by Adam Hartung | Dec 23, 2016 | Advertising, Marketing, Trends, Web/Tech
‘Tis the season of holiday giving. We hunt for just the right gift, for just the right person, to make sure they know we care about them. This act of matching a gift to the person has tremendous importance, because it demonstrates care from the giver about the recipient.
Once advertising was like that. Marketers built brands with loving care. They worked very hard to know the target for their brand (and product) and they carefully crafted every nuance of the brand – imagery, typography, colors, images, sounds – even spokespeople (famous or created) to project that brand properly for the intended customers. We’ve seen great brand images over time, from Tony the Tiger promoting cereal to start your day to Ronald McDonald bringing a family together.
SAUL LOEB/AFP/Getty Images
Ad placement delivered the brand’s gift to the customer.
And, once upon a time, how that brand was placed in front of targeted customers was every bit as crafted as the brand itself. Marketers worked with ad agencies to make sure newspaper, magazine, billboard location, radio show or TV program matched the brand. The brand was considered linked not just to the medium, but to the message that medium projected. Want to sell a muscle car, you promoted it via media focused on sports, DIY projects, men’s health – a positive connection between the media’s message/content and the advertiser’s goal for the brand.
And marketers knew that if they put their brand with the right media content, in front of their targets, it would lead to brand identification, brand enhancement, and sales growth. The objective wasn’t how many people saw the ads, but putting the ad in front of the right people, associated with the right content, to build on the brand’s value, and make the products more appealing to target buyers. Placement led to sales.
Just like finding the right gift is important for the holidays, matching the gift to the recipient, finding the right ad placement was very important to the customer. It was an act of diligence on the part of the advertiser to demonstrate to target customers “hey, I know you. I get where you’re coming from. I connect with you.”
Then the internet changed everything.
In the old days marketers really didn’t know how many people connected with their ads post-placement. There were raw numbers on readers/listeners/viewers, but nothing specific. There was a lot of trust by the marketer that “owned” brand placed in working with the ad agencies to link the brand to the right media – the right content – so that brand would flourish and product sales would grow.
Yes, ads were measured for their appeal, how well they were remembered and audience coverage. But these metrics, and especially raw volume numbers, were each just one piece of how to craft the brand and deliver the message. It was reaching the right people that mattered, and that required people to make media decisions – and that required really knowing the content tied to the ad being placed.
Marketers clearly understood that customers knew the product paid for those ads to promote that content. Customers linked the brand and the content, and thus it was important to make sure they matched. The content had to be right for the ad to have its intended affect.
But in the internet age, all that caring about customers, branding and links to the right content began disappearing. Instead, ad decisions were dominated by metrics – “how many placements did my ad receive?” “how many people saw my ad?” “how many people clicked on my ad?” “how many page views does this web site generate?” “how many page views does this writer/blogger generate?” The brand was being lost – the customer was being lost – in identifying how many people saw the ad, and whether or not they clicked on it, and where they went after the ad was presented on the web page.
And, the worst of all, “Do we have the information to know who this internet surfer is, follow them, and deliver ads to them as they cross pages and web sites?” At this point, content no longer mattered. If some page viewer was known to be looking for a desk, ads for desks would be placed on page after page the reader (potential customer) visited — regardless the content!
Marketers allowed their brands to be disconnected from the content entirely – ouch.
In the era of programmatic ad buying, content no longer matters. Follow the target, hammer on them with ads, even if the brand is positioned first next to information on weather, and next on a site about buying inexpensive baby clothes, and next on a site about high end power tools.
The care and crafting of ad buying, which was crucial to brand building and demonstrating customers really mattered to those who created and crafted the products, and brand, was lost.
In 2016, we saw the ultimate in forgetting brand value while programmatically placing ads. “Fake news” emerged. And marketers started to see their ads next to those fake (often invented and totally false) stories, just like they would be placed next to legitimate information. The breakdown between content and brand was complete. In the unbridled pursuit of “eyeballs” brands were paying for the worst any media could offer – not journalism or legitimate content, but outright crap.
The election served to demonstrate this in an entirely new way. People went to websites, formerly considered “fringe,” such as Breitbart, to find out information on candidates and their supporters. And there would be ads. The ad was following the eyeballs, no longer the content. Family product ads, such as for cereal, were suddenly appearing next to content that was in no way associated with the marketer’s goal for that brand image.
And by being content independent, these programmatic ads were not just harming the brands – they supported bad journalism, and bad content.
“Click bait” became ever more important. With no people involved in ad buying, ads were no longer were tied to content so there was no “editorial” management of how the ad was placed. What those smart ad buyers once did, helping to build the brand, was lost. Now, any writer who could figure out how to use the right key words – and often outrageous content (of any kind) – was able to pull eyeballs. If s/he could pull eyeballs – regardless of the content – they pulled ads. And that pulled dollars.
Media brand value was dramatically lost – and journalism suffered.
In other words, you no longer needed the credibility of a brand like NBC, Wall Street Journal, ESPN, Forbes, etc. to obtain ads. Those old media brands worked hard to make edited content, reliable content, available to readers – and something a brand marketer could understand and use to build her customer base. But now all a publisher/producer needed was something that brought in eyeballs – and often the more outrageous, more salacious, more demeaning, more hostile, more ridiculous the content the more eyeballs were attracted (like watching a train wreck).
And the more this pulled ad money to non-journalistic, bad content, and away from legitimate content providers that focused on building their brand, the more it hurt journalism and marketing. What a decade ago seemed like a possible fear came true in 2016. Unharnessed media access by everyone was proven to lead to the growth of bad journalism as funds for good research, writing, editing and masthead curating was lost to those who demonstrated merely the ability to pull eyeballs.
Those who have benefited from this shift think programmatic ad buying is great. To them if people want to read from their site, look at their photos, cartoons and other images, or watch videos then these site owners claim there is no reason that advertisers should complain. “If people want this content, then why shouldn’t we be paid to create it. This is a monetized democracy of the media putting the customer in control.”
But that is simply not true. Customers link the brand message to the content on the screen. And there should be care taken to make sure that content and the brand message link. And that’s where programmatic ad buying is failing everyone.
Net/net, we need people involved in ad placement. Just as we care about the gifts we give at holidays, it takes a personal touch to make that selection work. It takes people to craft the delivery of ads.
Hopefully in 2017, the lessons of 2016 will become very clear, causing marketers and advertisers to rely far less on programmatic, and get people involved in ad placement once again. For the good of brands and for decent content.
Happy Holidays!

by Adam Hartung | Oct 26, 2016 | Growth Stall, Innovation, Investing, Leadership, Web/Tech
Apple AAPL -0.72% announced sales and earnings yesterday. For the first time in 15 years, ever since it rebuilt on a strategy to be the leader in mobile products, full year sales declined. After three consecutive down quarters, it was not unanticipated. And Apple’s guidance for next quarter was for investors to expect a 1% or 2% improvement in sales or earnings. That’s comparing to the disastrous quarter reported last January, which started this terrible year for Apple investors.
