
by Adam Hartung | Jun 5, 2018 | Investing, Retail, Strategy, Trends, Web/Tech
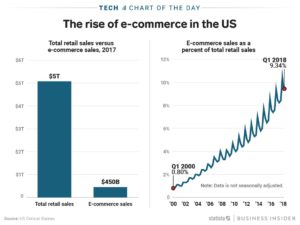
The US e-commerce market is just under 10% the size of entire retail market. On the face of it this would indicate that the game is far from over for big traditional retail. After all, how could such a small segment kill profits for such a huge industry based on enormous traditional players?
Yet, Sears – once a Dow Jones component and the world’s most powerful retailer – has announced it will close 100 more stores. The Kmart/Sears chain is now only 894 stores – down from thousands at its peak and 1,275 just last year. Revenue dropped 30% versus a year ago, and quarterly losses of $424M were almost 15% of revenues.
But, that ignores marginal economics. It often doesn’t take a monster change in one factor to have a huge impact on the business model. Let’s say Sales are $100. Less Cost of Goods sold of $75. That leaves a Gross Margin of $25. Selling, General and Administrative costs are 20%, so Operating Income is only $5. The Net Margin before Interest and Taxes is 5%. (BTW, these are the actual percentages of Walmart from 1/31/18.)
Now, in comes a new competitor – like Amazon.com. They have no stores, no store clerks, and minimal inventory due to “e-storefront” selling. So, they are able to lower prices by 5%. That seems pretty small – just a 5% discount compared to typical sales of 20%, 30% even 50% (BOGO) in retail stores. Amazon’s 5% price reduction seems like no big deal to established firms.
But, Walmart has to lower prices by 5% in response, which lowers revenues to $95. But the stores, clerks, inventory, distribution centers and trucks all largely remain. With Cost of Goods Sold still $75, Gross Margin falls to $20. Fixed headquarters costs, general and administrative costs don’t change, so they remain at $20. This leaves Operating Income of …$0.
(For more detailed analysis see “Bigger is Not Always Better – Why Amazon is Worth More than Walmart” from July, 2015.)
How can Walmart survive with no profits? It can’t. To get some margin back, Walmart has to start shutting stores, selling assets, cutting pay, using automation to cut headcount, beating on vendors to offer them better prices. This earns praise as “a low cost operation.” When in fact, this makes Walmart a less competitive company, because it’s footprint and service levels decline, which encourages people to do more shopping on-line. A vicious circle begins of trying to recapture lost profitability, while sales are declining rather than growing.
Walmart was (and is) huge. Even Sears was much bigger than Amazon.com at the beginning. But to compete with Amazon.com both had to lower prices on ALL of their products in ALL of their stores. So the hit to Walmart’s, and Sears’, revenue is a huge number. Though Amazon.com was a much, much smaller company, its impact explodes on the larger competitor P&L’s.
This disruption is felt across the entire industry: ALL traditional retailers are forced to match Amazon and other e-commerce companies, even though there is no way they can cut costs enough to compete. Thus, Toys-R-Us, Radio Shack, Claire’s and Bon-Ton have declared bankruptcy in 2018, and the once great, dominant Sears is on the precipice of extinction.
All of which is good news for Amazon.com investors. Amazon.com has 40% market share of the entire e-commerce business. The fact that e-commerce is only 10% of all retail is great news for Amazon investors. That means there is still an enormously large market of traditional retail available to convert to on-line sales.
The shift to e-commerce will not be stopping, or even slowing. Since January, 2010 the future has been easily predictable for traditional retail’s decline. The next few years will see a transition of an additional $2.5 trillion on-line, which is 5X the size of the existing e-commerce market!
As stores close new competitors will emerge in the e-commerce market. But undoubtedly the big winner will be the company with 40% market share today – Amazon.com. So what will Amazon’s stock be worth when sales are 5x larger (or more) and Amazon can increase profits by making leveraging its infrastructure and slow future investments?
Twenty years ago, Amazon was a retail ant. And retail elephants ignored it. But that was foolish, because Amazon had a different business model with an entirely different cost of operations. And now the elephants are falling fast, due to their inability to adapt to new market conditions and maintain their growth.
