
by Adam Hartung | Jul 17, 2015 | Current Affairs, General, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle
Most analysts, and especially “chartists,” put a lot of emphasis on earnings per share (EPS) and stock price movements when determining whether to buy a stock. Unfortunately, these are not good predictors of company performance, and investors should beware.
Most analysts are focused on short-term, meaning quarter-to-quarter, performance. Their idea of long-term is looking back 1 year, comparing this quarter to same quarter last year. As a result, they fixate on how EPS has done, and will talk about whether improvements in EPS will cause the “multiple” (meaning stock price divided by EPS) will “expand.” They forecast stock price based upon future EPS times the industry multiple. If EPS is growing, they expect the stock to trade at the industry multple, or possibly somewhat better. Grow EPS, hope to grow the multiple, and project a higher valuation.
Analysts will also discuss the “momentum” (meaning direction and volume) of a stock. They look at charts, usually less than one year, and if price is going up they will say the momentum is good for a higher price. They determine the “strength of momentum” by looking at trading volume. Movements up or down on high volume are considered more meaningful than on low volume.
But, unfortunately, these indicators are purely short-term, and are easily manipulated so that they do not reflect the actual performance of the company.
At any given time, a CEO can decide to sell assets and use that cash to buy shares. For example, McDonald’s sold Chipotle and Boston Market. Then leadership took a big chunk of that money and repurchased company shares. That meant McDonalds took its two fastest growing, and highest value, assets and sold them for short-term cash. They traded growth for cash. Then leadership spent that cash to buy shares, rather than invest in in another growth vehicle.
 This is where short-term manipulation happens. Say a company is earning $1,000 and has 1,000 shares outstanding, so its EPS is $1. The industry multiple is 10, so the share price is $10. The company sells assets for $1,000 (for purposes of this exercise, let’s assume the book value on those assets is $1,000 so there is no gain, no earnings impact and no tax impact.)
This is where short-term manipulation happens. Say a company is earning $1,000 and has 1,000 shares outstanding, so its EPS is $1. The industry multiple is 10, so the share price is $10. The company sells assets for $1,000 (for purposes of this exercise, let’s assume the book value on those assets is $1,000 so there is no gain, no earnings impact and no tax impact.)
Company leadership says its shares are undervalued, so to help out shareholders it will “return the money to shareholders via a share repurchase” (note, it is not giving money to shareholders, just buying shares. $1,000 buys 100 shares. The number of shares outstanding now falls to 900. Earnings are still $1,000 (flat, no gain,) but dividing $1,000 by 900 now creates an EPS of $1.11 – a greater than 10% gain! Using the same industry multiple, the analysts now say the stock is worth $1.11 x 10 = $11.10!
Even though the company is smaller, and has weaker growth prospects, somehow this “refocusing” of the company on its “core” business and cutting extraneous noise (and growth opportunities) has led to a price increase.
Worse, the company hires a very good investment banker to manage this share repurchase. The investment banker watches stock buys and sells, and any time he sees the stock starting to soften he jumps in and buys some shares, so that momentum remains strong. As time goes by, and the repurchase program is not completed, selectively he will make large purchases on light trading days, thus adding to the stock’s price momentum.
The analysts look at these momentum indicators, now driven by the share repurchase program, and deem the momentum to be strong. “Investors love the stock” the analysts say (even though the marginal investors making the momentum strong are really company management) and start recommending to investors they should anticipate this company achieving a multiple of 11 based on earnings and stock momentum. The price now goes to $1.11 x 11 = $12.21.
Yet the underlying company is no stronger. In fact one could make the case it is weaker. But, due to the higher EPS, better multiple and higher share price the CEO and her team are rewarded with outsized multi-million dollar bonuses.
But, companies the last several years did not even have to sell assets to undertake this kind of manipulation. They could just spend cash from earnings. Earnings have been at record highs, and growing, for several years. Yet most company leaders have not reinvested those earnings in plant, equipment or even people to drive further growth. Instead they have built huge cash hoards, and then spent that cash on share buybacks – creating the EPS/Multiple expansion – and higher valuations – described above.
This has been so successful that in the last quarter untethered corporations have spent $238B on buybacks, while earning only $228B. The short-term benefits are like corporate crack, and companies are spending all the money they have on buybacks rather than reinvesting in growth.
Where does the extra money originate? Many companies have borrowed money to undertake buybacks. Corporate interest rates have been at generational (if not multi-generational) lows for several years. Interest rates were kept low by the Federal Reserve hoping to spur borrowing and reinvestment in new products, plant, etc to drive economic growth, more jobs and higher wages. The goal was to encourage companies to take on more debt, and its associated risk, in order to generate higher future revenues.
Many companies have chosen to borrow money, but rather than investing in growth projects they have bought shares. They borrow money at 2-3%, then buy shares – which can have a much higher immediate impact on valuation – and drive up executive compensation.
This has been wildly prevalent. Since the Fed started its low-interest policy it has added $2.37trillion in cash to the economy. Corporate buybacks have totaled $2.41trillion.
This is why a company can actually have a crummy business, and look ill-positioned for the future, yet have growing EPS and stock price. For example, McDonald’s has gone through rounds of store closures since 2005, sold major assets, now has more stores closing than opening, and has its largest franchisees despondent over future prospects. Yet, the stock has tripled since 2005! Leadership has greatly weakened the company, put it into a growth stall (since 2012,) and yet its value has gone up!
Microsoft has seen its “core” PC market shrink, had terrible new product launches of Vista and Windows 8, wholly failed to succeed with a successful mobile device, written off billions in failed acquisitions, and consistently lost money in its gaming division. Yet, in the last 10 years it has seen EPS grow and its share price double through the power of share buybacks from its enormous cash hoard and ability to grow debt. While it is undoubtedly true that 10 years ago Microsoft was far stronger, as a PC monopolist, than it is today – its value today is now higher.
Share buybacks can go on for several years. Especially in big companies. But they add no value to a company, and if not exceeded by re-investments in growth markets they weaken the company. Long term a company’s value will relate to its ability to grow revenues, and real profits. If a company does not have a viable, competitive business model with real revenue growth prospects, it cannot survive.
Look no further than HP, which has had massive buybacks but is today worth only what it was worth 10 years ago as it prepares to split. Or Sears Holdings which is now worth 15% of its value a decade ago. Short term manipulative actions can fool any investor, and actually artificially keep stock prices high, so make sure you understand the long-term revenue trends, and prospects, of any investment. Regardless of analyst recommendations.
by Adam Hartung | Jul 8, 2015 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Microsoft announced today it was going to shut down the Nokia phone unit, take a $7.6B write-off (more than the $7.2B they paid for it,) and lay off another 7,800 employees. That makes the layoffs since CEO Nadella took the reigns almost 26,000. Finding any good news in this announcement is a very difficult task.
 Unfortunately, since taking over as Microsoft’s #1 leader, Mr. Nadella has been remarkably predictable. Like his peer CEOs who take on the new role, he has slashed and burned employment, shut down at least one big business, taken massive write-offs, and undertaken at least one wildly overpriced acquisition (Minecraft) that is supposed to be a game changer for the company. He apparently picked up the “Turnaround CEO Playbook” after receiving the job and set out on the big tasks!
Unfortunately, since taking over as Microsoft’s #1 leader, Mr. Nadella has been remarkably predictable. Like his peer CEOs who take on the new role, he has slashed and burned employment, shut down at least one big business, taken massive write-offs, and undertaken at least one wildly overpriced acquisition (Minecraft) that is supposed to be a game changer for the company. He apparently picked up the “Turnaround CEO Playbook” after receiving the job and set out on the big tasks!
Yet he still has not put forward a strategy that should encourage investors, employees, customers or suppliers that the company will remain relevant long-term. Amidst all these big tactical actions, it is completely unclear what the strategy is to remain a viable company as customers move, quickly and in droves, to mobile devices using competitive products.