Yet, most analysts remain bullish on Apple stock. At a price/earnings (P/E) of 13.5, it is by far the cheapest tech stock. iPad sales are stagnant, iPhone sales are declining, Apple Watch sales dropped some 70% and Chromebook breakout sales caused a 20% drop in Mac Sales. Yet most analysts believe that something will improve and Apple will get its mojo back.
Only, the odds are against Apple. As I pointed out last January, Apple’s value took a huge hit because stagnating sales caused the company to completely lose its growth story. And, the message that Apple doesn’t know how to grow just keeps rolling along. By last quarter – July – I wrote Apple had fallen into a Growth Stall. And that should worry investors a lot.

Ten Deadly Sins Of Networking
Companies that hit growth stalls almost always do a lot worse before things improve – if they ever improve. Seventy-five percent of companies that hit a growth stall have negative growth for several quarters after a stall. Only 7% of companies grow a mere 6%. To understand the pattern, think about companies like Sears, Sony, RIM/Blackberry, Caterpillar Tractor. When they slip off the growth curve, there is almost always an ongoing decline.
And because so few regain a growth story, 70% of the companies that hit a growth stall lose over half their market capitalization. Only 5% lose less than 25% of their market cap.
Why? Because results reflect history, and by the time sales and profits are falling the company has already missed a market shift. The company begins defending and extending its old products, services and business practices in an effort to “shore up” sales. But the market shifted, either to a competitor or often a new solution, and new rev levels do not excite customers enough to create renewed growth. But since the company missed the shift, and hunkered down to fight it, things get worse (usually a lot worse) before they get better.
Think about how Microsoft MSFT -0.42% missed the move to mobile. Too late, and its Windows 10 phones and tablet never captured more than 3% market share. A big miss as the traditional PC market eroded.
Right now there is nothing which indicates Apple is not going to follow the trend created by almost all growth stalls. Yes, it has a mountain of cash. But debt is growing faster than cash now, and companies have shown a long history of burning through cash hoards rather than returning the money to shareholders.
Apple has no new products generating market shifts, like the “i” line did. And several products are selling less than in previous quarters. And the CEO, Tim Cook, for all his operational skills, offers no vision. He actually grew testy when asked, and his answer about a “strong pipeline” should be far from reassuring to investors looking for the next iPhone.
Will Apple shares rise or fall over the next quarter or year? I don’t know. The stock’s P/E is cheap, and it has plenty of cash to repurchase shares in order to manipulate the price. And investors are often far from rational when assessing future prospects. But everyone would be wise to pay attention to patterns, and Apple’s Growth Stall indicates the road ahead is likely to be rocky.

by Adam Hartung | Sep 23, 2016 | Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Television, Web/Tech
In early August Tesla announced it would be buying SolarCity. The New York Times discussed how this combination would help CEO Elon Musk move toward his aspirations for greater clean energy use. But the Los Angeles Times took the companies to task for merging in the face of tremendous capital needs at both, while Tesla was far short of hitting its goals for auto and battery production.
Since then the press has been almost wholly negative on the merger. Marketwatch’s Barry Randall wrote that the deal makes no sense. He argues the companies are in two very different businesses that are not synergistic – and he analogizes this deal to GM buying Chevron. He also makes the case that SolarCity will likely go bankrupt, so there is no good reason for Tesla shareholders to “bail out” the company. And he argues that the capital requirements of the combined entities are unlikely to be fundable, even for its visionary CEO.
 Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
But short-sellers are clearly not long-term investors. And there is a lot more ability for this deal to succeed and produce tremendous investor returns than anyone could ever glean from studying historical financial statements of both companies.
GM buying Chevron is entirely the wrong analogy to compare with Tesla buying SolarCity. Instead, compare this deal to what happened in the creation of television after General Sarnoff, who ran RCA, bought what he renamed NBC.
The world already had radio (just as we already have combustion powered cars.) The conundrum was that nobody needed a TV, especially when there were no TV programs. But nobody would create TV programs if there were no consumers with TVs. General Sarnoff realized that both had to happen simultaneously – the creation of both demand, and supply. It would only be by the creation, and promotion, of both that television could be a success. And it was General Sarnoff who used this experience to launch the first color televisions at the same time as NBC launched the first color programming – which fairly quickly pushed the industry into color.
Skeptics think Mr. Musk and his companies are in over their heads, because there are manufacturing issues for the batteries and the cars, and the solar panel business has yet to be profitable. Yet, the older among us can recall all the troubles with launching TV.
Early sets were not only expensive, they were often problematic, with frequent component failures causing owners to take the TV to a repairman. Often reception was poor, as people relied on poor antennas and weak network signals. It was common to turn on a set and have “snow” as we called it – images that were far from clear. And there was often that still image on the screen with the words “Technical Difficulties,” meaning that viewers just waited to see when programming would return. And programming was far from 24×7 – and quality could be sketchy. But all these problems have been overcome by innovation across the industry.
Yes, the evolution of electric cars will involve a lot of ongoing innovation. So judging its likely success on the basis of recent history would be foolhardy. Today Tesla sells 100% of its cars, with no discounts. The market has said it really, really wants its vehicles. And everybody who is offered electric panels with (a) the opportunity to sell excess power back to the grid and (b) financing, takes the offer. People enjoy the low cost, sustainable electricity, and want it to grow. But lacking a good storage device, or the inability to sell excess power, their personal economics are more difficult.
Electricity production, electricity storage (batteries) and electricity consumption are tightly linked technologies. Nobody will build charging stations if there are no electric cars. Nobody will build electric cars if there are not good batteries. Nobody will make better batteries if there are no electric cars. Nobody will install solar panels if they can’t use all the electricity, or store what they don’t immediately need (or sell it.)
This is not a world of an established marketplace, where GM and Chevron can stand alone. To grow the business requires a vision, business strategy and technical capability to put it all together. To make this work someone has to make progress in all the core technologies simultaneously – which will continue to improve the storage capability, quality and safety of the electric consuming automobiles, and the electric generating solar panels, as well as the storage capabilities associated with those panels and the creation of a new grid for distribution.
This is why Mr. Musk says that combining Tesla and SolarCity is obvious. Yes, he will have to raise huge sums of money. So did such early pioneers as Vanderbilt (railways,) Rockefeller (oil,) Ford (autos,) and Watson (computers.) More recently, Steve Jobs of Apple became heroic for figuring out how to simultaneously create an iPhone, get a network to support the phone (his much maligned exclusive deal with AT&T,) getting developers to write enough apps for the phone to make it valuable, and creating the retail store to distribute those apps (iTunes.) Without all those pieces, the ubiquitous iPhone would have been as successful as the Microsoft Zune.