_________________________________________________________________________
Author’s Note: In June, 2007 I was asked to predict WalMart’s future. Here are the predictions I made 11 years ago:
- “In 5 years (2012) Walmart would not have succeeded internationally” [True: Mexico, China, Germany all failed]
- “In 5 years (2012) Walmart would no new businesses, and its revenue will be stalled” [True]
- In 5 years (2012) Walmart would be spending more on stock repurchases then investing in its own stores or distribution” [True – and the Walton’s were moving money out of Walmart to other investments]
- “In 10 years (2017) Walmart would take a dramatic act, and make an acquisition” [True: Jet.com]
- “In 10 years (2017 Walmart’s value would not keep up with the stock market” [from 6/2007 to 6/2017 WMT went from $48 to $75 up 56.25%, DIA went from $134 to $180 up 34.3%, AMZN went from $70 to $1,000 up 1,330% or 13.3x]
- “In 30 years (2037) Walmart will only be known as “a once great company, like General Motors”

by Adam Hartung | Jan 23, 2018 | Disruptions, Investing, Retail, Trends
Business Insider is projecting a “tsunami” of retail store closings in 2018 — 12,000 (up from 9,000 in 2017.) Also, the expect several more retailers will file bankruptcy, including Sears.
Duh. Nothing surprising about those projections. In mid-2016, Wharton Radio interviewed me about Sears, and I made sure everyone clearly understood I expect it to fail. Soon. In December, 2016 I overviewed Sears’ demise, predicted its inevitable failure, and warned everyone that all traditional retail was going to get a lot smaller. I again recommended dis-investing your portfolio of retail. By March, 2017 the handwriting was so clear I made sure investors knew that there were NO traditional retailers worthy of owning, including Walmart. By October, 2017 I wrote about the Waltons cashing out their Walmart ownership, indicating nobody should be in the stock – or any other retailer.
The trend is unmistakable, and undeniable. The question is – what are you going to do about it? In July, 2015 Amazon became more valuable than Walmart, even though much smaller. I explained why that made sense – because the former is growing and the latter is shrinking. Companies that leverage trends are always worth more. And that fact impacts YOU! As I wrote in February, 2017 the “Amazon Effect” will change not only your investments, but how you shop, the value of retail real estate (and thus all commercial real estate,) employment opportunities for low-skilled workers, property and sales tax revenues for all cities impacting school and infrastructure funding, and all supply chain logistics. These trends are far-reaching, and no business will be untouched.
Don’t just say “oh my, retailers are crumbling” and go to the next web page. You need to make sure your strategy is leveraging the “Amazon Effect” in ways that will help you grow revenues and profits. Because your competition is making plans to use these trends to hurt your business if you don’t make the first move. Need help?

by Adam Hartung | Mar 22, 2017 | In the Whirlpool, Investing, Retail
(Photo by Scott Olson/Getty Images)
Traditional retailers just keep providing more bad news. Payless Shoes said it plans to file bankruptcy next week, closing 500 of its 4,000 stores. Most likely it will follow the path of Radio Shack, which hasn’t made a profit since 2011. Radio Shack filed bankruptcy and shut a gob of stores as part of its “turnaround plan.” Then in February Radio Shack filed its second bankruptcy — most likely killing the chain entirely this time.
Sears Holdings finally admitted it probably can’t survive as a going concern this week. Sears has lost over $10 billion since 2010 — when it last showed a profit — and owes over $4 billion to its creditors. Retail stocks cratered Monday as the list of retailers closing stores accelerated: Sears, KMart, Macy’s, Radio Shack, JCPenney, American Apparel, Abercrombie & Fitch, The Limited, CVS, GNC, Office Depot, HHGregg, The Children’s Place and Crocs are just some of the household names that are slowly (or not so slowly) dying.
None of this should be surprising. By the time CEO Ed Lampert merged KMart with Sears the trend to e-commerce was already pronounced. Anyone could build an excel spreadsheet that would demonstrate as online retail grew, brick-and-mortar retail would decline. In the low margin world of retail, profits would evaporate. It would be a blood bath. Any retailer with any weakness simply would not survive this market shift — and that clearly included outdated store concepts like Sears, KMart and Radio Shack which long ago were outflanked by on-line shopping and trendier storefronts.
