by Adam Hartung | Nov 2, 2019 | Disruptions, Food and Drink, Innovation, Marketing, Strategy, Trends
The newsletters of Adam Hartung.
Keynote Speaker, Managing Partner, Author on Trends
Mighty Oaks from Tiny Acorns Grow – Beyond Meat
TREND: Beyond Meat (BYND, NASDAQ)
A big, new trend is emerging. Sales of plant based protein products may be small, but growth is remarkable. Could Beyond Meat be the next Netflix?

In Q3 2019, Beyond Meat’s revenue is up 2.5x (250%) vs Q3 2018 — which was up 2.5x (250%) over Q3 2017. Yes, you can say this growth is on a small base, given that last quarter was $100M revenue.
Imagine what it’s like growing that fast. Imagine the exhilaration of solving problems – like funding your accounts receivable that’s growing with accelerating orders. Or amping up production faster than ever imagined. Or meeting needs of your customers, retailers and restaurants. Or paying out big bonuses due to beating all your planned metrics.
It’s not that much fun to work at Cargill. Or Tyson Foods. Or Smithfield. Or any other traditional company producing beef, or pork, or chicken. Those are huge companies, with lots of people. But they aren’t maxing out sales and profits – and bonuses – like Beyond Meat.
It’s easy to ignore a start up. But one has to look at the relative growth of a company to judge its future. There were cracks in the growth rate at Blockbuster 6 years before it failed. And during that time, Blockbuster kept saying Netflix was a nit that didn’t matter. But Netflix was growing like the proverbial weed. Netflix wasn’t even half the size of Blockbuster when Blockbuster filed for bankruptcy.
With growth like Beyond Meat it didn’t take long to upset an entire industry biz model. Amazon still doesn’t sell as much as WalMart, but it wiped out a significant number of retailers by changing volumes enough to erase their profits. Think about the changes wrought on the advertising industry by Google, which has pretty much killed print ads. Look at what’s happened to other media ad models, like TV and radio, by Facebook’s growth. And entertainment has been entirely changed – where today the onetime distributor is one of the biggest content producers – Netflix.
In traditional marketing theory, Beyond Meat, like Netflix, is selling new products to existing markets.
Most disruptors enter the markets in the new product/new market quadrant of the Ansoff matrix. They create the new market just by entering. If they even see them as competitors, established businesses dismiss these potential disruptors because of established focus on current markets/current products with sustaining innovations. Selling new products to existing customers is the first step companies take as they start to innovate.
Kraft was on this path when they acquired a new productc with its purchase of Boca Burger in 2000. Kellogg’s and General Foods jumped into the alternative meat products at about the same time. Vegetarian burger substitutes threatened the success formula of meat products and were relegated to niche products. In 2018, Kraft’s incubator tried to relaunch Boca, but the smaller, more nimble start-ups had already captured consumers’ attention and reframed the market.
Beyond Meat had morphed quickly into a direct competitor to the meat industry by selling this new product to existing meat customers!
Riding the trends of climate change, sustainability and organic foods, Beyond Meat is starting to look like a true game changer. It may be small, but those other companies were too (along with Tesla, don’t forget, considered immaterial by GM, et.al.) Those who are in the traditional protein market (beef especially) had better pay attention – their profit model is already under attack!!
“The creation of a thousand forests is in one acorn.”
What’s on your company’s radar today?
Spark Partners is here to help as your coach on trends and innovation. We bring years of experience studying trends, organizations, and how to implement. We bring nimbleness to your strategy, and help you maximize your ability to execute.
Let us do an opportunity assessment for your organization. For less than your annual gym cost, or auto insurance premium, we could likely identify some good opportunities your blinders are hiding. Read my Assessment Page to learn more.
For more on how to include trends in your planning, I’ve created a “how-to” that you can adapt for your team. See my
Status Quo Risk Management Playbook.
Give us a
call today, or send an email, so we can talk about how you can be a leader, rather than follower. Or check out the rest of the
website to read up on what we do so we can create the right level of engagement for you.
Hartung Recent Blog Posts on Leadership, Investing, Trends
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.

by Adam Hartung | May 2, 2018 | Entrepreneurship, Food and Drink, Innovation, Marketing, Strategy
Execution – Implementation – Delivering — These are table stakes today. If you can’t do them you don’t get a seat at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
Take for example a small company named NakedWine.com that created a potential death trap for its business by implementing one crucial execution mis-step.
The NakedWine value proposition is simple. They will find wines you never heard of and skip the costs of distributors and retailers by matching the customer and winemaker. Customers ostensibly get wines far cheaper because the winemaker’s cost of marketing and sales are avoided. Decent value proposition for both the customer, and the manufacturer.
The NakedWine strategy is to convince people that the NakedWine wines will be good, month after month. The NakedWine brand is crucial, as customer trust is now not in the hands of the winemaker, nor wine aficionados that rate known wines on a point scale, or even the local retail shop owner or employee. Customers must trust NakedWine to put a good product in their hands. Customers who most likely know little or nothing about wines. NakedWines wants customers to trust them so much they will buy the company’s boxed selections month after month, delivered to their home. These customers likely don’t know what they are getting, and don’t much care, because they trust NakedWine to give them a pleasurable product at a price point which makes them happy. When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
But, NakedWines blew the whole strategy with one simple execution mistake.
Not everyone lives where they can accept a case of wine, due to weather. As northern Californians, maybe NakedWine leaders just forget how cold it is in Minneapolis, Chicago, Buffalo and Boston. Or how hot it is in Tucson, Phoenix, Houston, Palm Springs and Las Vegas. In these climates a case of wine left on a truck for a day – or 2 if the first delivery is missed – spells the end of that wine. Ruined by the temperature. Especially heat, as everyone who drinks beer or wine knows that a couple of hours at 90 degrees can kill those products completely.
