by Adam Hartung | Jun 3, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Were you ever told “pretty is as pretty does?” This homily means “don’t just look at the surface, it’s the underlying qualities that matter.” When I read analyst reviews of companies I’m often struck by how fascinated they are with the surface, and how weakly they seem to understand the underlying markets. Financials are a RESULT of management’s ability to provide competitive solutions, and no study of financials will give investors a true picture of management or the company’s future prospects.
The good:
Everyone should own Apple. The list of its market successes are clear, and well detailed at SeekingAlpha.com “Apple: The Most Undervalued Equity in Techdom.” The reason you should own Apple isn’t its past performance, but rather that the company has built a management team completely focused on the future. Apple is using scenario planning to create solutions that fit the way people want to work and live – not how they did things in the past.
And Apple managers are obsessive about staying ahead of competitors with better solutions that introduce new technologies, and higher levels of user productivity. By constantly being willing to disrupt the old ways of doing things, Apple keeps bringing better solutions to market via its ongoing investment in teams dedicated to developing new solutions and figuring out how they will adapt to fit unmet needs. And this isn’t just a “Steve Jobs thing” as the company’s entire success formula is built on the ability to plan for the future, and outperform competitors. We are seeing this now with the impending launch of iCloud (Marketwatch.com “Could Apple Still Surprise at Its Conference?“)
For nearly inexplicable reasons, many investors (and analysts) have not been optimistic about Apple’s future price. The company’s earnings have grown so fast that a mere fear of a slow-down has caused investors to retrench, expecting some sort of inexplicable collapse. Analysts look for creative negatives, like a recent financial analyst told me “Apple is second in value only to ExxonMobile, and I’m just not sure how to get my mind around that. Is it possible growth could be worth that much? I thought value was tied to assets.”
Uh, yes, growth is worth that much! Apple’s been growing at 100%. Perhaps it won’t continue to grow at that breakneck pace (or perhaps it will, there’s no competitor right now blocking its path), but even if it slows by 75% we’re still talking 25% growth – and that creates enormous value (compounded, 25% growth doubles your investment in 3 years.) When you find profitable growth from a company designed to repeat itself with new market introductions, you have a beautiful thing! And that’s a good investment.
Similarly, investors should really like Netflix. Netflix did what almost nobody does. It overcame fears of cannibalizing its base business (renting DVDs via mail-order) and introduced a streaming download service. Analysts decried this move, fearing that “digital sales would be far lower than physical sales.” But Netflix, with its focus firmly on the future and not the past, recognized that emerging competitors (like Hulu) were quickly changing the game. Their objective had to be to go where the market was heading, rather than trying to preserve an historical market destined to shrink. That sort of management thinking is a beautiful thing, and it has paid off enormously for Netflix.
Of course, those who look only at the surface worry about the pricing model at Netflix. They mostly worry that competitors will gore the Netflix digital ox. But what we can see is that the big competitors these analysts trot out for fear mongering – Wal-Mart, Amazon.com and Comcast – are locked-in to historical approaches, and not aggressively taking on Netflix. When you look at who has the #1 market position, the eyes and ears of customers, the subscriber/customer base and the delivery solution customers love you have to be excited about Netflix. After all, they are the leaders in a market that we know is going to shift their way – downloads. Sort of reminds you of Apple when they brought out the iPod and iTunes, doesn’t it?
The bad:
Google has been a great company. The internet wouldn’t be the internet if we didn’t have Google, the search engine that made the web easy and fast to use, plus gave us the ads making all of that search (and lots of content) free. But, the company has failed to deliver on its own innovations. Android is a huge market success, but unfortunately lock-in to its old mindset led Google to give the product away – just a tad underpriced. Other products, like Wave were great, but there hasn’t been enough White Space available for the products to develop into commercial successes. And we’ve all recently read how it happened that Google missed the emergence of social media, now positioning Facebook as a threaten to their long-term viability (AllThingsD.com “Schmidt Says Google’s Social Networking Problem is His Fault.“)
Chrome, Chromebooks and Google Wallet could be big winners. And there’s a new CEO in place who promises to move Google beyond its past glory. But these are highly competitive markets, Google isn’t first, it’s technology advantages aren’t as clear cut as in the old search days (PCWorld.com “Google Wallet Isn’t the Only Mobile POS Tool.”) Whether Google will regain its past glory depends on whether the company can overcome its dedication to its old success formula and actually disrupt its internal processes enough to take the lead with disruptive marketplace products.
Cisco is in a similar situation. A great innovator who’s products put us all on the web, and made us wi-fi addicted. But markets are shifting as people change their needs for costly internal networks, moving to the cloud, and other competitors (like NetApp) are the game changers in the new market. Cisco’s efforts to enter new markets have been fragmented, poorly managed, and largely ineffective as it spent too much energy focused on historical markets. Emblematic was the abandoned effort to enter consumer markets with the Flip camera, where its inability to connect with fast shifting market needs led to the product line shutdown and a loss of the entire investment (BusinessInsider.com “Cisco Kills the Flip Camera.”)
Cisco’s value is tied not to its historical market, but its ability to develop new ones. Even when they likely cannibalize old products. HIstorically Cisco did this well. But as customers move to the cloud it’s still not clear what Cisco will do to remain an industry leader. Whether Google and Cisco will ever be good investments again doesn’t look too good, today. Maybe. But only if they realign their investments and put in place teams dedicated to new, growth markets.
The ugly:
Another homily goes “beauty may be on the surface, but ugly goes clear to the bone.” Meaning? For something to be ugly, it has to be deeply flawed inside. And that’s the situation at Research in Motion and Microsoft. Optimistic investors describe both of these companies as potential “value stocks” that will find a way to “protect the installed base as an economic recovery develops” and “sell their products cheaply in developing countries that can’t afford new solutions” eventually leading to high dividend payouts as they milk old businesses. Right. That won’t happen, because these companies are on a self-destructive course to preserve lost markets which will eat up resources and leave them shells of their former selves.
Both companies were wildly successful. Both once had near-monopolies in their markets. But in both cases, the organizations became obsessed with defending and extending sales to their “core” or “base” customers using “core” technologies and products. This internal focus, and desire to follow best practices, led them to overspending on what worked in the past, while the market shifted away from them.
At RIMM the market has moved from enterprise servers and secure enterprise applications to local apps that access data via the cloud. People have moved from PCs to smartphones (and tablets) that allow them to do even more than they could do on old devices, and RIM’s devotion to its historical business base caused the company to miss the shift. Blackberry and Playbook have 1/10th the apps of leaders Apple and Android (at best) and are rapidly being competitively outrun.
Likewise, Microsoft has offered the market nothing new when it comes to emerging markets and unmet user needs as it has invested billions of dollars trying to preserve its traditional PC marketplace. Vista, Windows 7 and Office 2010 all missed the fact that users were going off the PC, and toward new solutions for personal productivity. Now the company is trying to play catch-up with its Skype acquisition, Nokia partnership (where sales are in a record, multi-year slide; SeekingAlpha.com “Nokia Deluged with Downgrades“) and a planned launch of Windows 8. Only they are against ferocious competition that has developed an enormous market lead, using lower cost technologies, and keep offering innovations that are driving additional market shift.
Companies that plan for the future, keep their eyes firmly focused on unmet needs and alternative competitors, and that accept and implement disruptions via internal teams with permission to be game-changers are the winners. They are good investments.
Big winners that keep seeking new opportunities, but fall into over-reliance (and focus) on historical markets and customers can move from being good investments to bad ones. They have to change their planning and competitive analysis, and start attacking old notions about their business to free up resources for doing new things. They can return to greatness, but only if they recognize market shifts and move aggressively to develop solutions for emerging needs in new markets.