Yet, not everyone is ready to give up on some retailers. Walmart, for example, still trades at $70 per share, which is higher than it traded in 2015 and about where it traded back in 2012. Some investors still think that there are brick-and-mortar outfits that are either immune to the trends, or will survive the shake-out and have higher profits in the future.
And that is why we have to be very careful about business myths. There are a lot of people that believe as markets shrink the ultimate consolidation will leave one, or a few, competitors who will be very profitable. Capacity will go away, and profits will return. In the end, they believe if you are the last buggy whip maker you will be profitable — so investors just need to pick who will be the survivor and wait it out. And, if you believe this, then you have justified owning Walmart.
Only, markets don’t work that way. As industries consolidate they end up with competitors who either lose money or just barely eke out a small profit. Think about the auto industry, airlines or land-line telecom companies.
Two factors exist which effectively forces all the profits out of these businesses and therefore make it impossible for investors to make money long-term.
First, competitive capacity always remains just a bit too much for the market need. Management, and often investors, simply don’t want to give up in the face of industry consolidation. They keep hoping to reach a rainbow that will save them. So capacity lingers and lingers — always pushing prices down even as costs increase. Even after someone fails, and that capacity theoretically goes away, someone jumps in with great hopes for the future and boosts capacity again. Therefore, excess capacity overhangs the marketplace forcing prices down to break-even, or below, and never really goes away.
Given the amount of retail real estate out there and the bargains being offered to anyone who wants to open, or expand, stores this problem will persist for decades in retail.
Second, demand in most markets keeps declining. Hopefuls project that demand will “stabilize,” thus balancing the capacity and allowing for price increases. Because demand changes aren’t linear, there are often plateaus that make it appear as if demand won’t go down more. But then something changes — an innovation, regulatory change, taste change — and demand takes another hit. And all the hope goes away as profits drop, again.
It is not a successful strategy to try being the “last man standing” in any declining market. No competitor is immune to these forces when markets shift. No matter how big, when trends shift and new forms of competition start growing every old-line company will be negatively affected. Whether fast, or slow, the value of these companies will continue declining until they eventually become worthless.
Nor is it successful long-term to try and segment the business into small groupings which management thinks can be protected. When Xerox brought to market photocopying, small offset press manufacturers (ABDick and Multigraphics ) said not to worry. Xeroxing might be OK in some office installations, but there were customer segments that would forever use lithography. Even as demand shrunk, well into the 1990s, they said that big corporations, industrial users, government entities, schools and other segments would forever need the benefits of lithography, so investors were safe. Today the small offset press market is a tiny fraction of its size in the 1960s. ABDick and Multigraphics both went through rounds of bankruptcies before disappearing. Xerography, its child desktop publishing, and its grandchild electronic screens, killed offset for almost all applications.
So don’t be lured into false hopes by retailers who claim their segment is “protected.” Short-term things might not look bad. But the market has already shifted to e-commerce and this is just round one of change. More and more innovations are coming that will make the need for traditional stores increasingly unnecessary.
Many readers have expressed their disappointment in my chronic warnings about Walmart. But those warnings are no different than my warnings about Sears Holdings. It’s just that the timing may be different. Both companies have been over-investing in assets (brick-and-mortar stores) that are declining in value as they have attempted to defend and extend their old business model. Both radically under-invested in new markets which were cannibalizing their old business. And, in the end, both will end up with the same results.
And this is true for all retailers that depend on traditional brick-and-mortar sales for their revenues and profits — it’s only a matter of when things will go badly, not if. So traditional retail is nowhere that any investor wants to be.

by Adam Hartung | Aug 26, 2016 | In the Swamp, Investing, Retail, Trends
Photographer: Luke Sharrett/Bloomberg
Walmart is in more trouble than its leadership wants to acknowledge. Investors
need to realize that it is up to Jet.com to turn around the ailing giant. And
that is a big task for the under $1 billion company.