The only time the customer finally connects with NakedWine is when that wine enters the house, and over the lips. But that step, that final step of getting the perishable wine to the customer safely, in good quality, and aligned with customer expectations was not viewed as part of the brand-building strategy. Instead, leadership decided at this step NakedWines should instead focus on costs. They would view delivery as completely generic – divorced from the brand-building effort. They would use the low–cost vendor, regardless of the service provided.
NakedWine decided to use Fedex Ground, even though Fedex has a terrible package tracking system. Fedex is unwilling to make sure (say, by drivers using a cell phone) that customers will be there to receive a shipment. The driver rings a bell – no answer and he’s on the run in seconds to make sure he’s meeting Fedex efficiency standards, even if the customer was delayed to the door by a phone call or other issue. When the customer requests Fedex send the driver back around again, Fedex is unwilling to attempt a second delivery within short time, or even any time that same day, after delivery fails. If a customer calls about a missed delivery, Fedex is unwilling to route a failed delivery to a temperature local Fedex Office location for customer pick-up. Or to tell the customer where they can meet the driver along his route to accept delivery. Despite a range of good options, the NakedWine product is forced to sit on that Fedex truck, bouncing around all day in the heat, or cold, being ruined. Fedex uses its lowest cost approach to delivery to offer the lowest cost bid, regardless of the impact on the product and/or customer experience, and NakedWine didn’t think about the impact choosing that bid would have on its brand building.
Brand Building at Every Step
Simply put, in addition to flyers, advertising and product discounts, NakedWine should have followed through on its brand building strategy at every step. It must source wines its customers will enjoy. And it must deliver that perishable product in a way that builds the brand – not put it at risk. For example, NakedWine should screen all orders for delivery location, in order to make sure there are no delivery concerns. If there are, someone at NakedWine should contact the customer to discuss with them issues related to shipping, such as temperature. If it is to be too hot or cold, they could highly recommend using a temperature controlled pick-up location so as not to put the product at risk. And they should build in fail-safe’s with the shipping company to handle delivery problems. That is implementing a brand building strategy all the way from value-proposition to delivery.
Leaders Execute Plans
Too often leaders will work hard on a strategy, and create a good value proposition. But then, for some unknown reason, they turn over “execution” to people who don’t really understand the strategy. Worse, leadership often makes the egregious error of pushing those who create the value delivery system to largely to focus on costs, or other wrong metrics, with little concern for the value proposition and strategy. The result is a great idea that goes off the rails. Because the value delivery system simply does not live up to expectations of the value proposition.
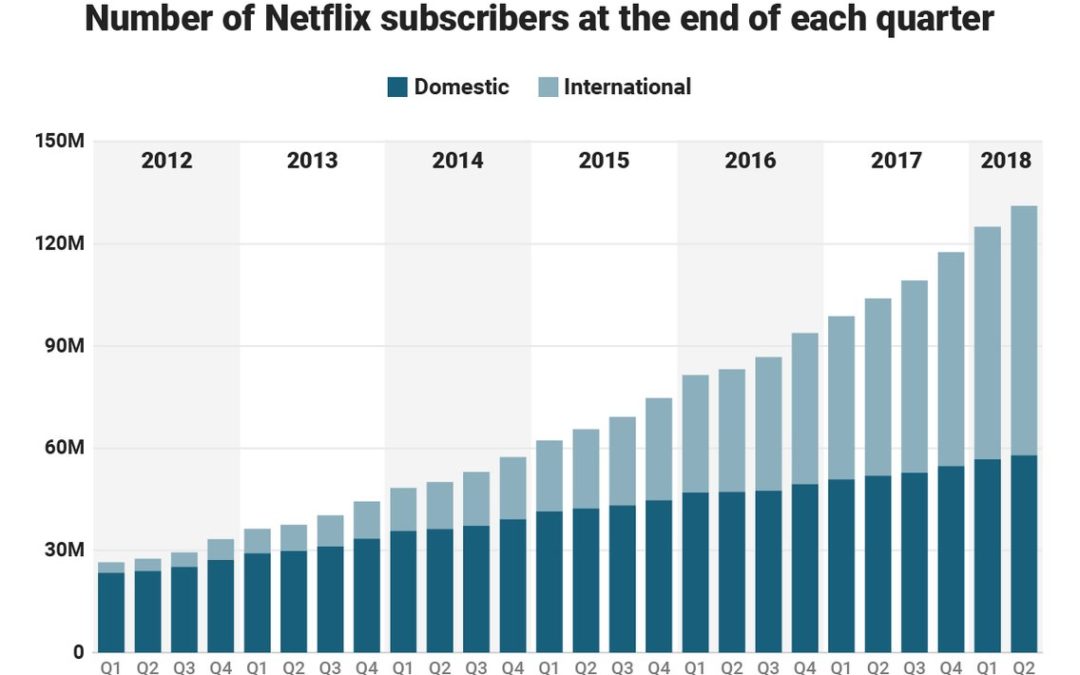
by Adam Hartung | Apr 25, 2018 | Entertainment, Film, Innovation, Investing, Retail
Netflix announced new subscriber numbers last week – and it exceeded expectations. Netflix now has over 130 million worldwide subscribers. This is up 480% in just the last 6 years – from under 30 million. Yes, the USA has grown substantially, more than doubling during this timeframe. But international growth has been spectacular, growing from almost nothing to 57% of total revenues. International growth the last year was 70%, and the contribution margin on international revenues has transitioned from negative in 2016 to over 15% – double the 4th quarter of 2017.
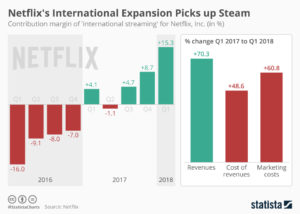
Accomplishing this is a remarkable story. Most companies grow by doing more of the same. Think of Walmart that kept adding stores. Then adding spin-off store brand Sam’s Club. Then adding groceries to the stores. Walmart never changed its strategy, leaders just did “more” with the old strategy. That’s how most people grow, by figuring out ways to make the Value Delivery System (in their case retail stores, warehouses and trucks) do more, better, faster, cheaper. Walmart never changed its strategy.