It gets ugly when companies lose their ability to see external market shifts because they are inwardly focused (inside their organizations, and inside their historical customer base or supply chain.) Their market sensing disappears, and their investments become committed on trying to defend old businesses in the face of changes far beyond their control. Their internal biases cause reduction of shareholder value as they spend money on acquisitions and new products that have negative rates of return in their overly-optimistic effort to regain past glory. Those situations almost never return to former beauty, as ugly internal processes lock them into repeating past behaviors even when its clear they need an entirely new approach to succeed.
by Adam Hartung | May 25, 2011 | Defend & Extend, Disruptions, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in, Openness, Transparency, Web/Tech
Nobody admits to being the innovation killer in a company. But we know they exist. Some these folks “dinosaurs that won’t change.” Others blame “the nay-saying ‘Dr. No’ middle managers.” But when you meet these people, they won’t admit to being innovation killers. They believe, deep in their hearts as well as in their everyday actions, that they are doing the right thing for the business. And that’s because they’ve been chosen, and reinforced, to be the Status Quo Police.
When a company starts it has no norms. But as it succeeds, in order to grow quickly it develops a series of “key success factors” that help it continue growing. In order to grow faster, managers – often in functional roles – are assigned the task of making sure the key success factors are unwaveringly supported. Consistency becomes more important than creativity. And these managers are reinforced, supported, even bonused for their ability to make sure they maintain the status quo. Even if the market has shifted, they don’t shift. They reinforce doing things according to the rules. Just consider:
Quality – Who can argue with the need to have quality? Total Quality Management (TQM,) Continuous Improvement (CI,) and Six Sigma programs all have been glorified by companies hoping to improve product or service quality. If you’re trying to fix a broken product, or process, these work pretty well at helping everyone do their job better.
But these programs live with the mantra “if you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it. Measure everything that’s important.” If you’re innovating, what do you measure? If you’re in a new technology, or manufacturing process, how do you know what you really need to do right? If you’re in a new market, how do you know the key metric for sales success? Is it number of customers called, time with customers, number of customer surveys, recommendation scores, lost sales reports? When you’re trying to do something new, a lot of what you do is respond quickly to instant feedback – whether it’s good feedback or bad.
The key to success isn’t to have critical metrics and measure performance on a graph, but rather to learn from everything you do – and usually to change. Quality people hate this, and can only stand in the way of trying anything new because you don’t know what to measure, or what constitutes a “good” measure. Don’t ever forget that Motorola pretty much invented Six Sigma, and what happened to them in the mobile phone business they pioneered?
Finance. All businesses exist to make money, so who can argue with “show me the numbers. Give me a business plan that shows me how you’re going to make money.” When your’e making an incremental investment to an existing asset or process, this is pretty good advice.
But when you’re innovating, what you don’t know far exceeds what you know. You don’t know how to meet unment needs. You don’t know the market size, the price that people will pay, the first year’s volume (much less year 5,) the direct cost at various volumes, the indirect cost, the cost of marketing to obtain customer attention, the number of sales calls it will take to land a sale, how many solution revisions will be necessary to finally put out the “right” solution, or how sales will ramp up quarterly from nothing. So to create a business plan, you have to guess.
And, oh boy, then it gets ugly. “Where did this number come from? That one? How did you determine that?” It’s not long until the poor business plan writer is ridden out of the meeting on a rail. He has no money to investigate the market, so he can’t obtain any “real” numbers, so the business plan process leads to ongoing investment in the old business, while innovation simply stalls.
Under Akia Morita Sony was a great innovator. But then an MBA skilled in finance took over the top spot. What once was the #1 electronics innovator in the globe has become, well, let’s say they aren’t Apple.
Legal – No company wants to be sued, or take on unnecessary risk. And when you’re selling something, lawyers are pretty good at evaluating the risk in that business, and lowering the risk. While making sure that all the compliance issues are met in order to keep regulators – and other lawyers – out of the business.
But when you’re starting something new, everything looks risky. Customers can sue you for any reason. Suppliers can sue you for not taking product, or using it incorrectly. The technology could fail, or have negative use repercussions. Reguators can question your safety standards, or claims to customers.
From a legal point of view, you’re best to never do anything new. The less new things you do, the less likely you are to make a mistake. So legal’s great at putting up roadblocks to make sure they protect the company from lawsuits, by making sure nothing really new happens. The old General Motors had plenty of lawyers making sure their cars were never too risky – or interesting.
R&D or Product Development – Who doesn’t think it’s good to be a leader in a specific technology? Technology advances have proven invaluable for companies in industries from computers to pharmaceuticals to tractors and even services like on-line banking. Thus R&D and Product Development wants to make sure investments advance the state of the technology upon which the company was built.
But all technologies become obsolete. Or, at least unprofitable. Innovators are frequently on the front end of adopting new technologies. But if they have to obtain buy-in from product development to obtain staffing or money they’ll be at the end of a never-ending line of projects to sustain the existing development trend. You don’t have to look much further than Microsoft to find a company that is great at pouring money into the PC platform (some $9B, 16% of revenue in 2009,) while the market moves faster each year to mobile devices and entertainment (Apple spent 1/8th the Microsoft budget in 2009.)
Sales, Marketing & Distribution – When you want to protect sales to existing customers, or maybe increase them by 5%, then doing more of what you’ve always done is smart. So money is spent to put more salespeople on key accounts, add more money to the advertising budget for the most successful (or most profitable) existing products. There are more rules about using the brand than lighters at a smoker’s convention. And it’s heresy to recommend endangering the distribution channel that has so successfully helped increase sales.
But innovators regularly need to behave differently. They need to sell to different people – Xerox sold to secretaries while printing press manufacturers sold to printers. The “brand” may well represent a bygone era, and be of no value to someone launching a new product; are you eager to buy a Zenith electronic device? Sprucing up the brand, or even launching something new, may well be a requirement for a new solution to be taken seriously.
And often, to be successful, a new solution needs to cut through the old, high-cost distribution system directly to customers if it is to succeed. Pre-Gerstner IBM kept adding key account sales people in hopes of keeping IT departments from switching out of mainframes to PCs. Sears avoided the shift to on-line sales successfully – and revenue keeps dropping in the stores.
Information Technology – To make more money you automate more functions. Computers are wonderful for reducing manpower in many tasks. So IT implements and supports “standard solutions” that are cost effective for the historical business. Likewise, they set up all kinds of user rules – like don’t go to Facebook or web sites from work – to keep people focused on productivity. And to make sure historical data is secure and regulations are met.
But innovators don’t have a solution mapped out, and all that automated functionality is an enormously expensive headache. When being creative, more time is spent looking for something new than trying to work faster, or harder, so access to more external information is required. Since the solution isn’t developed, there’s precious little to worry about keeping secure. Innovators need to use new tools, and have flexibility to discover advantageous ways to use them, that are far beyond the bounds of IT’s comfort zone.
Newspapers are loaded with automated systems to collect and edit news, to enter display ads, and to “Make up” the printed page fast and cheap. They have automated systems for classified advertising sales and billing, and for display ad billing. And systems to manage subscribers. That technology isn’t very helpful now, however, as newspapers go bankrupt. Now the most critical IT skills are pumping news to the internet in real-time, and managing on-line ads distributed to web users that don’t have subscriptions.
Human Resources – Growth pushes companies toward tighter job descriptions with clear standards for “the kinds of people that succeed around here.” When you want to hire people to be productive at an existing job, HR has the procedures to define the role, find the people and hire them at the most efficient cost. And they can develop a systematic compensation plan that treats everyone “fairly” based upon perceived value to the historical business.
