
Chart courtesy of Felix Richter, Statista.com https://www.statista.com/chart/9454/retail-space-per-1000-people/

Whole Food flagship store in Austin, Texas.
Amazon announced it was paying $13.7B to buy Whole Foods. While not without risks, there are a lot of reasons this is a great idea:
Building any retail chain takes a long time. Due to the intensity of competition, and low margins, building a grocery chain takes even longer. Amazon would have spent decades trying to create its own chain. Now it won’t lose all that time, and it won’t give competitors more time to figure out their strategies.
Few people realize that no grocer makes money selling groceries. Revenues do not cover the costs of inventory, buildings and labor. On its own, selling groceries loses money. Grocers survive on manufacturer “deal dollars.”
Companies like P&G, Nabisco, etc. pay grocers slotting fees to obtain shelf space, they pay premiums for eye level shelves and end caps, they pay new product fees to have grocers stock new items, they pay inventory fees to have grocers keep inventory on shelf and in back, they pay advertising fees to have signs in the stores and products in circulars, and they pay volume rebates for meeting, and exceeding, volume goals. It is these manufacturer “deal dollars” that cover the losses on the store operations and create a profit for investors.
One reason Whole Foods prices are so high is they stock less of the mass market goods and thus receive fewer deal dollars. Now Amazon can use Whole Foods to increase its volume in all products and dramatically increase its deal dollar inflow. Something that Amazon sorely missed as a “delivery only” grocer.
Grocery distribution is unique. For decades grocers have worked with manufacturers, cooperatives, growers and other suppliers to create the shortest, most efficient distribution of food with the lowest inventory. In many instances replenishment quantities are shipped based on manufacturer access to real grocer sales data. Amazon is the best at what it does, but to compete in groceries it needed a grocery distribution system – and with Whole Foods it obtains one at scale without having to create it.
Additionally Amazon will obtain the corporate infrastructure of a grocer, without having to build one on its own. All those buyers, merchandisers, real estate professionals, local ad buyers, etc. are there and ready to execute – something building would be very hard to do.
Whole Foods has 460 stores, and almost all are in great locations. Whole Foods focused on upscale, growing and often urban or suburban locations – all great for Amazon to grow its distribution footprint. And hard sites to find.
These can be used to sell other products, such as other grocery items, or some selection of Amazon products if that makes sense. Or these can be used to augment Amazon’s distribution system for local delivery – or as neighborhood drop-off locations for people who don’t want at-home delivery to pick up Amazon-purchased products. Or they can be sold/leased at very attractive prices.
“Whole Paycheck” has long been the knock on Whole Foods. As mentioned before, the lack of mass market items meant their products lacked deal dollars and thus had to be priced higher. And their stores are large, and not the best use of space. The result has been a lot of trouble keeping customers, and one of the lowest sales per square foot in the grocery industry.
Amazon can easily use its low-price position to alter the Whole Foods brand concept to include things like Pepsi, Coke, Bounty, Gain – a slew of branded consumer goods previously eschewed by Whole Foods. Adding these products could make the stores more useful to more customers, and greatly lower the average cost of a cart full of goods. On its own, this brand transition has been impossible for Whole Foods. As part of Amazon remaking the brand will be vastly easier.
If you shopped Amazon you know they really figure out your needs, and help you find what you want. Amazon keeps track of your searches and purchases, and makes recommendations that often help the shopping experience and delight us as customers.
But today all that information on grocery shopping is un-mined. Despite using a loyalty card, traditional grocers (and WalMart) have been unable to actually mine that information for better marketing. Now Whole Foods will be able to use Amazon’s incredible technology skills, including big data mining and artificial (or augmented) intelligence to actually help us make the grocery shopping experience better – less time intensive, and most likely less costly while still allowing us to fill our carts with what we need and what makes us happy.
$13.7B is only 65% of the cash Amazon had on hand end of last quarter. And Amazon has only $7.7B in long-term debt. With a $460B market cap Amazon could easily take on more debt without adding significant financial risk.
But even more important, Amazon has the amazingly cheap currency that is Amazon stock. Even at the offering price, Whole Foods trades at 34x earnings. Amazon trades at 185x earnings. Thus by swapping Amazon shares for Whole Foods shares Amazon lowers the price 80%! Amazon isn’t spending real dollars, it is using its stock – which is an incredibly valuable move for its shareholders.
For the last several years WalMart’s general merchandise sales have been declining due to the Amazon Effect and growing on-line competitor sales. For the last 3 years overall revenues have not grown at all. To maintain revenue Walmart has shifted increasingly to groceries – which account for well over half of all WalMart revenues. By purchasing Whole Foods, Amazon takes direct aim at the only part of WalMart’s “core” business that it has not attacked.
Walmart’s net profit before taxes is ~4%. If Amazon can use Whole Foods to combine stores and on-line sales to take just 3% of WalMart’s grocery business away it could remove from Walmart ($485B revenues * 60% grocery * 3% market share loss) a net revenue decline of ~$9B. Given that the cost of grocery goods sold is about 50% – that would mean a net loss in contribution of $4.5B – which would cut almost 25% out of Amazon’s $20B pre-tax income. Raise the share taken to 5% and Amazon could cut WalMart’s pre-tax income by $7.25B, or ~35%.
The negative impact of declining store sales on the fixed costs of WalMart is atrocious. Even small revenue drops mean cutting staff, cutting inventory, cutting store size and eventually closing stores. Look at how fast Sears and Kmart fell apart when sales started declining. Like dominoes falling, declining sales sets off a series of bad events that dooms almost all retailers – as the quickened pace of retail bankruptcy filings has proven.

The above analysis, taking 3-5% out of Walmart’s grocery sales, say over 3 years, would be a huge gain attributed to the creation of a new Whole Foods combined with Amazon’s e-commerce. Growing grocery revenues by $9-$14B would mean practically a doubling of Whole Foods. Which sounds enormous – and most likely impossible for Whole Foods to do on its own, even if it did launch some kind of e-commerce initiative.
But this is not so unlikely given Amazon’s track record. Amazon has been growing at over 25%/year, adding between $20-$25B of new revenues annually. In 3 years between 2013 and 2016 Amazon doubled its revenues. So it is not that unlikely to expect Amazon puts forward an extremely ambitious push to turn around Whole Foods, increase store sales and use the combined entities to grow delivery sales of groceries and other general merchandise.
Is there risk in this acquisition? Of course. Combining any two companies is fraught with peril – combining IT systems, distribution systems, customer systems and cultures leaves enormous opportunities for missteps and disaster. But the upsides are enormous. Overall, this is a bet Amazon investors should be glad leadership is making – and it is a great benefit for Whole Foods investors.

Originally posted: May 31, 2017
On the day after Memorial Day Amazon stock hit $1,000/share — a new record high. Amazon is up about 40% the last year. It’s market capitalization doubles Wal-mart. And the vast majority of investment analysts expect Amazon to rise further.

Amazon competes in dozens of international markets, as do many on-line retailers, yet the ‘Amazon Effect’ is far greater in the USA than anywhere else. And there’s a good reason — America is vastly over-served when it comes to traditional retail.

Chart courtesy of Felix Richter, Statista.com https://www.statista.com/chart/9454/retail-space-per-1000-people/
America is enormously over-built with retail space
Looking at square feet of retail space per 1,000 people, this infographic shows that, adjusted for population size, the USA has 8x the retail of Spain, 9x the retail of Italy, 11x the retail of Germany, 22x the retail of Mexico, 51x the retail of China and 400x the retail of India! Overall, this is remarkable. I’ve been to all of these countries, and in none did I feel that I was unable to buy things I needed. Clearly, the USA has had such a robust retail sector that it has dramatically over-expanded – with individual stores, suburban strip malls, elaborate horizontal malls, vertical urban malls and multi-floor urban retail complexes far outpacing the needs of American shoppers.
