
by Adam Hartung | Nov 2, 2019 | Disruptions, Food and Drink, Innovation, Marketing, Strategy, Trends
The newsletters of Adam Hartung.
Keynote Speaker, Managing Partner, Author on Trends
Mighty Oaks from Tiny Acorns Grow – Beyond Meat
TREND: Beyond Meat (BYND, NASDAQ)
A big, new trend is emerging. Sales of plant based protein products may be small, but growth is remarkable. Could Beyond Meat be the next Netflix?

In Q3 2019, Beyond Meat’s revenue is up 2.5x (250%) vs Q3 2018 — which was up 2.5x (250%) over Q3 2017. Yes, you can say this growth is on a small base, given that last quarter was $100M revenue.
Imagine what it’s like growing that fast. Imagine the exhilaration of solving problems – like funding your accounts receivable that’s growing with accelerating orders. Or amping up production faster than ever imagined. Or meeting needs of your customers, retailers and restaurants. Or paying out big bonuses due to beating all your planned metrics.
It’s not that much fun to work at Cargill. Or Tyson Foods. Or Smithfield. Or any other traditional company producing beef, or pork, or chicken. Those are huge companies, with lots of people. But they aren’t maxing out sales and profits – and bonuses – like Beyond Meat.
It’s easy to ignore a start up. But one has to look at the relative growth of a company to judge its future. There were cracks in the growth rate at Blockbuster 6 years before it failed. And during that time, Blockbuster kept saying Netflix was a nit that didn’t matter. But Netflix was growing like the proverbial weed. Netflix wasn’t even half the size of Blockbuster when Blockbuster filed for bankruptcy.
With growth like Beyond Meat it didn’t take long to upset an entire industry biz model. Amazon still doesn’t sell as much as WalMart, but it wiped out a significant number of retailers by changing volumes enough to erase their profits. Think about the changes wrought on the advertising industry by Google, which has pretty much killed print ads. Look at what’s happened to other media ad models, like TV and radio, by Facebook’s growth. And entertainment has been entirely changed – where today the onetime distributor is one of the biggest content producers – Netflix.
In traditional marketing theory, Beyond Meat, like Netflix, is selling new products to existing markets.
Most disruptors enter the markets in the new product/new market quadrant of the Ansoff matrix. They create the new market just by entering. If they even see them as competitors, established businesses dismiss these potential disruptors because of established focus on current markets/current products with sustaining innovations. Selling new products to existing customers is the first step companies take as they start to innovate.
Kraft was on this path when they acquired a new productc with its purchase of Boca Burger in 2000. Kellogg’s and General Foods jumped into the alternative meat products at about the same time. Vegetarian burger substitutes threatened the success formula of meat products and were relegated to niche products. In 2018, Kraft’s incubator tried to relaunch Boca, but the smaller, more nimble start-ups had already captured consumers’ attention and reframed the market.
Beyond Meat had morphed quickly into a direct competitor to the meat industry by selling this new product to existing meat customers!
Riding the trends of climate change, sustainability and organic foods, Beyond Meat is starting to look like a true game changer. It may be small, but those other companies were too (along with Tesla, don’t forget, considered immaterial by GM, et.al.) Those who are in the traditional protein market (beef especially) had better pay attention – their profit model is already under attack!!
“The creation of a thousand forests is in one acorn.”
What’s on your company’s radar today?
Spark Partners is here to help as your coach on trends and innovation. We bring years of experience studying trends, organizations, and how to implement. We bring nimbleness to your strategy, and help you maximize your ability to execute.
Let us do an opportunity assessment for your organization. For less than your annual gym cost, or auto insurance premium, we could likely identify some good opportunities your blinders are hiding. Read my Assessment Page to learn more.
For more on how to include trends in your planning, I’ve created a “how-to” that you can adapt for your team. See my
Status Quo Risk Management Playbook.
Give us a
call today, or send an email, so we can talk about how you can be a leader, rather than follower. Or check out the rest of the
website to read up on what we do so we can create the right level of engagement for you.