I predicted here in this blog the week Steve Ballmer announced the acquisition of Nokia in September, 2013 that it was “a $7.2B mistake.” I was off, because in addition to all the losses and restructuring costs Microsoft endured the last 7 quarters, the write off is $7.6B. Oops.
Why was I so sure it would be a mistake? Because between 2011 and 2013 Nokia had already lost half its market share. CEO Elop, who was previously a Microsoft senior executive, had committed Nokia completely to Windows phones, and the results were already catastrophic. Changing ownership was not going to change the trajectory of Nokia sales.
Microsoft had failed to build any sort of developer community for Windows 8 mobile. Developers need people holding devices to buy their software. Nokia had less than 5% share. Why would any developer build an app for a Windows phone, when almost the entire market was iOS or Android? In fact, it was clear that developing rev 2, 3, and 4 of an app for the major platforms was far more valuable than even bothering to port an app into Windows 8.
Nokia and Windows 8 had the worst kind of tortuous whirlpool – no users, so no developers, and without new (and actually unique) software there was nothing to attract new users. Microsoft mobile simply wasn’t even in the game – and had no hope of winning. It was already clear in June, 2012 that the new Windows tablet – Surface – was being launched with a distinct lack of apps to challenge incumbents Apple and Samsung.
By January, 2013 it was also clear that Microsoft was in a huge amount of trouble. Where just a few years before there were 50 Microsoft-based machines sold for every competitive machine, by 2013 that had shifted to 2 for 1. People were not buying new PCs, but they were buying mobile devices by the shipload – literally. And there was no doubt that Windows 8 had missed the mobile market. Trying too hard to be the old Windows while trying to be something new made the product something few wanted – and certainly not a game changer.
A year ago I wrote that Microsoft has to win the war for developers, or nothing else matters. When everyone used a PC it seemed that all developers were writing applications for PCs. But the world shifted. PC developers still existed, but they were not able to grow sales. The developers making all the money were the ones writing for iOS and Android. The growth was all in mobile, and Microsoft had nothing in the game. Meanwhile, Apple and IBM were joining forces to further displace laptops with iPads in commercial/enterprise uses.
Then we heard Windows 10 would change all of that. And flocks of people wrote me that a hybrid machine, both PC and tablet, was the tool everyone wanted. Only we continue to see that the market is wildly indifferent to Windows 10 and hybrids.
Imagine you write with a fountain pen – as most people did 70 years ago. Then one day you are given a ball point pen. This is far easier to use, and accomplishes most of what you want. No, it won’t make the florid lines and majestic sweeps of a fountain pen, but wow it is a whole lot easier and a darn site cheaper. So you keep the fountain pen for some uses, but mostly start using the ball point pen.
Then the fountain pen manufacturer says “hey, I have a contraption that is a ball point pen, sort of, and a fountain pen, sort of, combined. It’s the best of all worlds.” You would likely look at it, but say “why would I want that. I have a fountain pen for when I need it. And for 90% of the stuff I write the ball point pen is great.”
That’s the problem with hybrids of anything – and the hybrid tablet is no different. The entrenched sellers of old technology always think a hybrid is a good idea. But once customers try the new thing, all they want are advancements to the new thing. (Just look at the interest in Tesla cars compared to the stagnant sales of hybrid autos.)
And we’re up to Surface 3 now. When I pointed out in January, 2013 that the markets were rapidly moving away from Microsoft I predicted Surface and Surface Pro would never be important products. Reader outcry at that time from Microsoft devotees was so great that Forbes editors called me on the carpet and told me I lacked the data to make such a bold prediction. But I stuck by my guns, we changed some language so it was less blunt, and the article ran.
Two and a half years later and we’re up to rev number Surface 3. And still, almost nobody is using the product. Less than 5% market share. Right again. It wasn’t a technology prediction, it was a market prediction. Lacking app developers, and a unique use, the competition was, and remains, simply too far out front.
Windows 10 is, unfortunately, a very expensive launch. And to get people to use it Microsoft is giving it away for free. The hope is then users will hook onto the cloud-based Office 365 and Microsoft’s Azure cloud services. But this is still trying to milk the same old cow. This approach relies on people being completely unwilling to give up using Windows and/or Office. And we see every day that millions of people are finding alternatives they like just fine, thank you very much.
Gamers hated me when I recommended Microsoft should give (for free) xBox to Nintendo. Unfortunately, I learned few gamers know much about P&Ls. They all assumed Microsoft made a fortune in gaming. But anyone who’s ever looked at Microsoft’s financial filings knows that the Entertainment Division, including xBox, has been a giant money-sucking hole. If they gave it away it would save money, and possibly help leadership figure out a strategy for profitable growth.
Unfortunately, Microsoft bought Minecraft, in effect “doubling down” on the bet. But regardless of how well anyone likes the products, Microsoft is not making money. Gaming is a bloody war where Sony and Microsoft keep battling, and keep losing billions of dollars. The odds of ever earning back the $2.5B spent on Minecraft is remote.
The greater likelihood is that as write offs continue to eat away at profits, and as markets continue evolving toward mobile products offered by competitors hurting “core” Microsoft sales, CEO Nadella will eventually have to give up on gaming and undertake another Nokia-like event.
All investors risk looking at current events to drive decision-making. When Ballmer was sacked and Nadella given the CEO job the stock jumped on euphoria. But the last 18 months have shown just how bad things are for Microsoft. It is a near monopolist in a market that is shrinking. And so far Mr. Nadella has failed to define a strategy that will make Microsoft into a company that does more than try to milk its heritage.
I said the giant retailer Sears Holdings would be a big loser the day Ed Lampert took control of the company. But hope sprung eternal, and investors jumped on the Sears bandwagon, believing a new CEO would magically improve a worn out, locked-in company. The stock went up for over 2 years. But, eventually, it became clear that Sears is irrelevant and the share price increase was unjustified. And the stock tanked.
Microsoft looks much the same. The actions we see are attempts to defend & extend a gloried history. But they don’t add up to a strategy to compete for the future. HoloLens will not be a product capable of replacing Windows plus Office revenues. If developers are attracted to it enough to start writing apps. Cortana is cool, but it is not first. And competitive products have so much greater usage that developer learning curve gains are wildly faster. These products are not game changers. They don’t solve large, unmet needs.
And employees see this. As I wrote in my last column, it is valuable to listen to employees. As the bloom fell off the rose, and Nadella started laying people off while freezing pay, employee support of him declined dramatically. And employee faith in leadership is far lower than at competitors Apple and Google.
As long as Microsoft keeps playing catch up, we should expect more layoffs, cost cutting and asset sales. And attempts at more “hail Mary” acquisitions intended to change the company. All of which will do nothing to grow customers, provide better jobs for employees, create value for investors or greater revenue opportunities for suppliers.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 30, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership
24×7 Wall Street just released its fourth annual analysis of the worst companies to work for in America. By looking across all four reports it is possible to identify likely problems which will be valuable for investors, employees (current and prospective,) suppliers and communities to know.
 Trend 1- Low minimum wages & “Wage gap” issues remain a big deal
Trend 1- Low minimum wages & “Wage gap” issues remain a big deal
The lists are dominated by retailers. Of the 30 unique companies identified, exactly half (15) were retailers. A handful were on the list 2 or more years. Consistently these employees complained about low wages.
By paying minimum wage, and often refusing to hire employees full time, the companies keep costs of brick and mortar store operations lower.
However, this takes a toll on employee morale as overall pay does not meet minimum living standards. Further employees feel heavily overworked and stressed, while having no job security. Often this leads to employee unhappiness with senior management, frequently offering low evaluations of the CEO – who makes 1,000 times their annual earnings.
