
by Adam Hartung | Apr 3, 2018 | Computing, Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Mobile, Music
Do you still have a pile of compact discs? If so, why? When was the last time you listened to one? Like almost everyone else, you probably stream your music today. If you are just outdated, you listen to music you bought from iTunes or GooglePlay and store on your mobile device. But it would be considered prehistoric to tell people you carry around CDs for listening in your car – because you surely don’t own a portable CD player.
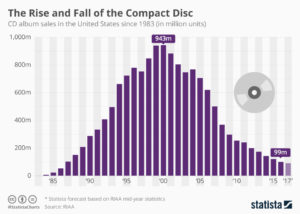
As the chart shows, CD sales exploded from nothing in 1983 to nearly 1B units in 2000. Now sales are less than 1/10th that number, due to the market shift expanded bandwidth allowed.
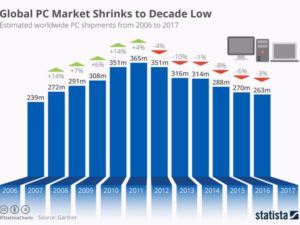
Do you still carry a laptop? If so, you are a dying minority. As PCs became more portable they became indispensable. Nobody left the office, or attended a meeting, without their laptop. That trend exploded until 2011, when PC sales peaked at 365M units. As the chart shows, in the 6 years since, PC sales have dropped by over 100M units, a 30% decline. The advent of mobile devices (smartphones and tablets) coupled with expanded connectivity and growing cloud services allowed mobility to reach entirely new levels – and people stopped carrying their PCs. And just like CDs are disappearing, so will PCs.
These charts dramatically show how quickly a new technology, or package of technologies, can change the way we behave. Simultaneously, they change the competitive landscape. Sony dominated the music industry, as a producer and supplier of hardware, when CDs dominated. But, as I wrote in 2012, the shift to more portable music caused Sony to fall into a rapid decline, and the company suffered 6 consecutive years (24 quarters) of falling sales and losses. The one-time giant was crippled by a technology shift they did not adopt. And they weren’t alone, as big box retailers such as Best Buy and Circuit City also faltered when these sales disappeared.
Once, Microsoft was synonymous with personal technology. Nobody maximized the value in PC growth more than Microsoft. But changing technology altered the competitive landscape, with Apple, Google, Samsung and Amazon emerging as the leaders. Microsoft, as the almost unnoticed launch of Windows 10 demonstrated, is struggling to maintain relevancy.
Too often we discount trends. Like Sony and Microsoft we think historical growth will continue, unabated. We find ways to discount market shifts, saying the products are “niche” and denigrating their quality. We will express our view that the market has “hiccuped” and will return to growth again. By the time we admit the shift is permanent new competitors have overtaken the lead, and we risk becoming totally obsolete. Like Toys-R-Us, Radio Shack, Sears and Motorola.
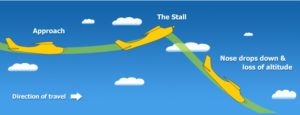
Aircraft stalls when not enough power to climb
The time for action is when the very first signs of shift happened. I’ve written a lot about “Growth Stalls” and they occur in just 2 quarters. 93% of the time a stalled company never again grows at a mere 2%/year. Look at how fast GE went from the best company in America to the worst. It is incredibly important that leadership react FAST when trends push customers toward new solutions, because it often takes very little time for the trend to make dying markets completely untenable.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 21, 2016 | In the Rapids, Leadership, Lifecycle, Television, Web/Tech
Netflix has been a remarkable company. Because it has accomplished something almost no company has ever done. It changed its business model, leading to new growth and higher profits.
Almost nobody pulls that off, because they remain stuck defending and extending their old model until they become irrelevant, or fail. Think about Blackberry, that gave us the smartphone business then lost it to Apple and its creation of the app market. Consider Circuit City, that lost enough customers to Amazon it could no longer survive. Sun Microsystems disappeared after PC servers caught up to Unix servers in capability. Remember the Bell companies and their land-line and long distance services, made obsolete by mobile phones and cable operators? These were some really big companies that saw their market shifts, but failed to “pivot” their strategy to remain competitive.