Relevancy Is Hard To Keep – Look At Sears
Nobody likes to think their business can disappear. What CEO wants to tell his investors or employees “we’re no longer relevant, and it looks like our customers are all going somewhere else for their solutions”? Unfortunately, most leadership teams become entrenched in the business model and deny serious threats to longevity, thus leading to inevitable failure as customers switch.
Gallery: “Walmart Goes Small”
In early September the Howard Johnson’s in Bangor, Maine will close. This will leave just one remaining HoJo in the USA. What was once an iconic brand with hundreds of outlets strung along the fast growing interstate highway system is now nearly dead. People still drive the interstate, but trends changed, fast food became a good substitute, and unable to update its business model this once great brand died.

AP Photo/Elise Amendola
Sears announced another $350 million quarterly loss this week. That makes $9 billion in accumulated losses the last several quarters. Since Chairman and CEO Ed Lampert took over, Sears and Kmart have seen same store sales decline every single quarter except one. Unable to keep its customers Mr. Lampert has been closing stores and selling assets to stem the cash drain. But to keep the company afloat his hedge fund, ESL, is loaning Sears Holdings SHLD -2.94% another $300 million. On top of the $500 million the company borrowed last quarter. That the once iconic company, and Dow Jones Industrial Average component, is going to fail is a foregone conclusion.
But most people still think this fate cannot befall the nearly $500 billion revenue behemoth Walmart. It’s simply too big to fail in most people’s eyes.
Walmart’s Crime Problem Is Another Telltale Sign Of Problems In The Business Model
Yet, the primary news about Walmart is not good. Bloomberg this week broke the news that one of the most crime-ridden places in America is the local Walmart store. One store in Tulsa, Oklahoma has had 5,000 police visits in the last five years, and four local stores have had 2,000 visits in the last year alone. Across the system, there is one violent crime in a Walmart every day. By constantly promoting its low cost strategy Walmart has attracted a class of customer that simply is more prone to committing crime. And policies implemented to hang onto customers, like letting them camp out overnight in the parking lots, serve to increase the likelihood of poverty-induced crime.
But this outcome is also directly related to Walmart’s business model and strategy. To promote low prices Walmart has automated more operations, and cut employees like greeters. Thus leadership brags about a 23% increase in sales/employee the last decade. But that has happened as the employment shrank by 400,000. Fewer employees in the stores encourages more crime.
In a real way Walmart has “outsourced” its security to local police departments. Experts say the cost to eliminate this security problem are about $3.2 billion – or about 20% of Walmart’s total profitability. Ouch! In a world where Walmart’s net margin of 3% is fully one-third lower than Target’s 4.6% the money just isn’t there any longer for Walmart to invest in keeping its stores safe.
With each passing month Walmart is becoming the “retailer of last resort” for people who cannot shop online. People who lack credit cards, or even bank accounts. People without the means, or capability, of shopping by computer, or paying electronically. People who have nowhere else to go to shop, due to poverty and societal conditions. Not exactly the ideal customer base for building a growing, profitable business.
Competitors Relentlessly Pick Away At Walmart’s Sales And Profits
To maintain revenues the last several years Walmart has invested heavily in transitioning to superstores which offer a large grocery section. But now Kroger KR -0.5%, Walmart’s no. 1 grocery competitor, is taking aim at the giant retailer, slashing prices on 1,000 items. Just like competition from the “dollar stores” has been attacking Walmart’s general merchandise aisles. Thus putting even more pressure on thinning margins, and leaving less money available to beef up security or entice new customers to the stores.
And the pressure from e-commerce is relentless. As detailed in the Wall Street Journal, Walmart has been selling online for about 15 years, and has a $14 billion online sales presence. But this is only 3% of total sales. And growth has been decelerating for several quarters. Last quarter Walmart’s e-commerce sales grew 7%, while the overall market grew 15% and Amazon ($100 billion revenues) grew 31%. It is clear that Walmart.com simply is not attracting enough customers to grow a healthy replacement business for the struggling stores.
Thus the acquisition of Jet.com.