As employees fight for higher wages, and a reduction in the “wage gap,” it will apply pressure to the sustainability of these retailers who rely on very low pay to maintain (or enhance) profits. The trend to a higher minimum wage will challenge profit growth – or maintenance – in these companies.
Trend 2 – Employees often “see change coming” and become negatively vocal
Jos. A Banks jumped onto the list as #4 in 2013. Just before a major shake-up and being acquired by Men’s Wearhouse. Family Dollar also appeared on the list in 2014 (#9,) only to be embroiled in a takeover battle with Dollar General, and finally aquired by Dollar Tree within 7 months. Office Max appeared on the list (#5) in 2012, and was acquired by Office Depot 8 months later. And, of course, Radio Shack made the list in 2012 (#3,) 2013 (#5) and 2014 (#11) only to file bankruptcy in 2015.
Employees can see when something bad is impending, likely jeopardizing their livelihoods, and start talking about it.
Similarly, growing internet threats are often picked-up by employees. hh Gregg employees started complaining loudly in 2014 (#8) as their 100% commission compensation became threatened by a growing Amazon.com. And that same year Books-A-Million was #1 on the list, as part time staffers saw the same advancing Amazon. And in 2012 Game Stop (#10) employees could see how the advancing Netflix and Hulu threatened the “core business” and started to light up the complaint section.
Trend 3 – Ignoring employee unhappiness while focusing on earnings can portend a disaster
Sears and KMart (collectively Sears Holdings) made the list in 3 of the 4 years. The stock was $66 in June, 2011, and $55 in 6/12 when it made #6. By 6/13 it had declined to $39, and made the list at #7. Starting 6/14 the stock was reasonably flat, and missed the list. But then in 6/17 the stock fell to 27 and reappeared twice – as both Sears and KMart.
Employees have consistently expressed their dismay with CEO Ed Lampert, and 80% actively dislike his leadership. After the Radio Shack experience, there is ample reason to listen more to these employees than the CEO who keeps promising a turnaround – amidst a long string of large quarterly losses and declining sales.
But this also opens the door for looking at some stocks that have defied employee unrest. Dillard’s made the list all 4 years. In 2012 the stock rose from $54 to $66, yet appeared #2 on the list. In 2013 the stock rose to $85 as it made the list #3. 2014 the stock made it to $119, and was sixth. In 2015 the stock peaked at $149, but has recently declined to $111 as it made the list #2.
Similarly Express Scripts rose from $53 in 2012 to $62 in 2013 when it appeared on the list in position #2. In 2014 it rose to $71 as it remained #2. And it 2015 the stock is at $85 as it topped the list #1.
It would be worthwhile to look at the clues employees are sending. Express Scripts employees are loudly complaining (louder than literally any other company) across multiple years of being overworked, overstressed, underpaid and without any job security. As are Dillard’s employees, who are the most outspoken in retail. How long will profit improvements be sustainable in these companies?
While the data is less clear on Dollar General, it appeared on the list as #4 in 2013. Then Family Dollar appeared on the list as #9 in 2014. Dollar General subsequently tried buying Family Dollar, and reappeared on the list as #10 in 2015. What are employees saying about the sustainability of the “dollar store” segment in a very tough retail market with growing internet competitors?
Any CEO can slash employee costs and payroll for a few years, but at some point the model simply collapses – aka, Sears Holdings and Radio Shack. Or there is a loss of identity as suffered by Office Max, Jos. A Banks and Family Dollar. It would be worthwhile for anyone to listen carefully to the feedback of these employees before investing in company equity, investing one’s livelihood as an employee, investing one’s resources to be a supplier, or investing one’s tax base as a community official.
There are a number of “one off” issues on the list. Companies appear once primarily due to bad CEO performance (Xerox, #5 this year, HP #8 in 2012 as the revolving door on the CEO office reached a high pitch.) Or due to some change in market competition.
But it is possible to look through these issues – which could become future trends but show limited insight today – to see that an aggregated employee view of leadership offers insights not always found in the P&L or management’s discussion of earnings. If you choose to put your resources into these companies, be aware of the risks warnings being sent by employees!
Please refer to the 24x7WallStreet.com site for deeper information on how the list was compiled, who is on each list, and their editor’s opinions of employee comments. 24×7 list in 2015 – 24×7 list in 2014 – 24×7 list in 2013 – 24×7 list in 2012

by Adam Hartung | Jun 22, 2015 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Lock-in
The Economic Policy Institute issued its most recent report on CEO pay yesterday, and the title makes the point clearly “Top CEOs Make 300 Times More than Typical Workers.” CEOs of the 350 largest US public companies now average $16,300,000 in compensation, while typical workers average about $53,000.
Actually, it is kind of remarkable that this stat keeps grabbing attention. The 300 multiple has been around since 1998. The gap actually peaked in 2000 at almost 376. There has been whipsawing, but it has averaged right around 300 for 15 years.
The big change happened in the 1990s. In 1965 the multiple was 20, and by 1978 it had risen only to 30. The next decade, going into 1990 saw the multiple rise to 60. But then from 1990 to 2000 it jumped from 60 to well over 300 – where it has averaged since. So it was long ago that large company CEO pay made its huge gains, and it such compensation has now become the norm.
But this does rile some folks. After all, when a hired CEO makes more in a single workday (based on 5 day week) than the worker does in an entire year, justification does become a bit difficult. And when we recognize that this has happened in just one generation it is a sea change.
 If average workers are angry, and some investors are angry, and politicians are increasingly speaking negatively about the topic why does CEO pay remain so high?
If average workers are angry, and some investors are angry, and politicians are increasingly speaking negatively about the topic why does CEO pay remain so high?
Reason 1 – Because they can
CEOs are like kings. They aren’t elected to their position, they are appointed. Usually after several years of grueling internecine political warfare, back-stabbing colleagues and gerrymandering the organization. Once in the position, they pretty much get to set their own pay.
Who can change the pay? Ostensibly the Board of Directors. But who makes up most Boards? CEOs (and former CEOs). It doesn’t do any Board member’s reputation any good with his peers to try and cut CEO pay. You certainly don’t want your objection to “Joe’s” pay coming up when its time to set your pay.
Honestly, if you could set your own pay what would it be? I reckon most folks would take as much as they could get.
Reason 2 – the Lake Wobegon effect
NPR (National Public Radio) broadcasts a show about a fictional, rural Minnesota town called Lake Wobegon where “the women are strong, the men are good-looking, and all of the children are above average.”
Nice joke, until you apply it to CEOs. The top 350 CEOs are accomplished individuals. Which 175 are above average, and which 175 are below average? Honestly, how does a Board judge? Who has the ability to determine if a specific CEO is above average, or below average?
So when the “average” CEO pay is announced, any CEO would be expected to go to the Board, tell them the published average and ask “well, don’t you think I’ve done a great job? Don’t you think I’m above average? If so, then shouldn’t I be compensated at some percentage greater than average?”
Repeat this process 350 times, every year, and you can see how large company CEO pay keeps going up. And data in the EPI report supports this. Those who have the greatest pay increase are the 20% who are paid the lowest. The group with the second greatest pay increase are the 20% in the next to lowest paid quintile. These lower paid CEOs say “shouldn’t I be paid at least average – if not more?”
The Board agrees to this logic, since they think the CEO is doing a good job (otherwise they would fire him.) So they step up his, or her, pay. This then pushes up the average. And every year this process is repeated, pushing pay higher and higher and higher.
Oh, and if you replace a CEO then the new person certainly is not going to take the job for below-average compensation. They are expected to do great things, so they must be brought in with compensation that is up toward the top. The recruiters will assure the Board that finding the right CEO is challenging, and they must “pay up” to obtain the “right talent.” Again, driving up the average.
Reason 3 – It’s a “King’s Court”
Today’s large corporations hire consultants to evaluate CEO performance, and design “pay for performance” compensation packages. These are then reviewed by external lawyers for their legality. And by investment bankers for their acceptability to investors. These outside parties render opinions as to the CEO’s performance, and pay package, and overall pay given.
