by Adam Hartung | Jan 14, 2015 | Investing, Retail, Trends
Retail sales fell .9% in December. Even excluding autos and gasoline, retail sales fell .3%. Further, November retail sales estimates were revised downward from an initial .7% gain to a meager .4%, and October sales advances were revised downward from a .5% gain to a mere .3%. Sales were down at electronic stores, clothing stores and department stores – all places we anticipated gains due to an improving economy, more jobs and more cash in consumer pockets.
Whoa, what’s happening? Wasn’t lower gasoline pricing going to free up cash for people to go crazy buying holiday gifts? Weren’t we all supposed to feel optimistic about our jobs, higher future wages and more money to spend after that horrible Great Recession thus leading us to splurge this holiday?
There were early signals that conventional wisdom was going to be wrong. Back on Black Friday (so named because it is supposedly the day when retailers turn a profit for the year) we learned sales came in a disappointing 11% lower than 2013. Barron’s analyzed press releases from Wal-Mart, and discerned that 2014 was a weaker Black Friday than 2013 and probably 2012. Simply put, fewer people went shopping on Black Friday than before, despite longer store hours, and they bought less.
So was this really a horrible holiday?
Retail store sales are only part of the picture. Increasingly, people are shopping on-line – and we all know it. According to ComScore, on-line sales made to users of PCs (this excludes mobile devices) were up 17% on Cyber Monday, in stark contrast to traditional brick-and-mortar. Exceeding $2B, it was the largest on-line retail day in history. The Day after Cyber Monday sales were up 27%, and the Green Monday (one week after Cyber Monday) sales were up 15% (all compared to year ago.) Overall, the week after Thanksgiving on-line sales rose 14%, and on Thanksgiving Day itself sales were up a whopping 32%. The week before Christmas (16th-21st) on-line sales surged 18%. According to IBM Digital Analytics the on-line November-December sales were up 13.9% vs. 2013.
The trend has never been more pronounced. Regardless of how much people are going to spend, they are spending less of it in traditional brick-and-mortar retail, and more of it on-line.
So, what about Wal-Mart? The chain remains mired in its traditional way of doing business. Even though same-store sales have been flat-to-down most of the last 2 years, and the number of full-line stores has declined in the USA, the chain remains committed quarter after quarter to defending its outdated success formula. Even in China, where Alibaba has demonstrated it can grow on-line ecommerce revenues more than 50%/year, Wal-Mart continues to try growing with a physical presence – even though it has been a tough, unsuccessful slog.
Yet, despite its bribery scandal in Mexico undertaken to prop up revenues, lawsuits due to over-worked, stressed truck drivers having accidents on double shifts killing and injuring people, and an inability to grow, Wal-Mart’s stock trades at near all-time highs. The stock has nearly doubled since 2011, even though the company is at odds with the primary retail, and demographic, trends.
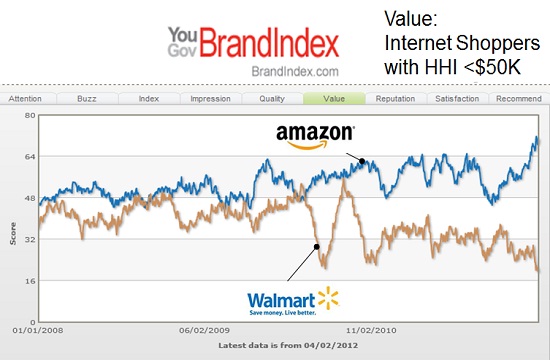
On the other end of the spectrum is Amazon.com. Amazon is still growing revenues at over 20%/year. And introducing successful new publishing and internet service businesses, expanding same day delivery (and even one hour delivery) in urban markets like New York City, as well as expansion of its Prime service to include more original programming with famed director Woody Allen after winning the Golden Globe award for its original series Transparent.
However, several analysts were trash talking Amazon in 2014. 20% growth has them worried, given that the company once grew at 40%. Even though Amazon’s growth is a serious reason companies like Wal-Mart cannot grow. And there is the perennial lack of profitability – including a larger than expected loss in the second quarter ; a loss which included a $170M write-off on FirePhones which never really found a customer base. The latter item led to a Fast Company brutal lambasting of CEO Jeff Bezos as a micro-manager out-of-touch with customers.