It is fair for investors to worry if Tesla can raise enough money to pull this off. But, we don’t know how creative Mr. Musk may become in organizing the resources and identifying investors. So far, Tesla has beaten all the skeptics who predicted failure based on price of the cars (Tesla has sold 100% of its production,) lack of range (now up to nearly 300 miles,) lack of charging network (Tesla built one itself) and charging time (now only 20 minutes.) It would be shortsighted to think that the creativity which has made Tesla a success so far will suddenly disappear. And thus remarkably thoughtless to base an analysis on the industry as it exists today, rather than how it might well look in 3, 5 and 10 years.
The combination of Tesla and SolarCity allows Tesla to have all the components to pursue greater future success. Investors with sufficient risk appetite are justified in supporting this merger because they will be positioned to receive the future rewards of this pioneering change in the auto and electric utility industries.
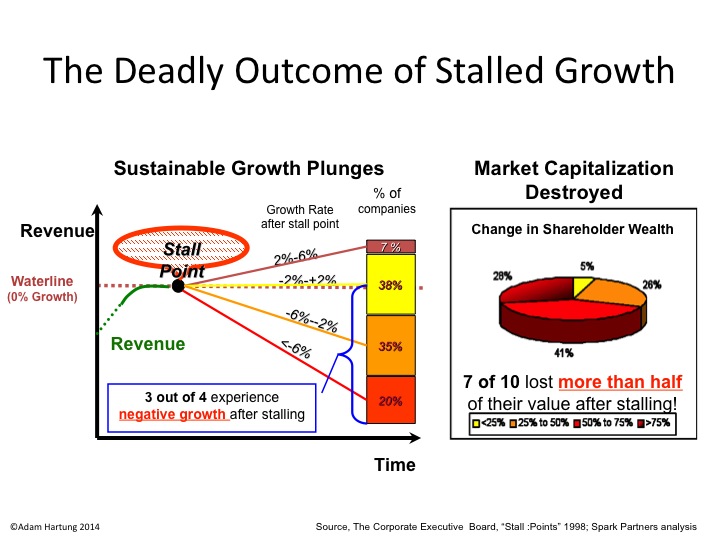
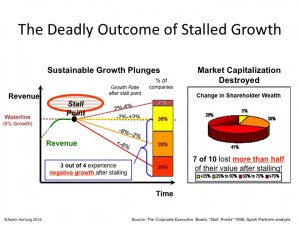
by Adam Hartung | Jul 27, 2016 | Food and Drink, Growth Stall, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
Growth Stalls are deadly for valuation, and both Mcdonald’s and Apple are in one.
August, 2014 I wrote about McDonald’s Growth Stall. The company had 7 straight months of revenue declines, and leadership was predicting the trend would continue. Using data from several thousand companies across more than 3 decades, companies in a Growth Stall are unable to maintain a mere 2% growth rate 93% of the time. 55% fall into a consistent revenue decline of more than 2%. 20% drop into a negative 6%/year revenue slide. 69% of Growth Stalled companies will lose at least half their market capitalization in just a few years. 95% will lose more than 25% of their market value. So it is a long-term concern when any company hits a Growth Stall.
 A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also closed 700 stores in 2015, and 500 in 2016. And he announced the company would move its headquarters from suburban Oakbrook to downtown Chicago, IL. While doing something, none of these actions addressed the fundamental problem of customers switching to competitive options that meet modern consumer food trends far better than McDonald’s.
A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also closed 700 stores in 2015, and 500 in 2016. And he announced the company would move its headquarters from suburban Oakbrook to downtown Chicago, IL. While doing something, none of these actions addressed the fundamental problem of customers switching to competitive options that meet modern consumer food trends far better than McDonald’s.
McDonald’s stock languished around $94/share from 8/2014 through 8/2015 – but then broke out to $112 in 2 months on investor hopes for a turnaround. At the time I warned investors not to follow the herd, because there was nothing to indicate that trends had changed – and McDonald’s still had not altered its business in any meaningful way to address the new market realities.
Yet, hopes remained high and the stock peaked at $130 in May, 2016. But since then, the lack of incremental revenue growth has become obvious again. Customers are switching from lunch food to breakfast food, and often switching to lower priced items – but these are almost wholly existing customers. Not new, incremental customers. Thus, the company trumpets small gains in revenue per store (recall, the number of stores were cut) but the growth is less than the predicted 2%. The only incremental growth is in China and Russia, 2 markets known for unpredictable leadership. The stock has now fallen back to $120.
Given that the realization is growing as to the McDonald’s inability to fundamentally change its business competitively, the prognosis is not good that a turnaround will really happen. Instead, the common pattern emerges of investors hoping that the Growth Stall was a “blip,” and will be easily reversed. They think the business is fundamentally sound, and a little management “tweaking” will fix everything. Small changes will lead to the classic hockey-stick forecast of higher future growth. So the stock pops up on short-term news, only to fall back when reality sets in that the long-term doesn’t look so good.
Unfortunately, Apple’s Q3 2016 results (reported yesterday) clearly show the company is now in its own Growth Stall. Revenues were down 11% vs. last year (YOY or year-over-year,) and EPS (earnings per share) were down 23% YOY. 2 consecutive quarters of either defines a Growth Stall, and Apple hit both. Further evidence of a Growth Stall exists in iPhone unit sales declining 15% YOY, iPad unit sales off 9% YOY, Mac unit sales down 11% YOY and “other products” revenue down 16% YOY.
This was not unanticipated. Apple started communicating growth concerns in January, causing its stock to tank. And in April, revealing Q2 results, the company not only verified its first down quarter, but predicted Q3 would be soft. From its peak in May, 2015 of $132 to its low in May, 2016 of $90, Apple’s valuation fell a whopping 32%! One could say it met the valuation prediction of a Growth Stall already – and incredibly quickly!
But now analysts are ready to say “the worst is behind it” for Apple investors. They are cheering results that beat expectations, even though they are clearly very poor compared to last year. Analysts are hoping that a new, lower baseline is being set for investors that only look backward 52 weeks, and the stock price will move up on additional company share repurchases, a successful iPhone 7 launch, higher sales in emerging countries like India, and more app revenue as the installed base grows – all leading to a higher P/E (price/earnings) multiple. The stock improved 7% on the latest news.
So far, Apple still has not addressed its big problem. What will be the next product or solution that will replace “core” iPhone and iPad revenues? Increasingly competitors are making smartphones far cheaper that are “good enough,” especially in markets like China. And iPhone/iPad product improvements are no longer as powerful as before, causing new product releases to be less exciting. And products like Apple Watch, Apple Pay, Apple TV and IBeacon are not “moving the needle” on revenues nearly enough. And while experienced companies like HBO, Netflix and Amazon grow their expanding content creation, Apple has said it is growing its original content offerings by buying the exclusive rights to “Carpool Karaoke“ – yet this is very small compared to the revenue growth needs created by slowing “core” products.