Unfortunately, these folks are hired by the CEO and his Board to render these opinions. Meaning, the person they judge is the one who pays them. Not the employees, not a company union, not an investor group and not government regulators. They are hired and paid by the people they are judging.
Thus, this becomes something akin to an old fashioned King’s Court. Who is in the Boardroom that gains if they object to the CEO pay package? If the CEO selects the Board (and they do, because investors, employees and regulators certainly don’t) and then they collectively hire an outside expert, does anyone in the room want that expert to say the CEO is overpaid?
If they say the CEO is overpaid, how do they benefit? Can you think of even one way? However, if they do take this action – say out of conscious, morality, historical comparisons or just obstreperousness – they risk being asked to not do future evaluations. And, even worse, such an opinion by these experts places their clients (the CEO and Board) at risk of shareholder lawsuits for not fulfilling their fiduciary responsibility. That’s what one would call a “lose/lose.”
And, let’s not forget, that even if you think a CEO is overpaid by $10million or $20million, it is still a rounding error in the profitability of these 350 large companies. Financially, to the future of the organization, it really does not matter. Of all the issues a Board discusses, this one is the least important to earnings per share. When the Board is considering the risks that could keep them up at night (cybersecurity, technology failure, patent infringement, compliance failure, etc.) overpaying the CEO is not “up the list.”
The famed newsman Robert Krulwich identified executive compensation as an issue in the 1980s. He pointed out that there were no “brakes” on executive compensation. There is no outside body that could actually influence CEO pay. He predicted that it would rise dramatically. He was right.
The only apparent brake would be government regulation. But that is a tough sell. Do Americans want Congress, or government bureaucrats, determining compensation for anyone? Americans can’t even hardly agree on a whether there should be a minimum wage at all, much less where it should be set. Rancor against executive compensation may be high, but it is a firecracker compared to the atomic bomb that would be detonated should the government involve itself in setting executive pay.
Not to mention that since the Supreme Court ruling in the case of Citizens United made it possible for companies to invest heavily in elections, it would be hard to imagine how much company money large company CEOs would spend on lobbying to make sure no such regulation was ever passed.
How far can CEO pay rise? We recently learned that Jamie Dimon, CEO of JPMorganChase, has amassed a net worth of $1.1B. It increasingly looks like there may not be a limit.
by Adam Hartung | Jun 14, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, Leadership, Web/Tech
Dick Costolo was let go from his role as CEO of Twitter, to be replaced by a former CEO that was also fired. Unfortunately, it looks very strongly as if the Board made this decision for the wrong reasons.
Even though investors have been unhappy with Twitter’s share price, as CEO Mr. Costolo was doing a decent job of growing the company and improving profits. And even though analysts keep offering reasons why he was fired, it looks mostly as if this was a political decision in a company with a “soap opera” executive culture. Investors should be worried.
Let’s compare Mr. Costolo to CEO Zuckerberg’s performance at Facebook, and Mr. Bezos’ performance at Amazon. The latter two have been widely heralded for their leadership, so it sets a pretty good bar.
None of these three companies have enough earnings to matter. If you aren’t a growth investor, and you always value a company on earnings, then none of these are your cup of tea. All are evaluated on revenue and user metrics.
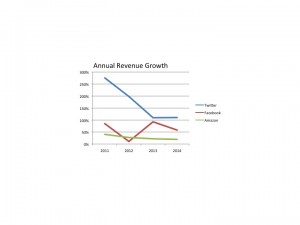 As you can see, Twitter’s revenue growth exceeds its comparators. Yes, its decline has been more dramatic, but we are comparing Twitter to companies that are much older and bigger. The net is to understand that revenues are growing, and at a better clip than Facebook and Amazon.
As you can see, Twitter’s revenue growth exceeds its comparators. Yes, its decline has been more dramatic, but we are comparing Twitter to companies that are much older and bigger. The net is to understand that revenues are growing, and at a better clip than Facebook and Amazon.
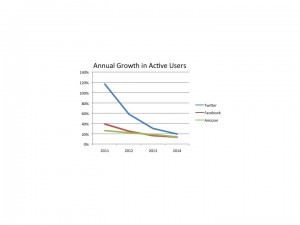 Next we should look at active monthly users. Again, these numbers are growing at all 3. And some analysts have said it is the deceleration in the rate of new user growth that doomed Mr. Costolo. But this defies logic given that during his tenure Twitter has dramatically outperformed its competition.
Next we should look at active monthly users. Again, these numbers are growing at all 3. And some analysts have said it is the deceleration in the rate of new user growth that doomed Mr. Costolo. But this defies logic given that during his tenure Twitter has dramatically outperformed its competition.
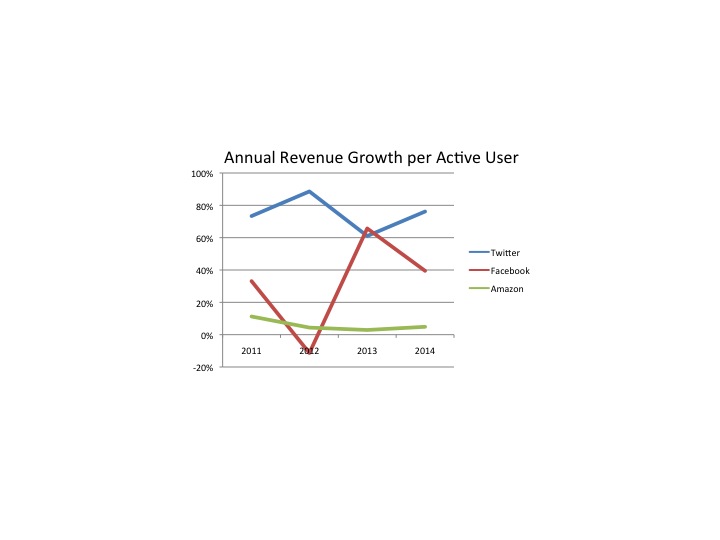
Lastly, let’s look at the “quality” of users. We can measure this by calculating the revenue per user. If this goes up, then the company is growing it top line by gaining more revenue per user – it is not “discounting” its way to higher volume. Instead,we can expect profits to improve based upon growth in this metric.
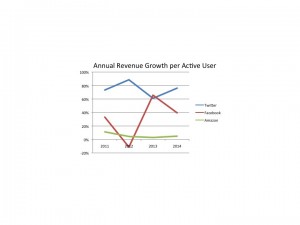 And here we can see that Twitter has wildly outperformed Facebook and Amazon. Twitter has grown its revenue per user by over 9-fold in the last 4 years, an excellent 75% per year compounded. Facebook, by comparison, roughly tripled its revenue/user (still very good) creating a 25%/year growth (certainly not to be sneezed at.) Amazon’s growth per user across the full 4 years was 25% – or about 4%/year.
And here we can see that Twitter has wildly outperformed Facebook and Amazon. Twitter has grown its revenue per user by over 9-fold in the last 4 years, an excellent 75% per year compounded. Facebook, by comparison, roughly tripled its revenue/user (still very good) creating a 25%/year growth (certainly not to be sneezed at.) Amazon’s growth per user across the full 4 years was 25% – or about 4%/year.
It isn’t hard to see that Mr. Costolo has been doing a pretty good job leading Twitter.
But Twitter has had a very checkered past when it comes to leaders. Several articles have been written about the revolving door on the CEO office, with founders back-stabbing each other as money is raised and efforts are made to improve company performance technologically and financially.
The Board has shown a proclivity to spend too much time listening to rumors, and previous CEOs. Rather than focusing on exactly how many users are coming aboard, and how much revenue is generated on those users.