All these stores created a very competitive retail environment. This competition, and the lack of any sort of national value added tax (VAT,) kept prices for most things in America among the lowest in the world. Simultaneously according to the Department of Labor, Retail is the third largest employer in America. Couple that with the enormous wholesale distribution networks of warehouses and truck fleets — and selling things becomes the country’s largest employer — even bigger than the sum total of all federal, state and local government employees .
Additionally, retail has produced the largest local taxes of any industry, combining local sales taxes with property taxes, which has funded schools and public works projects for decades. And this retail space has helped drive demand for all kinds of support services from utilities to maintenance.
U.S. retail consumers are tremendously over-served, and the market is set to collapse
But now retail is wildly overbuilt. Organic demand for all retail grows about equal to population growth, so about 3%/year. But retail real estate grew far faster since World War II as developers kept building more malls, and large retailers like Sears, KMart, Walmart, Target, Lowe’s and Home Depot built more stores. Now demand for products through traditional retail is declining. People are simply ordering on-line.
Net/net, America’s consumers are now over-served by retailers. There is too much space, and inventory. And now that store-to-home distribution has faded as a problem, with multiple carriers offering overnight service, people are increasingly happy to avoid stores altogether, greatly exacerbating the overcapacity problem. Thus, the ‘Amazon Effect’ has emerged, where stores are closing at a rapid rate and many retailers are failing altogether leaving vast amounts of empty retail space.
Foreign markets are under-served, and benefit from Amazon’s entry
Contrarily, in other countries consumers were to some extent under-served. They actually dealt with local stock-outs on desirable items. And frequently lived in a world with a lot less product choice. And, generally, international consumers expected to travel farther to shop at the few larger stores, malls and urban shopping centers with greater selections.
In those countries local economies became far less dependent on retail real estate for jobs — and for taxes. Most have little or no property taxes as deployed in the USA. Additionally, rather than adding a local sales tax to the price of goods, most countries use some sort of national VAT to collect the tax during distribution. When Amazon starts distributing in these markets it is seen as a good thing! Consumers have more choice, less hassle and often better service. Also, Amazon collects the VAT so no taxes are lost.
Contrarily, American communities could never stop adding retail space. Whenever Walmart or Best Buy wanted a new store, no community leaders turned down the potential local economic gains. But it led to too much space being built for a healthy sector, and certainly far too much given the market shift to on-line retail. Now retail is a classic over-served market, sort of like the need for stagecoaches and livery barns after the railroads were built.
Expect 50-67% of retail space to go vacant within a decade
How much retail space could go vacant in the USA? Just invert the multiples from above. For the USA to have the same retail space as Spain implies an 87.5% reduction, Italy -89%, Germany -91%, Mexico -95.5%. Thus it is not hard to imagine a full 50-67% of America’s retail space to be empty in just 5 or 10 years. Americans would still have 2-3 times the retail space of other developed markets.
There is no doubt Amazon is a good employer, and on-line sales growth will employ hundreds of thousands at Amazon, and millions across the marketplace. Further, most of those jobs will pay a lot better than traditional retail jobs. But there is no sugar-coating the huge impact the ‘Amazon Effect’ will have on local economies and jobs. America is vastly overbuilt and over-supplied by retailers. There will be a huge shake-out, with dozens of retail failures. And there will be enormous amounts of vacant property sitting around, looking for some kind of alternative use. And local communities will find it difficult to meet constituent needs as sales tax and property tax receipts fall dramatically.
As I wrote in my column on February 28, this is going to be an enormous shift. Far bigger than the offshoring of manufacturing. The ‘Amazon Effect’ is automating retailing in ways never imagined by those who built all that retail space. As people keep buying on-line there will be a collapse of retail space pricing, and a collapse of industry participants. Industry players always greatly under-estimate these shifts, so they aren’t projecting retail armaggedon. But in short order the need for retail will be like the need for dedicated, raised-floor computer centers to house mainframes, and later network hubs. It’s just going to go away.

The words “search” and “Google” are practically synonymous. We’ve even turned the name of the ubiquitous web application into a verb by telling people to “Google it.” And that’s good, because Alphabet’s revenue (that’s Google’s parent company) soared more than 25% in the last quarter, and over 90% of Alphabet’s revenue comes from Google AdWords. The more people search using Google, the more money Alphabet makes.
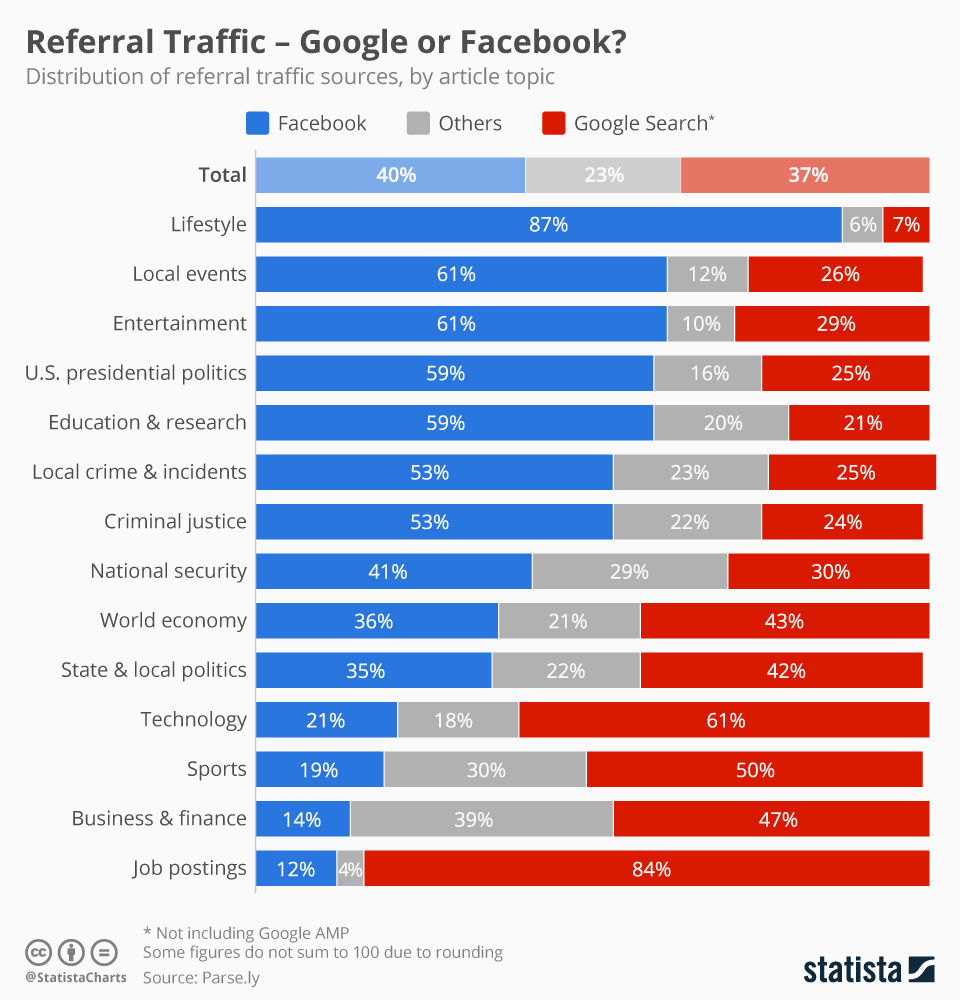
Chart courtesy of Martin Armstrong at Statista.com
But ever since Facebook came along, a new trend has started emerging. People often want answers to their questions within the context of their community. So “searches” are changing. People are going back to what they did before Google existed – they are asking for information from their friends. But online. And primarily using Facebook.