Netflix built a tremendous business delivering physical videos on tape and CD to homes, wiping out the brick-and-mortar stores like Blockbuster and Hollywood Video. By 2008 Netflix reached $1B revenues, reducing Blockbuster by a like amount. By 2010 Blockbuster was bankrupt. Netflix’ share price soared from $50/share to almost $300/share during 2011. By the end of 2012 CD shipments were dropping precipitously as streaming viewership was exploding. People thought Netflix was missing the wave, and the stock plummeted 75%. Most folks thought Netflix couldn’t pivot fast enough, or profitably, either.
But in 2013 Netflix proved the analysts wrong, and the company built a very successful – in fact market leading – streaming business. The shares soared, recovering all that lost value. By 2015 the company had more than doubled its previous high valuation.
But Netflix may be breaking entirely new ground in 2016. It is becoming a market leader in original programming. Something we long attributed to broadcasters and/or cable distributors like HBO and Showtime.
Today’s broadcast companies, like NBC, CBS and ABC, are offering less and less original programming. Overall there are 3 hours/night of prime time television which broadcasters used to “own” as original programming hours. Over the course of a year, allowing for holidays and one open night per week, that meant about 900 hours of programming for each network (including reruns as original programming.) But that was long ago.
 These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
Against that backdrop, Netflix has announced it will program 600 hours of original programming this year. That will approximately double any single large broadcast network. In a very real way, if you don’t want to watch sports or reality TV any more you probably will be watching some kind of “on demand” program. Either streamed from a cable service, or from a provider such as Netflix, Hulu or Amazon.
When it comes to original programming, the old broadcast networks are losing their relevancy to streaming technology, personal video devices and the customer’s ability to find what they want, when they want it – and increasingly at a quality they prefer – from streaming as opposed to broadcast media.
To complete this latest “pivot,” from a video streaming company to a true media company with its own content, Morgan Stanley has published that Netflix is now considered by customers as the #1 quality programming across streaming services. 29% of viewers said Netflix was #1, followed by long-time winner HBO now #2 with 21% of customers saying their programming is best. Amazon, Showtime and Hulu were seen as the best quality by 4%-5% of viewers.
So a decade ago Netflix was a CD distribution company. The largest customer of the U.S. Postal Service. Signing up folks to watch physical videos in their homes. Now they are the largest data streaming company on the planet, and one of the largest original programming producers and programmers in the USA – and possibly the world. And in this same decade we’ve watched the network broadcast companies become outlets for sports and reality TV, while cutting far back on their original shows. Sounds a lot like a market shift, and possibly Netflix could be the game changer, as it performs the first strategy double pivot in business history.

by Adam Hartung | Sep 22, 2015 | Current Affairs, Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation
A recent analyst took a look at the impact of electric vehicles (EVs) on the demand for oil, and concluded that they did not matter. In a market of 95million barrels per day production, electric cars made a difference of 25,000 to 70,000 barrels of lost consumption; ~.05%.
You can’t argue with his arithmetic. So far, they haven’t made any difference.
 But then he goes on to say they won’t matter for another decade. He forecasts electric vehicle sales grow 5-fold in one decade, which sounds enormous. That is almost 20% growth year over year for 10 consecutive years. Admittedly, that sounds really, really big. Yet, at 1.5million units/year this would still be only 5% of cars sold, and thus still not a material impact on the demand for gasoline.
But then he goes on to say they won’t matter for another decade. He forecasts electric vehicle sales grow 5-fold in one decade, which sounds enormous. That is almost 20% growth year over year for 10 consecutive years. Admittedly, that sounds really, really big. Yet, at 1.5million units/year this would still be only 5% of cars sold, and thus still not a material impact on the demand for gasoline.
This sounds so logical. And one can’t argue with his arithmetic.
But one can argue with the key assumption, and that is the growth rate.
Do you remember owning a Walkman? Listening to compact discs? That was the most common way to listen to music about a decade ago. Now you use your phone, and nobody has a walkman.