But Netflix is a very different story. The company started out distributing VHS tapes, and later DVDs, to homes via USPS, UPS and Fedex. It was competing with Blockbuster, Hollywood Video, Family Video and other traditional video stores. It won that battle, driving all of them to bankruptcy. But then to grow more Netflix invested far outside its “core” distribution skills and pioneered video streaming, competing with companies like DirecTV and Comcast. Eventually Netflix leaders raised prices on physical video distribution, cannibalizing that business, to raise money for investing in streaming technology. Streaming technology, however, was not enough to keep growing subscribers. Netflix leadership turned to creating its own content, competing with moviemakers, television and documentary producers, and broadcast television. The company now spends over $6B annually on content.
Think about those decisions. Netflix “pivoted” its strategy 3 times in one decade. Its “core” skill for growth changed from physical product distribution to network technology to content creation. From a “skills” perspective none of these have anything in common.
Could you do that? Would you do that?
How did Netflix do that? By focusing on its Value Proposition. By realizing that it’s Value Proposition was “delivering entertainment” Netflix realized it had to change its skill set 3 times to compete with market shifts. Had Netflix not done so, its physical distribution would have declined due to the emergence of Amazon.com, and eventually disappeared along with tapes and DVDs. Netflix would have followed Blockbuster into history. And as bandwidth expanded, and global networks grew, and dozens of providers emerged streaming purchased content profits would have become a bloodbath. Broadcasters who had vast libraries of content would sell to the cheapest streaming company, stripping Netflix of its growth. To continue growing, Netflix had to look at where markets were headed and redirect the company’s investments into its own content.
This is not how most companies do strategy. Most try to figure out one thing they are good at, then optimize it. They examine their Value Delivery System, focus all their attention on it, and entirely lose track of their Value Proposition. They keep optimizing the old Value Delivery System long after the market has shifted. For example, Walmart was the “low cost retailer.” But e-commerce allows competitors like Amazon.com to compete without stores, without advertising and frequently without inventory (using digital storefronts to other people’s inventory.) Walmart leaders were so focused on optimizing the Value Delivery System, and denying the potential impact of e-commerce, that they did not see how a different Value Delivery System could better fulfill the initial Walmart Value Proposition of “low cost.” The Walmart strategy never took a pivot – and now they are far, far behind the leader, and rapidly becoming obsolete.
Do you know your Value Proposition? Is it clear – written on the wall somewhere? Or long ago did you stop thinking about your Value Proposition in order to focus your intention on optimizing your Value Delivery System?
That fundamental strategy flaw is killing companies right and left – Radio Shack, Toys-R-Us and dozens of other retailers. Who needs maps when you have smartphone navigation? Smartphones put an end to Rand McNally. Who needs an expensive watch when your phone has time and so much more? Apple Watch sales in 2017 exceeded the entire Swiss watch industry. Who needs CDs when you can stream music? Sony sales and profits were gutted when iPods and iPhones changed the personal entertainment industry. (Anyone remember “boom boxes” and “Walkman”?)
I’ve been a huge fan of Netflix. In 2010, I predicted it was the next Apple or Google. When the company shifted strategy from delivering physical entertainment to streaming in 2011, and the stock tanked, I made the case for buying the stock. In 2015 when the company let investors know it was dumping billions into programming I again said it was strategically right, and recommended Netflix as a good investment. And I redoubled my praise for leadership when the “double pivot” to programming was picking up steam in 2016. You don’t have to be mystical to recognize a winner like Netflix, you just have to realize the company is using its strategy to deliver on its Value Proposition, and is willing to change its Value Delivery System because “core strength” isn’t important when its time to change in order to meet new market needs.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 3, 2018 | Computing, Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Mobile, Music
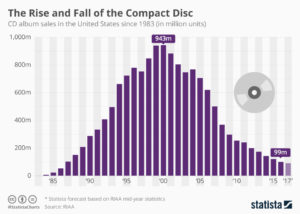
Do you still have a pile of compact discs? If so, why? When was the last time you listened to one? Like almost everyone else, you probably stream your music today. If you are just outdated, you listen to music you bought from iTunes or GooglePlay and store on your mobile device. But it would be considered prehistoric to tell people you carry around CDs for listening in your car – because you surely don’t own a portable CD player.
As the chart shows, CD sales exploded from nothing in 1983 to nearly 1B units in 2000. Now sales are less than 1/10th that number, due to the market shift expanded bandwidth allowed.
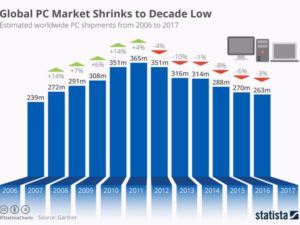
Do you still carry a laptop? If so, you are a dying minority. As PCs became more portable they became indispensable. Nobody left the office, or attended a meeting, without their laptop. That trend exploded until 2011, when PC sales peaked at 365M units. As the chart shows, in the 6 years since, PC sales have dropped by over 100M units, a 30% decline. The advent of mobile devices (smartphones and tablets) coupled with expanded connectivity and growing cloud services allowed mobility to reach entirely new levels – and people stopped carrying their PCs. And just like CDs are disappearing, so will PCs.
These charts dramatically show how quickly a new technology, or package of technologies, can change the way we behave. Simultaneously, they change the competitive landscape. Sony dominated the music industry, as a producer and supplier of hardware, when CDs dominated. But, as I wrote in 2012, the shift to more portable music caused Sony to fall into a rapid decline, and the company suffered 6 consecutive years (24 quarters) of falling sales and losses. The one-time giant was crippled by a technology shift they did not adopt. And they weren’t alone, as big box retailers such as Best Buy and Circuit City also faltered when these sales disappeared.
Once, Microsoft was synonymous with personal technology. Nobody maximized the value in PC growth more than Microsoft. But changing technology altered the competitive landscape, with Apple, Google, Samsung and Amazon emerging as the leaders. Microsoft, as the almost unnoticed launch of Windows 10 demonstrated, is struggling to maintain relevancy.