There is no doubt Google dominates keyword searching. But that type of searching has its shortcomings. How often have you found yourself doing multiple searches — adding words, adding phrases, dropping words, etc. trying to find what you were seeking? It’s a common problem, and we all know people who are better “Googlers” than others because of their skill at putting together key words to actually find what we want. And how often do we find ourselves lost in the initial batch of ads, but not finding the link we want? Or going through several pages of links in search of what we seek?
Context often matters. Take the classic problem of finding a place to eat. Googling an answer requires we enter the location, type of food, price point, and other info — which often doesn’t lead us to the desired information, but instead puts us into some kind of web site, or article, with restaurant review. What seems an easy question can be hard to answer when relying on key words.
But, we know how incredibly easy it is for a friend to answer this question. So when seeking a place to eat we use Facebook to ask our friends “hey, any ideas on where I should eat dinner?” Because they know us, and where we are, they fire back specific answers like “the Mexican place two blocks north is just for you,” or “spend the money to eat at that place across the street – pricey but worth it.” Your friends are loaded with context about you, your habits, your favorites and they can give great answers much faster than Google.
Think of these kind of referrals – for food, entertainment, directions, quick facts, local info — as “context based searches” rather than referrals. Instead of making a query with a string of key words, we use context to derive the answer — and our friends. Most people undertake far more of these kind of “searches” than keywords every day.
Even though Google is still growing incredibly fast, context searching — or referrals — pose a threat. People will use their network to answer questions. The web birthed on-line data, and we all quickly wanted engines to help us find that data. We were excited to use Excite, Lycos, InfoSeek, AltaVista and Ask Jeeves to name just a few of the early search engines. We gravitated toward Google because it was simply better. But with the growth of Facebook today we can ask our friends a question faster, and easier, than Google — and often we obtain better results.
Both Google and Facebook rely on ads for most of their revenue. But if consumer goods companies, event promoters, apparel manufacturers and other “core advertisers” realize that people are using Facebook to ask for information, rather than searching Google, where do you think they will spend their on-line ad dollars? Isn’t it better to have an ad for diapers on the screen when someone asks “what diapers do you like best?” than relying on someone to search for diaper reviews?
This is why Google+ with its Groups and Google Hangouts was such a big deal. Google+ allows users to come together in discussions much like Facebook. But Plus, Groups and Hangouts never really caught on, and Plus isn’t nearly as popular as Facebook discussions, or Instagram picture sharing or WhatsApp messaging. Today, when it comes to referral traffic Facebook has eclipsed Google. Five years ago most people would have guessed this would never happen.
I’m not saying that Google searches will decline, nor am I saying Google will stop growing, nor am I saying that Google’s other revenue generators, like YouTube, won’t grow. I am saying that Facebook as a platform is growing incredibly fast, and becoming an ever more powerful tool for users and advertisers. Possibly a lot more powerful than Google as people use it for more and more information gathering — and referrals. The more people make referrals on Facebook, the more it will attract advertisers, and potentially take searches away from Google.
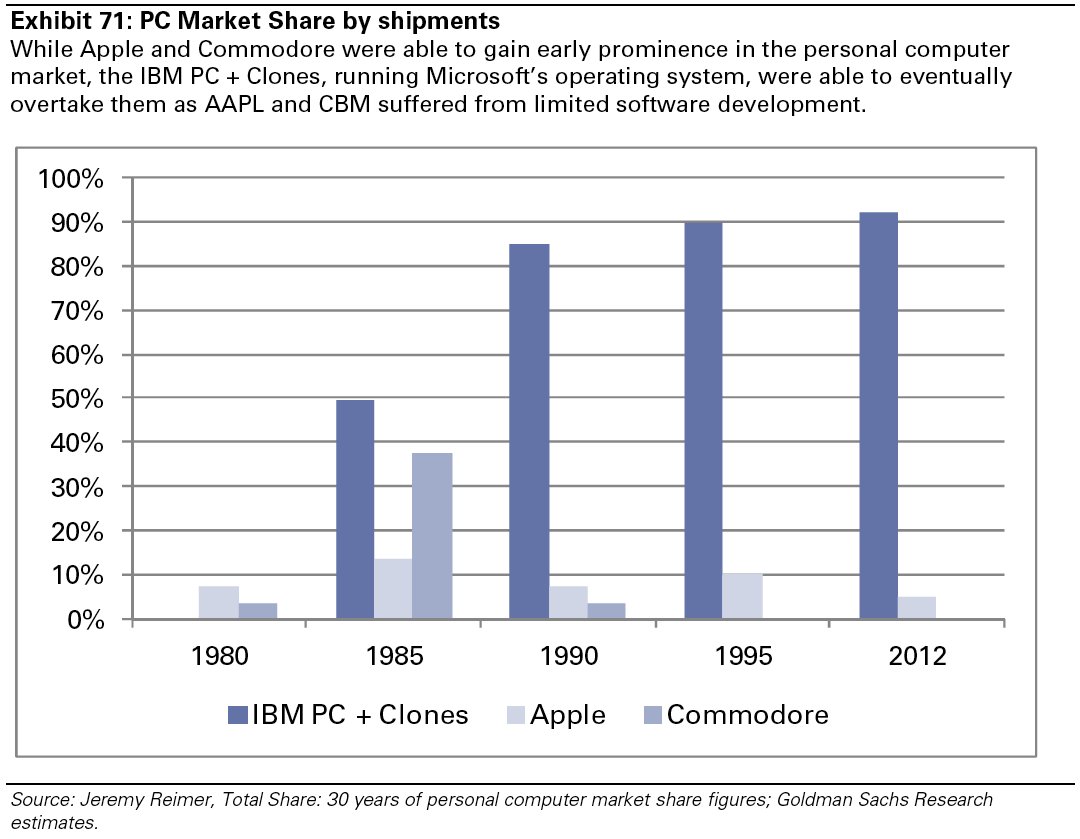
By comparison, this moment may be like the late 1980s when PC sales finally edged ahead of Apple Mac sales. At the time it didn’t look deadly for Apple. But it didn’t take long for the Wintel platform to dominate the market, and the Mac began its slide toward being a submarket favorite.



(Photo: CEO of Amazon.com, Inc. Jeff Bezos, TOMMASO BODDI/AFP/Getty Images)
Amazon.com is now worth about the same as Berkshire Hathaway. Amazon has had an amazing run-up in value. The stock is up 17% year to date, and 46% over the last 12 months. By comparison, Berkshire has risen 3.1% this year and Microsoft has risen 5.6% —while the S&P 500 is up 5.8%. Due to this greater value increase, Jeff Bezos has become the second richest man in the world, jumping past Warren Buffett while Bill Gates remains No. 1.
Obviously, it wouldn’t take much of a slip in Amazon, or a jump in Berkshire, to reverse the positions of the companies and their CEOs. But it is important to recognize what is happening when a barely profitable company that sells general merchandise, technology products (Kindles, Fires and Echos) and technology services (AWS) eclipses one of the most revered financial minds and successful investment managers of all time.

Warren Buffett (Photo by Paul Morigi/Getty Images for Fortune/Time Inc)
When Buffett started his magical machine he realized that capital was often in short supply. Companies had to ration capital, unable to build the means of production they desired. Banks were unwilling to lend when they perceived any risk, even when the risk was not that great. Simultaneously investment banks were highly inefficient. The industry was unwilling to support companies prior to going public, often uninterested in taking companies public, and poor at allocating additional capital to the highest return opportunities. By the time you were big enough to use an investment bank you really didn’t need them to raise capital – they just organized the transactions.
Berkshire Hathaway was a big winner at mastering finance during the industrial era. By putting money in the right place, at the right time, tremendous gains could be made. Berkshire didn’t have to be a manufacturer, it could make a higher rate of return by understanding how to deploy capital to industrial companies in a marketplace where capital was rationed. In other words, give people money when they need it and Berkshire could generate outsized returns.
