
by Adam Hartung | Jul 15, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership
Famed actor and comedian Tracy Morgan has filed a lawsuit against Walmart. He was seriously injured, and his companion and fellow comedian James McNair was killed, when their chauffeured vehicle was struck by a WalMart truck going too fast under the control of an overly tired driver.
It would be easy to write this off as a one-time incident. As something that was the mistake of one employee, and not a concern for management. Walmart is huge, and anyone could easily say “mistakes will happen, so don’t worry.” And as the country’s largest company (by sales and employees) Walmart is an easy target for lawsuits.
But that would belie a much more concerning situation. One that should have investors plenty worried.

Walmart isn’t doing all that well. It is losing customers, even as the economy recovers. For a decade Walmart has struggled to grow revenues, and same store sales have declined – only to be propped up by store closings. Despite efforts to grow offshore, attempts at international expansion have largely been flops. Efforts to expand into smaller stores have had mixed success, and are marginal at generating new revenues in urban efforts. Meanwhile, Walmart still has no coherent strategy for on-line sales expansion.
Unfortunately the numbers don’t look so good for Walmart, a company that is absolutely run by numbers. Every single thing that can be tracked in Walmart is tracked, and managed – right down the temperature in every facility (store, distribution hub, office) 24x7x365. When the revenue, inventory turns, margin, distribution costs, etc. aren’t going in the right direction Walmart is a company where leadership applies the pressure to employees, right down the chain, to make things better.
Unfortunately, a study by Northwestern University Kellogg School of Management has shown that when a culture is numbers driven it often leads to selfish, and unethical, behavior. When people are focused onto the numbers, they tend to stretch the ethical (and possibly legal) boundaries to achieve those numerical goals. A great recent example was the U.S. Veterans Administration scandal where management migrated toward lying about performance in order to meet the numerical mandates set by Secretary Shinseki.
Back in November, 2012 I pointed out that the Walmart bribery scandal in Mexico was a warning sign of big problems at the mega-retailer. Pushed too hard to create success, Walmart leadership was at least skirting with the law if not outright violating it. I projected these problems would worsen, and sure enough by November the bribery probe was extended to Walmart’s operations in Brazil, China and India.
We know from the many employee actions happening at Walmart that in-store personnel are feeling pressure to do more with fewer hours. It does not take a great leap to consider it possible (likely?) that distribution personnel, right down to truck drivers are feeling pressured to work harder, get more done with less, and in some instances being forced to cut corners in order to improve Walmart’s numbers.
Exactly how much the highest levels of Walmart knows about any one incident is impossible to gauge at this time. However, what should concern investors is whether the long-term culture of Walmart – obsessed about costs and making the numbers – has created a situation where all through the ranks people are feeling the need to walk closer to ethical, and possibly legal, lines. While it may be that no manager told the driver to drive too fast or work too many hours, the driver might have felt the pressure from “higher up” to get his load to its destination at a certain time – or risk his job, or maybe his boss’s.
If this is a widespread cultural issue – look out! The legal implications could be catastrophic if customers, suppliers and communities discover widespread unethical behavior that went unchecked by top echelons. The C suite executives don’t have to condone such behavior to be held accountable – with costs that can be exorbitant. Just ask the leaders at JPMorganChase and Citibank who are paying out billions for past transgressions.
Worse, we cannot expect the marketplace pressures to ease up any time soon for Walmart. Competitors are struggling mightily. JCPenney cannot seem to find anyone to take the vacant CEO job as sales remain below levels of several years ago, and the chain is most likely going to have to close several dozen (or hundreds) of stores. Sears/KMart has so many closed and underperforming stores that practically every site is available for rent if anyone wants it. And in the segment which is even lower priced than Walmart, the “dollar stores,” direct competitor Family Dollar saw 3rd quarter profits fall another 33% as too many stores and too few customer wreak financial havoc and portend store closings.