But innovators don’t know what kinds of people will be most successful. Often they need folks who think laterally, across lots fo tasks, rather than deeply about something narrow. Often they need people who are from different backgrounds, that are closer to the emerging market than the historical business. And pay has to be related to what these folks can get in the market, not what seems fair through the lens of the historical business. HR is rarely keen to staff up a new business opportunity with a lot of misfits who don’t appreciate their compensation plan – or the rules so carefully created to circumscribe behavior around the old business.
B.Dalton was America’s largest retail book seller when Amazon.com was founded by Jeff Bezos. Jeff knew nothing about books, but he knew the internet. B.Dalton knew about books, and claimed it knew what book buyers wanted. Two years later B.Dalton went bankrupt, and all those book experts became unemployed. Amazon.com now sells a lot more than books, as it ongoingly and rapidly expands its employee skill sets to enter new markets – like publishing and eReaders.
Innovation requires that leaders ATTACK the Status Quo Police. Everything done to efficiently run the old business is irrelevant when it comes to innovation. Functional folks need to be told they can’t force the innovatoirs to conform to old rules, because that’s exactly why the company needs innovation! Only by attacking the old rules, and being willing to allow both diversity and disruption can the business innovate.
Instead of saying “this isn’t how we do things around here” it is critical leaders make sure functional folks are saying “how can I help you innovate?” What was done in the name of “good business” looks backward – not forward. Status Quo cops have to be removed from the scene – kept from stopping innovation dead in its tracks. And if the internal folks can’t be supportive, that means keeping them out of the innovator’s way entirely.
Any company can innovate. Doing so requires recognizing that the Status Quo Police are doing what they were hired to do. Until you take away their clout, attack their role and stop them from forcing conformance to old dictums, the business can’t hope to innovate.
by Adam Hartung | May 16, 2011 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle, Lock-in, Web/Tech
In “Screening Large Cap Value Stocks” 24x7WallSt.com tries making the investment case for Dell. And backhandedly, for Hewlett Packard. The argument is as simple as both companies were once growing, but growth slowed and now they are more mature companies migrating from products into services. They have mounds of cash, and will soon start paying a big, fat dividend. So investors can rest comfortably that these big companies are a good value, sitting on big businesses, and less risky than growth stocks.
Nice story. Makes for good myth. Reality is that these companies are a lousy value, and very risky.
Dell grew remarkably fast during the PC growth heyday. Dell innovated computer sales, eschewing expensive distribution for direct-to-customer marketing and order-taking. Dell could sell individuals, or corporations, computers off-the-shelf or custom designed machines in minutes, delivered in days. Further, Dell eschewed the costly product development of competitors like Compaq in favor of using a limited number of component suppliers (Microsoft, Intel, etc.) and focusing on assembly. With Wal-Mart style supply chain execution Dell could deliver a custom order and be paid before the bill was due for parts. Quickly Dell was a money-making, high growth machine as it rode the growth of PC sales expansion.
But competitors learned to match Dell’s supply chain cost-cutting capabilities. Manufacturers teamed with retailers like Best Buy to lower distribution cost. As competition copied the use of common components product differences disappeared and prices dropped every month. Dell’s advantages started disappearing, and as they continued to follow the historical cost-cutting success formula with more outsourcing, problems developed across customer services. Competitors wreaked havoc on Dell’s success formula, hurting revenue growth and margins.
HP followed a similar path, chasing Dell down the cost curve and expanding distribution. To gain volume, in hopes that it would create “scale advantages,” HP acquired Compaq. But the longer HP poured printer profits into PCs, the more it fed the price war between the two big companies.
Worst for both, the market started shifting. People bought fewer PCs. Saturation developed, and reasons to buy new ones were few. Users began buying more smartphones, and later tablets. And neither Dell nor HP had any products in development where the market was headed, nor did their “core” suppliers – Microsoft or Intel.
That’s when management started focusing on how to defend and extend the historical business, rather than enter growth markets. Rather than moving rapidly to push suppliers into new products the market wanted, both extended by acquiring large consulting businesses (Dell famously bought Perot Systems and HP bought EDS) in the hopes they could defend their PC installed base and create future sales. Both wanted to do more of what they had always done, rather than shift with emerging market needs.
But not only product sales were stagnating. Services were becoming more intensely competitive – from domestic and offshore services providers – hampering sales growth while driving down margins. Hopes of regaining growth in the “core” business – especially in the “core” enterprise markets – were proving illusory. Buyers didn’t want more PCs, or more PC services. They wanted (and now want) new solutions, and neither Dell nor HP is offering them.
So the big “cash hoard” that 24×7 would like investors to think will become dividends is frittered away by company leadership – spent on acquisitions, or “special projects,” intended to save the “core” business. When allocating resources, forecasts are manipulated to make defensive investments look better than realistic. Then the “business necessity” argument is trotted out to explain why acquisitions, or price reductions, are necessary to remain viable, against competitors, even when “the numbers” are hard to justify – or don’t even add up to investor gains. Instead of investing in growth, money is spent trying to delay the market shift.
Take for example Microsoft’s recent acquisition of Skype for $8.5B. As Arstechnia.com headlined “Why Skype?” This acquisition is another really expensive effort by Microsoft to try keeping people using PCs. Even though Microsoft Live has been in the market for years, Microsoft keeps trying to find ways to invest in what it knows – PCs – rather than invest in solutions where the market is shifting. New smartphone/tablet products come with video capability, and are already hooked into networks. Skype is the old generation technology, now purchased for an enormous sum in an effort to defend and extend the historical base.
There is no doubt people are quickly shifting toward smartphones and tablets rather than PCs. This is an irreversable trend:  Chart source BusinessInsider.com
Chart source BusinessInsider.com
Executive teams locked-in to defending their past spend resources over-investing in the old market, hoping they can somehow keep people from shifting. Meanwhile competitors keep bringing out new solutions that make the old obsolete. While Microsoft was betting big on Skype last week Mediapost.com headlined “Google Pushes Chromebook Notebooks.” In a direct attack on the “core” customers of Dell and HP (and Microsoft) Google is offering a product to replace the PC that is far cheaper, easier to use, has fewer breakdowns and higher user satisfaction.
Chromebooks don’t have to replace all PCs, or even a majority, to be horrific for Dell and HP. They just have to keep sucking off all the growth. Even a few percentage points in the market throws the historical competitors into further price warring trying to maintain PC revenues – thus further depleting that cash hoard. While the old gladiators stand in the colliseum, swinging axes at each other becoming increasingly bloody waiting for one to die, the emerging competitors avoid the bloodbath by bringing out new products creating incremental growth.
People love to believe in “value stocks.” It sounds so appealing. They will roll along, making money, paying dividends. But there really is no such thing. New competitors pressure sales, and beat down margins. Markets shift wtih new solutions, leaving fewer customers buying what all the old competitors are selling, further driving down margins. And internal decision mechanisms keep leadership spending money trying to defend old customers, defend old solutions, by making investments and acquisitions into defensive products extending the business but that really have no growth, creating declining margins and simply sucking away all that cash. Long before investors have a chance to get those dreamed-of dividends.
This isn’t just a high-tech story. GM dominated autos, but frittered away its cash for 30 years before going bankrupt. Sears once dominated retailing, now its an irrelevent player using its cash to preserve declining revenues (did you know Woolworth’s was a Dow Jones company until 1997?). AIG kept writing riskier insurance to maintain its position, until it would have failed if not for a buyout. Kodak never quit investing in film (remember 110 cameras? Ektachrome) until competitors made film obsolete. Xerox was the “copier company” long after users switched to desktop publishing and now paperless offices.