Too often we discount trends. Like Sony and Microsoft we think historical growth will continue, unabated. We find ways to discount market shifts, saying the products are “niche” and denigrating their quality. We will express our view that the market has “hiccuped” and will return to growth again. By the time we admit the shift is permanent new competitors have overtaken the lead, and we risk becoming totally obsolete. Like Toys-R-Us, Radio Shack, Sears and Motorola.
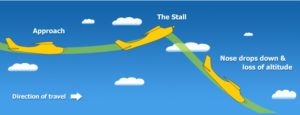
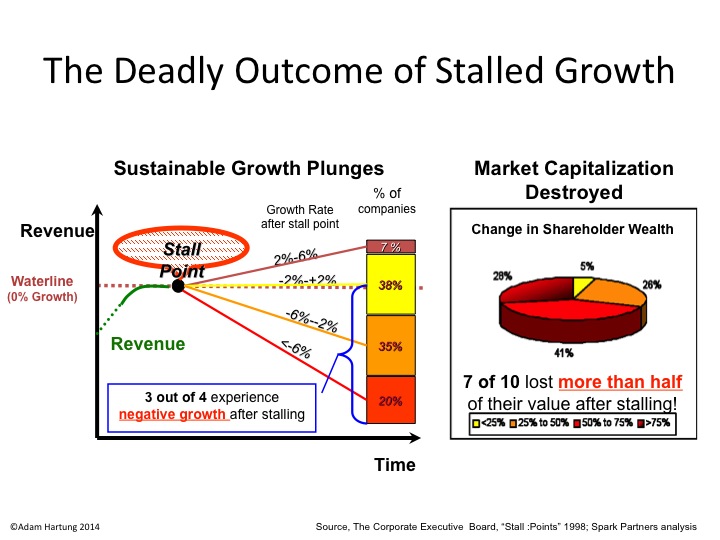
Aircraft stalls when not enough power to climb
The time for action is when the very first signs of shift happened. I’ve written a lot about “Growth Stalls” and they occur in just 2 quarters. 93% of the time a stalled company never again grows at a mere 2%/year. Look at how fast GE went from the best company in America to the worst. It is incredibly important that leadership react FAST when trends push customers toward new solutions, because it often takes very little time for the trend to make dying markets completely untenable.

by Adam Hartung | Jan 30, 2018 | Culture, Sports, Trends
“Business Insider says Japan has become “a demographic time bomb.” I guess it’s about time somebody realized that demographic trends are important, and that they can be effective for planning!
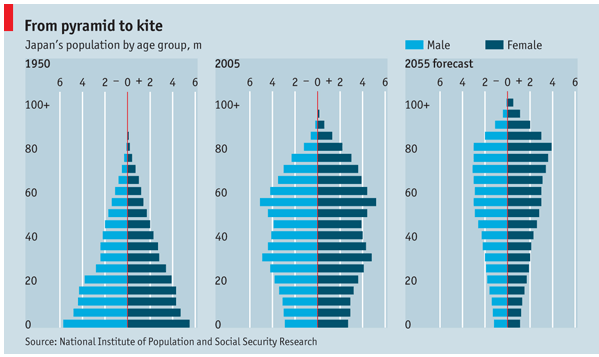
It was September, 2016 that I pointed out how important using demographic trends was for planning – and made it clear that Japan was facing a huge problem due to an aging population and unwillingness to allow immigrants. In January, 2017 I reiterated the importance of incorporating demographic trends into planning, demonstrating how they can be important for predicting workforce availability, cost of living, taxation and other critical business issues.
Take for example the NFL. In 2017 the league took another big ratings decline. The second consecutive year. But this was not hard to predict. In September, as the season started, I made it clear that kneeling players were not the problem for the NFL – the demographics of its primary viewers was the big problem. And I predicted that ratings would take a hit in 2017. Demographics have been clearly working against the league, and unless they find a way to bring in younger viewers – probably through rules changes – things are going to get a lot worse, affecting revenues and thus owner profits and even player salaries.
Are you incorporating demographics in your planning? If not, why not? Don’t know which demographic trends are important, or how to apply demographic trends to your business? If you’re stuck, not understanding this critical trend and how it will impact your business, why not give us a call?”

by Adam Hartung | Dec 22, 2017 | Advertising, Film, Innovation, Marketing, Trends
Here in late 2017, the biggest trends are: the 24 hour news cycle, animosity in broadcast and online media, fatigue from constant connection and interaction, international threats and our political climate. The holiday season is in the background struggling for attention.
How are people tuning out of this cacophony to get in the mood for the holidays?
The answer: Christmas movies! And which channel has 75% share of the new movies in 2017? If you have watched any TV since October, you’d know that it’s The Hallmark Channel. THC has produced over 20 original movies for the 2017 Christmas season and has seen viewership grow by 6.7% per year since 2013. THC is on track to surpass the 2016 season in viewership and its brand image is solidly wholesome.
Starting in October, THC runs seasonal programming with its successful “The Good Witch” series (no vampires!) and continues with “Countdown to Christmas” featuring original Hallmark-produced content.
Hallmark spent decades preparing to capture the benefits of these trends. It had become a source of family oriented, holiday-themed programming especially popular in recent years. Once only an ink and paper company, Hallmark expanded strategically in the 1970s with ornaments and cultural greeting cards and again in 1984 with its acquisition of Crayola drawing products. The company moved into direct retail in 1986 and ecommerce in the mid-1990s. Hallmark eCards was launched in 2005.
Hallmark capitalized on branded media content originally to support the core business and it now generates profits as a standalone business. In 2001, the Hallmark Channel was launched. The Hallmark Movie Channel was developed in 2004 which became Hallmark Movies and Mysteries in 2014. This year, the Hallmark Drama channel was launched further leveraging the brand.