So the market situation is not improving for Walmart. As competition has intensified, all signs point to a leadership which tried to do “more, better, faster, cheaper.” But there is no way to maintain the original Walmart strategy in the face of the on-line competitive onslaught which is changing the retail game. Walmart has continued to do “more of the same” trying to defend and extend its old success formula, when it was a disruptive innovator that stole its revenues and cut into profits. Now all signs point to a company which is in grave danger of over-extending its success formula to the point of unethical, and potentially illegal, behavior.
If that doesn’t scare the heck out of Walmart investors I can’t imagine what would.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 19, 2014 | Current Affairs, Disruptions, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
Yesterday Amazon launched its new Kindle Fire smartphone.
“Ho-hum” you, and a lot of other people, said. “Why?” “What’s so great about this phone?”
The market is dominated by Apple and Samsung, to the point we no longer care about Blackberry – and have pretty much forgotten about all the money spent by Microsoft to buy Nokia and launch Windows 8. The world doesn’t much need a new smartphone maker – as we’ve seen with the lack of excitement around Google/Motorola’s product launches. And, despite some gee-whiz 3D camera and screen effects, nobody thinks Amazon has any breakthrough technology here.
But that would be completely missing the point. Amazon probably isn’t even thinking of competing heads-up with the 2 big guns in the smartphone market. Instead, Amazon’s target is everyone in retail. And they should be scared to death. As well as a lot of consumer products companies.

Amazon’s new Kindle Fire smartphone
Apple’s iPod and iPhones have some 400,000 apps. But most people don’t use over a dozen or so daily. Think about what you do on your phone:
- Talk, texting and email
- Check the weather, road conditions, traffic
- Listen to music, or watch videos
- Shopping (look for products, prices, locations, specs, availability, buy)
Now, you may do several other things. But (maybe not in priority,) these are probably the top 4 for 90% of people.
If you’re Amazon, you want people to have a great shopping experience. A GREAT experience. You’ve given folks terrific interfaces, across multiple platforms. But everything you do with an app on iPhones or Samsung phones involves negotiating with Apple or Google to be in their store – and giving them revenue. If you could bypass Apple and Google – a form of retail “middleman” in Amazon’s eyes – wouldn’t you?
Amazon has already changed retail markedly. Twenty years ago a retailer would say success relied on 2 things:
- Store location and layout. Be in the right place, and be easy to shop.
- Merchandise the goods well in the store, and have them available.
Amazon has killed both those tenets of retail. With Amazon there is no store – there is no location. There are no aisles to walk, and no shelves to stock. There is no merchandising of products on end caps, within aisles or by tagging the product for better eye appeal. And in 40%+ cases, Amazon doesn’t even stock the inventory. Availability is based upon a supplier for whom Amazon provides the storefront and interface to the customer, sending the order to the supplier for a percentage of the sale.
And, on top of this, the database at Amazon can make your life even easier, and less time consuming, than a traditional store. When you indicate you want item “A” Amazon is able to show you similar products, show you variations (such as color or size,) show you “what goes with” that product to make sure you buy everything you need, and give you different prices and delivery options.
Many retailers have spent considerably training employees to help customers in the store. But it is rare that any retail employee can offer you the insight, advice and detail of Amazon. For complex products, like electronics, Amazon can provide detail on all competitive products that no traditional store could support. For home fix-ups Amazon can provide detailed information on installation, and the suite of necessary ancillary products, that surpasses what a trained Home Depot employee often can do. And for simple products Amazon simply never runs out of stock – so no asking an aisle clerk “is there more in the back?”
And it is impossible for any brick-and-mortar retailer to match the cost structure of Amazon. No stores, no store employees, no cashiers, 50% of the inventory, 5-10x the turns, no “obsolete inventory,” no inventory loss – there is no way any retailer can match this low cost structure. Thus we see the imminent failure of Radio Shack and Sears, and the chronic decline in mall rents as stores go empty.
Some retailers have tried to catch up with Amazon offering goods on-line. But the inventory is less, and delivery is still often problematic. Meanwhile, as they struggle to become more digital these retailers are competing on ground they know precious little about. It is becoming commonplace to read about hackers stealing customer data and wreaking havoc at Michaels Stores and Target. Thus on-line customers have far more faith in Amazon, which has 2 decades of offering secure transactions and even offers cloud services secure enough to support major corporations and parts of the U.S. government.