Like McDonald’s stock, Apple’s stock is likely to move upward short-term. Investor hopes are hard to kill. Long-term investors will hold their stock, waiting to see if something good emerges. Traders will buy, based upon beating analyst expectations or technical analysis of price movements. Or just belief that the P/E will expand closer to tech industry norms. But long-term, unless the fundamental need for new products that fulfill customer trends – as the iPad, iPhone and iPod did for mobile – it is unclear how Apple’s valuation grows.
by Adam Hartung | Jun 14, 2016 | Defend & Extend, Investing, Leadership, Web/Tech
Microsoft is buying Linked-In, and we should expect this to be a disaster.
It is clear why Linked-in agreed to be purchased. As revenues have grown, gross margins have dropped precipitously, and the company is losing money. And LInked-in still receives 2/3 of its revenue from recruiting ads (the balance is almost wholly subscription fees,) unable to find a wider advertiser base to support growth. Although membership is rising, monthly active users (MAUs, the most important gauge of social media growth) is only 9% – like Twitter, far below the 40% plus rate of Facebook and upcoming networks. With only 106M MAUs, Linked in is 1/3 the size of Twitter, and 1/15th the size of Facebook. And its $1.5B Lynda acquisition is far, far, far from recovering its investment – or even demonstrating viability as a business.
Even though the price is below the all-time highs for LNKD investors, Microsoft’s offer is far above recent trading prices and a big windfall for them.
But for Microsoft investors, this is a repeat of the pattern that continues to whittle away at their equity value.
 Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.
Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.
But the world changed. Today PC sales continue their multi-year, accelerating decline, while some markets (such as education) are shifting to Chromebooks for low cost desktop/laptop computing, growing their sales and share. Meanwhile, mobile devices have been the growth market for years. Networks are largely public (rather than private) and storage is primarily in the cloud – and supplied by Amazon. Solutions are spread all around, from Google Drive to apps of every flavor and variety. People spend less computing cycles creating documents, spreadsheets and presentations, and a lot more cycles either searching the web or on Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, YouTube and Snapchat.
But Microsoft’s leadership still would like to capture that old world. They still hope to put the genie back in the bottle, and have everyone live and work entirely on Microsoft. And somehow they have deluded themselves into thinking that buying Linked-in will allow them to return to the “good old days.”
Microsoft has not done a good job of integrating its own solutions like Office 365, Skype, Sharepoint and Dynamics into a coherent, easy to use, and to some extent mobile, solution. Yet, somehow, investors are expected to believe that after buying Linked-in the two companies will integrate these solutions into the LInked-in social platform, enabling vastly greater adoption/use of Office 365 and Dynamics as they are tied to Linked-in Sales Navigator. Users will be thrilled to have their personal information analyzed by Microsoft big data tools, then sold to advertisers and recruiters. Meanwhile, corporations will come back to Microsoft in droves as they convert Linked-in into a comprehensive project management tool that uses Lynda to educate employees, and 365 to push materials to employees – and allow document collaboration – all across their mobile devices.
Do you really believe this? It might run on the Powerpoint operating system, but this vision will take an enormous amount of code integration. And with Linked-in operated as separate company within Microsoft, who is going to do this integration? This will involve a lot of technical capability, and based on previous performance it appears both companies lack the skills necessary to pull it off. How this mysterious, magical integration will happen is far, far from obvious, or explained in the announcement documents. Sounds a lot more like vaporware than a straightforward software project.
And who thinks that today’s users, from individuals to corporations, have a need for this vision? While it may sound good to Microsoft, have you heard Linked-in users saying they want to use 365 on Linked in? Or that they’ll continue to use Linked-in if forced to buy 365? Or that they want their personal information data mined for advertisers? Or that they desire integration with Dynamics to perform Linked-in based CRM? Or that they see a need for a social-network based project management tool that feeds up training documents or collaborative documents? Are people asking for an integrated, holistic solution from one vendor to replace their current mobile devices and mobile solutions that are upgraded by multiple vendors almost weekly?
And, who really thinks Microsoft is good at acquisition integration? Remember aQuantive? In 2007 Microsoft spent $6B (an 85% premium to market price) to purchase this digital ad agency in order to build its business in the fast growing digital ad space. Don’t feel bad if you don’t remember, because in 2012 Microsoft wrote it off. Of course, there was the buy-it-and-write-it-off pattern repeated with Nokia. Microsoft’s success at taking “bold moves” to expand beyond its core business has been nothing less than horrible. Even the $1.2B acquisition of Yammer in 2012 to make Sharepoint more collaborative and usable has been unsuccessful, even though rolled out for free to 365 users. Yammer is adding nothing to Microsoft’s sales or value as competitor Slack has reaped the growth in corporate messaging.
The only good news story about Microsoft acquisitions is that they missed spending $44B to buy Yahoo – which is now on the market for $5B. Whew, thank goodness that one got away!
Microsoft’s leadership primed the pump for this week’s announcement by having the Chairman talk about investing outside of the company’s core a couple of weeks ago. But the vast majority of analysts are now questioning this giant bet, at a price so high it will lower Microsoft’s earnings for 2 years. Analysts are projecting about a $2B revenue drop for $90B Microsoft next year, and this $26B acquisition will deliver only a $3B bump. Very, very expensive revenue replacement.
Despite all the lingo, Microsoft simply cannot seem to escape its past. Its acquisitions have all been designed to defend and extend its once great history – but now outdated. Customers don’t want the past, they are looking to the future. And no matter how hard they try, Microsoft’s leaders simply appear unable to define a future that is not tightly linked to the company’s past. So investors should expect Linked-In’s future to look a lot like aQuantive. Only this one is going to be the most painful yet in the long list of value transfer from Microsoft investors to the investors of acquired companies.

by Adam Hartung | May 27, 2016 | Investing, Mobile, Trends, Web/Tech
Snapchat filed its latest fundraising with the SEC this week. According to TechCrunch, $1.8 billion cash was added to the company, based on a current valuation in the range of $18 billion to $20 billion. Not bad for a company with 2015 revenues of about $59 million. And quite a high valuation for a one-product company that probably nobody who reads this column has ever used – or even knows anything about.
Why is Snapchat so highly valued? Because revenue estimates are for $250 million to $350 million in 2016, and up to $1 billion for 2017. From 50 million daily active users in March, 2014 Snapchat has grown to 110 million users by December, 2015 – so a growth rate of about 50% per year. And this growth has not been all USA, over half the Snapchat users are from Europe and the rest of the world – and the non-USA markets are growing the fastest. Clearly, at 20 times 2017 revenue estimates, investors are expecting dramatic growth in users, and revenue to continue. They anticipate numbers of the magnitude that drove the valuation of Google (over $500 billion) and Facebook ($340 billion).
What is Snapchat? It is the complete opposite of this column. Snapchat is like Twitter only without the text. Of course, most of my readers don’t tweet either, so that may not help. It is a picture or 10 second video messaging app. But, most of my readers don’t use messaging apps either, so that may not be helpful.