It was a great strategy for supporting companies in the Industrial Age. And a great way to make money when capital was hard to come by.
But the world has changed. Two important things happened First, capital became a lot easier to acquire. Deregulation and a vast expansion of financial services led to a greater willingness to lend by banks, larger secondary markets for bank-originated products that carried risk, the creation of venture capital and private equity firms willing to invest in riskier opportunities, and a dramatic growth in investment banking globally making it far easier to go public and raise equity. Capital became vastly more available, and the cost of capital dropped dramatically.
This made finding opportunities for outsized returns just based on investing considerably more difficult. And thus every year it has become harder for Berkshire Hathaway to find investment opportunities that exceed market rates of return. Berkshire isn’t doing poorly, but it now competes in a world of many competitors who have driven down returns for everyone. Thus, Berkshire’s returns increasingly move toward the market norm.
The Industrial Era is dead — usher in the Information Era. Second, we are no longer in the Industrial Age. Sometime in the 1990s (economic historians will pin it to a specific date eventually) the world transitioned into the Information Age. In the Information Age assets are no longer worth as much as they previously were. Instead, information has become much more valuable. What a business knows about customers, markets and supply chains is worth more than the buildings, machines and trucks that actually make up the physical economy. The value from having information has become much higher than the value of things — or of providing capital to purchase things.
In the Information Era, few companies have mastered the art of information management better than Amazon.com. Amazon doesn’t succeed because it has great retail stores, or great product inventory or even great computers. Amazon’s success is based on knowing things about markets and its customers. Amazon has piles and piles of data, and Amazon monetizes that information into sales.
By studying customer habits, every time they buy something, Amazon has been able to make the company more valuable to customers. Often Amazon is able to tell a customer what they need before they realize they need it. And Amazon is able to predict the flow of new product introductions, and predict sales for manufacturers with great accuracy. Amazon is able to understand what media customers want, and when they’ll want it. Amazon is able to predict a business’ “cloud needs” before that business knows – and predict the customer’s likely future services needs long before the customer knows.
In the Information Age, Amazon is one of the very, very best information companies out there. It knows how to obtain information, analyze those mounds of “big data” to determine and predict needs, then connect customers with things they want to buy. Being great at information means that Amazon, even with its relatively poor current profits, is positioned to capitalize on its intellectual property for years to come. Not without competition. But with a tremendous competitive lead.
So, how is your portfolio allocated? Are you invested in assets, or information? Accumulating assets is a very hard way to make high rates of return. But creating sales, and profits, out of information is far easier today. The relative change in the value of Amazon and Berkshire is telling investors that it is now smarter to be long information rich companies than asset rich companies.
If you’re long GE, GM, 3M and Walmart how well will you do in an economy where information is more valuable than assets? If you don’t own data rich, analytically intensive companies like Amazon, Facebook, Alphabet/Google and Netflix how would you expect to make above-average rates of return?
And where is your business investing? Are you still putting most of your attention on how you allocate capital, in a world where capital is abundant and cheap? Are you focusing your attention on getting the most out of what you know about markets, customers and suppliers, or just making and selling more stuff? Do you invest in projects to give you insights competitors don’t have, or in making more of the products you have — or launching product version X?
And are you being smart about how you manage your most important information tool — your talented employees? Information is worthless without insight. It is critical companies today do all they can to help employees develop insights, and then rapidly deploy those insights to grow sales. If you spend a few hours pouring over expenses to find dimes, consider letting that activity go in order to spend hours brainstorming how to find new markets and new product opportunities that can generate a lot more revenue dollars.

(Photo by Spencer Platt/Getty Images)
Howard Schultz is one of those CEO legends. Like Steve Jobs, Larry Ellison, Jeff Bezos and Mark Zuckerberg, he turned a startup into a huge, mega-billion dollar company – and in the process created an entirely new market. This isn’t easy to do, and that’s why business acolytes and the media turn these people into heroes.
But, is it right to hand-wring over Schultz’s departure as CEO? After all, things have not been pretty for investors since Mr. Jobs turned over Apple to his hand-picked successor Tim Cook. However, could this change mean something better is in store for shareholders?
First, let’s address the very popular myth that when Mr. Schultz left Starbucks in 2000 his successors nearly destroyed the company – and Starbucks was saved only by Mr. Schultz returning with his tremendous creativity and servant leadership. While it is great propaganda for making the Schultz as hero story more appealing, it isn’t exactly accurate.
His successor, Orin Smith, far outperformed Mr. Schultz, more than tripling the chain to over 9,000 stores and expanding revenue to over $5 billion in just four years! He expanded the original model internationally, began adding many new varieties of coffee and other drinks, and even added food. These enhancements were tremendously successful at bringing in additional revenue, even if the average store revenue fell as smaller stores were added in places like airports, hotels and entertainment venues.
In 2007 Starbucks fourth quarter saw 22% revenue increase, and for the year 21% growth. Comparable store sales grew 5%. International margins expanded, and net earnings grew over 19% from $564 million to $673 million.
Starbucks’ stock, from 2000 when Mr. Schultz departed into 2006 rose 375%, from $4 to just under $19 per share. Not the ruination that some seem to think was happening.
But Mr. Schultz did not like the diversification, even if it produced more revenue and profit. He joined the chorus of analysts that beat down the P/E ratio, and the stock price, as the company expanded beyond its “core” coffee store business.
When the Great Recession hit, and people realized they could live without $4 per cup of coffee and a $50 per day habit, revenues plummeted, as they did for many restaurants and retailers. Mr. Schultz seized the opportunity to return to his old job as CEO. That the downturn in Starbucks had far more to do with the greatest economic debacle since the 1930s was overlooked as Mr. Schultz blamed everything on the previous CEO and his leadership team – firing them all.
What returning CEO Schultz did was far from creative. He simply stopped all the projects that didn’t fit his definition of the “core” Starbucks he created. And he closed 600 stores in 2009 then 300 more in 2010 – making the chain smaller as new store openings stopped. Although the popular myth is that Starbucks stagnated under Mr. Schultz successors, the opposite was true. The chain expanded both its “core” and new incremental revenues from 2000 though 2008. But as Mr. Schultz returned as CEO from 2008 through 2011 Starbucks actually did stagnate , with virtually no growth.
Since 2012 Starbucks has returned to doing what it did prior to 2000 – opening more stores. Growing from 17,000 to 25,000 stores. Refocused on its very easy to understand, if dated, business model analysts loved the simpler company and bid up the P/E to over 30 – creating a trough (2008) to peak (2016) increase in adjusted stock price from $4 to $60 – an incredible 15 times!
But, more realistically one should compare the price today to that of 2006, before the entire market crashed and analysts turned negative on the profitable Starbucks diversification and business model expansion. That gain is a more modest 300% – basically a tripling over a decade – far less a gain for investors than happened under the 2000-2006 era of Mr. Schultz’s successors.
Mr. Schultz succeeded in returning Starbucks to its “core.” But now he’s leaving a much more vulnerable company. As my fellow Forbes contributor Richard Kestenbaum has noted, retail success requires innovation. Starbucks is now almost everywhere, leaving little room for new store expansion. Yet it has abandoned other revenue opportunities pioneered under Messrs. Smith and Donald. And competition has expanded dramatically – both via direct coffee store competitors and the emergence of new gathering spots like smoothie stores, tech stores and fast casual restaurants that are attracting people away from a coffee addiction.
At some point Starbucks and its competition will saturate the market. And tastes will change. And when that happens, growth will be a lot harder to find. As McDonald’s and WalMart have learned, business models grow tired and customers switch . Exciting new competitors emerge, like Starbucks once was, and Amazon.com is increasingly today.