Hartung Recent Blog Posts on Leadership, Investing, Trends
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.

by Adam Hartung | May 9, 2019 | Innovation, Marketing, Strategy, Trends
Market Threat Assessment
Recent studies of senior managers have shown that being blindsided by a disruption is the largest unresolved concern in strategy development today.
That fear is too often real because disruption typically begins where it is least visible to management- on the fringes of the existing target markets. And, once the disruption “pirate ship” is sighted on the horizon, not only is it probably too late, but companies react poorly.
Some research of corporate responses to disruption has shown that most companies ignore the threat, fortify existing positions or attempt to buy innovation. The first choice is not an option for an ongoing business. Fortification through distribution changes, product model proliferation and discounting only buys some additional time while wasting resources. Once a disruption enters the market, there’s little time for organic innovation efforts so companies often make acquisitions attempting to buy innovation. Sadly, given the risk profile and limited experience in innovation, these are often sustaining innovations which are swept aside by the wave of disruption.
A very large example is when Microsoft fell behind in the mobile market in 2014 and purchased Nokia, a weak player in mobile phones to get access to this market. The joint project, the Lumina phone, failed to catch on and Microsoft’s share fell by 50%- fail. Cisco tried to catch up with the photography trend by acquiring Pure Digital, the maker of low cost Flip cameras. Unfortunately, shortly after the acquisition, the high-resolution sensors included in smartphones took photography to a new level. Bye, Flip! Trend monitoring would have predicted this natural evolution as a high risk threat.
To anticipate external changes, marketing departments have embraced big data as a powerful tool to help companies identify new markets and consumer preferences. These tools use the past to predict the short-term future which is reasonable in a steady market. The problem is that big data cannot anticipate dynamic disruption.
But, you and your staff can.
As a key input to your next strategy workshop, use trends! As a start, gather info from the people closest to your market and further using Porter’s five force model. See my articles on Scenarios to expand these trends to actionable goals.
What’s on your company’s radar today?
We are here to help as your coach on trends and innovation. We bring years of experience studying trends, organizations, and how to implement. We bring nimbleness to your strategy, and help you maximize your ability to execute.
Go the www.adamhartung.com and view the Assessment Page. Send me a reply to this email, or call me today, and let’s start talking about what trends will impact your organization and what you’ll need to do to pivot toward greater success.

by Adam Hartung | May 1, 2019 | Disruptions, Innovation, Marketing, Strategy
Find Opportunities Out of the Box
If your company is like most businesses, your list of new product or service ideas looks like a sales wish list- new features at a lower cost. Marketing or product management may go a step further and group the ideas into product line extensions or possibly entries into new market segments. Unfortunately, while generating revenue in the short run, this process leaves the company vulnerable to competition and missing opportunities in the long run.
Well, you are not alone. Since about 2012, the pace of innovation has slowed even in the popular market of social media. According to KeyMedia, “What was once a world of diversity and originality has slowly started to look like a bad case of déjà vu… (as platforms are) becoming more similar to each other…”
Most companies devote resources to a quadrant on the innovation matrix known as “sustaining innovation.” They improve existing products sold to existing customers. It’s low risk, true, but it’s also low return. Why do companies follow this death spiral? It’s because “innovation” has gotten a bad reputation.
According to Inc. magazine, “…many (business) people have come to equate the idea of innovation with disruptive innovation. But the fact is that for most businesses, placing big bets on high-risk ideas is not only unfeasible, it’s unwise.”
The Ansoff matrix of new and existing markets and products is usually interpreted as 4 quadrants. It is much more than that: it is a continuum between sustaining and disruptive innovation. .
Adam Hartung often tells clients, “Get out of the box, then think!” This applies directly to the Ansoff model. Once a company sees the matrix, not as fixed “boxes” but as a spectrum of opportunities, markets are viewed not as filled with risk, but filled with opportunities!