Think of texting, only you don’t actually text. Instead you send a picture or short video. That’s it. Pretty simple. Just a way to send your friends pics and videos with your phone – although you can be creative with the pictures and make changes.
People who use Snapchat find it addictive. They may send dozens, or hundreds, of pictures daily. To single friends, groups, or even all their friends – since users can pick who gets the pic.
For many of my readers, this must seem ridiculous. Who would want to send, or receive, several pictures every day from some, or many, of your colleagues and friends?
In 1927 Fred Bernard [trivia] popularized the phrase we use today “
A picture is worth a thousand words.” And today, that is more true than ever. Pictures are replacing words for a vast and growing segment of the population. This is now a very fast growing trend, and it is projected to continue.
“Why is this a trend, and not a fad?” you may ask. The answer goes to the heart of how we use language and images. For thousands of years very few people knew how to read or write. To promulgate information, religious and government leaders would have artists paint images that told the story they wanted spread. These images were then taken from town to town, and people were taught the stories by having someone explain the picture. Then the image could be recalled by the population. It was only after the advent of mass education that using written words became the primary medium for providing information.
Simultaneously, paintings were really expensive. And early photography was expensive. Both mediums were used primarily to memorialize a story, or event. Thus there were relatively few of these images, and they were often treasured, hung on walls or kept in albums for later review. Most of my readers are still stuck in the historical context of thinking of pictures as memorials.
But today images are extremely cheap and easy. Almost everyone has a phone with a camera. So it is easy to take a picture, and it is easy to view a picture. Pictures have become free. And if you can replace a thousand words with one photo, it is far more efficient – and thus from a resource perspective photos are far cheaper (think of how long it takes to write an email as opposed to taking a picture). Given that this flip in resources required has happened, and that the use of mobile technology is growing worldwide and will never revert, we know that this is not s short-term fad, but rather a trend.
Once we communicated by telephone calls. That has dropped dramatically because real-time communication takes a lot more effort to coordinate and implement than asynchronous communication. I can email or text any time I want, and my friend can receive that message when it is convenient for her. And she can choose to respond at her convenience, or not respond at all. Thus email and texting exploded due to the technical capability and their improved economy. Today we have the ability to communicate in pictures or short videos which is even more information dense, and even more economical.
I’m sure many of my readers are saying “well, that may be good for someone else, but not for me.” And that’s good, because you read these columns. But factually, the number of readers is destined to decrease as the number of viewers go up.
There’s a reason every time you open an on-line magazine column you are bombarded by short videos ads. They are more communication dense and they are more successful at capturing attention – even if they do irritate you.
There’s a reason that fewer and fewer people read books, and rely instead on columns like this one to gain insights. And there’s a reason more and more people connect on Facebook rather than sending emails – and rather than sending snail mail (when was the last time you actually mailed someone a birthday card?). Haven’t you ever watched a YouTube video rather than read an instruction manual? While you may not imagine using pictures to replace language, the fact is it is happening with increasing frequency, and lots of people are making the switch. Thus it is a trend that will affect how we do many things for many years into the future.
Snapchat has capitalized on this new trend by making an app which allows you and your friends to communicate far more information a whole lot faster. Rather than interrupting your friends with a phone call (they may be busy right now,) or writing them an email or text message, you can just send them a photo. Have you ever used your phone to photo a label and sent it to someone who’s shopping for you? Or taken a photo of an item so you can find an exact replacement? That same action now can become your way of communicating – of telling your current story. Don’t tell your friends what you had for lunch, just send a photo. Don’t tell your friends you are shopping on Madison Avenue, just take a picture. Pictures are not archives, but rather just a fast, more compact and information filled form of communication.
Snapchat did not discover a new bio-pharmaceutical. It did not create a breakthrough new technology, such as extended battery life. It did not identify a sales opportunity in a far flung country. Nor did it have a breakthrough manufacturing process. Rather, merely by being the leader at implementing an emerging trend Snapchat’s founders have created $20 billion of current value.
Now that you know this trend, what are you going to do so you can capture additional value for your business?
by Adam Hartung | May 10, 2016 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
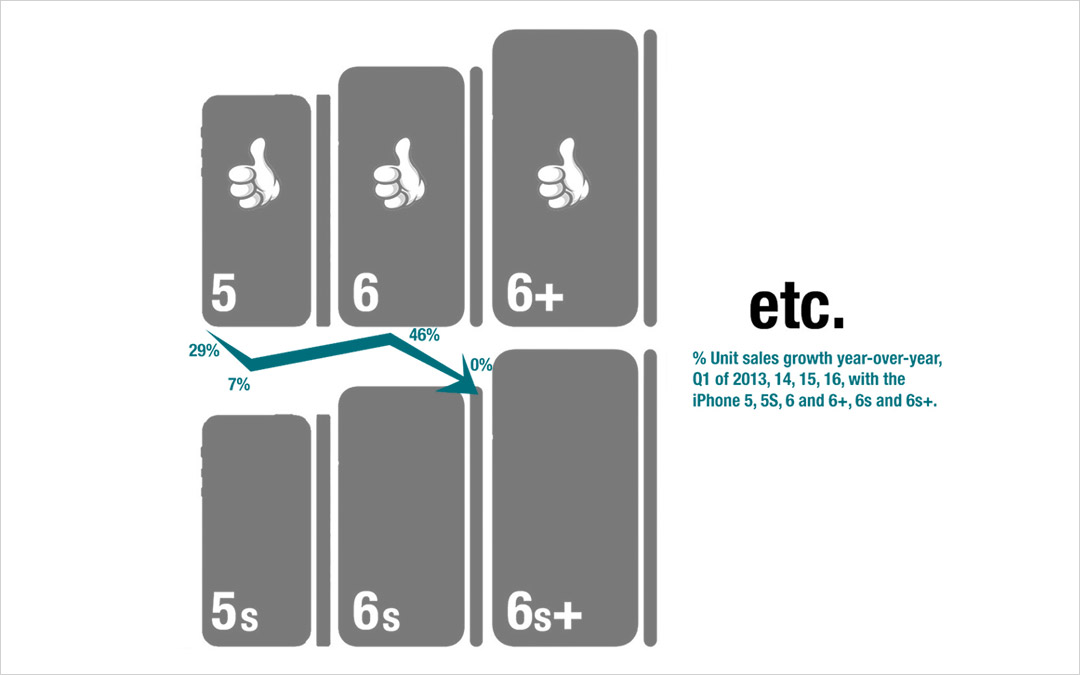
My last column focused on growth, and the risks inherent in a Growth stall. As I mentioned then, Apple will enter a Growth Stall if its revenue declines year-over-year in the current quarter. This forecasts Apple has only a 7% probability of consistently growing just 2%/year in the future.