Mr. Schultz has said he is vastly more confident in this change of leadership than he was the last time he left – largely because he feels this hand-picked team (as if he didn’t pick the last team, by the way) will continue to remain tightly focused on defending and extending Starbucks “core” business. This approach sounds all too familiar – like Jobs selection of Cook – and the risks for investors are great.
A focus on the core has real limits. Diminishing returns do apply. And P/E compression (from the very high 30+ today) could cause Starbucks to lose any investor upside, possibly even cause the stock to decline. If Mr. Schultz’s departure was opening the door for more innovation, new business expansion and a change to new trends that sparked growth one could possibly be excited. But there is real reason for concern – just as happened at Apple.

In early August Tesla announced it would be buying SolarCity. The New York Times discussed how this combination would help CEO Elon Musk move toward his aspirations for greater clean energy use. But the Los Angeles Times took the companies to task for merging in the face of tremendous capital needs at both, while Tesla was far short of hitting its goals for auto and battery production.
Since then the press has been almost wholly negative on the merger. Marketwatch’s Barry Randall wrote that the deal makes no sense. He argues the companies are in two very different businesses that are not synergistic – and he analogizes this deal to GM buying Chevron. He also makes the case that SolarCity will likely go bankrupt, so there is no good reason for Tesla shareholders to “bail out” the company. And he argues that the capital requirements of the combined entities are unlikely to be fundable, even for its visionary CEO.
 Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
But short-sellers are clearly not long-term investors. And there is a lot more ability for this deal to succeed and produce tremendous investor returns than anyone could ever glean from studying historical financial statements of both companies.
GM buying Chevron is entirely the wrong analogy to compare with Tesla buying SolarCity. Instead, compare this deal to what happened in the creation of television after General Sarnoff, who ran RCA, bought what he renamed NBC.
The world already had radio (just as we already have combustion powered cars.) The conundrum was that nobody needed a TV, especially when there were no TV programs. But nobody would create TV programs if there were no consumers with TVs. General Sarnoff realized that both had to happen simultaneously – the creation of both demand, and supply. It would only be by the creation, and promotion, of both that television could be a success. And it was General Sarnoff who used this experience to launch the first color televisions at the same time as NBC launched the first color programming – which fairly quickly pushed the industry into color.
Skeptics think Mr. Musk and his companies are in over their heads, because there are manufacturing issues for the batteries and the cars, and the solar panel business has yet to be profitable. Yet, the older among us can recall all the troubles with launching TV.
Early sets were not only expensive, they were often problematic, with frequent component failures causing owners to take the TV to a repairman. Often reception was poor, as people relied on poor antennas and weak network signals. It was common to turn on a set and have “snow” as we called it – images that were far from clear. And there was often that still image on the screen with the words “Technical Difficulties,” meaning that viewers just waited to see when programming would return. And programming was far from 24×7 – and quality could be sketchy. But all these problems have been overcome by innovation across the industry.
Yes, the evolution of electric cars will involve a lot of ongoing innovation. So judging its likely success on the basis of recent history would be foolhardy. Today Tesla sells 100% of its cars, with no discounts. The market has said it really, really wants its vehicles. And everybody who is offered electric panels with (a) the opportunity to sell excess power back to the grid and (b) financing, takes the offer. People enjoy the low cost, sustainable electricity, and want it to grow. But lacking a good storage device, or the inability to sell excess power, their personal economics are more difficult.
Electricity production, electricity storage (batteries) and electricity consumption are tightly linked technologies. Nobody will build charging stations if there are no electric cars. Nobody will build electric cars if there are not good batteries. Nobody will make better batteries if there are no electric cars. Nobody will install solar panels if they can’t use all the electricity, or store what they don’t immediately need (or sell it.)
This is not a world of an established marketplace, where GM and Chevron can stand alone. To grow the business requires a vision, business strategy and technical capability to put it all together. To make this work someone has to make progress in all the core technologies simultaneously – which will continue to improve the storage capability, quality and safety of the electric consuming automobiles, and the electric generating solar panels, as well as the storage capabilities associated with those panels and the creation of a new grid for distribution.
This is why Mr. Musk says that combining Tesla and SolarCity is obvious. Yes, he will have to raise huge sums of money. So did such early pioneers as Vanderbilt (railways,) Rockefeller (oil,) Ford (autos,) and Watson (computers.) More recently, Steve Jobs of Apple became heroic for figuring out how to simultaneously create an iPhone, get a network to support the phone (his much maligned exclusive deal with AT&T,) getting developers to write enough apps for the phone to make it valuable, and creating the retail store to distribute those apps (iTunes.) Without all those pieces, the ubiquitous iPhone would have been as successful as the Microsoft Zune.
It is fair for investors to worry if Tesla can raise enough money to pull this off. But, we don’t know how creative Mr. Musk may become in organizing the resources and identifying investors. So far, Tesla has beaten all the skeptics who predicted failure based on price of the cars (Tesla has sold 100% of its production,) lack of range (now up to nearly 300 miles,) lack of charging network (Tesla built one itself) and charging time (now only 20 minutes.) It would be shortsighted to think that the creativity which has made Tesla a success so far will suddenly disappear. And thus remarkably thoughtless to base an analysis on the industry as it exists today, rather than how it might well look in 3, 5 and 10 years.
The combination of Tesla and SolarCity allows Tesla to have all the components to pursue greater future success. Investors with sufficient risk appetite are justified in supporting this merger because they will be positioned to receive the future rewards of this pioneering change in the auto and electric utility industries.
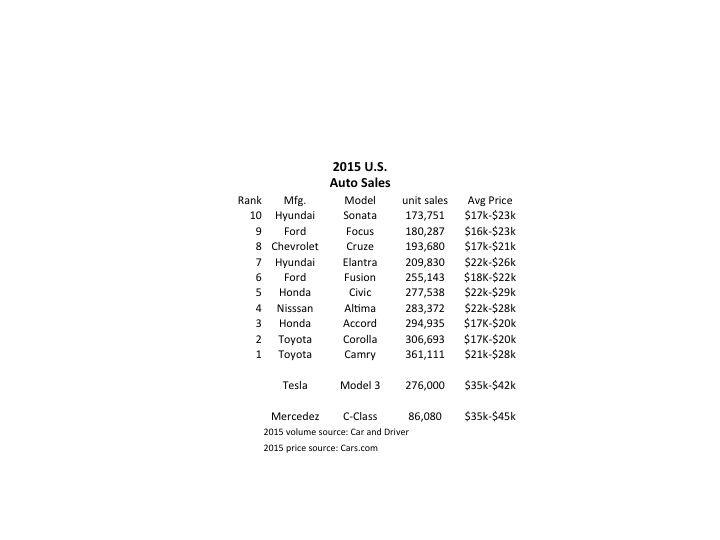
Tesla started taking orders for the Model 3 last week, and the results were remarkable. In 24 hours the company took $1,000 deposits for 198,000 vehicles. By end of Saturday the $1,000 deposits topped 276,000 units. And for a car not expected to be available in any sort of volume until 2017. Compare that with the top selling autos in the U.S. in 2015:
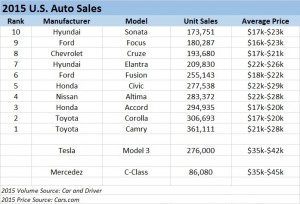 Remarkably, the Model 3 would rank as the 6th best selling vehicle all of last year! And with just a few more orders, it will likely make the top 5 – or possibly top 3! And those are orders placed in just one week, versus an entire year of sales for the other models. And every buyer is putting up a $1,000 deposit, something none of the buyers of top 10 cars did as they purchased product widely available in inventory. [Update 7 April – Tesla reports sales exceed 325,000, which would make the Model 3 the second best selling car in the USA for the entire year 2015 – accomplished in less than one week.]