Consider Ricoh’s new “clickable paper” that combines the print channel, with an app and that integrates to social media or a website. Not disruptive in the classical sense, but an adjacent product and adjacent market segment that makes print relevant to tech savvy consumers. Or Dr. Dre’s Beats headphones that combine pre-equalized sound with noise cancellation and style- a clever and highly successful blend of existing technologies, vigorously marketed.
Uncovering these market opportunities that can deliver improved returns at a manageable risk for the firm. New products will also generate an increasing percentage of revenue leading to continued growth. Companies that master this process have a long range radar to identify potential opportunities in a process called, “continuous innovation”.
What’s on your company’s radar today?
We are here to help as your coach on trends and innovation. We bring years of experience studying trends, organizations, and how to implement. We bring nimbleness to your strategy, and help you maximize your ability to execute.
Go the website and view the Assessment Page. Send me a reply to this email, or call me today, and let’s start talking about what trends will impact your organization and what you’ll need to do to pivot toward greater success.

by Adam Hartung | Jul 30, 2018 | Innovation, Investing, Software, Strategy, Trends, Web/Tech
On July 26, 2018 Facebook set a record for the most value lost in one day by a single company. An astonishing $119B of market value was destroyed as the shares sank more than $40. For many investors, it was the sky falling.
As most of you know, I’ve followed Facebook closely since it went public in 2012. And, I’ve long been an admirer. I said buy it at the IPO, and I’m saying buy it now. Click on the title of any of the posts to read the full content.
To summarize, Facebook may be under attack, but it is barely wounded. And it is not in the throes of demise. The long-term trends all favor the social media’s ongoing growth, and higher values in the future. Below I’ll offer some of my previous blogs that are well worth revisiting amidst the current Facebook angst.
FANG (Facebook, Amazon, Netflix and Google) investing is still the best bet in the market. They have outperformed for years, and will continue to do so. Why? Because they are growing revenues and profits faster than any other major companies in the market. And “Growth is Good” (paraphrasing Gordon Gekko.) If you have any doubts about the importance of growth, go talk to Immelt of GE or Lampert of Sears.
Don’t forget, for years now Facebook is more than Facebook.com. It’s smart acquisition programs have dramatically increased the platform’s reach with video, messaging, texting and eventually peer-to-peer video. Facebook’s leadership has built a very adaptable company, able to change the product to meet growing user (and customer) needs.
Facebook is on a path toward significant communication domination. Facebook today is sort of the New York Times, Washington Post, Los Angeles Times and about 90% of the rest of the nation’s newspapers all in one. Nobody is close to challenging Facebook’s leadership in news distribution, and all news is increasingly going on-line.
For all these reasons, you really do want to own Facebook. Especially at this valuation. It’s getting a chance to buy Facebook at its value when the year started, and Facebook is that much bigger, stronger, and adapted to changing privacy regulations that were still a mystery back then.
Oh, one last thing (paraphrasing Steve Jobs.) Facebook actually isn’t the biggest one day drop in stock valuation, despite what you’ve read.
Stocks are priced in dollars, and dollars are subject to inflation. So we should look at historical drops in inflation adjusted dollars. Even though inflation has been mostly below 3% since the 1990s, from 2000 to today the dollar has inflated by 46%. So inflation-adjusted, the biggest one day value destruction actually belongs to Intel, which lost $131B in September, 2000. And Microsoft is only slightly in third place, having lost $117B in April, 2000. So keep this in mind when you think about the long-term opportunity for Facebook.
Now Published! “Facebook- The Making of a Great Company” ebook by Adam Hartung.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 20, 2018 | Boards of Directors, Growth Stall, Investing, Manufacturing, Strategy
An American epoch has ended. General Electric was part of the first ever Dow Jones Index in 1896. When the Dow Jones Industrial Average was formed in 1907 GE was a participant. GE has been the only company to remain on the index. All other original companies long ago completely disappeared.