This usually happens when a company falls into Defend & Extend (D&E) management. D&E management is when the bulk of management attention, and resources, flow into protecting the “core” business by seeking ways to use sustaining innovations (rather than disruptive innovations) to defend current customers and extend into new markets. Unfortunately, this rarely leads to high growth rates, and more often leads to compressed margins as growth stalls. Instead of working on breakout performance products, efforts are focused on ways to make new versions of old products that are marginally better, faster or cheaper.
 Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
For example, Apple’s CEO has trumpeted the company’s installed base of 1B iPhones, and stated they will be a future money maker. He bragged about the 20% growth in “services,” which are iPhone users taking advantage of Apple Music, iCloud storage, Apps and iTunes. This shows management’s desire to extend sales to its “installed base” with sustaining software innovations. Unfortunately, this 20% growth was a whopping $1.2B last quarter, which was 2.4% of revenues. Not nearly enough to make up for the decline in “core” iPhone, iPad or Mac sales of approximately $9.5B.
Apple has also been talking a lot about selling in China and India. Unfortunately, plans for selling in India were at least delayed, if not thwarted, by a decision on the part of India’s regulators to not allow Apple to sell low cost refurbished iPhones in the country. Fearing this was a cheap way to dispose of e-waste they are pushing Apple to develop a low-cost new iPhone for their market. Either tactic, selling the refurbished products or creating a cheaper version, are efforts at extending the “core” product sales at lower margins, in an effort to defend the historical iPhone business. Neither creates a superior product with new features, functions or benefits – but rather sustains traditional product sales.
Of even greater note was last week’s announcement that Apple inked a partnership with SAP to develop uses for iPhones and iPads built on the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platform. This announcement revealed that SAP would ask developers on its platform to program in Swift in order to support iOS devices, rather than having a PC-first mentality.
This announcement builds on last year’s similar announcement with IBM. Now 2 very large enterprise players are building applications on iOS devices. This extends the iPhone, a product long thought of as great for consumers, deeply into enterprise sales. A market long dominated by Microsoft. With these partnerships Apple is growing its developer community, while circumventing Microsoft’s long-held domain, promoting sales to companies as well as individuals.
And Apple has shown a willingness to help grow this market by introducing the iPhone 6se which is smaller and cheaper in order to obtain more traction with corporate buyers and corporate employees who have been iPhone resistant. This is a classic market extension intended to sustain sales with more applications while making no significant improvements in the “core” product itself.
And Apple’s CEO has said he intends to make more acquisitions – which will surely be done to shore up weaknesses in existing products and extend into new markets. Although Apple has over $200M of cash it can use for acquisitions, unfortunately this tactic can be a very difficult way to actually find new growth. Each would be targeted at some sort of market extension, but like Beats the impact can be hard to find.
Remember, after all revenue gains and losses were summed, Apple’s revenue fell $7.6B last quarter. Let’s look at some favorite analyst acquisition targets to explain:
- Box could be a great acquisition to help bring more enterprise developers to Apple. Box is widely used by enterprises today, and would help grow where iCloud is weak. IBM has already partnered with Box, and is working on applications in areas like financial services. Box is valued at $1.45B, so easily affordable. But it also has only $300M of annual revenue. Clearly Apple would have to unleash an enormous development program to have Box make any meaningful impact in a company with over $500B of revenue. Something akin of Instagram’s growth for Facebook would be required. But where Instagram made Facebook a pic (versus words) site, it is unclear what major change Box would bring to Apple’s product lines.
- Fitbit is considered a good buy in order to put some glamour and growth onto iWatch. Of course, iWatch already had first year sales that exceeded iPhone sales in its first year. But Apple is now so big that all numbers have to be much bigger in order to make any difference. With a valuation of $3.7B Apple could easily afford FitBit. But FitBit has only $1.9B revenue. Given that they are different technologies, it is unclear how FitBit drives iWatch growth in any meaningful way – even if Apple converted 100% of Fitbit users to the iWatch. There would need to be a “killer app” in development at FitBit that would drive $10B-$20B additional annual revenue very quickly for it to have any meaningful impact on Apple.
- GoPro is seen as a way to kick up Apple’s photography capabilities in order to make the iPhone more valuable – or perhaps developing product extensions to drive greater revenue. At a $1.45B valuation, again easily affordable. But with only $1.6B revenue there’s just not much oomph to the Apple top line. Even maximum Apple Store distribution would probably not make an enormous impact. It would take finding some new markets in industry (enterprise) to build on things like IoT to make this a growth engine – but nobody has said GoPro or Apple have any innovations in that direction. And when Amazon tried to build on fancy photography capability with its FirePhone the product was a flop.
- Tesla is seen as the savior for the Apple Car – even though nobody really knows what the latter is supposed to be. Never mind the actual business proposition, some just think Elon Musk is the perfect replacement for the late Steve Jobs. After all the excitement for its products, Tesla is valued at only $28.4B, so again easily affordable by Apple. And the thinking is that Apple would have plenty of cash to invest in much faster growth — although Apple doesn’t invest in manufacturing and has been the king of outsourcing when it comes to actually making its products. But unfortunately, Tesla has only $4B revenue – so even a rapid doubling of Tesla shipments would yield a mere 1.6% increase in Apple’s revenues.
- In a spree, Apple could buy all 4 companies! Current market value is $35B, so even including a market premium $55B-$60B should bring in the lot. There would still be plenty of cash in the bank for growth. But, realize this would add only $8B of annual revenue to the current run rate – barely 25% of what was needed to cover the gap last quarter – and less than 2% incremental growth to the new lower run rate (that magic growth percentage to pull out of a Growth Stall mentioned earlier in this column.)
Such acquisitions would also be problematic because all have P/E (price/earnings) ratios far higher than Apple’s 10.4. FitBit is 24, GoPro is 43, and both Box and Tesla are infinite because they lose money. So all would have a negative impact on earnings per share, which theoretically should lower Apple’s P/E even more.
Acquisitions get the blood pumping for investment bankers and media folks alike – but, truthfully, it is very hard to see an acquisition path that solves Apple’s revenue problem.
All of Apple’s efforts big efforts today are around sustaining innovations to defend & extend current products. No longer do we hear about gee whiz innovations, nor do we hear about growth in market changing products like iBeacons or ApplePay. Today’s discussions are how to rejuvenate sales of products that are several versions old. This may work. Sales may recover via growth in India, or a big pick-up in enterprise as people leave their PCs behind. It could happen, and Apple could avoid its Growth Stall.
But investors have the right to be concerned. Apple can grow by defending and extending the iPhone market only so long. This strategy will certainly affect future margins as prices, on average, decline. In short, investors need to know what will be Apple’s next “big thing,” and when it is likely to emerge. It will take something quite significant for Apple to maintain it’s revenue, and profit, growth.