Remember watching movies on DVDs? Remember going to Blockbuster, et.al. to rent a DVD? That was common just a decade ago. Now you likely have shelved the DVD player, lost track of your DVD collection and stream all your entertainment. Bluckbuster, infamously, went bankrupt.
Do you remember when you never left home without your laptop? That was the primary tool for digital connectivity just 6 years ago. Now almost everyone in the developed world (and coming close in the developing) carries a smartphone and/or tablet and the laptop sits idle. Sales for laptops have declined for 5 years, and a lot faster than all the computer experts predicted.
Markets that did not exist for mobile products 10 years ago are now huge. Way beyond anyone’s expectations. Apple alone has sold over 48million mobile devices in just 3 months (Q3 2015.) And replacing CDs, Apple’s iTunes was downloading 21million songs per day in 2013 (surely more by now) reaching about 2billion per quarter. Netflix now has over 65million subscribers. On average they stream 1.5hours of content/day – so about 1 feature length movie. In other words, 5.85billion streamed movies per quarter.
What has happened to old leaders as this happened? Sony hasn’t made money in 6 years. Motorola has almost disappeared. CD and DVD departments have disappeared from stores, bankrupting Circuit City and Blockbuster, and putting a world of hurt on survivors like Best Buy.
The point? When markets shift, they often shift a lot faster than anyone predicts. 20%/year growth is nothing. Growth can be 100% per quarter. And the winners benefit unbelievably well, while losers fall farther and faster than we imagine.
Tesla was barely an up-and-comer in 2012 when I said they would far outperform GM, Ford and Toyota. The famous Bob Lutz, a long-term widely heralded auto industry veteran chastised me in his own column “Tesla Beating Detroit – That’s Just Nonsense.”
Mr. Lutz said I was comparing a high-end restaurant to McDonald’s, Wendy’s and Pizza Hut, and I was foolish because the latter were much savvier and capable than the former. He should have used as his comparison Chipotle, which I predicted would be a huge winner in 2011. Those who followed my advice would have made more money owning Chipotle than any of the companies Mr. Lutz preferred.
The point? Market shifts are never predicted by incumbents, or those who watch history. The rate of change when it happens is so explosive it would appear impossible to achieve, and far more impossible to sustain. The trends shift, and one market is rapidly displaced by another.
While GM, Ford and Toyota struggle to maintain their mediocrity, Tesla is winning “best car” awards one after another – even “breaking” Consumer Reports review system by winning 103 points out of a maximum 100, the independent reviewer liked the car so much. Tesla keeps selling 100% of its production, even at its +$100K price point.
So could the market for EVs wildly grow? BMW has announced it will make all models available as electrics within 10 years, as it anticipates a wholesale market shift by consumers promoted by stricter environmental regulations. Petroleum powered car sales will take a nosedive.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) points out that EVs are just .08% of all cars today. And of the 665,000 on the road, almost 40% are in the USA, where they represent little more than a rounding error in market share. But there are smaller markets where EV sales have strong share, such as 12% in Norway and 5% in the Netherlands.
So what happens if Tesla’s new lower priced cars, and international expansion, creates a sea change like the iPod, iPhone and iPad? What happens if people can’t get enough of EVs? What happens if international markets take off, due to tougher regulations and higher petrol costs? What happens if people start thinking of electric cars as mainstream, and gasoline cars as old technology — like two-way radios, VCRs, DVD players, low-definition picture tube TVs, land line telephones, fax machines, etc?
What if demand for electric cars starts doubling each quarter, and grows to 35% or 50% of the market in 10 years? If so, what happens to Tesla? Apple was a nearly bankrupt, also ran, tiny market share company in 2000 before it made the world “i-crazy.” Now it is the most valuable publicly traded company in the world.
Already awash in the greatest oil inventory ever, crude prices are down about 60% in the last year. Oil companies have already laid-off 50,000 employees. More cuts are planned, and defaults expected to accelerate as oil companies declare bankruptcy.