And Amazon, so far, hasn’t even had to make a profit. It’s lofty price/earnings multiple of 500 indicates just how little “e” there is in its p/e. Amazon keeps pouring money into new ways to succeed, rather than returning money to shareholders via stock buybacks or dividends. Or dumping it into chronic store remodels, or new store construction.
Today, you could shop at Amazon from your browser on any laptop, tablet or phone. Or, if you really enjoy shopping on-line you can now obtain a new tablet or phone from Amazon which makes your experience even better. You can simply take a picture of something you want, and your new Amazon smartphone will tell you how to buy it on-line, including price and delivery. No need to leave the house. Want to see the product in full 360 degrees? You have it on your 3D phone. And all your buying experience, customer reviews, and shopping information is right at your fingertips.
Amazon is THE game changer in retail. Kindle was a seminal product that has almost killed book publishers, who clung way too long to old print-based business models. Kindle Fire took direct aim at traditional retailers, from Macy’s to Wal-Mart, in an effort to push the envelope of on-line shopping. And now the Kindle Fire smartphone puts all that shopping power in your palm, convenient with your other most commonplace uses such as messaging, fact finding, listening or viewing.
This is not a game changing smartphone in comparison with iPhone 5 or Galaxy S 5. But, as another salvo in the ongoing war for controlling the retail marketplace this is another game changer. It continues to help everyone think about how they shop today, and in the future. For anyone in retail, this may well be seen as another important step toward changing the industry forever, and making “every day low prices” an obsolete (and irrelevant) retail phrase. And for consumer goods companies this means the need to distribute products on-line will forever change the way marketing and selling is done – including who makes how much profit.
by Adam Hartung | May 30, 2014 | Current Affairs, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Sports, Web/Tech
Anyone who reads my column knows I’ve been no fan of Steve Ballmer as CEO of Microsoft. On multiple occasions I chastised him for bad decisions around investing corporate funds in products that are unlikely to succeed. I even called him the worst CEO in America. The Washington Post even had difficulty finding reputable folks to disagree with my argument.
Unfortunately, Microsoft suffered under Mr. Ballmer. And Windows 8, as well as the Surface tablet, have come nowhere close to what was expected for their sales – and their ability to keep Microsoft relevant in a fast changing personal technology marketplace. In almost all regards, Mr. Ballmer was simply a terrible leader, largely because he had no understanding of business/product lifecycles.
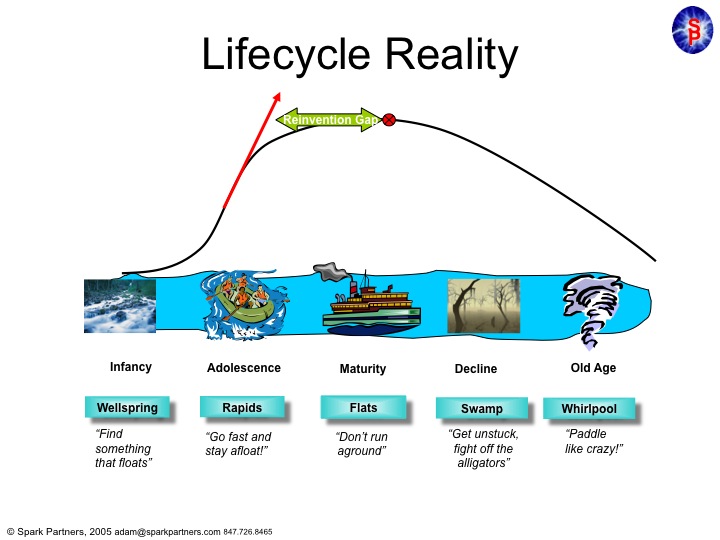
 Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates, who did a remarkable job of taking a start-up company from the Wellspring of an idea into one of the fastest growing adolescents of any American company.
Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates, who did a remarkable job of taking a start-up company from the Wellspring of an idea into one of the fastest growing adolescents of any American company.