The good news is that Apple does sell for a lowly P/E of 10 today. That is incredibly low for a company as profitable as Apple, with such a large installed base and so many market extensions – even if its growth has stalled. Even if Apple is caught in the Innovator’s Dilemma (i.e. Clayton Christensen) and shifting its strategy to defending and extending, it is very lowly valued. So the stock could continue to perform well. It just may never reach the P/E of 15 or 20 that is common for its industry peers, and investors envisioned 2 or 3 years ago. Unless there is some new, disruptive innovation in the pipeline not yet revealed to investors.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 27, 2016 | Food and Drink, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Retail, Software, Web/Tech
Growth fixes a multitude of sins. If you grow revenues enough (you don’t even need profits, as Amazon has proven) investors will look past a lot of things. With revenue growth high enough, companies can offer employees free meals and massages. Executives and senior managers can fly around in private jets. Companies can build colossal buildings as testaments to their brand, or pay to have thier names on public buildings. R&D budgets can soar, and product launches can fail. Acquisitions are made with no concerns for price. Bonuses can be huge. All is accepted if revenues grow enough.
Just look at Facebook. Today Facebook announced today that for the quarter ended March, 2016 revenues jumped to $5.4B from $3.5B a year ago. Net income tripled to $1.5B from $500M. And the company is basically making all its revenue – 82% – from 1 product, mobile ads. In the last few years Facebook paid enormous premiums to buy WhatsApp and Instagram – but who cares when revenues grow this fast.
Anticipating good news, Facebook’s stock was up a touch today. But once the news came out, after-hours traders pumped the stock to over $118//share, a new all time high. That’s a price/earnings (p/e) multiple of something like 84. With growth like that Facebook’s leadership can do anything it wants.
But, when revenues slide it can become a veritable poop puddle. As Apple found out.
Rumors had swirled that Apple was going to say sales were down. And the stock had struggled to make gains from lows earlier in 2016. When the company’s CEO announced Tuesday that sales were down 13% versus a year ago the stock cratered after-hours, and opened this morning down 10%. Breaking a streak of 51 straight quarters of revenue growth (since 2003) really sent investors fleeing. From trading around $105/share the last 4 days, Apple closed today at ~$97. $40B of equity value was wiped out in 1 day, and the stock trades at a p/e multiple of 10.
The new iPhone 6se outsold projections, iPads beat expectations. First year Apple Watch sales exceeded first year iPhone sales. Mac sales remain much stronger than any other PC manufacturer. Apple iBeacons and Apple Pay continue their march as major technologies in the IoT (Internet of Things) market. And Apple TV keeps growing. There are about 13M users of Apple’s iMusic. There are 1.5M apps on the iTunes store. And the installed base keeps the iTunes store growing. Share buybacks will grow, and the dividend was increased yet again. But, none of that mattered when people heard sales growth had stopped. Now many investors don’t think Apple’s leadership can do anything right.
 Yet, that was just one quarter. Many companies bounce back from a bad quarter. There is no statistical evidence that one bad quarter is predictive of the next. But we do know that if sales decline versus a year ago for 2 consecutive quarters that is a Growth Stall. And companies that hit a Growth Stall rarely (93% of the time) find a consistent growth path ever again. Regardless of the explanations, Growth Stalls are remarkable predictors of companies that are developing a gap between their offerings, and the marketplace.
Yet, that was just one quarter. Many companies bounce back from a bad quarter. There is no statistical evidence that one bad quarter is predictive of the next. But we do know that if sales decline versus a year ago for 2 consecutive quarters that is a Growth Stall. And companies that hit a Growth Stall rarely (93% of the time) find a consistent growth path ever again. Regardless of the explanations, Growth Stalls are remarkable predictors of companies that are developing a gap between their offerings, and the marketplace.
Which leads us to Chipotle. Chipotle announced that same store sales fell almost 30% in Q1, 2016. That was after a 15% decline in Q4, 2015. And profits turned to losses for the quarter. That is a growth stall. Chipotle shares were $750/share back in early October. Now they are $417 – a drop of over 44%.
Customer illnesses have pointed to a company that grew fast, but apparently didn’t have its act together for safe sourcing of local ingredients, and safe food handling by employees. What seemed like a tactical problem has plagued the company, as more customers became ill in March.
Whether that is all that’s wrong at Chipotle is less clear, however. There is a lot more competition in the fast casual segment than 2 years ago when Chipotle seemed unable to do anything wrong. And although the company stresses healthy food, the calorie count on most portions would add pounds to anyone other than an athlete or construction worker – not exactly in line with current trends toward dieting. What frequently looks like a single problem when a company’s sales dip often turns out to have multiple origins, and regaining growth is nearly always a lot more difficult than leadership expects.
Growth is magical. It allows companies to invest in new products and services, and buoy’s a stock’s value enhancing acquisition ability. It allows for experimentation into new markets, and discovering other growth avenues. But lack of growth is a vital predictor of future performance. Companies without growth find themselves cost cutting and taking actions which often cause valuations to decline.
Right now Facebook is in a wonderful position. Apple has investors rightly concerned. Will next quarter signal a return to growth, or a Growth Stall? And Chipotle has investors heading for the exits, as there is now ample reason to question whether the company will recover its luster of yore.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 21, 2016 | In the Rapids, Leadership, Lifecycle, Television, Web/Tech
Netflix has been a remarkable company. Because it has accomplished something almost no company has ever done. It changed its business model, leading to new growth and higher profits.
Almost nobody pulls that off, because they remain stuck defending and extending their old model until they become irrelevant, or fail. Think about Blackberry, that gave us the smartphone business then lost it to Apple and its creation of the app market. Consider Circuit City, that lost enough customers to Amazon it could no longer survive. Sun Microsystems disappeared after PC servers caught up to Unix servers in capability. Remember the Bell companies and their land-line and long distance services, made obsolete by mobile phones and cable operators? These were some really big companies that saw their market shifts, but failed to “pivot” their strategy to remain competitive.
Netflix built a tremendous business delivering physical videos on tape and CD to homes, wiping out the brick-and-mortar stores like Blockbuster and Hollywood Video. By 2008 Netflix reached $1B revenues, reducing Blockbuster by a like amount. By 2010 Blockbuster was bankrupt. Netflix’ share price soared from $50/share to almost $300/share during 2011. By the end of 2012 CD shipments were dropping precipitously as streaming viewership was exploding. People thought Netflix was missing the wave, and the stock plummeted 75%. Most folks thought Netflix couldn’t pivot fast enough, or profitably, either.
But in 2013 Netflix proved the analysts wrong, and the company built a very successful – in fact market leading – streaming business. The shares soared, recovering all that lost value. By 2015 the company had more than doubled its previous high valuation.
But Netflix may be breaking entirely new ground in 2016. It is becoming a market leader in original programming. Something we long attributed to broadcasters and/or cable distributors like HBO and Showtime.
Today’s broadcast companies, like NBC, CBS and ABC, are offering less and less original programming. Overall there are 3 hours/night of prime time television which broadcasters used to “own” as original programming hours. Over the course of a year, allowing for holidays and one open night per week, that meant about 900 hours of programming for each network (including reruns as original programming.) But that was long ago.