This lack of analyst support has seriously hurt Amazon.com share performance. From 2010 to early 2014 the stock quadrupled in value from $100 to $400. But over the past year the stock has fallen back 25%. After dropping to $300/share in April, the stock has rallied but then retrenched no less than 3 times, and is now trading very close to its 52 week low. And, it shows no momentum, trading below its moving average.
Which is why investors in Wal-Mart should sell, and reinvest in Amazon.com.
All the trends point to Wal-Mart being overvalued. Its revenues show no signs of achieving any substantial growth. And, despite its sheer size, all retail trends are working against the behemoth. It has been trying to find a growth engine for 10 years, but nothing has come to fruition – including big investments in offshore markets. The company keeps trying to defend & extend its old success formula, thus creating a bigger and bigger gap between itself and future market success.
Simultaneously, Amazon.com continues to invest in major developing trends. From publishing to television programming to cloud/web services and even general retail, everything into which Amazon invests is growing. And even though this is a company with $100B in revenues, it is still growing at a remarkable 20%. While some analysts may wish the investment rate would slow, and that Amazon would never make mistakes (like Firephone,) the truth is that Amazon is putting money into projects which have pretty good odds of making sizable money as it helps change the game in multiple markets.
Think of investing like paddling a canoe. When you are investing against trends, it’s like paddling up the river. You can make progress, but it is hard. And, one little mistake and you easily slip backward. Lose any momentum at all and you could completely turn around and disappear (like happened to Circuit City, and now both Sears and JCPenney.) When you invest with the trends it is like paddling down the river. The trend, like a current, keeps you moving in the right direction. You can still make mistakes, but the odds are quite a lot higher you will make your destination easily, and with resources to spare. That’s why the sales results for December are important. The show traditional retailers are paddling up river, while on-line retailers are paddling down-river.
I don’t know if Wal-Mart’s stock value has peaked, but it is hard to understand why anybody would expect it to go higher. It could continue to rise, but there are ample reasons to expect investors will figure out how tough future profits will be for Wal-Mart and dispose of their positions. On the other hand, even though Amazon.com could continue to slide down further there are even more reasons to expect it will have great future quarters with revenue gains and – eventually – those long-sought-after profits that some analysts seek. Meanwhile, Amazon is investing in projects with internal rates of return far higher than most other companies because they are following major trends. Odds are pretty good that in a few years the trends will make investors happy they own Amazon, and dropped out of Wal-Mart.

by Adam Hartung | Nov 12, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership
We see it all too often. A successful business seems to lose its way. Somehow, after decades of success, its results soften, then tumble and the company becomes a victim of its competition. We scratch our heads and wonder, “why did that happen?”
Pizza Hut is well on its way to disappearing. Kind of like Pizza Inn, A&W and Howard Johnson’s. And that seems kind of remarkable considering the company at one time defined pizza for most Americans. From a fast growing franchise in the 1960s to a high profile acquisition by PepsiCo in the 1970s, to anchoring the Yum Brands spin out from PepsiCo in 1997, Pizza Hut just finished 8 straight quarters of declining same store sales. Pizza Hut was once a concept as hot as Apple Stores, but now it looks more like Sears. How could this happen?

When Pizza Hut was growing it locked in on its success formula. And one of the biggest Lock-ins was its name. Pizza Hut was a place where you ate pizza, and the buildings all looked the same with that hut-like red roof. At a time when few Americans outside the northeast ate pizza, this Wichita, Kansas founded (and headquartered until the 1990s) company told people what a pizzeria should look like, and what you should eat.
The company was ardent about controlling what franchisees served. No nachos, or other trendy foods, because they didn’t fit the pizza theme. No delivery, because good pizza required you eat it immediately from the oven. Pizza should be thick and hearty, even served in a deep dish so you have plenty of bread and feel really full. Whether anyone in Italy ever a pizza anything like this really did not matter.
And Pizza Hut would help guide customers as to what toppings they wanted — and usually there should be at least 3 – by offering pre-designed pizzas with names like “meat lovers,” “supreme,” “super supreme” or “veggie lover’s” so an uninformed clientele (originally prairie state, then midwestern, then expanding into the southwest and the south) could buy the product without a lot of fuss.