GE did so well because its leadership had been able to constantly change the company to keep it relevant, and growing. During the century prior to hiring Jeff Immelt as CEO GE went from light bulbs to generating electricity and making all kinds of electrical infrastructure equipment, electric locomotives, mainframe computers, medical equipment, computer services, financial services, entertainment…. The list is very long.
Although not all GE CEOs were great, the Board was able to place CEOs in office who could sense market shifts and make good decisions. GE leadership thoughtfully analyzed markets, and made investment decisions to sell businesses that were not growing. And they made investment decisions to invest in trends which created growth. One of the best of these was Jack Welch, who developed the nickname “Neutron Jack” for his willingness to jettison businesses that were not growing and leading their industry, while willingly investing in entirely new growth markets where trends showed high rates of return like financial services and entertainment – wildly “non-industrial” markets.
But CEO Immelt was completely tone-deaf to the outside world. He was wholly unable to understand how to lead a team that could make good investments. Instead under Immelt’s leadership GE over-invested in historical products where they were losing advantage but trying to “keep up.” Selling businesses that were growing but faced stiff competition, rather than investing in growth. And refusing to invest in new external growth opportunities that could keep revenues increasing – and drive a higher GE market capitalization.
All the way back in 2009 I pointed out that GE was in a Growth Stall, and had only a 7% chance of consistently growing at 2%. I warned investors. At the time I said GE had to go all-out on a growth strategy, or things would turn ugly. But a lot of investors, employees – and apparently the Board of Directors – were ready to blame the Growth Stall on the economy. And blame it on Welch, who had been gone for 8 years. And say GE was lucky Immelt saved the company from bankruptcy with a loan from Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway.
Say what? Saved the company? Why did Immelt, and the Board, let GE get into such terrible shape? It was time to replace the CEO, not double down on his failed strategy.
Six years ago, May, 2012, I published in Forbes “5 CEOs that Should Have Already Been Fired.” At the time I said Immelt was the 4th worst CEO in America. I cited the 2009 column, and pointed out things really weren’t any better in 2012 than in 2009. That column had well over 1million reads. There was no way GE’s board was not aware of the column, and the realization that Immelt was a horrible CEO.
The Board of #3 (Walmart) fired Mike Duke. And the Board of #1 (Microsoft) fired Steve Ballmer. There is no real board at #2 Sears (which will file bankruptcy soon enough) because the CEO is also the largest shareholder (via his hedge fund) and he controls all board decisions. He should have fired himself, but had too much ego. But the board of GE – well it did nothing. Even though GE almost went bankrupt under Immelt, and its value was being destroyed quarter after quarter it left him in place.
I revisited the performance of these five CEOs and their companies in August, 2014 and reminded hundreds of thousands of readers – which I’m sure included GE’s Board of Directors – that company revenues had declined every year since 2009. And this string of failures had caused the company’s value to decline by 2/3. Yet, the board did nothing to replace this horrific CEO.
By March, 2017 I was so exasperated I finally titled my column “GE Needs a New Strategy and a New CEO.” Again, I detailed all the things that went wrong. It took 7 more months before the Board pushed Immelt out. But the new CEO failed to offer a better strategy, continuing to promote the notion of selling businesses to raise cash to “fix” the broken businesses – without identifying any growth strategy at all.
The only thing that can “fix” GE – save it from being dismembered and sold off – is a growth strategy. I offered how the new CEO could undertake this effort in October, 2017. But the Board, still wholly incompetent, still isn’t listening. Nobody should be surprised that GE is now removed from the Dow, and the new CEO is clearly without a clue how to find a path back to relevancy.
Too bad for investors, employees, suppliers, customers and the communities where the GE businesses reside. This didn’t have to happen. But due to an incompetent Board of Directors, which did nothing to properly govern an incompetent CEO, it did. And there’s little doubt it won’t be long before GE meets the same end as DuPont.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 5, 2018 | Investing, Retail, Strategy, Trends, Web/Tech
The US e-commerce market is just under 10% the size of entire retail market. On the face of it this would indicate that the game is far from over for big traditional retail. After all, how could such a small segment kill profits for such a huge industry based on enormous traditional players?