Remarkably, the Model 3 would rank as the 6th best selling vehicle all of last year! And with just a few more orders, it will likely make the top 5 – or possibly top 3! And those are orders placed in just one week, versus an entire year of sales for the other models. And every buyer is putting up a $1,000 deposit, something none of the buyers of top 10 cars did as they purchased product widely available in inventory. [Update 7 April – Tesla reports sales exceed 325,000, which would make the Model 3 the second best selling car in the USA for the entire year 2015 – accomplished in less than one week.]
Even more astonishing is the average selling price. Note that top 10 cars are not highly priced, mostly in the $17,000 to $25,000 price range. But the Tesla is base priced at $35,000, and expected with options to sell closer to $42,000. That is almost twice as expensive as the typical top 10 selling auto in the U.S.
Tesla has historically been selling much more expensive cars, the Model S being its big seller in 2015. So if we classify Tesla as a “luxury” brand and compare it to like-priced Mercedes Benz C-Class autos we see the volumes are, again, remarkable. In under 1 week the Model 3 took orders for 3 times the volume of all C-Class vehicles sold in the U.S. in 2015.
[Car and Driver top 10 cars; Mercedes Benz 2015 unit sales; Tesla 2015 unit sales; Model 3 pricing]
Although this has surprised a large number of people, the signs were all pointing to something extraordinary happening. The Tesla Model S sold 50,000 vehicles in 2015 at an average price of $70,000 to $80,000. That is the same number of the Mercedes E-Class autos, which are priced much lower in the $50,000 range. And if you compare to the top line Mercedes S-Class, which is only slightly more expensive at an average $90,0000, the Model S sold over 2 times the 22,000 units Mercedes sold. And while other manufacturers are happy with single digit percentage volume growth, in Q4 Tesla shipments were 75% greater in 2015 than 2014.
In other words, people like this brand, like these cars and are buying them in unprecedented numbers. They are willing to plunk down deposits months, possibly years, in advance of delivery. And they are paying the highest prices ever for cars sold in these volumes. And demand clearly outstrips supply.
Yet, Tesla is not without detractors. From the beginning some analysts have said that high prices would relegate the brand to a small niche of customers. But by outselling all other manufacturers in its price point, Tesla has demonstrated its cars are clearly not a niche market. Likewise many analysts argued that electric cars were dependent on high gasoline prices so that “economic buyers” could justify higher prices. Yet, as gasoline prices have declined to prices not seen for nearly a decade Tesla sales keep going up. Clearly Tesla demand is based on more than just economic analysis of petroleum prices.
People really like, and want, Tesla cars. Even if the prices are higher, and if gasoline prices are low.
Emerging is a new group of detractors. They point to the volume of cars produced in 2015, and first quarter output of just under 15,000 vehicles, then note that Tesla has not “scaled up” manufacturing at anywhere near the necessary rate to keep customers happy. Meanwhile, constructing the “gigafactory” in Nevada to build batteries has slowed and won’t meet earlier expectations for 2016 construction and jobs. Even at 20,000 cars/quarter, current demand for Model S and Model 3 They project lots of order cancellations would take 4.5 years to fulfill.
Which leads us to the beauty of sales growth. When products tap an under- or unfilled need they frequently far outsell projections. Think about the iPod, iPhone and iPad. There is naturally concern about scaling up production. Will the money be there? Can the capacity come online fast enough?
Of course, of all the problems in business this is one every leader should want. It is certainly a lot more fun to worry about selling too much rather than selling too little. Especially when you are commanding a significant price premium for your product, and thus can be sure that demand is not an artificial, price-induced variance.
With rare exceptions, investors understand the value of high sales at high prices. When gross margins are good, and capacity is low, then it is time to expand capacity because good returns are in the future. The Model 3 release projects a backlog of almost $12B. Booked orders at that level are extremely rare. Further, short-term those orders have produced nearly $300million of short-term cash. Thus, it is a great time for an additional equity offering, possibly augmented with bond sales, to invest rapidly in expansion. Problematic, yes. Insolvable, highly unlikely.
On the face of it Tesla appears to be another car company. But something much more significant is afoot. This sales level, at these prices, when the underlying economics of use seem to be moving in the opposite direction indicates that Tesla has tapped into an unmet need. It’s products are impressing a large number of people, and they are buying at premium prices. Based on recent orders Tesla is vastly outselling competitive electric automobiles made by competitors, all of whom are much bigger and better resourced. And those are all the signs of a real Game Changer.

A recent analyst took a look at the impact of electric vehicles (EVs) on the demand for oil, and concluded that they did not matter. In a market of 95million barrels per day production, electric cars made a difference of 25,000 to 70,000 barrels of lost consumption; ~.05%.
You can’t argue with his arithmetic. So far, they haven’t made any difference.
 But then he goes on to say they won’t matter for another decade. He forecasts electric vehicle sales grow 5-fold in one decade, which sounds enormous. That is almost 20% growth year over year for 10 consecutive years. Admittedly, that sounds really, really big. Yet, at 1.5million units/year this would still be only 5% of cars sold, and thus still not a material impact on the demand for gasoline.
But then he goes on to say they won’t matter for another decade. He forecasts electric vehicle sales grow 5-fold in one decade, which sounds enormous. That is almost 20% growth year over year for 10 consecutive years. Admittedly, that sounds really, really big. Yet, at 1.5million units/year this would still be only 5% of cars sold, and thus still not a material impact on the demand for gasoline.
This sounds so logical. And one can’t argue with his arithmetic.
But one can argue with the key assumption, and that is the growth rate.
Do you remember owning a Walkman? Listening to compact discs? That was the most common way to listen to music about a decade ago. Now you use your phone, and nobody has a walkman.
Remember watching movies on DVDs? Remember going to Blockbuster, et.al. to rent a DVD? That was common just a decade ago. Now you likely have shelved the DVD player, lost track of your DVD collection and stream all your entertainment. Bluckbuster, infamously, went bankrupt.
Do you remember when you never left home without your laptop? That was the primary tool for digital connectivity just 6 years ago. Now almost everyone in the developed world (and coming close in the developing) carries a smartphone and/or tablet and the laptop sits idle. Sales for laptops have declined for 5 years, and a lot faster than all the computer experts predicted.
Markets that did not exist for mobile products 10 years ago are now huge. Way beyond anyone’s expectations. Apple alone has sold over 48million mobile devices in just 3 months (Q3 2015.) And replacing CDs, Apple’s iTunes was downloading 21million songs per day in 2013 (surely more by now) reaching about 2billion per quarter. Netflix now has over 65million subscribers. On average they stream 1.5hours of content/day – so about 1 feature length movie. In other words, 5.85billion streamed movies per quarter.
What has happened to old leaders as this happened? Sony hasn’t made money in 6 years. Motorola has almost disappeared. CD and DVD departments have disappeared from stores, bankrupting Circuit City and Blockbuster, and putting a world of hurt on survivors like Best Buy.
The point? When markets shift, they often shift a lot faster than anyone predicts. 20%/year growth is nothing. Growth can be 100% per quarter. And the winners benefit unbelievably well, while losers fall farther and faster than we imagine.
Tesla was barely an up-and-comer in 2012 when I said they would far outperform GM, Ford and Toyota. The famous Bob Lutz, a long-term widely heralded auto industry veteran chastised me in his own column “Tesla Beating Detroit – That’s Just Nonsense.”
Mr. Lutz said I was comparing a high-end restaurant to McDonald’s, Wendy’s and Pizza Hut, and I was foolish because the latter were much savvier and capable than the former. He should have used as his comparison Chipotle, which I predicted would be a huge winner in 2011. Those who followed my advice would have made more money owning Chipotle than any of the companies Mr. Lutz preferred.