It is not hard to imagine that if EVs really take off amidst a major market shift, oil companies will definitely see a precipitous decline in demand that happens much faster than anticipated.
To little Tesla, which sold only 1,500 cars in 2010 could very well be positioned to make an enormous difference in our lives, and dramatically change the fortunes of its shareholders — while throwing a world of hurt on a huge company like Exxon (which was the most valuable company in the world until Apple unseated it.)
[Note: I want to thank Andreas de Vries for inspiring this column and assisting its research. Andreas consults on Strategy Management in the Oil & Gas industry, and currently works for a major NOC in the Gulf.]

by Adam Hartung | Apr 1, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
“Hope springs eternal in the human breast” (Alexander Pope)
As it does for most investors. People do not like to accept the notion that a business will lose relevancy, and its value will fall. Especially really big companies that are household brand names. Investors, like customers, prefer to think large, established companies will continue to be around, and even do well. It makes everyone feel better to have a optimistic attitude about large, entrenched organizations.
And with such optimism investors have cheered Microsoft for the last 15 months. After a decade of trading up and down around $26/share, Microsoft stock has made a significant upward move to $41 – a new decade-long high. This price has people excited Microsoft will reach the dot.com/internet boom high of $60 in 2000.
After discovering that Windows 8, and the Surface tablet, were nowhere near reaching sales expectations after Christmas 2012 – and that PC sales were declining faster than expected – investors were cheered in 2013 to hear that CEO Steve Ballmer would resign. After much speculation, insider Satya Nadella was named CEO, and he quickly made it clear he was refocusing the company on mobile and cloud. This started the analysts, and investors, on their recent optimistic bent.
CEO Nadella has cut the price of Windows by 70% in order to keep hardware manufacturers on Windows for lower cost machines, and he announced the company’s #1 sales and profit product – Office – was being released on iOS for iPad users. Investors are happy to see this action, as they hope that it will keep PC sales humming. Or at least slow the decline in sales while keeping manufacturers (like HP) in the Microsoft Windows fold. And investors are likewise hopeful that the long awaited Office announcement will mean booming sales of Office 365 for all those Apple products in the installed base.
But, there’s a lot more needed for Microsoft to succeed than these announcements. While Microsoft is the world’s #1 software company, it is still under considerable threat and its long-term viability remains unsure.
Windows is in a tough spot. After this price decline, Microsoft will need to increase sales volume by 2.5X to recoup lost profits. Meanwhile, Chrome laptops are considerably cheaper for customers and more profitable for manufacturers. And whether this price cut will have any impact on the decline in PC sales is unclear, as users are switching to mobile products for ease-of-use reasons that go far beyond price. Microsoft has taken an action to defend and extend its installed base of manufacturers who have been threatening to move, but the impact on profits is still likely to be negative and PC sales are still going to decline.
Meanwhile, the move to offer Office on iOS is clearly another offer to defend the installed Office marketplace, and unlikely to create a lot of incremental revenue and profit growth. The PC market has long been much bigger than tablets, and almost every PC had Office installed. Shrinking at 12-14% means a lot less Windows Office is being sold. And, In tablets iOS is not 100% of the market, as Android has substantial share. Offering Office on iOS reaches a lot of potential machines, but certainly not 100% as has been the case with PCs.
Further, while there are folks who look forward to running Office on an iOS device, Office is not without competition. Both Apple and Google offer competitive products to Office, and the price is free. For price sensitive users, both individuals and corporations, after 4 years of using competitive products it is by no means a given they all are ready to pay $60-$100 per device per year. Yes, there will be Office sales Microsoft did not previously have, but whether it will be large enough to cover the declining sales of Office on the PC is far from clear. And whether current pricing is viable is far, far from certain.
While these Microsoft products are the easiest for consumers to understand, Nadella’s move to make Microsoft successful in the mobile/cloud world requires succeeding with cloud products sold to corporations and software-as-service providers. Here Microsoft is late, and facing substantial competition as well.