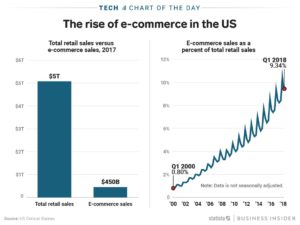
Yet, Sears – once a Dow Jones component and the world’s most powerful retailer – has announced it will close 100 more stores. The Kmart/Sears chain is now only 894 stores – down from thousands at its peak and 1,275 just last year. Revenue dropped 30% versus a year ago, and quarterly losses of $424M were almost 15% of revenues.
But, that ignores marginal economics. It often doesn’t take a monster change in one factor to have a huge impact on the business model. Let’s say Sales are $100. Less Cost of Goods sold of $75. That leaves a Gross Margin of $25. Selling, General and Administrative costs are 20%, so Operating Income is only $5. The Net Margin before Interest and Taxes is 5%. (BTW, these are the actual percentages of Walmart from 1/31/18.)
Now, in comes a new competitor – like Amazon.com. They have no stores, no store clerks, and minimal inventory due to “e-storefront” selling. So, they are able to lower prices by 5%. That seems pretty small – just a 5% discount compared to typical sales of 20%, 30% even 50% (BOGO) in retail stores. Amazon’s 5% price reduction seems like no big deal to established firms.
But, Walmart has to lower prices by 5% in response, which lowers revenues to $95. But the stores, clerks, inventory, distribution centers and trucks all largely remain. With Cost of Goods Sold still $75, Gross Margin falls to $20. Fixed headquarters costs, general and administrative costs don’t change, so they remain at $20. This leaves Operating Income of …$0.
(For more detailed analysis see “Bigger is Not Always Better – Why Amazon is Worth More than Walmart” from July, 2015.)
How can Walmart survive with no profits? It can’t. To get some margin back, Walmart has to start shutting stores, selling assets, cutting pay, using automation to cut headcount, beating on vendors to offer them better prices. This earns praise as “a low cost operation.” When in fact, this makes Walmart a less competitive company, because it’s footprint and service levels decline, which encourages people to do more shopping on-line. A vicious circle begins of trying to recapture lost profitability, while sales are declining rather than growing.
Walmart was (and is) huge. Even Sears was much bigger than Amazon.com at the beginning. But to compete with Amazon.com both had to lower prices on ALL of their products in ALL of their stores. So the hit to Walmart’s, and Sears’, revenue is a huge number. Though Amazon.com was a much, much smaller company, its impact explodes on the larger competitor P&L’s.
This disruption is felt across the entire industry: ALL traditional retailers are forced to match Amazon and other e-commerce companies, even though there is no way they can cut costs enough to compete. Thus, Toys-R-Us, Radio Shack, Claire’s and Bon-Ton have declared bankruptcy in 2018, and the once great, dominant Sears is on the precipice of extinction.
All of which is good news for Amazon.com investors. Amazon.com has 40% market share of the entire e-commerce business. The fact that e-commerce is only 10% of all retail is great news for Amazon investors. That means there is still an enormously large market of traditional retail available to convert to on-line sales.
The shift to e-commerce will not be stopping, or even slowing. Since January, 2010 the future has been easily predictable for traditional retail’s decline. The next few years will see a transition of an additional $2.5 trillion on-line, which is 5X the size of the existing e-commerce market!
As stores close new competitors will emerge in the e-commerce market. But undoubtedly the big winner will be the company with 40% market share today – Amazon.com. So what will Amazon’s stock be worth when sales are 5x larger (or more) and Amazon can increase profits by making leveraging its infrastructure and slow future investments?
Twenty years ago, Amazon was a retail ant. And retail elephants ignored it. But that was foolish, because Amazon had a different business model with an entirely different cost of operations. And now the elephants are falling fast, due to their inability to adapt to new market conditions and maintain their growth.