The returning CEO was himself previously replaced. And during his tenure there were many technical problems. Why he would be inserted, and the best performing CEO in company history shunted aside is completely unclear. But for investors, employees, users (of which I am one) and customers this change in leadership looks to be poorly conceived, and quite concerning. Mr. Costolo was doing a pretty good job.
Data on revenues came from Marketwatch for Twitter, Facebook and Amazon. Data on users (in Amazon’s case customers) came from Statista.com for Twitter, Facebook and Amazon. Charts were created by Adam Hartung (C).

by Adam Hartung | May 31, 2015 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Web/Tech
Information technology (IT) services company Computer Sciences Corporation (CSC) recently announced it is splitting into two separate companies. One will “focus” on commercial markets, the other will “focus” on government contracts. Ostensibly, as we’ve heard before, leadership would like investors, employees and customers to believe this is the answer for a company that has incurred a number of high profile failed contracts, a turnover in leadership, vast losses and declining revenue.
Oh boy.
After years of poor performance, and an investigation by the UK parliament into a failed contract for the National Health Services, in 2012 CSC brought in a new CEO. Like most new CEOs, his first action was to announce a massive cost-cutting program. That primarily meant vast layoffs. So out the door went thousands of people in order to hopefully improve the P&L.
Only a services company doesn’t have any hard assets. The CSC business requires convincing companies, or government agencies, to let them take over their data centers, or PC deployment, or help desk, or IT development, or application implementation – in other words to outsource some part (or all) of the IT work that could be done internally. Winning this work has been an effort to demonstrate you can hire better people, that are more productive, at lower cost than the potential client.
So when CSC undertook a massive layoff, service levels declined. It was unavoidable. Where before CSC had 10 people doing something (or 1,000) now they have 7 (or 700). It’s not hard to imagine what happens next. Morale declines as layoffs ensue, and the overworked remaining employees feel (and perhaps really are) overworked. People leave for better jobs with higher pay and less stress. Yet, the contract requirements remain, so clients often start complaining about performance, leading to more pressure on the remaining employees. A vicious whirlpool of destruction starts, as things just keep getting worse.
Immediately after taking the CEO job in 2012 Mike Lawrie declared a massive $4.3B loss. This allowed him to “bring forward” anticipated costs of the anticipated layoffs, cancelled contracts, etc. Most importantly, it allowed him to “cost shift” future costs into his first year in the job – the year in which he would not be fired, regardless how much he wrote off. This is a classic financial machination applied by “turnaround CEOs” in order to blame the last guy for not being truthful about how badly things were, while guaranteeing the end of the new guy’s first year would show a profit due to the huge cost shift.
True to expectations, after one year with Lawrie as CEO, CSC declared a $1B profit for fyscal 2013 (about 20% of the previous write-off.) But then fyscal 2014 returned to the previous norm, as profits shrunk to just $674M on about $12B revenues (~5% net margin.) For 4th quarter of fyscal 2015 revenues dropped another 12.6% – not hard to imagine given the layoffs and ensuing customer dissatisfaction. Most troubling, the commercial part of CSC, which represents 75% of revenue, saw all parts of the business decline between 15-20%, while the federal contracting (much harder to cancel) remained flat. This is not the trajectory of a turnaround.
CEO Lawrie blames the deteriorating performance on execution missteps. And he has promised to keep his eyes carefully on the numbers. Although he has admitted that he doesn’t really know when, or if, CSC will return to any sort of growth.
No wonder that for more than a year prior to this split CSC was unable to sell itself. Despite a lot of hard effort, no banker was able to put together a deal for CSC to be purchased by a competitor or a private banking (hedge fund) operation.
If none of the professionals in making splits and turnarounds were willing to take on this deal, why should individual investors? In this case, watching people walk away should be a clear indicator of how bad things are, and how clueless leadership is regarding a fix for the problems.
The real problem at CSC isn’t “execution.” The real problem is that the market has shifted substantially. For decades CSC’s outsourcing business was the norm. But today companies don’t need a lot of what CSC outsources. They are closing down those costly operations and replacing them with cloud services, cloud application development and implementation, mobile deployments and significant big data analytics. Or looking for new services to solve problems like cybersecurity threats. CSC quite simply hasn’t done anything in those markets, and it is far, far behind. It is a big dinosaur rapidly being overtaken by competitors moving more quickly to new solutions.
One of CSC’s biggest competitors is IBM, which itself has had a series of woes. However, IBM has very publicly set up a partnership with Apple and is moving rapidly to develop industry-specific software as a service (SaaS) offerings that are mobile and operate in the cloud. These targeted enterprise solutions in health care, finance and other industries are designed to make the services offered by CSC obsolete.
Although it may have had a huge client base of 1,000 customers. And CSC brags that 175 of the Fortune 500 buy some services from it, exactly what does CSC bring to the table to keep these customers? Years of cost cutting means the company has not invested in the kinds of solutions being offered by IBM and competitors such as Accenture, HP and Dell domestically – and WiPro, TCS (Tata Consulting Services,) Infosys and Cognizant offshore. Not to mention dozens of up-and-coming small competiters who are right on the market for targeted solutions with the latest technology such as 6D Gobal Technologies. CSC is still stuck in its 1980s consulting model, and skill set, in a world that is vastly different today.
 CSC has no idea how to “focus” on clients. That would mean investing in modern solutions to rapidly changing client needs. CSC failed to do that 15 years ago when most outsourcing involved heavy use of offshore resources. And CSC has never caught up. Leadership overly relied on selling old services, and discounting. It’s model caused it to underbid projects, until the UK government almost shut the company down for its inability to deliver, and constantly hiding actual results.
CSC has no idea how to “focus” on clients. That would mean investing in modern solutions to rapidly changing client needs. CSC failed to do that 15 years ago when most outsourcing involved heavy use of offshore resources. And CSC has never caught up. Leadership overly relied on selling old services, and discounting. It’s model caused it to underbid projects, until the UK government almost shut the company down for its inability to deliver, and constantly hiding actual results.
Now CSC lacks any of the capabilities, people or skills to offer clients what they want. Its diffuse customer base is more a liability than a benefit, because these customers are “end of life” for the services CSC offers. Years of declining revenues demonstrate that as value declines, contracts are either allowed to go to very cheap offshore providers, lapse completely or cancelled early in order to shift client resources to more important projects where CSC cannot compete.
This split is just an admission that leadership has no idea what to do next. Customers are leaving, and revenues are declining. Margins, at 5%, are terrible and there is no money to invest in anything new. Some of the world’s best investors have looked at CSC deeply and chosen to walk away. For employees and individual investors it is time to admit that CSC has a limited future, and it is time to find far greener pastures.
by Adam Hartung | May 12, 2015 | Current Affairs, Leadership
NFL Commissioner Roger Goodall slammed Tom Brady and the New England Patriots today for what seemed, to many, like a pretty minor thing. Under-inflating balls to give the quarterback and receivers a small advantage would seem a far cry from the kind of offense causing you to suspend an MVP player for 4 games, fine the team owner $1M, and take away the coach’s #1 draft pick for 2016 and #4 draft pick for 2017.

But, largely, the Commissioner had little choice. And yes, he is making an example out of this situation.
In America the NFL is the sport. Where baseball was once “America’s game” that is no longer true. Today the NFL generates almost as much revenue as major league baseball (MLB) and the NBA combined. Players make more money than S&P 500 CEOs – and they are about the only people who do!
But the NFL has a raft of culture issues. First of all, it is really violent. The litany of players with lifetime injuries from football is remarkable. It seems like few who play in the NFL are able to go on to “regular lives” due to the remarkable stress the game puts on huge bodies colliding at remarkable speeds. There is no doubt that the game has led to many debilitating concussions, and players have been committing suicide at a surprising rate.
Remember “Bountygate?” From 2009 to 2011 the New Orleans Saints ownership and coaches paid players bonuses – “bounties” – if they injured an opposing player bad enough to have him removed from the game. This kind of thing was found to be endemic, and that some coaches had long promoted paying for injuring opposing players.