Just last week Google cut the price of its Compute Engine cloud infrastructure (IaaS) platform and App Engine cloud app platform (PaaS) products 30-32%. Google cut the price of its Cloud Storage and BigQuery (big data analytics) services by 68% and 85% as it competes headlong for customers with Amazon. Amazon, which has the first-mover position and large customers including the U.S. federal government, cut prices within 24 hours for its EC2 cloud computing service by 30%, and for its S3 storage service by over 50%. Amazon also reduced prices on its RDS database service approximately 28%, and its Elasticache caching service by over 33%.
To remain competitive, Microsoft had to react this week by chopping prices on its Azure cloud computing products 27%-35%, reducing cloud storage pricing 44%-65%, and whacking prices on its Windows and Linux memory-intensive computing products 27%-35%. While these products have allowed the networking division formerly run by now CEO Nadella to be profitable, it will be increasingly difficult to maintain old profit levels on existing customers, and even a tougher problem to profitably steal share from the early cloud leaders – even as the market grows.
While optimism has grown for Microsoft fans, and the share price has moved distinctly higher, it is smart to look at other market leaders who obtained investor favorability, only to quickly lose it.
Blackberry was known as RIM (Research in Motion) in June, 2007 when the iPhone was launched. RIM was the market leader, a near monopoly in smart phones, and its stock was riding high at $70. In August, 2007, on the back of its dominant status, the stock split – and moved on to a split adjusted $140 by end of 2008. But by 2010, as competition with iOS and Android took its toll RIM was back to $80 (and below.) Today the rechristened company trades for $8.
Sears was once the country’s largest and most successful retailer. By 2004 much of the luster was coming off when KMart purchased the company and took its name, trading at only $20/share. Following great enthusiasm for a new CEO (Ed Lampert) investors flocked to the stock, sure it would take advantage of historical brands such as DieHard, Kenmore and Craftsman, plus leverage its substantial real estate asset base. By 2007 the stock had risen to $180 (a 9x gain.) But competition was taking its toll on Sears, despite its great legacy, and sales/store started to decline, total sales started declining and profits turned to losses which began to stretch into 20 straight quarters of negative numbers. Meanwhile, demand for retail space declined, and prices declined, cutting the value of those historical assets. By 2009 the stock had dropped back to $40, and still trades around that value today — as some wonder if Sears can avoid bankruptcy.
Best Buy was a tremendous success in its early years, grew quickly and built a loyal customer base as the #1 retail electronics purveyor. But streaming video and music decimated CD and DVD sales. On-line retailers took a huge bite out of consumer electronic sales. By January, 2013 the stock traded at $13. A change of CEO, and promises of new formats and store revitalization propped up optimism amongst investors and by November, 2014 the stock was at $44. However, market trends – which had been in place for several years – did not change and as store sales lagged the stock dropped, today trading at only $25.
Microsoft has a great legacy. It’s products were market leaders. But the market has shifted – substantially. So far new management has only shown incremental efforts to defend its historical business with product extensions – which are up against tremendous competition that in these new markets have a tremendous lead. Microsoft so far is still losing money in on-line and gaming (xBox) where it has lost almost all its top leadership since 2014 began and has been forced to re-organize. Nadella has yet to show any new products that will create new markets in order to “turn the tide” of sales and profits that are under threat of eventual extinction by ever-more-capable mobile products.
While optimism springs eternal long-term investors would be smart to be skeptical about this recent improvement in the stock price. Things could easily go from mediocre to worse in these extremely competitive global tech markets, leaving Microsoft optimists with broken dreams, broken hearts and broken portfolios.
Update: On April 2 Microsoft announced it is providing Windows for free to all manufacturers with a 9″ or smaller display. This is an action to help keep Microsoft competitive in the mobile marketplace – but it does little for Microsoft profitability. Android from Google may be free, but Google’s business is built on ad sales – not software sales – and that’s dramatically different from Microsoft that relies almost entirely on Windows and Office for its profitability
Update: April 3 CRN (Computer Reseller News) reviewed Office products for iOS – “We predict that once the novelty of “Office for iPad” wears off, companies will go back to relying on the humble, hard-working third parties building apps that are as stable, as handsome and far more capable than those of Redmond. It’s not that hard to do.”
by Adam Hartung | Oct 23, 2009 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, eBooks, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in, Music
If you try standing in the way of a market shift you are going to get treated like the poor cowboy who stands in front of a cattle stampede. The outcome isn't pretty. Yet, we still have lots of leaders trying to Defend & Extend their business with techniques that are detrimental to customers. And likely to have the same impact on customers as the cowpoke shooting a pistol over the head of the herd.