The hope is that this extremely unprofitable $1 billion online retailer will turn around Walmart’s fortunes. Imbue it with much higher growth, and enhanced profitability. But will Walmart make this transition. Is leadership ready to cannibalize the stores for higher electronic sales? Are they willing to make stores smaller, and close many more, to shift revenues online? Are they willing to suffer Amazon-like profits (or losses) to grow? Are they willing to change the Walmart brand to something different, while letting Jet.com replace Walmart as the dominant brand? Are they willing to give up on the past, and let new leadership guide the company forward?
If they do then Walmart could become something very different in the future. If they really realize that the market is shifting, and that an extreme change is necessary in strategy and tactics then Walmart could become something very different, and remain competitive in the highly segmented and largely online retail future. But if they don’t, Walmart will follow Sears into the whirlpool, and end up much like Howard Johnson’s.
by Adam Hartung | May 15, 2016 | In the Swamp, Investing, real estate, Retail
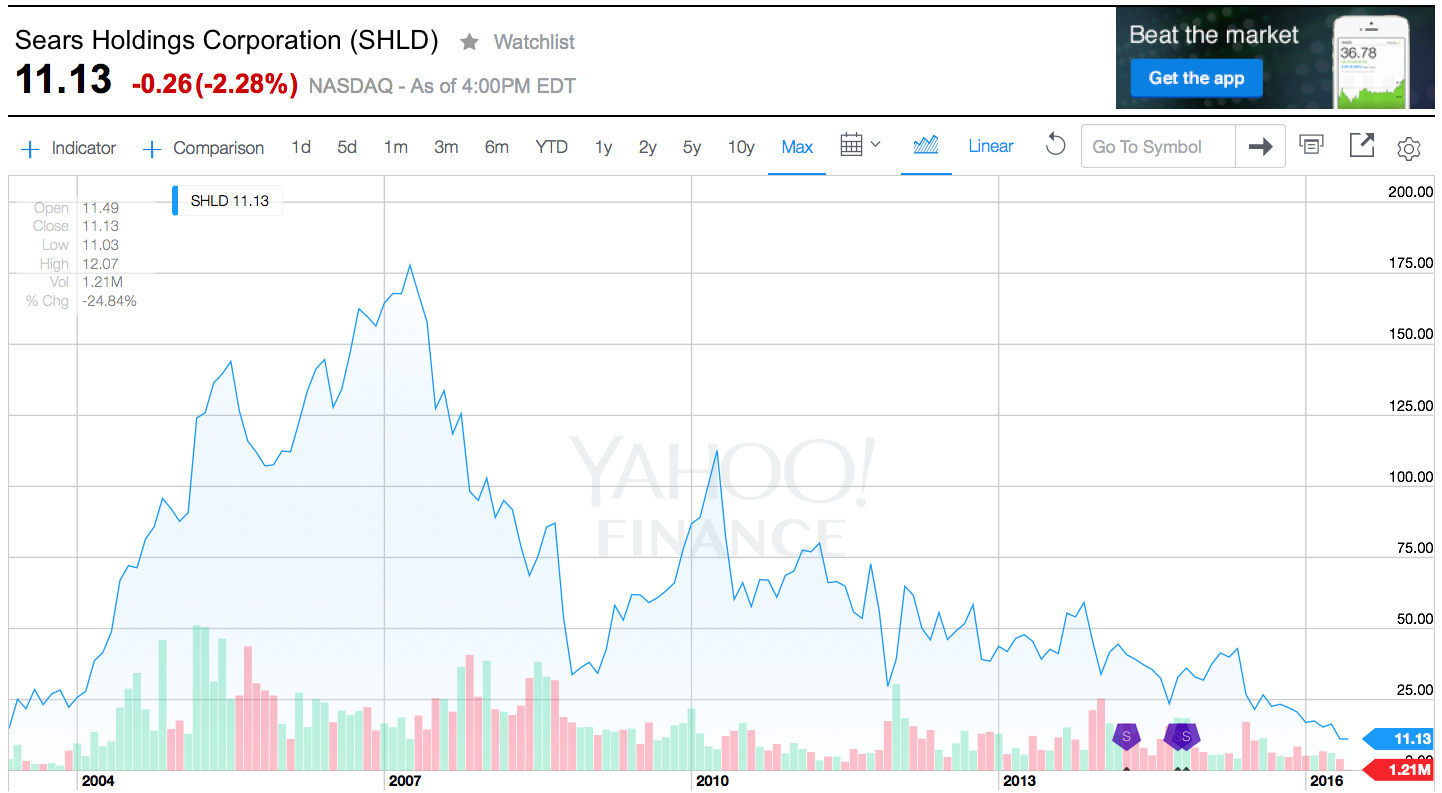
Last week Sears announced sales and earnings. And once again, the news was all bad. The stock closed at a record, all time low. One chart pretty much sums up the story, as investors are now realizing bankruptcy is the most likely outcome.