_________________________________________________________________________
Author’s Note: In June, 2007 I was asked to predict WalMart’s future. Here are the predictions I made 11 years ago:
- “In 5 years (2012) Walmart would not have succeeded internationally” [True: Mexico, China, Germany all failed]
- “In 5 years (2012) Walmart would no new businesses, and its revenue will be stalled” [True]
- In 5 years (2012) Walmart would be spending more on stock repurchases then investing in its own stores or distribution” [True – and the Walton’s were moving money out of Walmart to other investments]
- “In 10 years (2017) Walmart would take a dramatic act, and make an acquisition” [True: Jet.com]
- “In 10 years (2017 Walmart’s value would not keep up with the stock market” [from 6/2007 to 6/2017 WMT went from $48 to $75 up 56.25%, DIA went from $134 to $180 up 34.3%, AMZN went from $70 to $1,000 up 1,330% or 13.3x]
- “In 30 years (2037) Walmart will only be known as “a once great company, like General Motors”

by Adam Hartung | May 2, 2018 | Entrepreneurship, Food and Drink, Innovation, Marketing, Strategy
Execution – Implementation – Delivering — These are table stakes today. If you can’t do them you don’t get a seat at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
Take for example a small company named NakedWine.com that created a potential death trap for its business by implementing one crucial execution mis-step.
The NakedWine value proposition is simple. They will find wines you never heard of and skip the costs of distributors and retailers by matching the customer and winemaker. Customers ostensibly get wines far cheaper because the winemaker’s cost of marketing and sales are avoided. Decent value proposition for both the customer, and the manufacturer.
The NakedWine strategy is to convince people that the NakedWine wines will be good, month after month. The NakedWine brand is crucial, as customer trust is now not in the hands of the winemaker, nor wine aficionados that rate known wines on a point scale, or even the local retail shop owner or employee. Customers must trust NakedWine to put a good product in their hands. Customers who most likely know little or nothing about wines. NakedWines wants customers to trust them so much they will buy the company’s boxed selections month after month, delivered to their home. These customers likely don’t know what they are getting, and don’t much care, because they trust NakedWine to give them a pleasurable product at a price point which makes them happy. When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
But, NakedWines blew the whole strategy with one simple execution mistake.
Not everyone lives where they can accept a case of wine, due to weather. As northern Californians, maybe NakedWine leaders just forget how cold it is in Minneapolis, Chicago, Buffalo and Boston. Or how hot it is in Tucson, Phoenix, Houston, Palm Springs and Las Vegas. In these climates a case of wine left on a truck for a day – or 2 if the first delivery is missed – spells the end of that wine. Ruined by the temperature. Especially heat, as everyone who drinks beer or wine knows that a couple of hours at 90 degrees can kill those products completely.
The only time the customer finally connects with NakedWine is when that wine enters the house, and over the lips. But that step, that final step of getting the perishable wine to the customer safely, in good quality, and aligned with customer expectations was not viewed as part of the brand-building strategy. Instead, leadership decided at this step NakedWines should instead focus on costs. They would view delivery as completely generic – divorced from the brand-building effort. They would use the low–cost vendor, regardless of the service provided.
NakedWine decided to use Fedex Ground, even though Fedex has a terrible package tracking system. Fedex is unwilling to make sure (say, by drivers using a cell phone) that customers will be there to receive a shipment. The driver rings a bell – no answer and he’s on the run in seconds to make sure he’s meeting Fedex efficiency standards, even if the customer was delayed to the door by a phone call or other issue. When the customer requests Fedex send the driver back around again, Fedex is unwilling to attempt a second delivery within short time, or even any time that same day, after delivery fails. If a customer calls about a missed delivery, Fedex is unwilling to route a failed delivery to a temperature local Fedex Office location for customer pick-up. Or to tell the customer where they can meet the driver along his route to accept delivery. Despite a range of good options, the NakedWine product is forced to sit on that Fedex truck, bouncing around all day in the heat, or cold, being ruined. Fedex uses its lowest cost approach to delivery to offer the lowest cost bid, regardless of the impact on the product and/or customer experience, and NakedWine didn’t think about the impact choosing that bid would have on its brand building.