All of these were once called “value investments.” However, all were really traps. Although Dell’s stock has gyrated wildly for the last decade, investors have lost money as the stock has gone from $25 to $15. HP investors have fared a bit better, but the long-term trending has only had the company move from about $40 to $45. Dell and HP keep investing cash in trying to find past glory in old markets, but customers shift to the new market and money is wasted.
When companies stop growing, it’s because markets shift. After markets shift, there isn’t any value left. And management efforts to defend the old success formula with investments in extensions simply fritter away investor money. That’s why they are really value traps. They are actually risky investments, because without growth there is little likelihood investors will ever see a higher stock price, and eventually they always collapse – it’s just a matter of when. Meanwhile, riding the swings up and down is best left for day traders – and you sure don’t want to be long the stock when the final downturn hits.
by Adam Hartung | May 3, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
For the first time in 20 years, Apple’s quarterly profit exceeded Microsoft’s (see BusinessWeek.com “Microsoft’s Net Falls Below Apple As iPad Eats Into Sales.) Thus, on the face of things, the companies should be roughly equally valued. But they aren’t. This week Microsoft’s market capitalization is about $215B, while Apple’s is about $365B – about 70% higher. The difference is, of course, growth – and how a lack of it changes management!
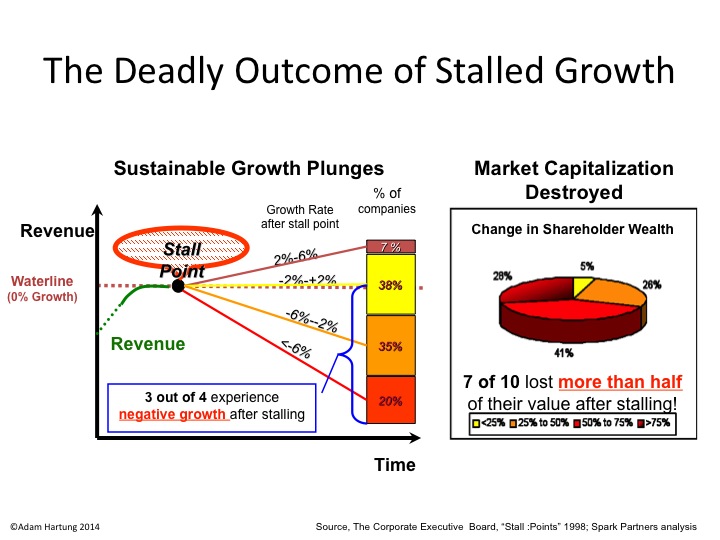
According to the Conference Board, growth stalls are deadly.
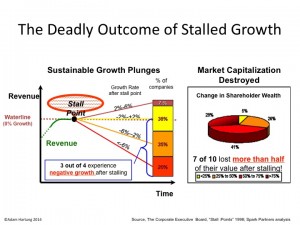
When companies hit a growth stall, 93% of the time they are unable to maintain even a 2% growth rate. 75% fall into a no growth, or declining revenue environment, and 70% of them will lose at least half their market capitalization. That’s because the market has shifted, and the business is no longer selling what customers really want.
At Microsoft, we see a company that has been completely unable to deal with the market shift toward smartphones and tablets:
- Consumer PC shipments dropped 8% last quarter
- Netbook sales plunged 40%
Quite simply, when revenues stall earnings become meaningless. Even though Microsoft earnings were up, it wasn’t because they are selling what customers really want to buy. In stalled companies, executives cut costs in sales, marketing, new product development and outsource like crazy in order to prop up earnings. They can outsource many functions. And they go to the reservoir of accounting rules to restate depreciation and expenses, delaying expenses while working to accelerate revenue recognition.
Stalled company management will tout earnings growth, even though revenues are flat or declining. But smart investors know this effort to “manufacture earnings” does not create long-term value. They want “real” earnings created by selling products customers desire; that create incremental, new demand. Success doesn’t come from wringing a few coins out of a declining market – but rather from being in markets where people prefer the new solutions.
Mobile phone sales increased 20% (according to IDC), and Apple achieved 14% market share – #3 – in USA (according to MediaPost.com) last quarter. And in this business, Apple is taking the lion’s share of the profits:

Image provided by BusinessInsider.com
When companies are growing, investors like that they pump earnings (and cash) back into growth opportunities. Investors benefit because their value compounds. In a stalled company investors would be better off if the company paid out all their earnings in dividends – so investors could invest in the growth markets.
But, of course, stalled companies like Microsoft and Research in Motion, don’t do that. Because they spend their cash trying to defend the old business. Trying to fight off the market shift. At Microsoft, money is poured into trying to protect the PC business, even as the trend to new solutions is obvious. Microsoft spent 8 times as much on R&D in 2009 as Apple – and all investors received was updates to the old operating system and office automation products. That generated almost no incremental demand. While revenue is stalling, costs are rising.
At Gurufocus.com the argument is made “Microsoft Q3 2011: Priced for Failure“. Author Alex Morris contends that because Microsoft is unlikely to fail this year, it is underpriced. Actually, all we need to know is that Microsoft is unlikely to grow. Its cost to defend the old business is too high in the face of market shifts, and the money being spent to defend Microsoft will not go to investors – will not yield a positive rate of return – so investors are smart to get out now!
Additionally, Microsoft’s cost to extend its business into other markets where it enters far too late is wildly unprofitable. Take for example search and other on-line products: 
Chart source BusinessInsider.com
While much has been made of the ballyhooed relationship between Nokia and Microsoft to help the latter enter the smartphone and tablet businesses, it is really far too late. Customer solutions are now in the market, and the early leaders – Apple and Google Android – are far, far in front. The costs to “catch up” – like in on-line – are impossibly huge. Especially since both Apple and Google are going to keep advancing their solutions and raising the competitive challenge. What we’ll see are more huge losses, bleeding out the remaining cash from Microsoft as its “core” PC business continues declining.
Many analysts will examine a company’s earnings and make the case for a “value play” after growth slows. Only, that’s a mythical bet. When a leader misses a market shift, by investing too long trying to defend its historical business, the late-stage earnings often contain a goodly measure of “adjustments” and other machinations. To the extent earnings do exist, they are wasted away in defensive efforts to pretend the market shift will not make the company obsolete. Late investments to catch the market shift cost far too much, and are impossibly late to catch the leading new market players. The company is well on its way to failure, even if on the surface it looks reasonably healthy. It’s a sucker’s bet to buy these stocks.
Rarely do we see such a stark example as the shift Apple has created, and the defend & extend management that has completely obsessed Microsoft. But it has happened several times. Small printing press manufacturers went bankrupt as customers shifted to xerography, and Xerox waned as customers shifted on to desktop publishing. Kodak declined as customers moved on to film-less digital photography. CALMA and DEC disappeared as CAD/CAM customers shifted to PC-based Autocad. Woolworths was crushed by discount retailers like KMart and WalMart. B.Dalton and other booksellers disappeared in the market shift to Amazon.com. And even mighty GM faltered and went bankrupt after decades of defend behavior, as customers shifted to different products from new competitors.
Not all earnings are equal. A dollar of earnings in a growth company is worth a multiple. Earnings in a declining company are, well, often worthless. Those who see this early get out while they can – before the company collapses.
Update 5/10/11 – Regarding announced Skype acquisition by Microsoft
That Microsoft has apparently agreed to buy Skype does not change the above article. It just proves Microsoft has a lot of cash, and can find places to spend it. It doesn’t mean Microsoft is changing its business approach.
Skype provides PC-to-PC video conferencing. In other words, a product that defends and extends the PC product. Exactly what I predicted Microsoft would do. Spend money on outdated products and efforts to (hopefully) keep people buying PCs.