Under Mr. Gates leadership Microsoft single-handedly overtook the original PC innovator – Apple – and left it a niche company on the edge of bankruptcy in little over a decade.
Mr. Gates kept Microsoft’s growth constantly in the double digits by not only making superior operating system software, but by pushing the company into application software which dominated the desktop (MS Office.) And when the internet came along he had the vision to be out front with Internet Explorer which crushed early innovator, and market maker, Netscape.
But then Mr. Gates turned the company over to Mr. Ballmer. And Mr. Ballmer was a leader lacking vision, or innovation. Instead of pushing Microsoft into new markets, as had Mr. Gates, he allowed the company to fixate on constant upgrades to the products which made it dominant – Windows and Office. Instead of keeping Microsoft in the Rapids of growth, he offered up a leadership designed to simply keep the company from going backward. He felt that Microsoft was a company that was “mature” and thus in need of ongoing enhancement, but not much in the way of real innovation. He trusted the market to keep growing, indefinitely, if he merely kept improving the products handed him.
As a result Microsoft stagnated. A “Reinvention Gap” developed as Vista, Windows 7, then Windows 8 and one after another Office updates did nothing to develop new customers, or new markets. Microsoft was resting on its old laurels – monopolistic control over desktop/laptop markets – without doing anything to create new markets which would keep it on the old growth trajectory of the Gates era.
Things didn’t look too bad for several years because people kept buying traditional PCs. And Ballmer famously laughed at products like Linux or Unix – and then later at entertainment devices, smart phones and tablets – as Microsoft launched, but then abandoned products like Zune, Windows CE phones and its own tablet. Ballmer kept thinking that all the market wanted was a faster, cheaper PC. Not anything really new.
And he was dead wrong. The Reinvention Gap emerged to the public when Apple came along with the iPod, iTunes, iPhone and iPad. These changed the game on Microsoft, and no longer was it good enough to simply have a better edition of an outdated technology. As PC sales began declining it was clear that Ballmer’s leadership had left the company in the Swamp, fighting off alligators and swatting at mosquitos with no strategy for how it would regain relevance against all these new competitors.
So the Board pushed him out, and demoted Gates off the Chairman’s throne. A big move, but likely too late. Fewer than 7% of companies that wander into the Swamp avoid the Whirlpool of demise. Think Univac, Wang, Lanier, DEC, Cray, Sun Microsystems (or Circuit City, Montgomery Wards, Sears.) The new CEO, Satya Nadella, has a much, much more difficult job than almost anyone thinks. Changing the trajectory of Microsoft now, after more than a decade creating the Reinvention Gap, is a task rarely accomplished. So rare we make heros of leaders who do it (Steve Jobs, Lou Gerstner, Lee Iacocca.)
So what will happen at the Clippers?
Critically, owning an NBA team is nothing like competing in the real business world. It is a closed marketplace. New competitors are not allowed, unless the current owners decide to bring in a new team. Your revenues are not just dependent upon you, but are even shared amongst the other teams. In fact your revenues aren’t even that closely tied to winning and losing. Season tickets are bought in advance, and with so many games away from home a team can do quite poorly and still generate revenue – and profit – for the owner. And this season the Indiana Pacers demonstrated that even while losing, fans will come to games. And the Philadelphia 76ers drew crowds to see if they would set a new record for the most consecutive games lost.
In America the major sports only modestly overlap, so you have a clear season to appeal to fans. And even if you don’t make it into the playoffs, you still share in the profits from games played by other teams. As a business, a team doesn’t need to win a championship to generate revenue – or make a profit. In fact, the opposite can be true as Wayne Huizenga learned owning the Championship winning Florida Marlins baseball team. He payed so much for the top players that he lost money, and ended up busting up the team and selling the franchise!
In short, owning a sports franchise doesn’t require the owner to understand lifecycles. You don’t have to understand much about business, or about business competition. You are protected from competitors, and as one of a select few in the club everyone actually works together – in a wholly uncompetitive way – to insure that everyone makes as much money as possible. You don’t even have to know anything about managing people, because you hire coaches to deal with players, and PR folks to deal with fans and media. And as said before whether or not you win games really doesn’t have much to do with how much money you make.