That is the kind of testosterone driven behavior that the NFL’s leadership realized was going to seriously damage the game, if not push it into legal regulation. While some fans (and in football, fan is truly short for fanatic) may have thought the practice a terrific reincarnation of Roman gladiator games, culturally this kind of behavior made the game less “family friendly” and likely to end up with ever more legal problems. The coaches were suspended, and the team lost draft picks.
Unfortunately, the NFL – despite its high pay – is nothing like baseball when it was the glory sport of America. In those days players had strict behavioral rules, and they could lose money – even their jobs – for simply getting drunk in public, or caught fornicating with someone other than their wife. Arguing with umpires caused multi-game suspensions, and fans sought out players with the quiet demeanor of Joe Dimaggio.
The NFL is rife with players struggling with criminal prosecution. Between January and July of 2013, 27 players were arrested. Between 2000 and 2013 two teams had 40 players arrested, and one had 35. The three least criminalistic teams in the league had 9 to 11 players put in handcuffs. It is a far too common sight on the news – NFL players handcuffed, or explaining to cameras why they were arrested. This is a big problem for a league that would like its players to be role models, and encourage mothers to allow their children to play the game – or go to games.
The Patriots have had their own problems. In 2007 coach Patriots’ Belichick was caught stealing signals from the New York Jets coaches. “Spygate” caused Commissioner Goodall to fine the coach $500,000 – the largest fine in history to that date. Additionally the team was stripped of its 2008 first round draft and fined $250,000. It was another example, like Bountygate, of a culture accepting of the notion that owners, coaches and players should “do whatever it takes to win,” and rules (or etiquette) be darned.
Then in 2013 Patriots’ player Aaron Hernandez was arrested for murder. Eventually he was arrested on two additional murder counts, and in just the last few months he was convicted on murder charges. As the news rolled out, we learned Mr. Hernandez had a long criminal record, including bar fights and shootings, going back to 2007. It appears as if the Patriots and the NFL turned a blind eye toward a very dangerous person – in order for the team to win more games. The “win at all costs” again appeared to be culturally dominant.
Now we have “deflategate.” Coach Belichick again in the spotlight, apparently for trying more tricks to gain an advantage – even if unfair. As the investigation continued the question became “even if Tom Brady didn’t know why the balls were deflated, as someone who touched the ball on every play why didn’t he report the issue to his coaches? Why didn’t he take personal responsibility for what could well be a rule violation, and seek to find the true answer? Why didn’t he try to play by the rules, and take care of this issue?” Instead, it appeared he was more than happy to take advantage of the situation, even if it was against the rules. Again, win at all costs – including breaking the rules.
Unfortunately this is now moving into the stadium. In recent TV interviews several people have pooh-poohed the whole issue. “What’s the big deal? Really? All this fuss over something so small?” And the comment heard over and over in “man-on-the-street” interviews “if you get caught, you get penalized.” Really – not that Mr. Brady should have reported this situation and fixed it – but rather that he got caught is all that mattered. It’s OK to cheat, just don’t get caught.
The NFL has a culture issue. In some stadiums the language is so course, and the fans so rough, that minors should never attend. And, as we said in an earlier time, “unfit company for a lady.” Tied, unfortunately, to players and coaches who implement a culture of violence, cheating and doing whatever one must to win – rather than simply playing a game.
And that is where Commissioner Goodall has to take action. He leads the league. He is the “man at the top.” It is his job, as leader, to set the tone on culture. If the NFL is to be “America’s sport” it’s his job to set the cultural tone for the sport, and demonstrate good leadership for his business, the owners, the coaches and the players. If we want fans to be sportsmanlike, it has to start with the players and those who are part of the NFL.
So there is no choice but to make an example of Mr. Brady. He sensed there was a problem. But he would rather win, and be MVP, than be honest. Wow, what a role model. And Mr. Belichick, now in in controversy #2, leads us to question if anything matters to him other than winning a superbowl ring – even if it means hiring a gun-toting shooter who can’t stay out of bar fights. And the Commissioner, like many of us, has to wonder, what is going on in that Patriots’ organization that Mr. Robert Kraft owns? What cultural tone is he setting, as the man atop the team? Is his view “win at all costs” and the rules be darned?
The NFL has a culture problem. Commissioner Goodall has his hands full. He has to deal with individualistic owners, who are rich and very powerful in their local communities. He has fans that are often far more caring of their team winning than playing by the rules. And he has players that, too often, or a very short step from prison – or committing horrendous acts of violence on the field that can maim or kill another player. He has to take stiff action, when he can, if he is to make any difference at all in trying to keep this culture from going completely off the rails.
Learn more about my public speaking, Board involvement and growth consulting at www.AdamHartung.com, or connect with me on LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter.

by Adam Hartung | May 8, 2015 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership
McDonald’s just had another lousy quarter. All segments saw declining traffic, revenues fell 11%. Profits were off 33%. Pretty well expected, given its established growth stall.
A new CEO is in place, and he announced is turnaround plan to fix what ails the burger giant. Unfortunately, his plan has been panned by just about everyone. Unfortunately, its a “me too” plan that we’ve seen far too often – and know doesn’t work:
- Reorganize to cut costs. By reshuffling the line-up, and throwing out a bunch of bodies management formerly said were essential, but now don’t care about, they hope to save $300M/year (out of a $4.5B annual budget.)
- Sell off 3,500 stores McDonald’s owns and operate (about 10% of the total.) This will further help cut costs as the operating budgets shift to franchisees, and McDonald’s book unit sales creating short-term, one-time revenues into 2018.
- Keep mucking around with the menu. Cut some items, add some items, try a bunch of different stuff. Hope they find something that sells better.
- Try some service ideas in which nobody really shows any faith, like adding delivery and/or 24 hour breakfast in some markets and some stores.
 Needless to say, none of this sounds like it will do much to address quarter after quarter of sales (and profit) declines in an enormously large company. We know people are still eating in restaurants, because competitors like 5 Guys, Meatheads, Burger King and Shake Shack are doing really, really well. But they are winning primarily because McDonald’s is losing. Even though CEO Easterbrook said “our business model is enduring,” there is ample reason to think McDonald’s slide will continue.
Needless to say, none of this sounds like it will do much to address quarter after quarter of sales (and profit) declines in an enormously large company. We know people are still eating in restaurants, because competitors like 5 Guys, Meatheads, Burger King and Shake Shack are doing really, really well. But they are winning primarily because McDonald’s is losing. Even though CEO Easterbrook said “our business model is enduring,” there is ample reason to think McDonald’s slide will continue.
Possibly a slide into oblivion. Think it can’t happen? Then what happened to Howard Johnson’s? Bob’s Big Boy? Woolworth’s? Montgomery Wards? Size, and history, are absolutely no guarantee of a company remaining viable.
In fact, the odds are wildly against McDonald’s this time. Because this isn’t their first growth stall. And the way they saved the company last time was a “fire sale” of very valuable growth assets to raise cash that was all spent to spiffy up the company for one last hurrah – which is now over. And there isn’t really anything left for McDonald’s to build upon.
Go back to 2000 and McDonald’s had a lot of options. They bought Chipotle’s Mexican Grill in 1998, Donato’s Pizza in 1999 and Boston Market in 2000. These were all growing franchises. Growing a LOT faster, and more profitably, than McDonald’s stores. They were on modern trends for what people wanted to eat, and how they wanted to be served. These new concepts offered McDonald’s fantastic growth vehicles for all that cash the burger chain was throwing off, even as its outdated yellow stores full of playgrounds with seats bolted to the floors and products for 99cents were becoming increasingly not only outdated but irrelevant.