The point? Market shifts are never predicted by incumbents, or those who watch history. The rate of change when it happens is so explosive it would appear impossible to achieve, and far more impossible to sustain. The trends shift, and one market is rapidly displaced by another.
While GM, Ford and Toyota struggle to maintain their mediocrity, Tesla is winning “best car” awards one after another – even “breaking” Consumer Reports review system by winning 103 points out of a maximum 100, the independent reviewer liked the car so much. Tesla keeps selling 100% of its production, even at its +$100K price point.
So could the market for EVs wildly grow? BMW has announced it will make all models available as electrics within 10 years, as it anticipates a wholesale market shift by consumers promoted by stricter environmental regulations. Petroleum powered car sales will take a nosedive.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) points out that EVs are just .08% of all cars today. And of the 665,000 on the road, almost 40% are in the USA, where they represent little more than a rounding error in market share. But there are smaller markets where EV sales have strong share, such as 12% in Norway and 5% in the Netherlands.
So what happens if Tesla’s new lower priced cars, and international expansion, creates a sea change like the iPod, iPhone and iPad? What happens if people can’t get enough of EVs? What happens if international markets take off, due to tougher regulations and higher petrol costs? What happens if people start thinking of electric cars as mainstream, and gasoline cars as old technology — like two-way radios, VCRs, DVD players, low-definition picture tube TVs, land line telephones, fax machines, etc?
What if demand for electric cars starts doubling each quarter, and grows to 35% or 50% of the market in 10 years? If so, what happens to Tesla? Apple was a nearly bankrupt, also ran, tiny market share company in 2000 before it made the world “i-crazy.” Now it is the most valuable publicly traded company in the world.
Already awash in the greatest oil inventory ever, crude prices are down about 60% in the last year. Oil companies have already laid-off 50,000 employees. More cuts are planned, and defaults expected to accelerate as oil companies declare bankruptcy.
It is not hard to imagine that if EVs really take off amidst a major market shift, oil companies will definitely see a precipitous decline in demand that happens much faster than anticipated.
To little Tesla, which sold only 1,500 cars in 2010 could very well be positioned to make an enormous difference in our lives, and dramatically change the fortunes of its shareholders — while throwing a world of hurt on a huge company like Exxon (which was the most valuable company in the world until Apple unseated it.)
[Note: I want to thank Andreas de Vries for inspiring this column and assisting its research. Andreas consults on Strategy Management in the Oil & Gas industry, and currently works for a major NOC in the Gulf.]

How clearly I remember. I was in the finals of my third grade arithmetic competition. Two of us at the chalkboard, we both scribbled the numbers read to us as fast as we could, did the sum and whirled to look at the judges. Only my competitor was a hair quicker than me, so I was not the winner.
As we walked to the car my mother was quite agitated. “You lost to a GIRL” she said; stringing out that last word like it was some filthy moniker not fit for decent company to here. Born in 1916, to her it was a disgrace that her only son lost a competition to a female.
But it hit me like a tsunami wall. I had underestimated my competitor. And that was stupid of me. I swore I would never again make the mistake of thinking I was better than someone because of my male gender, white skin color, protestant christian upbringing or USA nationality. If I wanted to succeed I had to realize that everyone who competes gets to the end by winning, and they can/will beat me if I don’t do my best.
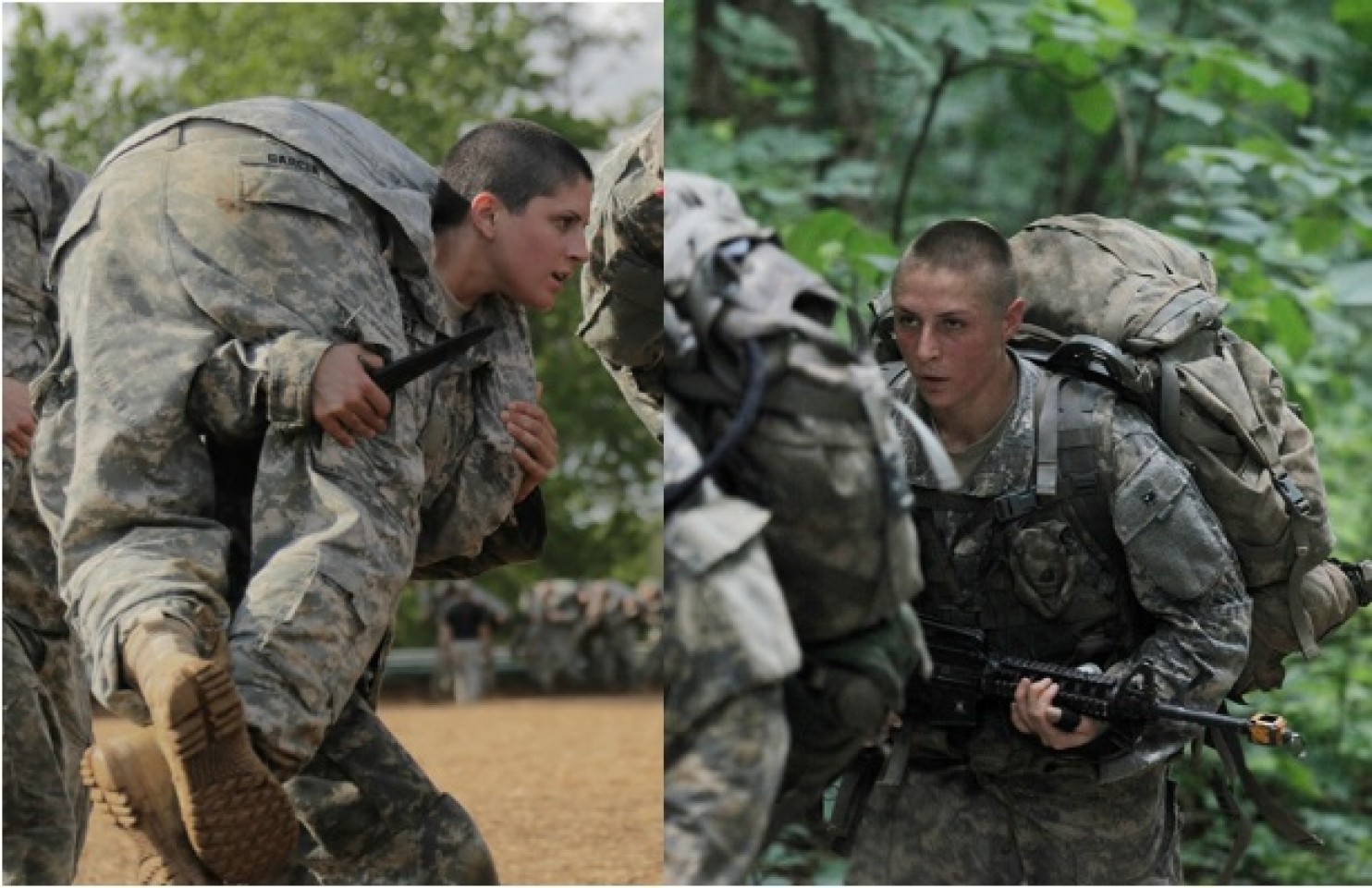
 This week 1st Lt. Shaye Haver, 25, and Capt. Kristen Griest, 26, graduated Army Ranger training. Maybe the toughest military training in the world. And they were awarded their tabs because they were good – not because they were women.
This week 1st Lt. Shaye Haver, 25, and Capt. Kristen Griest, 26, graduated Army Ranger training. Maybe the toughest military training in the world. And they were awarded their tabs because they were good – not because they were women.
In retrospect, it is somewhat incredible that it took this long for our country to begin training all people at this level. If someone is good, why not let them compete? In what way is it smart to hold back someone from competing based on something as silly as their skin color, gender, religious beliefs or sexual orientation?