But smartphones and tablets will soon support video chat from the device; built in. And these devices are already connected to networks – telecom and wifi – when sold. The future for Skype does not look rosy. To the contrary, we can expect Skype to become one of those features we recall, but don’t need, in about 24 to 36 months. Why boot up a PC to do a video chat you can do right from your hand-held, always-on, device?
The Skype acquisition is a predictable Defend & Extend management move. It gives the illusion of excitement and growth, when it’s really “so much ado about nothing.” And now there are $8.5B fewer dollars to pay investors to invest in REAL growth opportunities in growth markets. The ongoing wasting of cash resources in an effort to defend & extend, when the market trends are in another direction.
by Adam Hartung | Apr 26, 2011 | Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Summary:
- Everyone discriminates in hiring – just some is considered bad, and some considered good
- Only “good discrimination” inevitably leads to homogeneity and “group think” leaving the business vulbnerable to market shifts
- Efforts to defend & extend the historical success formula moves beyond hiring to include using internal bias to favor improvement projects and disfavor innovations
- Amazon has grown significantly more than Wal-Mart, and it’s value has quadrupled while Wal-mart’s has been flat, because it has moved beyond its original biases
The long list of people attacking Wal-Mart includes a class-action law suit between former female workers and their employer. The plaintiffs claim Wal-Mart systematically was biased, via its culture, to pay women less and limit their promotion opportunities. The case is prompting headlines like BNet.com‘s “Does Your Company Help You Discriminate?”
Actually, all cultures – and hiring programs – are designed to discriminate. It’s just that some discrimination is legal, and some is not. At Google it’s long been accepted that the bias is toward quant jocks and those with highest IQs. That’s not illegal. Saying that men, or white people, or Christians make better employees is illegal. But there is risk in all hiring bias – even the legal kind. To avoid the illegal discrimination, its smarter to overcome the “natural bias” that cultures create for hiring. And the good news is that this is better for the business’s growth and rate of return!
Successful organizations build a profile of “who did well around here – and why” as they grow. It doesn’t take long until that profile is what they seek. The downside is that quickly there’s not a lot of heterogeneity in the hiring – or the workforce. That leads to “group think,” which reinforces “not invented here.” Everyone becomes self-assured of their past success, and believes that if they keep doing “more of the same” the future will work out fine. Whether Wal-Mart’s hiring biases were legal – or not – it is clear that the group think created at Wal-Mart has kept it from innovating and moving into new markets with more growth.
Markets shift. New products, technologies and business practices emerge. New competitors figure out ways of providing new solutions. Customers drift toward new offerings, and growth slows. Unfortunately, bias keeps the early winner from accepting this market shift – so the company falls into serious growth troubles trying to do more, better, faster, cheaper of what worked before. Look at Dell, still trying to compete in PCs with its supply chain focus long after competitors have matched their pricing and started offering superior customer service and other advantages. Meanwhile, the market growth has moved away from PCs into products (tablets, smartphones) Dell doesn’t even sell.
Wal-Mart excels at its success formula of big, boring, low price stores. And its bias is to keep doing more of the same. Only, that’s not where the growth is in retailing any longer. The market for “cheap” is pretty well saturated, and now filled with competitors that go one step further being cheap (like Dollar General,) or largely match the low prices while offering better store experience (like Target) or better selection and varied merchandise (like Kohl’s). Wal-Mart is stuck, when it needs to shift. But its bias toward “doing what Sam Walton did that made us great” has now made Wal-Mart the target for every other retailer, and stymied Wal-Mart’s growth.
A powerful sign of status quo bias shows itself when leaders and managers start overly relying on “how we’ve done things here” and “the numbers.” The former leads to accepting recommendations fro hiring and promotion based upon similarity with previous “winners.” Investment opportunities to defend and extend what’s always been done sail through reviews, because everyone understands the project and everyone believes that the results will appear.
Nearly all studies of operational improvement projects show that returns rarely achieve the anticipated outcomes. Because these projects reinforce the status quo, they are assumed to be highly accurate projections. But planned efficiences do not emerge. Headcount reductions do not happen. Unanticipated costs emerge. And, most typically, competitors copy the project and achieve the same results, leading to price reductions across the board benefitting customers rather than company profits.
Doing more of the same is easily approved and rarely questioned – whether hiring, or investing. And if things don’t work out as expected results are labeled “business necessity” and everyone remains happy they made the original decision, even if it did nothing for market share, or profit improvement. Or perhaps turns out to have been illegal (remember Enron and Worldcom?)
To really succeed it is important we overcome biases. Look no further than Amazon. Amazon could have been an on-line book retailer. But by overcoming early biases, in hiring and new projects, Amazon has grown more than Wal-Mart the last decade – and has a much brighter future. Amazon now leads in a large number of retail segments, far beyond books. It has products which allow anyone to take almost any product to market – using the Amazon on-line tools, as well as inventory management.
And in publishing Amazon has become a powerhouse by helping self-published authors find distribution which was before unavailable, giving us all a much larger variety of book products. More recently Amazon pioneered e-Readers with Kindle, developing the technology as well as the inventory to make Kindle an enormous success. Simultaneously Amazon now offers a series of technical products providing companies access to the cloud for data and applications.
Where most companies would say “that’s not our business” Amazon has taken the approach of “if people want it, why don’t we supply it?” Where most organizations use numbers to kill projects – saying they are too risky or too small to matter or too low on “risk adjusted” rate of return Amazon creates a team, experiments and obtains real market information. Instead of worrying whether or not the initial project is a success or failure, market input is treated as learning and used to adapt. By continuously looking for new opportunities, and pushing those opportunities, Amazon keeps growing.
Every business develops a bias. Overcoming that bias is critical to success. From hiring to decision making, internal status quo police try to reinforce the bias and limit change. Often on the basis of “too much risk” or “too far from our core.” But that bias inevitably leads to stalled growth. Because new competitors never stop beating down rates of return on old success formulas, and markets never stop shifting.
Wal-Mart should look upon this lawsuit not as a need to defend and extend its past practices, but rather a wake-up call to be more open to diversity – in all aspects of its business. Wal-mart doesn’t need to win this lawsuit neary as badly as it needs to create an ability to adapt. Until then, I’d recommend investors sell Wal-Mart, and buy Amazon.com.
Chart of WMT stock performance compared to AMZN last 5 years (source Yahoo.com)

by Adam Hartung | Apr 17, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Research in Motion pioneered the smartphone business. While Motorola, Samsung and others thought the answer to market growth was making ever cheaper mobile phones, RIM figured out that corporations wanted to put phones in employee hands, control usage cost, while also securely offering email distribution and texting. Blackberry handsets and servers met user needs while providing IT departments with everything they needed.
This success formula was a winner, driving tremendous growth for RIM. People joke about their “crackberry” connecting them to their company 24×7, but it was a tremendous productivity enhancer. RIM produced a consistent string of growing revenues and earnings, meeting or exceeding projections. RIM still dominates the “enterprise” smartphone business. The overwhelming majority of mobile phones issued by companies are still Blackberries.
“RIM’s CEO is Annoyed that People Don’t Appreciate Our Profits” headlined Silicon Alley Insider. He can’t understand why the stock languishes, despite meeting financial projections. When challenged about whether or not RIM is as secure as it claims, “RIM CEO Abruptly Ends an Interview After Getting Annoyed About Security Questons” (SAI).
That the CEO is annoyed is the first of two reasons you need to sell RIMM now. If you are waiting for a recovery to old highs, forget about it. Won’t happen. Can’t happen.
The mobile phone/smartphone market has taken an enormous shift. Apple’s iPhone introduced the “app” phenomenon – allowing smartphone users to do a plethora of things on their devices that aren’t possible on a Blackberry. If we just count apps, as a baseline, iPhone users can do some 350,000 things that Blackberry users cannot. Additionally, iPhones – and increasingly Android phones – are simply a lot easier to use, with bigger touch screens, more built-in functionality and easier user navigation.