This success formula may sound cliche today, but it worked. And it worked really well for 30 years, then pretty well for another 10-15. But, eventually, doing the same thing over, and over, and over, and over had less appeal. Almost everyone in the country knew what a Pizza Hut was, what the stores looked like and what the product was like. Competitors came along by the dozens with all kinds of variations, and different kinds of service – like being in a mall, or delivering the product. Inevitably this competition led to price wars. To keep customers Pizza Hut had to lower its prices, even offering 2 pizzas for the price of one. Pizza Hut never lost track of its success formula, and never stopped doing what once made it great. But margins eroded, and then sales started declining.
Lots of people don’t care about Pizza Hut any more. They want an alternative. An alternative product, like California Pizza Kitchen or Wolfgang Pucks. Or an alternative to pizza altogether like the new “fast casual” chains such as Chipotle’s, Baja Fresh or Panera. For a whole raft of reasons, people decided that although they once ate Pizza Hut (even ate a LOT of it) they were going to eat something else.
But Pizza Hut was locked in. First, its name. Pizza. Hut. To fulfill the “brand promise” of that name everything about that store is pre-designed. From the outside to the inside tables to the equipment in the kitchen. 6,300 stores that are almost identical. Any change and you have to make 6,300 changes. Adding new product categories means reprinting 126,000 menus, changing 6,300 kitchen layouts, buying 6,300 new ovens, figuring out the service utensils for 6,300 wait staff. That’s lock-in. Making any change is so hard that the incentive is entirely toward improve what you’ve always done rather than doing something new.
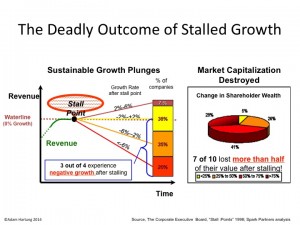
Growth Stalls are Deadly
Eventually, like Pizza Hut, growth stalls. It only takes 2 quarters of declining sales to hit a growth stall, and when that happens less than 7% of businesses will ever again consistently grow at a meager 2%. Growth stalls tell us “hey, the market shifted. What you’re doing isn’t selling any more.”
But most management teams don’t think about a market shift, and instead react by trying to do more of the same. They treat this like its an operational problem. More quality campaigns, more money spent on advertising, more promotions, asking employees to work a little harder, more product for the same (or lower) price – more, better, faster, cheaper. But this doesn’t work, because the problem lies in a market shift away from your “core” that requires an entirely different strategy.
Because management is incented to ignore this shift as long as possible, the company soon becomes irrelevant. Customers know they’ve been going to competitors, and they start to realize it’s been a long time since they bought from that old supplier. They realize their interest in that old company and its products has simply gone away. They don’t pay attention to the ads. And they don’t have any interest in new product announcements. Actually, they find the company irrelevant. Even when the discounts are big, they don’t buy. They do business where they identify with the company and its products, even when those products cost more.
And thus the results start to tumble horribly. Only by now management is so far removed from market trends that it has no idea how to regain relevancy. In Pizza Hut’s case, leadership is undertaking what they’d like to think is a brand overhaul that will change its position in customers’ minds. But, unfortunately, they are doing the ultimate in defend & extend management to try and save the old success formula.
Pizza Hut is introducing a maze of new ways to have its old product, in its old stores. 10 crust choices, 6 sauce choices, 22 of those pre-designed pizza offerings, 5 different liquids you can have dribbled over the pizza, and a rash of exotic new toppings – like banana. So now you can order your pizza 1,000 different ways (actually, more like 10,000.) Oh, and this is being launched with a big increase in traditional advertising. In other words, an insane implementation of what the company has always done; giving customers an American style pizza, in a hut, promoted on TV – even most likely buying what is now considered iconic – a Super Bowl ad.
Yum Brands investors have reasons to be concerned. Pizza Hut is really important to sales and earnings. But its leaders are intent on doing more of the same, even though the market has already shifted. The prognosis does not look good.

by Adam Hartung | Oct 28, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in, Television
I’m a “Boomer,” and my generation could have been called the Coke generation. Our parents started every day with a cup of coffee, and they drank either coffee or water during the day. Most meals were accompanied by either water, or iced tea.