Most sports franchise owners are known more for their idiosyncrasies than their business acumen. They can be loud and obnoxious all they want (with very few limits.) And now that Mr. Ballmer has no investors to deal with – or for that matter vendors or cooperative parties in a complex ecosystem like personal technology – he doesn’t have to fret about understanding where markets are headed or how to compete in the future.
When it comes to acting like a person who knows little about business, but has a huge ego, fiery temper and loves to be obnoxious there is no better job than being a sports franchise owner. Mr. Ballmer should fit right in.

by Adam Hartung | May 16, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
IBM had a tough week this week. After announcing earnings on Wednesday IBM fell 2%, dragging the Dow down over 100 points. And as the Dow reversed course to end up 2% on the week, IBM continued to drag, ending down almost 3% for the week.
Of course, one bad week – even one bad earnings announcement – is no reason to dump a good company’s stock. The short term vicissitudes of short-term stock trading should not greatly influence long-term investors. But in IBM’s case, we now have 8 straight quarters of weaker revenues. And that HAS to be disconcerting. Managing earnings upward, such as the previous quarter, looks increasingly to be a short-term action, intended to overcome long-term revenues declines which portend much worse problems.
This revenue weakness roughly coincides with the tenure of CEO Virginia Rometty. And in interviews she increasingly is defending her leadership, and promising that a revenue turnaround will soon be happening. That it hasn’t, despite a raft of substantial acquisitions, indicates that the revenue growth problems are a lot deeper than she indicates.

CEO Rometty uses high-brow language to describe the growth problem, calling herself a company steward who is thinking long-term. But as the famous economist John Maynard Keynes pointed out in 1923, “in the long run we are all dead.” Today CEO Rometty takes great pride in the company’s legacy, pointing out that “Planes don’t fly, trains don’t run, banks don’t operate without much of what IBM does.”
But powerful as that legacy has been, in markets that move as fast as digital technology any company can be displaced very fast. Just ask the leadership at Sun Microsystems that once owned the telecom and enterprise markets for servers – before almost disappearing and being swallowed by Oracle in just 5 years (after losing $200B in market value.) Or ask former CEO Steve Ballmer at Microsoft, who’s delays at entering mobile have left the company struggling for relevancy as PC sales flounder and Windows 8 fails to recharge historical markets.
CEO Rometty may take pride in her earnings management. But we all know that came from large divestitures of the China business, and selling the PC and server business. As well as significant employee layoffs. All of which had short-term earnings benefits at the expense of long-term revenue growth. Literally $6B of revenues sold off just during her leadership.
Which in and of itself might be OK – if there was something to replace those lost sales. (Even if they didn’t have any profits – because at least we have faith in Amazon creating future profits as revenues zoom.)
What really worries me about IBM are two things that are public, but not discussed much behind the hoopla of earnings, acquisitions, divestitures and all the talk, talk, talk regarding a new future.
CNBC reported (again, this week,) that 121 companies in the S&P 500 (27.5%) cut R&D in the first quarter. And guess who was on the list? IBM, once an inveterate leader in R&D has been reducing R&D spending. The short-term impact? Better quarterly earnings. Long term impact????
The Washington Post reported this week about the huge sums of money pouring out of corporations into stock buybacks rather than investing in R&D, new products, new capacity, enhanced marketing, sales growth, etc. $500B in buybacks this year, 34% more than last year’s blistering buyback pace, flowed out of growth projects. To make matters worse, this isn’t just internal cash flow going for buybacks, but companies are actually borrowing money, increasing their debt levels, in order to buy their own stock!
And the Post labels as the “poster child” for this leveraged stock-propping behavior…. IBM. IBM
“in the first quarter bought back more than $8 billion of its own stock, almost all of it paid for by borrowing. By reducing the number of outstanding shares, IBM has been able to maintain its earnings per share and prop up its stock price even as sales and operating profits fall.