Brand Building at Every Step
Simply put, in addition to flyers, advertising and product discounts, NakedWine should have followed through on its brand building strategy at every step. It must source wines its customers will enjoy. And it must deliver that perishable product in a way that builds the brand – not put it at risk. For example, NakedWine should screen all orders for delivery location, in order to make sure there are no delivery concerns. If there are, someone at NakedWine should contact the customer to discuss with them issues related to shipping, such as temperature. If it is to be too hot or cold, they could highly recommend using a temperature controlled pick-up location so as not to put the product at risk. And they should build in fail-safe’s with the shipping company to handle delivery problems. That is implementing a brand building strategy all the way from value-proposition to delivery.
Leaders Execute Plans
Too often leaders will work hard on a strategy, and create a good value proposition. But then, for some unknown reason, they turn over “execution” to people who don’t really understand the strategy. Worse, leadership often makes the egregious error of pushing those who create the value delivery system to largely to focus on costs, or other wrong metrics, with little concern for the value proposition and strategy. The result is a great idea that goes off the rails. Because the value delivery system simply does not live up to expectations of the value proposition.

by Adam Hartung | Mar 20, 2018 | Investing, Leadership, Lock-in, Marketing, Strategy, Transportation
Do you remember the songs, and videos, from 2008 “United Breaks Guitars?” After United Airlines destroyed musician Dave Carroll’s guitar he chronicled the months-long journey he took trying to replace it. In the end, United told him “F**k you” as customer service blew him off completely. He went on to make a few million dollars with his songs and parody about the horrible experience. Because so many people felt they were abused like Mr. Carroll.
“United Breaks Guitars” was a hit because so many people related to the terrible customer experience on United.  “The Unfriendly Skies” was the motto of customers, mocking the airlines “Friendly Skies” ads. It was clear that by 2008 United did not care about customers. Moving headlong to constantly lower operating costs, United built a culture that focused solely on efficiency, leading to terrible customer service, unhappy customers and employees that were a lot more worried about being yelled at by their bosses for not cutting costs than creating any customer satisfaction.
“The Unfriendly Skies” was the motto of customers, mocking the airlines “Friendly Skies” ads. It was clear that by 2008 United did not care about customers. Moving headlong to constantly lower operating costs, United built a culture that focused solely on efficiency, leading to terrible customer service, unhappy customers and employees that were a lot more worried about being yelled at by their bosses for not cutting costs than creating any customer satisfaction.
Things certainly haven’t changed. In 2017, United ejected a 69 year old physician from a plane, breaking his nose, knocking out his teeth and giving him a concussion. That created an uproar. Yet within a week United killed the world’s largest bunny rabbit in an airplane holding bin. But, even worse, last week United actually killed a puppy by forcing it be placed in an overhead bin. At least the dog United sent on a 1,000 mile unexpected flight to Japan survived, and the interviewed owner said he felt lucky the airline hadn’t killed his pet. Of course United refunded their money – which as you can imagine was a slap in the face to all these people who were so abused.
Unfortunately, United is just the worst of a bunch of bad airlines. Customer service really isn’t any better on Delta, American, JetBlue or Southwest. Saying these other airlines are better is just picking out a less heinous member of the Khmer Rouge Army.
STRATEGY MATTERS
This all goes back to deregulation. When President Carter allowed the airlines to charge as they like the industry really had no idea what it was going to do. There was chaos for years. But eventually consolidation kicked-in, and cutting cost was the only thing all 3 majors agreed upon. Buy more market share, as opposed to winning it with customer service, then slash the costs. This did the wonderfulness of leading all of them to file bankruptcy! Some twice! What a grand industry strategy!