But our generation loved Coca-Cola. Most of our parents limited our consumption, much to our frustration. Some parents practically refused to let the stuff in the house. In progressive homes as children we were usually only allowed one, or at most two, bottles per day. We chafed at the controls, and when we left home we started drinking the sweet cola as often as we could.
It didn’t take long before we supplanted our parent’s morning coffee with a bottle of Coke (or Diet Coke in more modern times.) We seemingly could not get enough of the product, as bottle size soared from 8 ounces to 12 to 16 and then quarts and eventually 2 liters! Portion control was out the window as we created demand that seemed limitless.
Meanwhile, Americans exported our #1 drink around the world. From 1970 onward Coke was THE iconic American brand. We saw ads of people drinking Coke in every imaginable country. International growth seemed boundless as people from China to India started consuming the irresistible brown beverage.

My how things change. Last week Coke announced third quarter earnings, and they were down 14%. The CEO admitted he was struggling to find growth for the company as soda sales were flat. U.S. sales of carbonated beverages have been declining for a decade, and Coke has not developed a successful new product line – or market – to replace those declines.
Coke is a victim of changing customer preferences. Once a company that helped define those preferences, and built the #1 brand globally, Coke’s leadership shifted from understanding customers and trends in order to build on those trends towards defending & extending sales of its historical product. Instead of innovating, leadership relied on promotion and tactics which had helped the brand grow 30 years ago. They kept to their old success formula as trends shifted the market into new directions.
Coke began losing its relevancy. Trends moved in a new direction. Healthfulness led customers to decide they wanted a less calorie rich, nutritionally starved drink. And concerns grew over “artificial” products, such as sweeteners, leading customers away from even low calorie “diet” colas.
Meanwhile, younger generations started turning to their own new brands. And not just drinks. Instead of holding a Coke, increasingly they hold an iPhone. Where once it was hip to hang out at the Coke machine, or the fountain stand, now people would rather hang out at a Starbucks or Peet’s Coffee. Where once Coke was identified and matched the aspirations of the fast growing Boomer class, now it is replaced with a Prada handbag or other accessory from an LVMH branded luxury product.
Where once holding a Coke was a sign of being part of all that was good, now the product is largely passe. Trends have moved, and Coke didn’t. Coke leadership relied too much on its past, and failed to recognize that market shifts could affect even the #1 global brand. Coke leaders thought they would be forever relevant, just do more of what worked before. But they were wrong.
Unfortunately, CEO Muhtar Kent announced a series of changes that will most likely further hurt the Coca-Cola company rather than help it.
First, and foremost, like almost all CEOs facing an earnings problem the company will cut $3B in costs. The most short-term of short-term actions, which will do nothing to help the company find its way back toward being a prominent brand-leading icon. Cost cuts only further create a “hunker-down” mindset which causes managers to reduce risk, rather than look for breakthrough products and markets which could help the company regain lost ground. Cost cutting will only further cause remaining management to focus on defending the past business rather than finding a new future.
Second, Coca-Cola will sell off its bottlers. Interestingly, in the 1980s CEO Roberto Goizueta famously bought up the distributorships, and made a fortune for the company doing so. By the year 2000 he was honored, along with Jack Welch of GE, as being one of the top 2 CEOs of the century for his ability to create shareholder value. But now the current CEO is selling the bottling operations – in order to raise cash. Once again, when leadership can’t run a business that makes money they often sell off assets to generate cash and make the company smaller – none of which benefits shareholders.
Third, fire the Chief Marketing Officer. Of course, somebody has to be blamed! The guy who has done the most to bring Coca-Cola’s brand out of traditional advertising and promote it in an integrated manner across all media, including managing successful programs for the Olympics and World Cup, has to be held accountable. What’s missing in this action is that the big problem is leadership’s fixation with defending its Coke brand, rather than finding new growth businesses as the market moves away from carbonated soft drinks. And that is a problem that requires the CEO and his entire management team to step up their strategy efforts, not just fire the leader who has been updating the branding mechanisms.