Many companies sponsored radio shows in the 1920s through the war years. Serials featuring one company’s products appeared in 1928 on radio. In 1952, Proctor and Gamble sponsored the first TV soap opera featuring one company (“The Guiding Light”). But The Hallmark Hall of Fame was there first on Christmas Eve in 1951 sponsoring a made-for-TV opera, “Amahl and the Night Visitors.”
Written by Gian Carlo Menotti in less than two months and timed for a one hour TV slot, “Amahl” has become, probably, the most performed opera in history.
Hallmark wasn’t the first mover in sponsored media content, but it had learned to experiment with new media. The company was positioned to take advantage of the trend toward family friendly broadcast content and this year was ready to give the nation a place to rest and escape from the chaos. A bit like the story of Amahl and Christmas itself.
Once just a card company, Hallmark followed market trends to expand its business and become a leader in content marketing which is now one of the hottest areas in all marketing. And both the new video content and large library were ready for the current trend- streaming video!
by Adam Hartung | Oct 30, 2017 | Food and Drink, Growth Stall, Investing, Leadership, Retail
Understand Growth Stalls So You Can Avoid GM, JCPenney and Chipotle
Companies, like aircraft, stall when they don’t have enough “power” to continue to climb.
Everybody wants to be part of a winning company. As investors, winners maximize portfolio returns. As employees winners offer job stability and career growth. As communities winners create real estate value growth and money to maintain infrastructure. So if we can understand how to avoid the losers, we can be better at picking winners.
It has been 20 years since we recognized the predictive power of Growth Stalls. Growth Stalls are very easy to identify. A company enters a Growth Stall when it has 2 consecutive quarters, or 2 successive quarters vs the prior year, of lower revenues or profits. What’s powerful is how this simple measure indicates the inability of a company to ever grow again.
Only 7% of the time will a company that has a Growth Stall ever grow at greater than 2%/year. 93% of these companies will never achieve even this minimal growth rate. 38% will trudge along with -2% to 2% growth, losing relevancy as it develops no growth opportunities. But worse, 55% of companies will go into decline, with sales dropping at 2% or more per year. In fact 20% will see sales drop at 6% or more per year. In other words, 93% of companies that have a Growth Stall simply will not grow, and 55% will go into immediate decline.
Growth Stalls happen because the company is somehow “out of step” with its marketplace. Often this is a problem with the product line becoming less desirable. Or it can be an increase in new competitors. Or a change in technology either within the products or in how they are manufactured. The point is, something has changed making the company less competitive, thus losing sales and/or profits.
Unfortunately, leadership of most companies react to a Growth Stall by doubling down on what they already do. They vow to cut costs in order to regain lost margin, but this rarely works because the market has shifted. They also vow to make better products, but this rarely matters because the market is moving toward a more competitive product. So the company in a Growth Stall keeps doing more of the same, and fortunes worsen.
But, inevitably, this means someone else, some company who is better aligned with market forces, starts doing considerably better.
This week analysts at Goldman Sachs lowered GM to a sell rating. This killed a recent rally, and the stock is headed back to $40/share, or lower, values it has not maintained since recovering from bankruptcy after the Great Recession. GM is an example of a company that had a Growth Stall, was saved by a government bailout, and now just trudges along, doing little for employees, investors or the communities where it has plants in Michigan.

Tesla- enough market power to gain share “uphill”?
By understanding that GM, Ford and Chrysler (now owned by Fiat) all hit Growth Stalls we can start to understand why they have simply been a poor place to invest one’s resources. They have tried to make cars cheaper, and marginally better. But who has seen their fortunes skyrocket? Tesla. While GM keeps trying to make a lot of cars using outdated processes and technologies Tesla has connected with the customer desire for a different auto experience, selling out its capacity of Model S sedans and creating an enormous backlog for Model 3. Understanding GM’s Growth Stall would have encouraged you to put your money, career, or community resources into the newer competitor far earlier, rather than the no growth General Motors.
This week, JCPenney’s stock fell to under $3/share. As JCPenney keeps selling real estate and clearing out inventory to generate cash, analysts now say JCPenney is the next Sears, expecting it to eventually run out of assets and fail. Since 2012 JCP has lost 93% of its market value amidst closing stores, laying off people and leaving more retail real estate empty in its communities.
In 2010 JCPenney entered a Growth Stall. Hoping to turn around the board hired Ron Johnson, leader of Apple’s retail stores, as CEO. But Mr. Johnson cut his teeth at Target, and he set out to cut costs and restructure JCPenney in traditional retail fashion. This met great fanfare at first, but within months the turnaround wasn’t happening, Johnson was ousted and the returning CEO dramatically upped the cost cutting.
The problem was that retail had already started changing dramatically, due to the rapid growth of e-commerce. Looking around one could see Growth Stalls not only at JCPenney, but at Sears and Radio Shack. The smart thing to do was exit those traditional brick-and-mortar retailers and move one’s career, or investment, to the huge leader in on-line sales, Amazon.com. Understanding Growth Stalls would have helped you make a good decision much earlier.
This recent quarter Chipotle Mexican Grill saw analysts downgrade the company, and the stock took another hit, now trading at a value not seen since the end of 2012. Chipotle leadership blamed bad results on higher avocado prices, temporary store closings due to hurricanes, paying out damages due to a “one time event” of hacking, and public relations nightmares from rats falling out of a store ceiling in Texas and a norovirus outbreak in Virginia. But this is the typical “things will all be OK soon” sorts of explanations from a leadership team that failed to recognize Chipotle’s Growth Stall.
 Prior to 2015, Chipotle was on a hot streak. It poured all its cash into new store openings, and the share price went from $50 from the 2006 IPO to over $700 by end of 2015; a 14x improvement in 9 years. But when it was discovered that ecoli was in Chipotle’s food the company’s sales dropped like a stone. It turned out that runaway growth had not been supported by effective food safety processes, nor effective store operations processes that would meet the demands of a very large national chain.