As charted in my last column, RIM has only about 5% the apps of iPhone. And less than 10% the apps of Android. Even Microsoft will soon provide more apps than Blackberry. But the CEO of RIM is stuck – defending his company and its success formula – rather than aggressively migrating the company into new products. He’s hoping all those company employees, including execs, now carrying 2 phones – their corporate Blackberry and personal iPhone – will keep doing that.
He’s letting the re-invention gap between RIMM and Apple/Google widen with every passing quarter. While no other provider offers the “enterprise solution” of RIM, increasingly the gap between the usability of new solutions and RIM is widening. It won’t be long before users won’t put up with having 2 phones – and the loser will clearly be RIM
And it won’t be long before people completely stop carrying laptops as well. Rather quickly we are seeing a market shift to tablets. Into this market RIMM launched its Playbook product last week. And that’s the second reason you need to sell RIMM.
We all know the iPad has been a remarkable success. To date, nobody has developed a tablet that users, or reviewers, find comparable. Unfortunately, RIM launched its Playbook tablet to entirely consistent reviews, such as “The Playbook: Blackberry’s ‘Unfinished’ Product” headlined at TheWeek.com. The Playbook simply isn’t comparable to an iPad – and doesn’t look like it ever will be.
Most concerning, to use a Playbook you must also have a Blackberry. Playbook relies on the Blackberry to provide connectivity – via Bluetooth. In other words, RIM is trying to keep customers locked-in to Blackberries, using Playbook to defend and extend the original company product. Playbook doesn’t even look like it’s ever intended to be a stand-alone winner. And that’s a really bad strategy.
RIM sees Playbook is seen as an extension of the Blackberry product line; the first in a transition to a new operating system for all products. Not a product designed to compete heads-up against other tablets. It lacks apps, it lacks its own connectivity, it has a smaller screen, and it doesn’t have the intuitive interface. Basically, it’s an effort to try and keep Blackberry users on Blackberries – an effort to defend and extend the original success formula.
When markets shift it is absolutely critical competitors shift with them. Xerox invented desktop publishing at its PARC facility, but tried to defend xerography and lost the new market to Apple. Kodak invented digital cameras, but tried to defend the film business and lost the new market to Japanese competitors. When the CEO tries to defend and extend the old success formula after a market shifts only bad things happen. When new products are extensions of old products, while competitors are bringing out game changers, the world only becomes uglier and uglier for the stuck, old-line competitor.
The analysts are right. RIM has no future growth. Companies are already switching into iPhones, iPads and Androids. Simultaneously, Microsoft will pour billions into helping Nokia push Windows 7 phones and future tablets the next 2 years, and that will be targeted right at “enterprise users” which are RIM’s “core.” Microsoft will spend far more resources than RIM could ever match trying to defend its “installed base.” RIMM is stuck fighting to keep current users, while the market growth is elsewhere, and those emerging competitors are quickly going to hollow out RIM’s market.
There’s simply no way RIM can increase its value. Time to sell.
Update 4/20/2011 Goldman Sachs Survey Results – CIO intention to adopt Tablets by Operating System provider:

Published in SiliconAlleyInsider.com
by Adam Hartung | Mar 31, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Leadership, Lock-in
Here’s a link to a very short video (1-2 minutes) posted on Facebook today about Lock-in. Hope you enjoy! Please provide feedback and comments!
Adam Hartung on Lock-in – Why we do it, and how to be better by managing it! Includes a discussion about using social media – why it is so important, why so many people are overlooking these tools and the success application can create.
I was recently asked to be interviewed regarding most of the major themes of “Create Marketplace Disruption” and why they are timely – and important – to businesses globally. A few exerpts from those interviews have been edited, and are being sent to me for posting on YouTube and Facebook. This is the first in the series.
by Adam Hartung | Mar 25, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in
It is unlikely anyone in business or government thinks productivity is a bad thing. Productive students get their homework done faster, and learn more in the available time. Productive musicians make more recordings, and tend to learn more over their careers. And productive companies produce more goods and services with less inputs – like labor – thus offering more to customers at lower cost while making more money for investors. At a national level, the more productive we are at everything from growing wheat to making cabinets to writing smartphone apps improves the quantity of goods available to our population – growing the gross domestic product (GDP.) Improving productivity is one of the most critical activities to creating and maintaining a healthy economy, improving incomes and generating wealth.
Then why is American policy so anti-productivity?
American manufacturers today are about the most productive in the world. In the Wall Street Journal's "The Truth About U.S. Manufacturing" we learn that American factory workers are producing triple the output of 1972. The use of ever more sophisticated equipment, often with digital controls, and a higher trained workforce has made it possible to make more and more stuff with less and less labor. While considerable manufacturing has gone offshore, it is not because our workers are competitively unproductive. To the contrary, productivity is amongst the highest in the world!
Unfortunately, most of America's business/economic policy at the government level has been trying to preserve jobs that are, well, not that productive. Take for example agriculture subsidies. They pay farmers to produce less and otherwise make less productive use of land, feedstocks, grains, etc. By giving farmers (most of which are now huge corporations, not the "family farm" circa 1970 and before) subsidies it actually lowers agricultural productivity.
Similarly, bank and auto bailouts (and all subsidies to any manufacturer) in effect lowers productivity. It gives money to a bank, which makes nothing. Or to an unproductive manufacturer to keep its plant operating when the value of the output is insufficient to cover costs. These spending programs serve only to defend and extend the least productive jobs in society – jobs that are economically unviable. By spending money in these areas the government attempts to preserve the old (companies such as GM and Chrysler) at the expense of productivity.
America can create highly productive jobs
"Amazon.com On Hiring Spree" is the Seattle Times headline. Amazon has revolutionized book retailing, publishing and is changing a number of other markets as well. The result is a far more productive workforce in these industries than previous competitors. Borders, to cite a recent example, could not be nearly as efficient selling or publishing books with its out of date model, so it recently followed 90% of other book sellers into bankruptcy. The more productive company, Amazon, is hiring people as fast as it can to grow its business. Its productivity allows Amazon to sell more and create jobs.
Had the government chosen to bail out Borders there would have been a public outcry. Why should we protect the jobs of those store shelf stockers? Likewise, as the number of printed books drops, replaced by digital books, should it be government policy to subsidize book (or magazine, or newspaper) publishers/printers? Whenever a business is no longer competitively productive – whether it be agricultural, manufacturing or anything else – bailouts serve only to keep the unproductive competitor alive. Which actually harms the more competitive company that subsequently must fight the subsidized competitor.
The right policy would be to subsidize Amazon. Amazon is growing. Theoretically, the more money Amazon has the faster it could grow and the more jobs it could create. But, of course, nobody feels good about subsidizing a growing, profitable concern. And Amazon isn't asking for subsidies, anyway.
Our public investments are shifting in the wrong direction.
The right public policy is to invest in creating new Amazons. New businesses that create products and services which are desirable to customers, productively using resources and creating jobs. By helping these new businesses get going the government spending creates new markets. Government money "primes the pump" for investors. Early stage funding allows the business to get started, create a product or service, generate initial revenues, demonstrate a P&L and entice others to invest. The payback to society is a growing enterprise that creates jobs, both of which creates future tax revenues which repay the early investment funding.
The current administration touts investing in the tools for creating growth. In early February the MercuryNews.com reported on a Presidential speech in Michigan, "Obama Promotes Plan for Near Universal High-Speed Wireless." But, like previous Presidential administrations, this is just a lot of talk. While Mr. Obama may think national wireless technology to promote economic growth is good, there is no money for it. In the same article it is noted that Michigan congressional representatives, who resoundingly backed putting billions into the auto bailouts, question the efficacy of investing in emerging infrastructure tools. Protecting the past, while questioning (or opposing) investments in the future.