Chart Source: Yahoo Finance 5/13/16
Quick Rundown: In January, 2002 Kmart is headed for bankruptcy. Ed Lampert, CEO of hedge fund ESL, starts buying the bonds. He takes control of the company, makes himself Chairman, and rapidly moves through proceedings. On May 1, 2003, KMart begins trading again. The shares trade for just under $15 (for this column all prices are adjusted for any equity transactions, as reflected in the chart.)
Lampert quickly starts hacking away costs and closing stores. Revenues tumble, but so do costs, and earnings rise. By November, 2004 the stock has risen to $90. Lampert owns 53% of Kmart, and 15% of Sears. Lampert hires a new CEO for Kmart, and quickly announces his intention to buy all of slow growing, financially troubled Sears.
In March, 2005 Sears shareholders approve the deal. The stock trades for $126. Analysts praise the deal, saying Lampert has “the Midas touch” for cutting costs. Pumped by most analysts, and none moreso than Jim Cramer of “Mad Money” fame (Lampert’s former roommate,) in 2 years the stock soars to $178 by April, 2007. So far Lampert has done nothing to create value but relentlessly cut costs via massive layoffs, big inventory reductions, delayed payments to suppliers and store closures.
Homebuilding falls off a cliff as real estate values tumble, and the Great Recession begins. Retailers are creamed by investors, and appliance sales dependent Sears crashes to $33.76 in 18 months. On hopes that a recovering economy will raise all boats, the stock recovers over the next 18 months to $113 by April, 2010. But sales per store keep declining, even as the number of stores shrinks. Revenues fall faster than costs, and the stock falls to $43.73 by January, 2013 when Lampert appoints himself CEO. In just under 2.5 years with Lampert as CEO and Chairman the company’s sales keep falling, more stores are closed or sold, and the stock finds an all-time low of $11.13 – 25% lower than when Lampert took KMart public almost exactly 13 years ago – and 94% off its highs.
What happened?
Sears became a retailing juggernaut via innovation. When general stores were small and often far between, and stocking inventory was precious, Sears invented mail order catalogues. Over time almost every home in America was receiving 1, or several, catalogues every year. They were a major source of purchases, especially by people living in non-urban communities. Then Sears realized it could open massive stores to sell all those things in its catalogue, and the company pioneered very large, well stocked stores where customers could buy everything from clothes to tools to appliances to guns. As malls came along, Sears was again a pioneer “anchoring” many malls and obtaining lower cost space due to the company’s ability to draw in customers for other retailers.
To help customers buy more Sears created customer installment loans. If a young couple couldn’t afford a stove for their new home they could buy it on terms, paying $10 or $15 a month, long before credit cards existed. The more people bought on their revolving credit line, and the more they paid Sears, the more Sears increased their credit limit. Sears was the “go to” place for cash strapped consumers. (Eventually, this became what we now call the Discover card.)
In 1930 Sears expanded the Allstate tire line to include selling auto insurance – and consumers could not only maintain their car at Sears they could insure it as well. As its customers grew older and more wealthy, many needed help with financia advice so in 1981 Sears bought Dean Witter and made it possible for customers to figure out a retirement plan while waiting for their tires to be replaced and their car insurance to update.
To put it mildly, Sears was the most innovative retailer of all time. Until the internet came along. Focused on its big stores, and its breadth of products and services, Sears kept trying to sell more stuff through those stores, and to those same customers. Internet retailing seemed insignificantly small, and unappealing. Heck, leadership had discontinued the famous catalogues in 1993 to stop store cannibalization and push people into locations where the company could promote more products and services. Focusing on its core customers shopping in its core retail locations, Sears leadership simply ignored upstarts like Amazon.com and figured its old success formula would last forever.
