuations to decline.
Right now Facebook is in a wonderful position. Apple has investors rightly concerned. Will next quarter signal a return to growth, or a Growth Stall? And Chipotle has investors heading for the exits, as there is now ample reason to question whether the company will recover its luster of yore.













 A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also
A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also 