The result: What was once the bluest of blue-chip companies now has a debt-to-equity ratio that is the highest in its history. As Zero Hedge put it, IBM has embarked on a strategy to “postpone the day of income statement reckoning by unleashing record amounts of debt on what was once upon a time a pristine balance sheet.”
In the case of IBM, looking beyond the short-term trees at the long-term forest should give investors little faith in the CEO or the company’s future growth prospects. Much is being hidden in the morass of financial machinations surrounding acquisitions, divestitures, debt assumption and stock buybacks. Meanwhile, revenues are declining, and investments in R&D are falling. This cannot bode well for the company’s long-term investor prospects, regardless of the well scripted talking points offered last week.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 1, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
“Hope springs eternal in the human breast” (Alexander Pope)
As it does for most investors. People do not like to accept the notion that a business will lose relevancy, and its value will fall. Especially really big companies that are household brand names. Investors, like customers, prefer to think large, established companies will continue to be around, and even do well. It makes everyone feel better to have a optimistic attitude about large, entrenched organizations.
And with such optimism investors have cheered Microsoft for the last 15 months. After a decade of trading up and down around $26/share, Microsoft stock has made a significant upward move to $41 – a new decade-long high. This price has people excited Microsoft will reach the dot.com/internet boom high of $60 in 2000.
After discovering that Windows 8, and the Surface tablet, were nowhere near reaching sales expectations after Christmas 2012 – and that PC sales were declining faster than expected – investors were cheered in 2013 to hear that CEO Steve Ballmer would resign. After much speculation, insider Satya Nadella was named CEO, and he quickly made it clear he was refocusing the company on mobile and cloud. This started the analysts, and investors, on their recent optimistic bent.
CEO Nadella has cut the price of Windows by 70% in order to keep hardware manufacturers on Windows for lower cost machines, and he announced the company’s #1 sales and profit product – Office – was being released on iOS for iPad users. Investors are happy to see this action, as they hope that it will keep PC sales humming. Or at least slow the decline in sales while keeping manufacturers (like HP) in the Microsoft Windows fold. And investors are likewise hopeful that the long awaited Office announcement will mean booming sales of Office 365 for all those Apple products in the installed base.
But, there’s a lot more needed for Microsoft to succeed than these announcements. While Microsoft is the world’s #1 software company, it is still under considerable threat and its long-term viability remains unsure.
Windows is in a tough spot. After this price decline, Microsoft will need to increase sales volume by 2.5X to recoup lost profits. Meanwhile, Chrome laptops are considerably cheaper for customers and more profitable for manufacturers. And whether this price cut will have any impact on the decline in PC sales is unclear, as users are switching to mobile products for ease-of-use reasons that go far beyond price. Microsoft has taken an action to defend and extend its installed base of manufacturers who have been threatening to move, but the impact on profits is still likely to be negative and PC sales are still going to decline.
Meanwhile, the move to offer Office on iOS is clearly another offer to defend the installed Office marketplace, and unlikely to create a lot of incremental revenue and profit growth. The PC market has long been much bigger than tablets, and almost every PC had Office installed. Shrinking at 12-14% means a lot less Windows Office is being sold. And, In tablets iOS is not 100% of the market, as Android has substantial share. Offering Office on iOS reaches a lot of potential machines, but certainly not 100% as has been the case with PCs.
Further, while there are folks who look forward to running Office on an iOS device, Office is not without competition. Both Apple and Google offer competitive products to Office, and the price is free. For price sensitive users, both individuals and corporations, after 4 years of using competitive products it is by no means a given they all are ready to pay $60-$100 per device per year. Yes, there will be Office sales Microsoft did not previously have, but whether it will be large enough to cover the declining sales of Office on the PC is far from clear. And whether current pricing is viable is far, far from certain.
While these Microsoft products are the easiest for consumers to understand, Nadella’s move to make Microsoft successful in the mobile/cloud world requires succeeding with cloud products sold to corporations and software-as-service providers. Here Microsoft is late, and facing substantial competition as well.