But in a change of leadership McDonald’s decided to sell off all these concepts. Donato’s in 2003, Chipotle went public in 2006 and Boston Market was sold to a private equity firm in 2007. All of that money was used to fund investments in McDonald’s store upgrades, additional supply chain restructuring and advertising. The “strategy” at that time was to return to “strategic focus.” Something that lots of analysts, investors and old-line franchisees love.
But look what McDonald’s leaders gave up via this decision to re-focus. McDonald’s received $1.5B for Chipotle. Today Chipotle is worth $20B and is one of the most exciting fast food chains in the marketplace (based on store growth, revenue growth and profitability – as well as customer satisfaction scores.) The value of all of the growth gains that occurred in these 3 chains has gone to other people. Not the investors, employees, suppliers or franchisees of McDonald’s.
We have to recognize that in the mid-2000s McDonald’s had the option of doing 180degrees opposite what it did. It could have put its resources into the newer, more exciting concepts and continued to fidget with McDonald’s to defend and extend its life even as trends went the other direction. This would have allowed investors to reap the gains of new store growth, and McDonald’s franchisees would have had the option to slowly convert McDonald’s stores into Donato’s, Chipotle’s or Boston Market. Employees would have been able to work on growing the new brands, creating more revenue, more jobs, more promotions and higher pay. And suppliers would have been able to continue growing their McDonald’s corporate business via new chains. Customers would have the benefit of both McDonald’s and a well run transition to new concepts in their markets. This would have been a win/win/win/win/win solution for everyone.
But it was the lure of “focus” and “core” markets that led McDonald’s leadership to make what will likely be seen historically as the decision which sent it on the track of self-destruction. When leaders focus on their core markets, and pull out all the stops to try defending and extending a business in a growth stall, they take their eyes off market trends. Rather than accepting what people want, and changing in all ways to meet customer needs, leaders keep fiddling with this and that, and hoping that cost cutting and a raft of operational activities will save the business as they keep focusing ever more intently on that old core business. But, problems keep mounting because customers, quite simply, are going elsewhere. To competitors who are implementing on trends.
The current CEO likes to describe himself as an “internal activist” who will challenge the status quo. But he then proves this is untrue when he describes the future of McDonald’s as a “modern, progressive burger company.” Sorry dude, that ship sailed years ago when competitors built the market for higher-end burgers, served fast in trendier locations. Just like McDonald’s 5-years too late effort to catch Starbucks with McCafe which was too little and poorly done – you can’t catch those better quality burger guys now. They are well on their way, and you’re still in port asking for directions.
McDonald’s is big, but when a big ship starts taking on water it’s no less likely to sink than a small ship (i.e. Titanic.) And when a big ship is badly steered by its captain it flounders, and sinks (i.e. Costa Concordia.) Those who would like to think that McDonald’s size is a benefit should recognize that it is this very size which now keeps McDonald’s from doing anything effective to really change the company. Its efforts (detailed above) are hemmed in by all those stores, franchisees, commitment to old processes, ingrained products hard to change due to installed equipment base, and billions spent on brand advertising that has remained a constant even as McDonald’s lost relevancy. It is now sooooooooo hard to make even small changes that the idea of doing more radical things that analysts are requesting simply becomes impossible for existing management.
And these leaders, frankly, aren’t even going to try. They are deeply wedded, committed, to trying to succeed by making McDonald’s more McDonald’s. They are of the company and its history. Not the CEO, or anyone on his team, reached their position by introducing a revolutionary new product, much less a new concept – or for that matter anything new. They are people who “execute” and work to slowly improve what already exists. That’s why they are giving even more decision-making control to franchisees via selling company stores in order to raise cash and cut costs – rather than using those stores to introduce radical change.
These are not “outside thinkers” that will consider the kinds of radical changes Louis V. Gerstner, a total outsider, implemented at IBM – changing the company from a failing mainframe supplier into an IT services and software company. Yet that is the only thing that will turn around McDonald’s. The Board blew it once before when it sold Chipotle, et.al. and put in place a core-focused CEO. Now McDonald’s has fewer resources, a lot fewer options, and the gap between what it offers and what the marketplace wants is a lot larger.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 30, 2015 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Last week saw another slew of quarterly earnings releases. For long term investors, who hold stocks for years rather than months, these provide the opportunity to look at trends, then compare and contrast companies to determine what should be in their portfolio. It is worthwhile to compare the trends supporting the valuations of market leaders Google and Facebook.
 Google once again reported higher sales and profits. And that is a good thing. But, once again, the price of Google’s primary product declined. Revenues increased because volume gains exceeded the price decline, which indicates that the market for internet ads keeps growing. But this makes 15 straight quarters of price declines for Google. Due to this long series of small declines, the average price of Google’s ads (cost per click) has declined 70%* since Q3 2011!
Google once again reported higher sales and profits. And that is a good thing. But, once again, the price of Google’s primary product declined. Revenues increased because volume gains exceeded the price decline, which indicates that the market for internet ads keeps growing. But this makes 15 straight quarters of price declines for Google. Due to this long series of small declines, the average price of Google’s ads (cost per click) has declined 70%* since Q3 2011!
While this is a miraculous example of what economists call demand elasticity, one has to wonder how long growth will continue to outpace price degradation. At some point the marginal growth in demand may not equal the marginal decline in pricing. Should that happen, revenues will start going down rather than up.
Part of what drives this price/growth effect has been the creation of programmatic ad buying, which allows Google to place more ads in more specific locations for advertisers via such automated products as AdMob, AdExchange and DoubleClick Bid Manager. But such computerized ad buying relies on ever more content going onto the web, as well as ever more consumption by internet users.
Further, Google’s revenues are almost entirely search-based advertising, and Google dominates this category. But this is largely a PC-related sale. Today 67.5% of Google ad revenue is from PC searches, while only 32.5% is from mobile searches. Due to this revenue skew, and the fact that people do more mobile interaction via apps, messaging apps and social media than browser, search ad growth has fallen considerably. What was a 24% year over year growth rate in Q1 2012 has dropped to more like 15% for the last 8 quarters.
So while the market today is growing, and Google is making more money, it is possible to see that the growth is slowing. And Google’s efforts to create mobile ad sales outside of search has largely failed, as witnessed by the recent death of Google+ as competition for Twitter or Facebook. It is the market shift, to mobile, which creates the greatest threat to Google’s ability to grow; certainly at historical rates.
Simultaneously, Facebook’s announcements showed just how strongly it is continuing to dominate both social media and mobile, and thus generate higher revenues and profits with outstanding growth. The #1 site for social media and messenger apps is Facebook, by quite a large margin. But, Facebook’s 2014 acquisition of What’sApp is now #2. WhatsApp has doubled its monthly active users (MAUs) just since the acquisition, and now reaches 800million. Growth is clearly accelerating, as this is from a standing start in 2011.
Facebook Messenger at #3, just behind WhatsApp. And #5 is Instagram, another Facebook acquisition. Altogether 4 of the top 5 sites, and the ones with greatest growth on mobile, are Facebook. And they total over 3billion MAUs, growing at over 300million new MAUs/month. Thus Facebook has already emerged as the dominant force, with the most users, in the fast-growing, accelerating, mobile and app sectors. (Just as Google did in internet search a decade ago, beating out companies like Yahoo, Ask Jeeves, etc.)
Google is moving rapidly to monetize this user base. From nothing in early 2012, Facebook’s mobile revenue is now $2.5B/quarter and represents 67% of global revenue (the inverse of Google’s revenues.) Further, Facebook is now taking its own programmatic ad buying tool, Atlas, to advertisers in direct competition with Google. Only Atlas places ads on both social media and internet browser pages – a one-two marketing punch Google has not yet cracked.