Our country, in fact much of mankind, has had a long history of holding people back from competing. Those in power like to stay in power, and will use about any tool they can to maintain the status quo – and keep themselves in charge. They will use private clubs, secret organizations, high investment rates, difficult admission programs, laws and social mores to “keep each to his own kind” as I heard far too often throughout my youth.
As I went to college I never forgot my 3rd grade experience, and I battled like crazy to be at the top of every class. It was clear to me there were a lot of people as smart as I was. If I wanted to move forward, it would be foolish to expect I would rise just because the status quo of the time protected healthy white males. There were plenty of women, people of color, and folks with different religions who wanted the spot I wanted – and they would win that spot. Maybe not that day, but soon enough.
In the 1980s I did a project for The Boston Consulting Group in South Africa. As I moved around that segregated apartheid country it was clear to me that those supporting the status quo did so out of fear. They weren’t superior to the native South Africans. But the only way they could maintain their lifestyle was to prohibit these other people from competing.
And that proved to be untenable. The status quo fell, and when it did many of European extraction quickly fled – unable to compete with those they long kept from competing.
In the last 30 years we’ve coined the term “diversity” for allowing people to compete. I guess that is a nice, politically favorable way to say we must overcome the status quo tools used to hold people back. But the drawback is that those in power can use the term to imply someone is allowed to compete, or even possibly wins, only because they were given “special permission” which implies “special terms.”
That is unfortunate, because most of the time the only break these folks got was being allowed to, finally, compete. Once in the competition they frequently have to deal with lots of attacks – even from their own teammates. Jim Thorpe was a Native American who mesmerized Americans by winning multiple Gold Medals at the 1912 Olympics, and embarrassing the Germans then preaching national/racial superiority as they planned the launch of WW1. But, once back on American soil it didn’t take long for his own countrymen to strip Mr. Thorpe of his medals, unhappy that he was an “Indian” rather than a white man. He tragically died a homeless alcoholic.
And never forget all the grief Jackie Robinson bore as the first African-American professional athlete. Branch Rickey overcame the status quo police by giving Mr. Robinson a chance to play in the all-white professional major league baseball. But Mr. Robinson endured years of verbal and physical abuse in order to continue competing, well over and beyond anything suffered by any of his white peers. (For a taste of the difficulties catch the HBO docudrama “42.”)
In 2014, 4057 highly trained, fit soldiers entered Ranger training. 1,609 (40%) graduated. In this latest class 364 soldiers started; 136 graduated (37%.) Officers Griest and Haver are among the very best, toughest, well trained, well prepared, well armed and smartest soldiers in the entire world. (If you have any doubts about this I encourage you to watch the HBO docudrama “Lone Survivor” about Army Rangers trapped behind enemy lines in Afghanistan.)
Officers Griest and Haver are like every other Ranger. They are not “diverse.” They are good. Every American soldier who recognizes the strength of character and tenacity it took for them to become Rangers will gladly follow their orders into battle. They aren’t women Rangers, they are Rangers.
When all Americans learn the importance of this lesson, and begin to see the world this way, we will allow our best to rise to the top. And our history of finding and creating great leadership will continue.

Last week the National Association of Corporate Directors (NACD) pre-released some results of its 2015–2016 Public Company Governance Survey. One major finding is that the makeup of Boards is changing, for the betterment of investors – and most likely everyone else in business.
Boards once had members that almost never changed. Little was required of Directors, and accountability for Board members was low. Since passage of the Securities Act of 1933, little had been required of Board members other than to applaud management and sign-off on the annual audit. And there was nothing investors could do if a Board “checked out,” even in the face of poorly performing management.
But this has changed. According to NACD, 72% of public boards reported they either added or changed a director in the last year. That is up from 64% in the previous year. Board members, and especially committee chairs, are spending a lot more time governing corporations. As a result “retiring in job” has become nearly impossible, and Board diversity is increasingly quite quickly. And increased Board diversity is considered good for business.
Remember Enron, Arthur Anderson, Worldcom and Tyco? At the century’s turn executives in large companies were working closely with their auditors to undertake risky business propositions yet keep these transactions and practices “off the books.” As these companies increasingly hired their audit firm to also provide business consulting, the auditors found it easier to agree with aggressive accounting interpretations that made company financials look better. Some companies went so far as to lie to investors and regulators about their business, until their companies failed from the risks and unlawful activities.
 As a result Congress passed the Sarbanes Oxley act in 2002 (SOX,) which greatly increased the duties of Board Directors – as well as penalties if they failed to meet their duties. This law required Boards to implement procedures to unearth off-balance sheet items, and potential illegal activities such as bribing foreign officials or failing to meet industry reporting requirements for health and safety. Boards were required to know what internal controls were in place, and were held accountable for procedures to implement those controls effectively. And they were also required to make sure the auditors were independent, and not influenced by management when undertaking accounting and disclosure reviews. These requirements were backed up by criminal penalties for CEOs and CFOs that fiddled with financial statements or retaliated on whistle blowers – and Boards were expected to put in place systems to discover possibly illegal executive behavior.
As a result Congress passed the Sarbanes Oxley act in 2002 (SOX,) which greatly increased the duties of Board Directors – as well as penalties if they failed to meet their duties. This law required Boards to implement procedures to unearth off-balance sheet items, and potential illegal activities such as bribing foreign officials or failing to meet industry reporting requirements for health and safety. Boards were required to know what internal controls were in place, and were held accountable for procedures to implement those controls effectively. And they were also required to make sure the auditors were independent, and not influenced by management when undertaking accounting and disclosure reviews. These requirements were backed up by criminal penalties for CEOs and CFOs that fiddled with financial statements or retaliated on whistle blowers – and Boards were expected to put in place systems to discover possibly illegal executive behavior.
In short, Sarbanes Oxley increased transparency for investors into the corporation. And it made Boards responsible for compliance. The demands on Board Directors suddenly skyrocketed.
In reaction to the failure of Lehman Brothers and the almost total bank collapse of 2008, Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act in 2010. Most of this complex legislation dealt with regulating the financial services industry, and providing more protections for consumers and American taxpayers from risky banking practices. But also included in Dodd-Frank were greater transparency requirements, such as details of executive compensation and how compensation was linked to company performance. Companies had to report such things as the pay ratio of CEO pay to average employee compensation (final rules issued last week,) and had to provide for investors to actually vote on executive compensation (called “say on pay.”) And responsibility for implementing these provisions, across all industries, fell again on the Board of Directors.
Thus, after 13 years of regulatory implementation, we are seeing change in corporate governance. What many laypeople thought was the Board’s job from 1940-2000 is finally, actually becoming their job. Real responsibility is now on the Directors’ shoulders. They are accountable. And they can be held responsible by regulators.
The result is a sea change in how Boards behave, and the beginnings of big change in Board composition. Board members are leaving in record numbers. Unable to simply hang around and collect a check for doing little, more are retiring. The average age is lowering. And diversity is increasing as more women, and people of color as well as non-European family histories are being asked onto Boards. Recognizing the need for stronger Boards to make sure companies comply with regulations they are less inclined to idly stand by and watch management. Instead, Boards are seeking talented people with diverse backgrounds to ask better questions and govern more carefully.
Most business people wax eloquently about the negative effect of regulations. It is easy to find academic studies, and case examples, of the added cost incurred due to higher regulation. But what many people fail to recognize are the benefits. Thanks to SOX and Dodd-Frank companies are far more transparent than ever in history, and transparency is increasing – much to the benefit of investors, suppliers, customers and communities. And corporate governance of everything from accounting to compensation to industry compliance is far more extensive, and better. Because Boards are responsible, they are stronger, more capable and improving at a rate previously unseen – with dramatic improvement in diversity. And we can thank Congress for the legislation which demanded better Board performance – to the betterment of all business.