Prior to 2015, Chipotle was on a hot streak. It poured all its cash into new store openings, and the share price went from $50 from the 2006 IPO to over $700 by end of 2015; a 14x improvement in 9 years. But when it was discovered that ecoli was in Chipotle’s food the company’s sales dropped like a stone. It turned out that runaway growth had not been supported by effective food safety processes, nor effective store operations processes that would meet the demands of a very large national chain.
But ever since that problem was discovered, management has failed to recognize its Growth Stall required a significant set of changes at Chipotle. They have attacked each problem like it was something needing individualized attention, and could be rectified quickly so they could “get back to normal.” And they hoped to turn around public opinion by launching nationwide a new cheese dip product in 2017, despite less than good social media feedback on the product from early customers. They kept attempting piecemeal solutions when the Growth Stall indicated something much bigger was engulfing the company.
What’s needed at Chipotle is a recognition of the wholesale change required to meet customer demands amidst a shift to more growth in independent restaurants, and changing millennial tastes. From the menu options, to app ordering and immediate delivery, to the importance of social media branding programs and customer testimonials as well as demonstrating commitment to social causes and healthier food Chipotle has fallen out-of-step with its marketplace. The stock has now lost 66% of its value in just 2 years amidst sales declines and growth stagnation.
We don’t like to study losers. But understanding the importance of Growth Stalls can be very helpful for your career and investments. If you identify who is likely to do poorly you can avoid big negatives. And understanding why the market shifted can lead you to finding a job, or investing, where leadership is headed in the right direction.
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.

by Adam Hartung | Oct 27, 2017 | Food and Drink, Growth Stall, Investing, Leadership, Retail
The Three Steps GE Should Take Now – And The Lessons For Your Business
Monitor displays General Electric Co. (GE) at the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) October, 2017. Photographer: Michael Nagle/Bloomberg
For years I have been negative on GE’s leadership. CEO Immelt led the dismantling of the once-great GE, making it a smaller company and one worth quite a bit less. The process has been devastating to many employees who lost their jobs, pensioners who have seen their benefits shrivel, communities with GE facilities that have suffered from investment atrophy, suppliers that have been squeezed out or displaced and investors that have seen the value of GE shares plummet.
But now there is a new CEO, a new leadership team and even some new faces on the Board of Directors. Some readers have informed me that it is easier to attack a weak leader than recommend a solution, and they have inquired as to what I think GE should do now. I do not see the GE situation as hopeless. The company still has an enormous revenue base, and vast assets it can use to fund a directional shift. And that’s what GE must do – make a serious shift in how it allocates resources.
Step 1 – Apply the First Rule of Holes
The first rule of holes is “when you find yourself in a hole, stop digging.” (Will Rogers, 1911) This seems simple. But far too many companies have their resourcing process on auto-pilot. Businesses that have not been growing, and often are not producing good returns on investment, continue to receive funding. Possibly because they are a legacy business that nobody wants to stop. Or possibly because leadership remains ever hopeful that tomorrow will somehow look like yesterday and the next round of money, or hiring, will change things to the way they were.
In fact, these businesses are in a hole, and spending more on them is continuing to dig. The investment hole just keeps getting bigger. The smart thing to do is just stop. Quit adding resources to a business that’s not adding value to the market capitalization. Just stop investing.
When Steve Jobs took over Apple he discontinued several Macintosh models, and cut funding for Macintosh development. The Mac was not going to save Apple’s declining fortunes. Apple needed new products for new markets, and the only way to make that happen was to stop putting so much money into the Mac business.
When streaming emerged CEO Reed Hastings of Netflix quit spending money on the traditional DVD/Video distribution business even though Netflix dominated it. He even raised the price. Only by stopping investments in traditional distribution could he turn the company toward streaming.
Step 2 – Identify the Trend that will Guide Your Strategy
All growth strategies build on trends. After receiving funding from Microsoft to avoid bankruptcy in 2000, Apple spent a year deciding its future lied in building on the trend to mobile. Once the trend was identified, all product development, and new product introductions, were targeted at being a leader in the mobile trend.
When the internet emerged GE CEO Jack Welch required all business units to create “DestroyYourBusiness.com” teams. This forced every business to look at the impact the internet would have on their business, including business model changes and emergence of new competitors. By focusing on the internet trend GE kept growing even in businesses not inherently thought of as “internet” businesses.
GE has to decide what trend it will leverage to guide all new growth projects. Given its large positions in manufacturing and health care it would make sense to at least start with IoT opportunities, and new opportunities to restructure America’s health care system. But even if not these trends, GE needs to identify the trend that it can build upon to guide its investments and grow.
Step 3 – Place Your Bets and Monetize
When Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg realized the trend in communications was toward pictures and video he took action to keep users on the company platform. First he bought Instagram for $1 billion, even though it had no revenues. Two years later he paid $19 billion for WhatsApp, gaining many new users as well as significant OTT technology. Both seemed very expensive acquisitions, but Facebook rapidly moved to increase their growth
and monetize their markets. Leaders of the acquired companies were given important roles in Facebook to help guide growth in users, revenues and profits.
Netflix leads the streaming war, but it has tough competition. So Netflix has committed spending over $6billion on new original content to keep customers from going to Amazon Prime, Hulu and others. This large expenditure is intended to allow ongoing subscriber growth domestically and internationally, as well as raise subscription prices.
This week CVS announced it is planning to acquire Aetna Health for $66 billion. On the surface it is easy to ask “why?” But quickly analysts offered support for the deal, ranging from fighting off Amazon in prescription sales to restructuring how health care costs are paid and how care is delivered. The fact that analysts see this acquisition as building on industry trends gives support to the deal and expectations for better future returns for CVS.
During the Immelt era, there were attempts to grow, such as in the “water business.” But the investments were not consistent, and there was insufficient effort placed on understanding how to monetize the business short- and long-term. Leadership did not offer a compelling vision for how the trends would turn into revenues and profits. Acquisitions were made, but lacking a strong vision of how to grow revenues, and an outsider’s perspective on how to lead the trend, very quickly short-term financial metrics built into GE’s review process led to bad decisions crippling these opportunities for growth. And today the consensus is that GE will likely sell its healthcare businessrather than make the necessary investments to grow it as CVS is doing.