Book publishers have a lot to worry about. Honestly, when did you last read a book? Every year the demand for books declines as people switch reading habits to shorter formats. And book readership becomes more concentrated in the small percentage of folks that read a LOT of books. And those folks are moving faster and faster to Kindle type digital e-book devices. So the market shift is pretty clear.
Yet according to the Wall Street Journal Scribner (division of Simon & Schuster) is delaying the release of Stephen King's latest book in e-format ("Publisher Delays Stephen King eBook"). They want to sell more printed books, so they hope to force the market to buy more paper copies by delaying the ebook for 6 weeks. They think that people will want to give this book as a gift, so they'll buy the paper copy because the ebook won't be out until 12/24.
So what will happen? Kindle readers I know don't want a paper book. They wait. Giving them a paper copy would create a reaction like "Oh, you shouldn't have. I mean, really, you shouldn't have." So the idea that this gets more printed books to e-reader owners is faulty. That also means that the several thousand copies which would get sold for e-readers don't. So you end up with lots of paper inventory, and unsatisfactory sales of both formats. That's called "lose-lose." And that's the kind of outcome you can expect when trying to Defend & Extend an outdated Success Formula.
Simultaneously, as book sales become fewer and more concentrated a higher percent of volume falls onto fewer titles. And that is exactly where WalMart, Target and Amazon compete. High volume, and for 2 of the 3 companies, limited selection. This gives the reseller more negotiating clout against the publisher. So as the big retailers look for ways to get people in the store, they are willing to sell books at below cost – loss leaders.
So now publishers are joining with the American Booksellers Association to seek an anti-trust case against the big retailers according to the Wall Street Journal again in "Are Amazon, WalMart and Target acting like Predators?" . Publishers want to try Defending their old pricing models, and as that crumbles in the face of market shifts they try using lawyers to stop the shift. That will probably work just as well as the lawsuits music publishers tried using to stop the distribution of MP3 tunes. Those lawsuits ended up making no difference at all in the shift to digital music consumption and distribution.
"Movie Fans Might Have to Wait To Rent New DVD Releases" is the Los Angeles Times headline. The studios like 20th Century Fox, Universal and Warner Brothers want individuals to buy more DVDs. So their plan is to refuse to sell DVDs to rental outfits like Netflix, Redbox and Blockbuster. Just like Scribner with its Stephen King book, they are hoping that people won't wait for the rental opportunity and will feel forced to go buy a copy. Like that's the direction the market is heading – right?
If they wanted to make a lot of money, the studios would be working hard to find a way to deliver digital format movies as fast as possible to people's PCs – the equivalent of iTunes for movies – not trying to limit distribution! That the market is shifting away from DVD sales is just like the shift away from music CD sales, and will not be fixed by making it harder to rent movies. Although it might increase the amount of piracy – just like similar actions backfired on the music studios 8 years ago.
Defending & Extending a business only works when it is in the Rapids of market growth. When growth slows, the market is moving on. Trying to somehow stop that shift never works. Only an arrogant internally-focused manager would think that the company can keep markets from shifting in a globally connected digital world. Consumers will move fast to what they want, and if they see a block they just run right over it – or go where you least want them to go (like to pirates out of China or Korea.)
They only way to deal with market shifts is to get on board. "Skate to where the puck will be" is the over-used Wayne Gretzsky quote. Be first to get there, and you can create a new Success Formula that captures value of new growth markets. And that's a lot more fun than getting trampled under a herd of shifting customers that you simply cannot control.






 These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.