 Then Chairman of American Airlines received Wall Street Journal front-page coverage for realizing people weren’t eating their olives in first class, so he ordered olives removed from the first class meals. He was cheered for saving $100K. But what folks missed was that he, and his peers leading the airlines, were systematically trying to figure out “how do we offer the least possible service.” By focusing on a strategy of lowering cost, and being doggedly determined in that strategy, soon nothing else mattered.
Then Chairman of American Airlines received Wall Street Journal front-page coverage for realizing people weren’t eating their olives in first class, so he ordered olives removed from the first class meals. He was cheered for saving $100K. But what folks missed was that he, and his peers leading the airlines, were systematically trying to figure out “how do we offer the least possible service.” By focusing on a strategy of lowering cost, and being doggedly determined in that strategy, soon nothing else mattered.
Today, there are no free meals in coach, and terrible meals in first class. Management angered employees into strikes and multi-year negotiations, beating down compensation and eliminating benefits leading to unhappiness so bad that in 2010 a Jet Blue flight attendant pulled the emergency exit and jumped out of the plane as he quit.
So, all the airlines in America stink. And, many domestic airlines in Europe, such as Ryan Air, have followed suit. The execs keep saying “all customers care about is price.” They use that excuse to create a culture so hostile to employees, and customers, that pretty soon employees are beating up customers and killing family pets (after charging extra to take the pet on the plane) and actually not caring.
Employees have become gestapos for the leadership – which has created a culture in which nobody wins. So flight attendants do as little as possible, because they don’t care about customers any more than leadership does. In 2017, a JetBlue attendant threw a family off flight because their toddler kicked the seat. When a woman complains about a child in seat next to her a Delta attendant throws her off the plane. And just last week when a 2 year old cries during boarding a Southwest attendant throws the child and her father off the plane.
Deregulation led to an oligopoly. Now, customers have no choice. Some of us fly almost every week on business, and it is pure hell. Nobody we deal with, from TSA to airport vendors to airline staff like customers. The culture has become “I’m abused, so you will be abused.” To fly is to succumb to being obsequious to ALL employees in your effort to not anger anyone, for fear they will deny you service. Or, worse, beat you up or kill your pet. But, honestly, there is nothing customers can do about it.
STRATEGY MATTERS
The leadership of the airlines, lacking regulation, implemented a strategy of “be low cost.” The result was creating a culture where employees routinely abuse customers in the process of trying to save a few dimes. If the next Mark Zuckerberg, Elon Musk or Reed Hastings showed up, do you think HR would hire them? Would the Board of Directors, so focused on the wrong strategy, consider any of them as CEO? The wrong strategy has led to the ruination of an entire industry, miserable employees, unhappy customers and marginal returns. It is a terrible culture.
So what is your strategy? Is your strategy creating the culture you want? Are you headed toward happy customers who want more of your product or service, and create growth? Or are you letting your lack of a forward-thinking strategy default you into operational cost cutting, and the movement toward a culture of misery that drives away employees, vendors and eventually customers?













 at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition. When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
 “The Unfriendly Skies” was the motto of customers, mocking the airlines “Friendly Skies” ads. It was clear that by 2008 United did not care about customers. Moving headlong to constantly lower operating costs, United built a culture that focused solely on efficiency, leading to terrible customer service, unhappy customers and employees that were a lot more worried about being yelled at by their bosses for not cutting costs than creating any customer satisfaction.
“The Unfriendly Skies” was the motto of customers, mocking the airlines “Friendly Skies” ads. It was clear that by 2008 United did not care about customers. Moving headlong to constantly lower operating costs, United built a culture that focused solely on efficiency, leading to terrible customer service, unhappy customers and employees that were a lot more worried about being yelled at by their bosses for not cutting costs than creating any customer satisfaction. Then Chairman of American Airlines received Wall Street Journal front-page coverage for realizing people weren’t eating their olives in first class, so he
Then Chairman of American Airlines received Wall Street Journal front-page coverage for realizing people weren’t eating their olives in first class, so he