Unfortunately, for the last 50 years American policy has been headed in the wrong direction! Innovation investment projects peaked around the Kennedy administration (early 1960s) with several American efforts to dominate new technologies through programs such as the famous "space race." Since then, less and less has gone into America's future, and more and more has been spent preserving the past – through entitlements, military spending and tax cuts which provide less and less incentive to invest in unproven projects.

Source: Silicon Alley Insider Chart of the Day from BusinessInsider.com
Since 1953 government "pump priming" by spending on R&D for innovations has declined by 50%!!! No longer is even 1% of Gross Domestic Product spent on R&D. Businesses, which require an immediate return on investment and are generally loath to spend money on things which are uncertain, have been left to fill the vacuum. As a result, total spending has been stagnant. Worse, most spending by business is on sustaining innovations – improvements which defend and extend an existing business – rather than on breakthroughs which create new markets, and a lot more jobs (for more on sustaining innovation investments by business read Clayton Christenson's books including "The Innovator's Dilemma.") Investment in innovation has been woefully underfunded, allowing America's economic leadership position to shrink.
America is driving innovation offshore
The Wall Street Journal has reported "More Companies Plan to Put R&D Offshore." When things are equal, business will invest where the costs are lowest. With little incentive to undertake innovation in America, increasingly U.S. companies are moving their R&D — along with manufacturing, customer service, telesales, etc. — to emerging markets. And their plans are to increase this movement offshore by 50-100% by 2015!
![[EMERGING]](http://si.wsj.net/public/resources/images/MK-BK032A_EMERG_NS_20110221173344.jpg)
What will happen if innovation investments move from America into emerging markets? Will intellectual property remain an American advantage? Will new product development be done in America, or elsewhere? If the manufacturing is already in these markets, is it hard to predict that new products will increasingly be made offshore as well? Asked another way, if we outsource the innovation jobs – what jobs will America have left?
A dramatic change in American policy is needed
Last week America started bombing Libya. Part of protecting the national interest. But, this is not free – reportedly costing Americans $100M/day. Two weeks is $1.4B (probably a lot more, to be honest.). Let's not debate whether this is necessary, but rather recognize (as Roseanne Rosannadanna used to say on Saturday Night Live) "it's always something." There are programs, policies, military bases, agricultural lands, national parks and jobs to protect in every district of America – and its interests around the globe. And that's increasingly where America's money goes. Not into innovation.
So why are Americans surprised that job growth struggles? When the head of GE, a company that has moved manufacturing, information technology, engineering and R&D to offshore centers across the last decade, is made head of the U.S. jobs initiative is there much doubt? When the spending and incentives, as well as the selected leaders, have as their #1 interest preserving the past – largely in areas where American productivity lags – why would anyone expect new job creation?
America's protectionist mentality is causing its lead in innovation to slip away. The President, administration officials, Senators and Congresspeople needs to quit thinking that talking about innovation is going to make any difference in investments, or job creation. If America wants to remain globally economically vibrant it requires a change in investments – starting with more money for R&D via grants, subsidies and tax breaks.
If America wants jobs, and healthy economic growth, it needs innovation. Innovation that will create new, highly productive jobs And that requires investing in the future, rather than spending all the money protecting the past.
by Adam Hartung | Mar 22, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Summary:
- The Japanese nuclear crisis is the result of historical industry decisions to build very large facilities and transmit power to distant locations – a strategy at risk of “force majure” activities
- U.S. electric utilities are locked-in to identical approaches to generation and transmission, which puts them at equal risk AND limits their willingness to innovate or implement new solutions
- Historical industry approaches to planning are all based on extending the past, even though new technologies and approaches offer potentially better, and less risky, solutions. Utilities are merely one example
- Google is expert in a far better planning approach, using scenario planning for identifying and taking to market innovations and new solutions
- All companies, would benefit from planning like Google, rather than using traditional approaches – and several are bullet listed below
- The electric utility industry really needs to adopt a Google approach, or everyone remains at risk
Everybody is now aware of the great radiation risk Japan faces from its damaged nuclear reactor powered electricity generators. This has repercussions on U.S. electric utilities, as Americans have renewed concerns about the safety of similar General Electric supplied reactors.
For example, Crain’s Chicago Business reports “Exelon Faces Regulatory Fallout After Japanese Nuclear Disaster.” The country’s largest nuclear plant operator is facing stepped-up reviews, likely delays in expansion, and discussions about long-term viability of facilities that are 30 years into an anticipated 40 year life. All of this threatens the viability of meeting affordable electricity needs for millions of midwestern Americans in as little as 5 years. And it puts a lot of risk on the viability of Exelon as a going concern should the regulators require extensive re-investment to keep the plants open, or build replacements – most likely without a rate increase. All utilities dependent upon nuclear – and coal as well – for generation are now facing significant challenges.
This points out a horrible weakness in planning by most participants in America’s electric utility industry. Almost all planning boils down to “we need to increase capacity to meet needs. The cost of new plants, plant expansions and transmission lines from massive facilities to customers is $X, therefore, we need to lobby regulators, rate-setters and the populace to allow us a rate increase of $.xxx per kilowatt hour to cover the cost.” Planning entirely driven by the past. Projecting the future based upon historical demand, sources of generation, cost of fuel, etc. utilities mostly keep planning to do what they have always done, and asking regulators and customers to fund doing what they always did. If you want anything new (like a renewables effort) then the companies want the cost for that added on top of the “business as usual” price increase.
But customers are increasingly tired of hearing about rising rates, while they are constantly trying to conserve. The old “compact” in which the price regulators guaranteed utilities a rate of return is under considerable stress. Increasingly, people are asking why they need to pay more, why these plants are so expensive, why the industry keeps doubling down on old technologies and fuel sources. Customers, and regulators, are asking for innovation, but the industry offers almost nothing, because it’s planning is all about extending the past, and defending its historical approach and investments.
Today we know that the industry’s future will not be like the past. Increasingly customers (with government support in many cases) are demanding changes in the sourcing of electricity. Requesting decommissioning of polluting generators (coal in particular), shut-downs of perceived risky, and now aging, nuclear facilities, more supply from renewable, or sustainable, sources — and without higher prices.
There are a lot of new technologies available. And some customers recommend a dramatic change in approach, from huge, centralized generation facilities to many smaller, safer, renewable generation facilities that are decentralized and closer to end-users. But most industry veterans are unable to even consider these options, because they see no way to get to the future from today. They are locked-in to defending and extending what the industry has always done, even if it means extending known risks, environmental concerns and creating higher prices for fuel and maintenance.
And that’s where Larry Page and Google have a lot to offer the utility industry planners. Instead of planning from the past forward, Google plans from the future back to the present. By helping employees develop future scenarios the leaders at Google identify far better solutions than the linear, historical planning approaches. Once a better future is identified, then the organization is unleashed to create that future by planning backward from the scenario, figuring out how to implement it.
Wired magazine, in “Larry Page Wants to Return Google to its Start-up Roots” gives great insights to how Google has created a $30B business in a decade – using scenario planning at the heart of its approach to business.
- Don’t fear being audacious when setting goals. Even if you don’t reach the ultimate goal, your improvement could be game-changing for the industry and greatly benefit the early adopter
- Instead of saying trying to help somebody with an immediate question, ask what would have the maximum impact in 10 years. Don’t just accept more of the same, look for the best answer
- Leaders should not fear being viewed as having stepped into the future, and returned to tell everyone what they’ve seen
- Don’t assume that the way things are done is the best way. Instead, ask “why is it done like that? Is there possibly a better way?”