But they were wrong. The traditional Sears market was niched up across big box retailers like Best Buy, clothiers like Kohls, tool stores like Home Depot, parts retailers like AutoZone, and soft goods stores like Bed, Bath & Beyond. The original need for “one stop shopping” had been overtaken by specialty retailers with wider selection, and often better pricing. And customers now had credit cards that worked in all stores. Meanwhile, for those who wanted to shop for many things from home the internet had taken over where the catalogue once began. Leaving Sears’ market “hollowed out.” While KMart was simply overwhelmed by the vast expansion of WalMart.
What should Lampert have done?
There was no way a cost cutting strategy would save KMart or Sears. All the trends were going against the company. Sears was destined to keep losing customers, and sales, unless it moved onto trends. Lampert needed to innovate. He needed to rapidly adopt the trends. Instead, he kept cutting costs. But revenues fell even faster, and the result was huge paper losses and an outpouring of cash.
To gain more insight, take a look at Jeff Bezos. But rather than harp on Amazon.com’s growth, look instead at the leadership he has provided to The Washington Post since acquiring it just over 2 years ago. Mr. Bezos did not try to be a better newspaper operator. He didn’t involve himself in editorial decisions. Nor did he focus on how to drive more subscriptions, or sell more advertising to traditional customers. None of those initiatives had helped any newspaper the last decade, and they wouldn’t help The Washington Post to become a more relevant, viable and profitable company. Newspapers are a dying business, and Bezos could not change that fact.
Mr. Bezos focused on trends, and what was needed to make The Washington Post grow. Media is under change, and that change is being created by technology. Streaming content, live content, user generated content, 24×7 content posting (vs. deadlines,) user response tracking, readers interactivity, social media connectivity, mobile access and mobile content — these are the trends impacting media today. So that was where he had leadership focus. The Washington Post had to transition from a “newspaper” company to a “media and technology company.”
So Mr. Bezos pushed for hiring more engineers – a lot more engineers – to build apps and tools for readers to interact with the company. And the use of modern media tools like headline testing. As a result, in October, 2015 The Washington Post had more unique web visitors than the vaunted New York Times. And its lead is growing. And while other newspapers are cutting staff, or going out of business, the Post is adding writers, editors and engineers. In a declining newspaper market The Washington Post is growing because it is using trends to transform itself into a company readers (and advertisers) value.
CEO Lampert could have chosen to transform Sears Holdings. But he did not. He became a very, very active “hands on” manager. He micro-managed costs, with no sense of important trends in retail. He kept trying to take cash out, when he needed to invest in transformation. He should have sold the real estate very early, sensing that retail was moving on-line. He should have sold outdated brands under intense competitive pressure, such as Kenmore, to a segment supplier like Best Buy. He then should have invested that money in technology. Sears should have been a leader in shopping apps, supplier storefronts, and direct-to-customer distribution. Focused entirely on defending Sears’ core, Lampert missed the market shift and destroyed all the value which initially existed in the great retail merger he created.
Impact?
Every company must understand critical trends, and how they will apply to their business. Nobody can hope to succeed by just protecting the core business, as it can be made obsolete very, very quickly. And nobody can hope to change a trend. It is more important than ever that organizations spend far less time focused on what they did, and spend a lot more time thinking about what they need to do next. Planning needs to shift from deep numerical analysis of the past, and a lot more in-depth discussion about technology trends and how they will impact their business in the next 1, 3 and 5 years.
Sears Holdings was a 13 year ride. Investor hope that Lampert could cut costs enough to make Sears and KMart profitable again drove the stock very high. But the reality that this strategy was impossible finally drove the value lower than when the journey started. The debacle has ruined 2 companies, thousands of employees’ careers, many shopping mall operators, many suppliers, many communities, and since 2007 thousands of investor’s gains. Four years up, then 9 years down. It happened a lot faster than anyone would have imagined in 2003 or 2004. But it did.
And it could happen to you. Invert your strategic planning time. Spend 80% on trends and scenario planning, and 20% on historical analysis. It might save your business.