Coca-Cola needs a significant strategy shift. Leadership focused too long on its aging brands, without putting enough energy into identifying trends and figuring out how to remain relevant. Now, people care a lot less about Coke than they did. They care more about other brands, like Apple. Globally. Unless there is a major shift in Coke’s strategy the company will continue to weaken along with its primary brand. That market shift has already happened, and it won’t stop.
For Coke to regain growth it needs a far different future which aligns with trends that now matter more to consumers. The company must bring forward products which excite people ,and with which they identify. And Coke’s leaders must move much harder into understanding shifts in media consumption so they can make their new brands as visible to newer generations as TV made Coke visible to Boomers.
Coke is far from a failed company, but after a decade of sales declines in its “core” business it is time leadership realizes takes this earnings announcement as a key indicator of the need to change. And not just simple things like costs. It must fundamentally change its strategy and markets or in another decade things will look far worse than today.

by Adam Hartung | Aug 6, 2014 | Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Innovation, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
Remember the RAZR phone? Whatever happened to that company?
Motorola has a great tradition. Motorola pioneered the development of wireless communications, and was once a leader in all things radio – as well as made TVs. In an earlier era Motorola was the company that provided 2-way radios (and walkie-talkies for those old enough to remember them) not only for the military, police and fire departments, but connected taxies to dispatchers, and businesses from electricians to plumbers to their “home office.”
Motorola was the company that developed not only the thing in a customer’s hand, but the base stations in offices and even the towers (and equipment on those towers) to allow for wireless communication to work. Motorola even invented mobile telephony, developing the cellular infrastructure as well as the mobile devices. And, for many years, Motorola was the market share leader in cellular phones, first with analog phones and later with digital phones like the RAZR.

But that was the former Motorola, not the renamed Motorola Solutions of today. The last few years most news about Motorola has been about layoffs, downsizings, cost reductions, real estate sales, seeking tenants for underused buildings and now looking for a real estate partner to help the company find a use for its dramatically under-utilized corporate headquarters campus in suburban Chicago.
How did Motorola Solutions become a mere shell of its former self?
Unfortunately, several years ago Motorola was a victim of disruptive innovation, and leadership reacted by deciding to “focus” on its “core” markets. Focus and core are two words often used by leadership when they don’t know what to do next. Too often investment analysts like the sound of these two words, and trumpet management’s decision – knowing that the code implies cost reductions to prop up profits.
But smart investors know that the real implication of “focusing on our core” is the company will soon lose relevancy as markets advance. This will lead to significant sales declines, margin compression, draconian actions to create short-term P&L benefits and eventually the company will disappear.
Motorola’s market decline started when Blackberry used its server software to help corporations more securely use mobile devices for instant communications. The mobile phone transitioned from a consumer device to a business device, and Blackberry quickly grabbed market share as Motorola focused on trying to defend RAZR sales with price reductions while extending the RAZR platform with new gimmicks like additional colors for cases, and adding an MP3 player (called the ROKR.) The Blackberry was a game changer for mobile phones, and Motorola missed this disruptive innovation as it focused on trying to make sustaining improvements in its historical products.
Of course, it did not take long before Apple brought out the iPhone and with all those thousands of apps changed the game on Blackberry. This left Motorola completely out of the market, and the company abandoned its old platform hoping it could use Google’s Android to get back in the game. But, unfortunately, Motorola brought nothing really new to users and its market share dropped to nearly nothing.
The mobile phone business quickly overtook much of the old Motorola 2-way radio business. No electrician or plumber, or any other business person, needed the old-fashioned radios upon which Motorola built its original business. Even police officers used mobile phones for much of their communication, making the demand for those old-style devices rarer with each passing quarter.
But rather than develop a new game changer that would make it once again competitive, Motorola decided to split the company into 2 parts. One would be the very old, and diminishing, radio business still sold to government agencies and niche business applications. This business was profitable, if shrinking. The reason was so that leadership could “focus” on this historical “core” market. Even if it was rapidly becoming obsolete.
The mobile phone business was put out on its own, and lacking anything more than an historical patent portfolio, with no relevant market position, it racked up quarter after quarter of losses. Lacking any innovation to change the market, and desperate to get rid of the losses, in 2011 Motorola sold the mobile phone business – formerly the industry creator and dominant supplier – to Google. Again, the claim was this would allow leadership to even better “focus” on its historical “core” markets.