- Is the obstacle to future success something that is impossible – say because of the laws of physics – or is the obstacle a need for resources – in engineering, scale design or implementation? Don’t confuse things that can’t be done with things that simply lack resources (even if the initial resource demand seems very high)
- When someone pitches an idea, leader’s should avoid questioning the viability. Rather, they should offer a variation that is an order of magnitude more ambitious and ask why the latter cannot be accomplished.
- Ask regulators what they want, and try really hard to achieve that goal rather than arguing with them. Offer creative solutions that are non-traditional, but that just might achieve the goal. Change the conversation to achieving the goal, rather than extending the past.
- If an idea requires creative thinking, be excited about it. Don’t hesitate to represent unrealistic expectations.
- Speed is really, really important. If there is merit, rush it toward the future state as fast as possible. Let implementation and the marketplace determine what’s successful, rather than trying to guess.
- Do the numbers, but don’t expect those who disagree to believe your numbers. It’s easy for people to pooh-pooh projections. Don’t let disagreement over forecasts stop you from proceeding.
- Don’t let potential legal problems stop you. Take action, and deal with legal issues when, and if, they arise.
Planning for the future, and being ambitious about what that future entails, has created a slew of new products from Google that have benefited everyone around the world. Google’s use of scenario planning to drive development and investments is a business implementation of an historical echo – asking not what Google needs from historical customers to succeed, but rather what Google can do to create something future customers will value. Google uses planning to rush headlong into providing a growing and profitable future, rather than trying to optimize the historical solution.
Giant, centralized distribution facilities that use nuclear or fossil fuels, then sending electricity over massive distances losing upwards of 70-80% of the power in transmission, is the historical utility industry approach. For a very long time it worked pretty darn well. But the limitations of that approach are being seen, and felt, in many locations – causing blackouts in various regions, health risks in others, rising polution levels, rising demands for limited fuels, higher costs (especially for maintenance and upgrades) and potential deadly disasters from unexpected events of mother nature. Industry outsiders question whether America’s growth will be limited (due to supply or pricing issues) if this approach is not changed.
Lots of options exist for the electric utility industry to do things differently. But it will take a big change in how the industry leaders plan. Maybe they’ll ask the folks at Google for a few ideas on how to change their approach to planning. Can you imagine a future where Google managed the electric grid?
by Adam Hartung | Mar 9, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, eBooks, Food and Drink, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in, Openness
Summary:
- McDonald's relies on operational improvements to raise profits, these are short-lived and give no growth
- McDonald's growth cycles, and investors forget long-term it isn't growing much at all
- You can't depend on recurring recessions to make your business look good
- Apple has shown how to create long-term revenue growth, and greater investor wealth, by developing new markets and solutions
- Investors in McDonald's are likely to be less pleased than investors in Apple
Subway is now #1 in size, as "McDonald's Loses World's Biggest Title to Subway" according to Crain's Chicago Business. The transition wasn't hard to predict, since Subway has been much larger in the USA for several years. Now Subway has gained on McDonald's internationally. What's striking about this is that McDonald's could see it coming, and really did nothing about it. While Subway keeps focused on growth, McDonald's has focused on preserving its historical business. And that bodes poorly for long-term investor performance.
For more than a decade McDonald's size has swung back and forth as it opened stores, then closed hundreds in an "operational improvement program," before opening another round of stores – to then repeat the cycle. McDonald's has not shown any US store growth for a long time, and has relied on expanding its traditional business offshore.
Even the menu remains almost unchanged, dominated by burgers, fries and soft drinks. "New" product rollouts have largely been repeats of decades old products, like McRib, which cycle on and off the menu. And the most "strategic" decision we hear about was executives spending countless hours, along with thousands of franchisees, trying to figure out whether or not to reduce the amount of cheese on a cheeseburger (which they did, saving billions of dollars.) Even though it spent almost a decade figuring out how to launch McCafe, the whole idea gets little atttention or promotion. There just isn't much energy put into innovation, or growth at McDonald's. Or even trying to be a leader in new marketing tools like social media, where chains like Papa John's have done much better.
Most people have forgotten that McDonald's acquired and funded the growth of Chipotle's, one of the fastest growing quick food chains. But in 2006 McDonald's leadership sold Chipotle's to raise cash to fund another one of those operational improvement rounds. The business that showed the most promise, that has much more growth opportunity than the tiring McDonald's brand, was sold off in order to Defend and Extend the known, but not so great, McDonald's.
Sort of like selling your patents in order to pay for maintenance and upgrades on the worn out plant tooling.
Soon after Chipotle's sale the "Great Recession" started. And people quit dining out – or went downmarket. Thousands of restaurants closed, and chains like Bennigan's declared bankruptcy. As people started eating a bit more frequently in McDonald's investors cheered. But, this was really more akin to the old phrase "even a stopped clock is right twice a day." McDonald's was the benefactor of an unanticipated economic event. And as the economy has improved McDonald's has cheered its improved oprations and higher profits. But, where is future growth? What will create long-term growth into 2015 and 2020? (To be honest, I'm not sure where this will be for Subway, either.)
This cycle of bust and repair – which will lead to another bust when a competitor or other external event challenges McDonald's unaltered success formula – is very different from what's happened at Apple. Rather than raising money to defend its historical business (the Macintosh business) Apple actually cut back its Mac products to fund development of new businesses – the big winner being iPod and iTunes. Then Apple focused on additional new markets, transforming smart phone growth with the iPhone and altering the direction of computing with the iPad. Rather than trying to Defend its past and Extend into new markets (like McDonald's international efforts) Apple has created, and led, new markets.
Performance at Apple has been much better than McDonald's. As we can see, only during the clock-stopped period at the height of the recession did investors lose faith in Apple's growth, while defaulting to defensiveness at McDonald's.

Chart source: Yahoo Finance
Steve Toback at bNet.com gives us insight into how Apple has driven its growth in "10 Ways to Think Different – Inside Apple's Cult-like Culture." These 10 points look nothing like the McDonald culture – or hardly any company that has growth problems. A quick scan gives insight to how any company can identify, develop and grow with new solutions in new markets:
- Empower employees to make a difference.
- Value what's important, not minutiae
- Love and cherish the innovators
- Do everything important internally
- Get marketing
- Control the message
- Little things make a big difference
- Don't make people do things, make them better at doing things
- When you find something that works, keep doing it
- Think different
What's most worrisome is that the protectionist culture we see at McDonald's, and frankly most U.S. companies, is the kind that led General Motors to years of faultering results and eventual bankruptcy. Recall that GM once bought Hughes Aircraft and EDS as growth devices (around 1980,) and opened the greenfield Saturn division to learn how to compete with offshore auto makers head-on. But the first two were sold, just like McDonald's sold Chipotle, to raise funds for propping up the poorly performing auto business. Saturn was gutted of its uniqueness in cost-saving programs to "align" it with the other auto divisions, and closed in the recent bankruptcy. (Read more detail on The Fall of GM in this short eBook.)
While McDonald's isn't at risk of immediate bankruptcy, investors need to understand that it's value is unlikely to rise much. Operational improvements are not the source of growth. They are short-term tactics to support historical behaviors which trade off short-term profit improvement for long-term new market development. In McDonald's case, this latest round of performance focus matched up with an economic downturn, unexpectedly benefitting McDonald's very quickly. But long-term value comes from creating new business opportunities that meet changing needs. And for that you need to not sell your innovations — instead, invest in them to drive growth.



![[EMERGING]](http://si.wsj.net/public/resources/images/MK-BK032A_EMERG_NS_20110221173344.jpg)