 These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
Against that backdrop, Netflix has announced it will program 600 hours of original programming this year. That will approximately double any single large broadcast network. In a very real way, if you don’t want to watch sports or reality TV any more you probably will be watching some kind of “on demand” program. Either streamed from a cable service, or from a provider such as Netflix, Hulu or Amazon.
When it comes to original programming, the old broadcast networks are losing their relevancy to streaming technology, personal video devices and the customer’s ability to find what they want, when they want it – and increasingly at a quality they prefer – from streaming as opposed to broadcast media.
To complete this latest “pivot,” from a video streaming company to a true media company with its own content, Morgan Stanley has published that Netflix is now considered by customers as the #1 quality programming across streaming services. 29% of viewers said Netflix was #1, followed by long-time winner HBO now #2 with 21% of customers saying their programming is best. Amazon, Showtime and Hulu were seen as the best quality by 4%-5% of viewers.
So a decade ago Netflix was a CD distribution company. The largest customer of the U.S. Postal Service. Signing up folks to watch physical videos in their homes. Now they are the largest data streaming company on the planet, and one of the largest original programming producers and programmers in the USA – and possibly the world. And in this same decade we’ve watched the network broadcast companies become outlets for sports and reality TV, while cutting far back on their original shows. Sounds a lot like a market shift, and possibly Netflix could be the game changer, as it performs the first strategy double pivot in business history.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 15, 2016 | Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
Leading tech tracking companies IDC and Gartner both announced Q1, 2016 PC sales results, and they were horrible. Sales were down 9.5%-11.5% depending on which tracker you asked. And that’s after a horrible Q4, 2015 when sales were off more than 10%. PC sales have now declined for 6 straight quarters, and sales are roughly where they were in 2007, 9 years ago.
Oh yeah, that was when the iPhone launched – June, 2007. And just a couple of years before the iPad launched. Correlation, or causation?
Amazingly, when Q4 ended the forecasters were still optimistic of a stabilization and turnaround in PC sales. Typical analyst verbage was like this from IDC, “Commercial adoption of Windows 10 is expected to accelerate, and consumer buying should also stabilize by the second half of the year. Most PC users have delayed an upgrade, but can only maintain this for so long before facing security and performance issues.” And just to prove that hope springs eternal from the analyst breast, here is IDC’s forecast for 2016 after the horrible Q1, “In the short term, the PC market must still grapple with limited consumer interest and competition from other infrastructure upgrades in the commercial market. Nevertheless….things should start picking up in terms of Windows 10 pilots turning into actual PC purchases.”
Fascinating. Once again, the upturn is just around the corner. People have always looked forward to upgrading their PCs, there has always been a “PC upgrade cycle” and one will again emerge. Someday. At least, the analysts hope so. Maybe?
Microsoft investors must hope so. The company is selling at a price/earnings multiple of 40 on hopes that Windows 10 sales will soon boom, and re-energize PC growth. Surely. Hopefully. Maybe?
 The world has shifted, and far too many people don’t like to recognize the shift. When Windows 8 launched it was clear that interest in PC software was diminishing. What was once a major front page event, a Windows upgrade, was unimportant. By the time Windows 10 came along there was so little interest that its launch barely made any news at all. This market, these products, are really no longer relevant to the growth of personal technology.
The world has shifted, and far too many people don’t like to recognize the shift. When Windows 8 launched it was clear that interest in PC software was diminishing. What was once a major front page event, a Windows upgrade, was unimportant. By the time Windows 10 came along there was so little interest that its launch barely made any news at all. This market, these products, are really no longer relevant to the growth of personal technology.
Back when I predicted that Windows 8 would be a flop I was inundated with hate mail. It was clear that Ballmer was a terrible CEO, and would soon be replaced by the board. Same when I predicted that Surface tablets would not sell well, and that all Windows devices would not achieve significant share. People called me “an Apple Fanboy” or a “Microsoft hater.” Actually, neither was true. It was just clear that a major market shift was happening in computing. The world was rapidly going mobile, and cloud-based, and the PC just wasn’t going to be relevant. As the PC lost relevancy, so too would Microsoft because it completely missed the market, and its entries were far too tied to old ways of thinking about personal and corporate computing – not to mention the big lead competitors had in devices, apps and cloud services.
I’ve never said that modern PCs are bad products. I have a son half way through a PhD in Neurobiological Engineering. He builds all kinds of brain models and 3 dimensional brain images and cell structure plots — and he does all kinds of very exotic math. His world is built on incredibly powerful, fast PCs. He loves Windows 10, and he loves PCs — and he really “doesn’t get” tablets. And I truly understand why. His work requires local computational power and storage, and he loves Windows 10 over all other platforms.
But he is not a trend. His deep understanding of the benefits of Windows 10, and some of the PC manufacturers as well as those who sell upgrade componentry, is very much a niche. While he depends heavily on Microsoft and Wintel manufacturers to do his work, he is a niche user. (BTW he uses a Nexus phone and absolutely loves it, as well. And he can wax eloquently about the advantages he achieves by using an Android device.)
Today, I doubt I will receive hardly any comments to this column. Because to most people, the PC is nearly irrelevant. People don’t actually care about PC sales results, or forecasts. Not nearly as much as, say, care about whether or not the iPhone 6se advances the mobile phone market in a meaningful way.
Most people do their work, almost if not all their work, on a mobile device. They depend on cloud and SaaS (software-as-a-service) providers and get a lot done on apps. What they can’t do on a phone, they do on a tablet, by and large. They may, or may not, use a PC of some kind (Mac included in that reference) but it is not terribly important to them. PCs are now truly generic, like a refrigerator, and if they need one they don’t much care who made it or anything else – they just want it to do whatever task they have yet to migrate to their mobile world.
The amazing thing is not that PC sales have fallen for 6 quarters. That was easy to predict back in 2013. The amazing thing is that some people still don’t want to accept that this trend will never reverse. And many people, even though they haven’t carried around a laptop for months (years?) and don’t use a Windows mobile device, still think Microsoft is a market leader, and has a great future. PCs, and for the most part Microsoft, are simply no more relevant than Sears, Blackberry, or the Encyclopedia Britannica. Yet it is somewhat startling that some people have failed to think about the impact this has on their company, companies that make PC software and hardware – and the impact this will have on their lives – and likely their portfolios.






 Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
 A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also
A new CEO was hired, and he implemented several changes. He implemented all-day breakfast, and multiple new promotions. He also  Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.
Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.


 These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
 The world has shifted, and far too many people don’t like to recognize the shift. When Windows 8 launched it was clear that interest in PC software was diminishing. What was once a major front page event, a Windows upgrade, was unimportant. By the time Windows 10 came along there was
The world has shifted, and far too many people don’t like to recognize the shift. When Windows 8 launched it was clear that interest in PC software was diminishing. What was once a major front page event, a Windows upgrade, was unimportant. By the time Windows 10 came along there was