Successful leadership means moving beyond traditional financial management to invest for growth
In the Welch era, GE made dozens of acquisitions. These were driven by a desire to build on trends. Welch did not fear investing in growth businesses, and he held leaders’ feet to the fire to produce successful results. If they didn’t achieve goals he let the people and/or the business go. Hence his nickname “Neutron Jack.”
For example, although GE had no background in entertainment, GE bought NBC at a time when viewership was growing and ad prices were growing even faster. This led to higher revenues and market cap for GE. On the other hand, when leaders at CALMA did not anticipate the shift in CAD/CAM from dedicated workstations to PCs, Welch saw them overly tied to old technology and unable to recognize the trend, so he immediately sold the business. He invested in businesses that added to valuation, and sold businesses that lacked a clear path to building on trends for higher value.
Being a caretaker, or steward, is no longer sufficient for business leadership. Competitors, and markets, shift too quickly. Leaders must anticipate trends, reduce investments in products, services and projects that are off the trend, and put resources to work where growth can create higher returns.
This is all possible at GE – if the new leadership has a vision for the future and starts allocating resources effectively. For now, all we can do is wait and see……
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.

by Adam Hartung | Sep 29, 2017 | Entertainment, Politics, Sports, Trends
LANDOVER, MD – SEPTEMBER 24: Washington Redskins players link arms during the national anthem before their game against the Oakland Raiders at FedExField on September 24, 2017 in Landover, Maryland. (Photo by Patrick Smith/Getty Images)
A recent top news story has been NFL players kneeling during the national anthem. The controversy was amplified when President Trump weighed in with objections to this behavior, and his recommendation that the NFL pass a rule disallowing it. This kind of controversy doesn’t make life easier for NFL leaders, but it really isn’t their biggest problem. Ratings didn’t start dropping recently, viewership has been declining since 2015.
NFL ratings stalled in 2015
NFL viewership had a pretty steady climb through 2014. But in 2015 ratings leveled. Then in 2016 viewership fell a whopping 9%. During the first 6 weeks of the 2016 regular season (into early October)viewership was down 11%. Through the first 9 weeks of 2016 ratings were down 14% before things finally leveled off. Although nobody had a clear explanation why viewership declined so markedly, there was widespread agreement that 2016 was a ratings crash for the league. Fox had its worst NFL viewership since 2008, and ESPN had its worst since 2005.
Interestingly, later analysis showed that overall people were watching 5% more games. But they were watching less of each game. In other words, fans had become more casual about their viewership. People were watching less TV, watching less cable, and that included live sports. And those who stream games almost never streamed the entire game.
And this behavior change wasn’t limited to the NFL. As reported at Politifact.com, Paulsen, editor in chief of Sports Media Watch said, “it’s really important to note the NFL is not declining while other leagues are increasing. NASCAR ratings are in the cellar right now. The NBA had some of its lowest rated games ever on network television last year… It’s an industry-wide phenomenon and the NFL isn’t immune to it anymore.” So the declining viewership problem is widespread, and much older than the recent national anthem controversy.
Live sports is not attracting new, younger viewers
Magna Global recently released its 2017 U.S. Sports Report. According to Radio + Television Business Report (RBR.com) the age of live sports viewers is scewing older. Much older. Today the average NFL viewer is at least 50. Similar to tennis, and college basketball and football. That’s second only to baseball at 57 – which was 50 as recently as 2000. But no sport is immune. NHL viewers are now typically 49. They were 33 in 2000. As simple arithmetic shows, the same folks are watching hockey but few new viewers are being attracted. Based on recent trends, Magna projects viewership for the Sochi Olympics and 2018 World Cup will both decline.
I’ve written before about the importance of studying demographic trends when planning. These trends are highly reliable, even if boring. And they provide a lot of insight. In the case of live sports watching, younger people simply don’t sit down and watch a complete game. Younger people have different behaviors. They watch an entire season of shows in one day. They multi-task, doing many things at once. And they prefer information in short bursts – like weekly blogs rather than a book. And they are more interested in outcomes, the final result, than watching how it happened. Where older people watch a game play-by-play, younger people simply want to know the major events and the final score.
To understand what’s happening with NFL ratings we really don’t have to look much further than simple demographics — the aging of the U.S. population — and the change in viewing behavior from older groups to younger groups.
Unfortunately, according to a recent CNN poll, while 56% of people under age 45 think the recent demonstrations are the right thing to do, 59% of those over 45 say the demonstrations are wrong. In its “core” NFL viewership folks don’t like the kneeling, so it would appear the NFL should heed the President’s advice. But, looking down the road, the NFL won’t succeed unless it finds a way to attract a younger audience. With younger people approving the demonstrations NFL leadership risks throwing the baby out with the bathwater if they knee-jerk control player behavior.
Understanding customer demographic trends, and adapting, is crucial to success
The demonstrations are interesting as an expression of American ideals. And they are gathering a lot of discussion. But they are not what’s plaguing NFL viewership. Today the NFL has a much bigger task of making changes to attract young people as viewers. Should leaders shorten the game’s length? Should they change rules to increase scoring and create more excitement during the game? Should they invest in more apps to engage viewers in play-by-play activity? Should they seek out ways to allow more gambling during the game? Whatever leadership does, the traditions of the NFL need to be tested and altered in order to attract new people to watching the game if they want to preserve the advertising dollars that make it a success.
When your business falters, do you look at long-term trends, or react to a short-term event? It’s easy for politicians and newscasters to focus on the short-term, creating headlines and controversy. But business leaders have an obligation to look much deeper, and longer term. It is critical we move beyond “that’s the way the game is played” to looking at how the game may need to change in order to remain relevant and engage new customers.