Google’s $17.3B Q1 2015 revenue is 30 times the revenue of Facebook. There is no doubt Google is growing, and generating enormous profits. But, for long-term investors, growth is slowing and there is reason to be concerned about the long term growth prospects of Google as the market shifts toward more social and more mobile. Google has failed to build any substantial revenues outside of search, and has had some notable failures recently outside its core markets (Google + and Google Glass.) Just how long Google will continue growing, and just how fast the market will shift is unclear. Technology markets have shown the ability to shift a lot faster than many people expected, leaving some painful losers in their wake (Dell, HP, Sun Microsystems, Yahoo, etc.)
Meanwhile, Facebook is squarely positioned as the leader, without much competition, in the next wave of market growth. Facebook is monetizing all things social and mobile at a rapid clip, and wisely using acquisitions to increase its strength. As these markets continue on their well established trends it is hard to be anything other than significantly optimistic for Facebook long-term.
* 1x .93 x .88 x .84 x .85 x .94 x .96 x .94 x .93 x .89 x .91 x .94 x .98 x .97 x .95 x .93 = .295

by Adam Hartung | Apr 25, 2015 | Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Transparency
If you don’t drink gin you may not know the brand Tanqueray, a product owned by Diageo. But Tanqueray has been around for almost 190 years, going back to the days when London Dry Gin was first created. Today Tanqueray is one of the most dominant gin brands in the world, and the leading brand in the USA.
 But gin is not a growth category. And Tanqueray, despite its great product heritage and strong brand position, has almost no growth prospects.
But gin is not a growth category. And Tanqueray, despite its great product heritage and strong brand position, has almost no growth prospects.
Any product that doesn’t grow sales cannot generate profits to spend on brand maintenance. Firstly, if due to nothing more than inflation, costs always go up over time. It takes rising sales to offset higher costs. Additionally, small competitors can niche the market with new products, cutting into leader sales. And competitors will undercut the leader’s price to steal volume/share in a stagnant market, causing margin erosion.
Category growth stalls are usually linked to substitute products stealing share in a larger definition of the marketplace. For example sales of laptop/desktop PCs stalled because people are now substituting tablets and smartphones. The personal technology market is growing, but it is in the newer product category stealing sales from the older product category.
This is true for gin sales, because older drinkers – who dominate today’s gin market – are drinking less spirits, and literally dying from old age. In the overall spirits market, younger liquor drinkers have preferred vodkas and flavored vodkas which are “smoother,” sweeter, and perceived as “lighter.”

So, what is a brand manager to do? Simply let trends obsolete their product line? Milk their category and give up money for investing somewhere else?
That may sound fine at a corporate level, where category portfolios can be managed by corporate vice presidents. But if you’re a brand manager and you want to become a future V.P., managing declining product sales will not get you into that promotion. And defending market share with price cuts, rebates and deals will cut into margin, ruin the brand position and likely kill your marketing career.
Keith Scott is the Senior Brand Manager for Tanqueray, and his team has chosen to regain product growth by using sustaining innovations in a smart way to attract new customers into the gin category. They are looking beyond the currently dwindling historical customer base of London Dry Gin drinkers, and working to attract new customers which will generate category growth and incremental Tanqueray sales. He’s looking to build the brand, and the category, rather than get into a price war.
Building on demographic trends, Tanqueray’s brand management is targeting spirit drinkers from 28-38. Three new Tanqueray brand extensions are being positioned for greatest appeal to increasingly adult tastes, while offering sophistication and linkage to one of the longest and strongest spirits brands.
 #1 – Tanqueray Rangpur is a highly citrus-flavored gin taking a direct assault on flavored vodkas. Although still very much a gin, with its specific herb-based taste, Rangpur adds a hefty, and uniquely flavored, dose of lime. This makes for a fast, easy to prepare gin and tonic or lime-based gimlet – 2 classic cocktails that have their roots in England but have been popular in the US since before prohibition. And, in defense of the brand, Rangpur is priced about 10-20% higher than London Dry.
#1 – Tanqueray Rangpur is a highly citrus-flavored gin taking a direct assault on flavored vodkas. Although still very much a gin, with its specific herb-based taste, Rangpur adds a hefty, and uniquely flavored, dose of lime. This makes for a fast, easy to prepare gin and tonic or lime-based gimlet – 2 classic cocktails that have their roots in England but have been popular in the US since before prohibition. And, in defense of the brand, Rangpur is priced about 10-20% higher than London Dry.
 #2 – Tanqueray Old Tom and Tanqueray Milacca appeal to the demographic that loves specialty, crafted products. The “craft” product movement has grown dramatically, and nowhere more powerfully than amongst 28-42 year old beer drinkers. Old Tom and Milacca leverage this trend. Both are “retro” products, harkening to gins over 100 years ago. They are made in small batches and have limited availability. They are targeted at the consumer that wants something new, unique, unusual and yet tied to old world notions of hand-made production and high quality. These craft products are priced 25-35% higher than traditional London Dry.
#2 – Tanqueray Old Tom and Tanqueray Milacca appeal to the demographic that loves specialty, crafted products. The “craft” product movement has grown dramatically, and nowhere more powerfully than amongst 28-42 year old beer drinkers. Old Tom and Milacca leverage this trend. Both are “retro” products, harkening to gins over 100 years ago. They are made in small batches and have limited availability. They are targeted at the consumer that wants something new, unique, unusual and yet tied to old world notions of hand-made production and high quality. These craft products are priced 25-35% higher than traditional London Dry.
#3 – Tanqueray No. 10 is a “super-premium” product pointed at the customer who wants to project maximum sophistication and wealth. No 10 uses a special manufacturing process creating a uniquely smooth and slightly citrus flavor. But this process loses 40% of the product to “tailings” compared to the industry standard 10% loss. No. 10 is the high-end defense of the Tanqueray brand (a “top shelf” product as its known in the industry) priced 75-90% higher than London Dry.

No. 10 is being promoted with “invitation only” events being held in major U.S. cities such as New York, Chicago and Atlanta. No. 10 “trunk events” bring in some of the hottest, newest designers to showcase the latest in apparel trends, accompanied by hot, new musical talent. No. 10 is associated with the sophistication of super-premium brands – individualized and rare products – in a members-only environment. Targeted at the primary demographic of 28-38, No. 10 events are designed to lure these consumers to this product they otherwise might overlook .
Rather than addressing their gin category growth stall with price cuts and other sales incentives, which would lead to brand erosion, price erosion, and margin erosion, the Tanqueray brand team is leveraging trends to bring new consumers to their category and generate profitable growth. These innovative brand extensions actually build brand value while leveraging identifiable market trends. Notice that all these sustaining innovations are actually priced higher than the highest volume London Dry core product, thus augmenting price – and hopefully margin.
Too often leaders see their market stagnate and use that as an excuse lower expectations and accept sales decline. They don’t look beyond their core market for new customers and sources of growth. They react to competition with the blunt axe of pricing actions, seeking to maintain volume as margins erode and competition intensifies. This accelerates product genericization, and kills brand value.
The Tanqueray brand team demonstrates how critical sustaining innovation can be for maintaining growth at all levels of an organization. Even the level of a single product or brand. They are using sustaining innovations to lure in new customers and grow the brand umbrella, while growing the category and achieving desired price realization. This is a lesson many brands, and companies, should emulate.

 This is where short-term manipulation happens. Say a company is earning $1,000 and has 1,000 shares outstanding, so its EPS is $1. The industry multiple is 10, so the share price is $10. The company sells assets for $1,000 (for purposes of this exercise, let’s assume the book value on those assets is $1,000 so there is no gain, no earnings impact and no tax impact.)
This is where short-term manipulation happens. Say a company is earning $1,000 and has 1,000 shares outstanding, so its EPS is $1. The industry multiple is 10, so the share price is $10. The company sells assets for $1,000 (for purposes of this exercise, let’s assume the book value on those assets is $1,000 so there is no gain, no earnings impact and no tax impact.)





