But the money from the Google sale was invested in trying to defend that old market, which is clearly headed for obsolescence. Profit pressures intensify every quarter as sales are harder to find when people have alternative solutions available from ever improving mobile technology.
As the historical market continued to weaken, and leadership learned it had under-invested in innovation while overspending to try to defend aging solutions, Motorola again cut the business substantially by selling a chunk of its assets – called its “enterprise business” – to a much smaller Zebra Technologies. The ostensible benefit was it would now allow Motorola leadership to even further “focus” on its ever smaller “core” business in government and niche market sales of aging radio technology.
But, of course, this ongoing “focus” on its “core” has failed to produce any revenue growth. So the company has been forced to undertake wave after wave of layoffs. As buildings empty they go for lease, or sale. And nobody cares, any longer, about Motorola. There are no news articles about new products, or new innovations, or new markets. Motorola has lost all market relevancy as its leaders used “focus” on its “core” business to decimate the company’s R&D, product development, sales and employment.
Retrenchment to focus on a core market is not a strategy which can benefit shareholders, customers, employees or the community in which a business operates. It is an admission that the leaders missed a major market shift, and have no idea how to respond. It is the language adopted by leaders that lack any vision of how to grow, lack any innovation, and are quickly going to reduce the company to insignificance. It is the first step on the road to irrelevancy.
Straight from Dr. Christensen’s “Innovator’s Dilemma” we now have another brand name to add to the list of those which were once great and meaningful, but now are relegated to Wikipedia historical memorabilia – victims of their inability to react to disruptive innovations while trying to sustain aging market positions – Motorola, Sears, Montgomery Wards, Circuit City, Sony, Compaq, DEC, American Motors, Coleman, Piper, Sara Lee………..

by Adam Hartung | Feb 24, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, Leadership, Transparency, Web/Tech
Facebook is acquiring WhatsApp, a company with at most $300M revenues, and 55 employees, for $19billion. That’s billion – with a “b.” An astonishing figure that is second only to HP’s acquisition of market leader Compaq, which had substantial revenues and profits, as tech acquisitions. $19B is 13 times Facebook’s (not WhatsApp’s) entire 2013 net income – and almost 2.5 times Facebook’s (again, not WhatsApp’s) 2013 gross revenues!
On the mere face of it this valuation should make the most dispassionate analyst swoon. In today’s world very established, successful companies sell for far, far lower valuations. Apple is valued at about 13 times earnings. Microsoft about 14 times earnings. Google 33 times. These are small fractions of the nearly infinite P/E placed on WhatsApp.
But there is a leadership lesson offered here by CEO Zuckerberg’s team that is well worth learning.
Irrelevancy can happen remarkably quickly. True in any industry, but especially in digital technology. Examples: Research-in-Motion/Blackberry. Motorola. Dell. HP all lost relevancy in months and are struggling. (For those who want non-tech examples think of Circuit City, Best Buy, Sears, JCPenney, Abercrombie and Fitch.) Each of these companies was an industry leader that lust its luster, most of its customers, a big chunk of its employees and much of its market valuation in months when the company missed a market shift.
Although leadership knew what it had historically done to sell products profitably, in a very short time market trends reduced the value of the company’s historical success formula leaving investors, as well as management, wondering how it was going to compete.
Facebook is not immune to changing market trends. Although it has been the benchmark for social media, it only achieved that goal after annihilating early leader MySpace. And although Facebook was built by youthful folks, trends away from using laptops and toward mobile devices have challenged the Facebook platform. Simultaneously, changing communication requirements have altered the use, and impact, of things like images, photos, charts and text. All of these have the potential impact of slowly (or not so slowly) eroding the value (which is noticably lofty) of Facebook.
Most leaders address these kinds of challenges by launching new products to leverage the trend. And Facebook did just that. Facebook not only worked on making the platform more mobile friendly, but developed its own platform apps for photos and texting and all kinds of new features.
But, and this is critical, external companies did a better job. Two years ago Instagram emerged as a leader in image sharing. And WhatsApp has developed a superior answer for messaging.