Note how boxing recently brought in a mixed martial arts fighter to take on the world champion. The outcome was nearly a foregone conclusion, but nobody cared because it brought in people to a boxing match that otherwise would not have been there. If you don’t recognize demographic shifts, and take actions to meet emerging trends you risk becoming as left behind as cricket, badminton, horseshoes, bocce ball and darts.
by Adam Hartung | Nov 17, 2016 | Food and Drink, In the Swamp, Innovation, Marketing, Trends
(PAUL J. RICHARDS/AFP/Getty Images)
McDonald’s has been trying for years to re-ignite growth. But, unfortunately for customers and investors alike, leadership keeps going about it the wrong way. Rather than building on new trends to create a new McDonald’s, they keep trying to defend extend the worn out old strategy with new tactics.
Recently McDonald’s leadership tested a new version of the Big Mac,first launched in 1967. They replaced the “special sauce” with Sriracha sauce in order to make the sandwich a bit spicier. They are now rolling it out to a full test market in central Ohio with 128 stores. If this goes well – a term not yet defined – the sandwich could roll out nationally.
This is a classic sustaining innovation. Take something that exists, make a minor change, and offer it as a new version. The hope is that current customers keep buying the original version, and the new version attracts new customers. Great idea, if it works. But most of the time it doesn’t.
Unfortunately, most people who buy a product like it the way it is. Slower Big Mac sales aren’t due to making bad sandwiches. They’re due to people changing their buying habits to new trends. Fifty years ago a Big Mac from McDonald’s was something people really wanted. Famously, in the 1970s a character on the TV series Good Times used to become very excited about going to eat his weekly Big Mac.
People who are still eating Big Macs know exactly what they want. And it’s the old Big Mac, not a new one. Thus the initial test results were “mixed” – with many customers registering disgust at the new product. Just like the failure of New Coke, a New Big Mac isn’t what customers are seeking.
After 50 years, times and trends have changed. Fewer people are going to McDonald’s, and fewer are eating Big Macs. Many new competitors have emerged, and people are eating at Panera, Panda Express, Zaxby’s, Five Guys and even beleaguered Chipotle. Customers are looking for a very different dining experience, and different food. While a version two of the Big Mac might have driven incremental sales in 1977, in 2017 the product has grown tired and out of step with too many people and there are too many alternative choices.
Similarly, McDonald’s CEO’s effort to revitalize the brand by adding ordering kiosks and table service in stores, in a new format labeled the “Experience of the Future,” will not make much difference. Due to the dramatic reconfiguration, only about 500 stores will be changed – roughly 3.5% of the 14,500 McDonald’s. It is an incremental effort to make a small change when competitors are offering substantially different products and experiences.
When a business, brand or product line is growing it is on a trend. Like McDonald’s was in the 1960s and 1970s, offering quality food, fast and at a consistent price nationwide at a time when customers could not count on those factors across independent cafes. At that time, offering new products – like a Big Mac – that are variations on the theme that is riding the trend is a good way to expand sales.
But over time trends change, and adding new features has less and less impact. These sustaining innovations, as Clayton Christensen of Harvard calls them, have “diminishing marginal returns.” That’s an academic’s fancy way of saying that you have to spend ever greater amounts to create the variations, but their benefits keep having less and less impact on growing, or even maintaining, sales. Yet, most leaders keep right on trying to defend & extend the old business by investing in these sustaining measures, even as returns keep falling.
Over time a re-invention gap is created between the customer and the company. Customers want something new and different, which would require the business re-invent itself. But the business keeps trying to tweak the old model. And thus the gap. The longer this goes on, the bigger the re-invention gap. Eventually customers give up, and the product, or company, disappears.
Think about portable hand held AM radios. If someone gave you the best one in the world you wouldn’t care. Same for a really good portable cassette tape player. Now you listen to your portable music on a phone. Companies like Zenith were destroyed, and Sony made far less profitable, as the market shifted from radios and cathode-ray televisions to more portable, smarter, better products.
Motorola, one of the radio pioneers, survived this decline by undertaking a “strategic pivot.” Motorola invested in cell phone technology and transformed itself into something entirely new and different – from a radio maker into a pioneer in mobile phones. (Of course leadership missed the transition to apps and smart phones, and now Motorola Solutions is a ghost of the former company.)
McDonald’s could have re-invented itself a decade ago when it owned Chipotle’s. Leadership could have stopped investing in McDonald’s and poured money into Chipotle’s, aiding the cannibalization of the old while simultaneously capturing a strong position on the new trend. But instead of pivoting, leadership sold Chipotle’s and used the money to defend & extend the already tiring McDonald’s brand.
Strategic pivots are hard. Just look at Netflix, which pivoted from sending videos in the mail to streaming, and is pivoting again into original content. But, they are a necessity if you want to keep growing. Because eventually all strategies become out of step with changing trends, and sustaining innovations fail to keep customers.
McDonald’s needs a very different strategy. It has hit a growth stall, and has a very low probability of ever growing consistently at even 2%. The company needs a lot more than sriracha sauce on a Big Mac if it is to spice up revenue and profit growth.







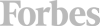

 at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition. When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.












 Prior to 2015, Chipotle was on a hot streak. It poured all its cash into new store openings, and the share price went from $50 from the 2006 IPO to over $700 by end of 2015; a 14x improvement in 9 years. But when it was discovered that ecoli was in Chipotle’s food the company’s sales dropped like a stone. It turned out that runaway growth had not been supported by effective food safety processes, nor effective store operations processes that would meet the demands of a very large national chain.
Prior to 2015, Chipotle was on a hot streak. It poured all its cash into new store openings, and the share price went from $50 from the 2006 IPO to over $700 by end of 2015; a 14x improvement in 9 years. But when it was discovered that ecoli was in Chipotle’s food the company’s sales dropped like a stone. It turned out that runaway growth had not been supported by effective food safety processes, nor effective store operations processes that would meet the demands of a very large national chain.