Historically leadership usually said “we need to find a way to beat these new guys.” They would make it hard to integrate new solutions with their dominant platform in an effort to block growth. They would spend huge amounts on marketing and branding to try overcoming the emerging leader. Often they filed intellectual property litigation in an effort to cause short-term business interuption and threaten viability. They might even try hiring the emerging company’s tech leader away to stop development.
All of these actions were efforts to defend & extend the early leader’s market position. Even though the market is shifting, and trends are developing externally from the company, leadership will tend to look inside for an answer. It will often ignore the trend, disparage the competition, keep promising improvements to its historical products and services and blanket the media with PR as to its stated superiority.
But, as that list (above) of companies that lost relevancy demonstrates, this rarely works. In a highly interconnected, fast-paced, globally competitive marketplace customers go where they want. Quickly. Often leaving the early leader with a management team (and Board of Directors) scratching its head and wondering how it lost so much market position, and value, so quickly.
Hand it to Mr. Zuckerberg’s team. Instead of ignoring trends in its effort to defend & extend its early lead, they reached out and brought the leader to them. $1B for Instagram was a big investment, especially so close to launching an IPO. But, it kept Facebook relevant in mobile platforms and imaging.
And making a nosebleed-creating $19B deal for WhatsApp focuses on maintaining relevancy as well. WhatsApp already processes almost as many messages as the entire telecom industry. It has 450million users with 70% active daily, which is already 60% the size of Facebook’s daily user community (550million.) By bringing these people into the Facebook corporate family it assures the company of continued relevancy as the market shifts. It doesn’t matter if these are the same people, or different people. The issue is that it keeps Facebook relevant, rather than losing relevance to a competitor.
How will this all be monetized into $19B? The second brilliant leadership call by Facebook is to not answer that question.
Facebook didn’t know how to monetize its early leadership in users, but management knew it had to find a way. Now the company has grown from almost no revenues in 2008 to almost $8B in just 5 years. (Does your company have a plan to add $8B/year of organic revenue growth by 2019?)
So just as Facebook had to find its revenue model (which it is still exploring,) Zuckerberg’s team allows the leadership of Instagram and WhatsApp to remain independent, operating in their own White Space, to grow their user base and learn how to monetize what is an extraordinarily large group of happy folks. When looking to grow in new markets, and you find a team with the skills to understand the trends, it is independence rather than integration that makes the most sense organizationally.
Thirdly, back to that valuation issue. $19B is a huge amount of money. Unless you don’t really spend $19B. Facebook has the blessed ability to print its own. Private money that it can use for such acquisitions. As long as Facebook has a very high market valuation it can make acquisitions with shares, rather than real money.
In the case of both Instagram and WhatsApp the acquisition is being made in a mix of cash, Facebook stock and restricted Facebook stock for employees. The latter two of these three items are not real money. They are simply pieces of paper giving claims to ownership of Facebook, which itself is valued at 22 times 2013 revenue and 116 times 2013 earnings. The price of those shares are all based on expectations; expectations which now require the performance of Instagram and WhatsApp to make happen.
By making acquisitions with Facebook shares the leadership team is able to link the newly acquired managers to the same overall goals as Facebook, while offering an extremely high price but without actually having to raise any money – or spend all that money.
All companies risk of becoming irrelevant. New technologies, customer behavior patterns, regulations, inventions and innovations constantly challenge old success formulas. Most leaders fall into a pattern of trying to defend & extend their old business in the face of market shifts, hastening the fall into irrelevancy. Or they try to acquire a new business, then integrate it into the old business which strips away the new business value and leads, inevitably, to irrelevancy.
The leaders of Facebook are giving us a lesson in an alternative approach. (1) Recognize the market shift. Accept it. If there is a better solution, rush toward it rather than ignoring it. (2) Bring it into the company, and leave it independent. Eschew integration and efforts to find “synergy.” (You never know, in 3 years the company may need to be renamed WhatsApp to reflect a new market paradigm.) (3) And as long as you can convince investors that you are maintaining your relevancy use your highly valued stock as currency to keep the company moving forward.
These are 3 great lessons for all leadership teams. And I continue to think Facebook is the one stock to own in 2014.