Just last week Google cut the price of its Compute Engine cloud infrastructure (IaaS) platform and App Engine cloud app platform (PaaS) products 30-32%. Google cut the price of its Cloud Storage and BigQuery (big data analytics) services by 68% and 85% as it competes headlong for customers with Amazon. Amazon, which has the first-mover position and large customers including the U.S. federal government, cut prices within 24 hours for its EC2 cloud computing service by 30%, and for its S3 storage service by over 50%. Amazon also reduced prices on its RDS database service approximately 28%, and its Elasticache caching service by over 33%.
To remain competitive, Microsoft had to react this week by chopping prices on its Azure cloud computing products 27%-35%, reducing cloud storage pricing 44%-65%, and whacking prices on its Windows and Linux memory-intensive computing products 27%-35%. While these products have allowed the networking division formerly run by now CEO Nadella to be profitable, it will be increasingly difficult to maintain old profit levels on existing customers, and even a tougher problem to profitably steal share from the early cloud leaders – even as the market grows.
While optimism has grown for Microsoft fans, and the share price has moved distinctly higher, it is smart to look at other market leaders who obtained investor favorability, only to quickly lose it.
Blackberry was known as RIM (Research in Motion) in June, 2007 when the iPhone was launched. RIM was the market leader, a near monopoly in smart phones, and its stock was riding high at $70. In August, 2007, on the back of its dominant status, the stock split – and moved on to a split adjusted $140 by end of 2008. But by 2010, as competition with iOS and Android took its toll RIM was back to $80 (and below.) Today the rechristened company trades for $8.
Sears was once the country’s largest and most successful retailer. By 2004 much of the luster was coming off when KMart purchased the company and took its name, trading at only $20/share. Following great enthusiasm for a new CEO (Ed Lampert) investors flocked to the stock, sure it would take advantage of historical brands such as DieHard, Kenmore and Craftsman, plus leverage its substantial real estate asset base. By 2007 the stock had risen to $180 (a 9x gain.) But competition was taking its toll on Sears, despite its great legacy, and sales/store started to decline, total sales started declining and profits turned to losses which began to stretch into 20 straight quarters of negative numbers. Meanwhile, demand for retail space declined, and prices declined, cutting the value of those historical assets. By 2009 the stock had dropped back to $40, and still trades around that value today — as some wonder if Sears can avoid bankruptcy.
Best Buy was a tremendous success in its early years, grew quickly and built a loyal customer base as the #1 retail electronics purveyor. But streaming video and music decimated CD and DVD sales. On-line retailers took a huge bite out of consumer electronic sales. By January, 2013 the stock traded at $13. A change of CEO, and promises of new formats and store revitalization propped up optimism amongst investors and by November, 2014 the stock was at $44. However, market trends – which had been in place for several years – did not change and as store sales lagged the stock dropped, today trading at only $25.
Microsoft has a great legacy. It’s products were market leaders. But the market has shifted – substantially. So far new management has only shown incremental efforts to defend its historical business with product extensions – which are up against tremendous competition that in these new markets have a tremendous lead. Microsoft so far is still losing money in on-line and gaming (xBox) where it has lost almost all its top leadership since 2014 began and has been forced to re-organize. Nadella has yet to show any new products that will create new markets in order to “turn the tide” of sales and profits that are under threat of eventual extinction by ever-more-capable mobile products.
While optimism springs eternal long-term investors would be smart to be skeptical about this recent improvement in the stock price. Things could easily go from mediocre to worse in these extremely competitive global tech markets, leaving Microsoft optimists with broken dreams, broken hearts and broken portfolios.
Update: On April 2 Microsoft announced it is providing Windows for free to all manufacturers with a 9″ or smaller display. This is an action to help keep Microsoft competitive in the mobile marketplace – but it does little for Microsoft profitability. Android from Google may be free, but Google’s business is built on ad sales – not software sales – and that’s dramatically different from Microsoft that relies almost entirely on Windows and Office for its profitability
Update: April 3 CRN (Computer Reseller News) reviewed Office products for iOS – “We predict that once the novelty of “Office for iPad” wears off, companies will go back to relying on the humble, hard-working third parties building apps that are as stable, as handsome and far more capable than those of Redmond. It’s not that hard to do.”

by Adam Hartung | Feb 18, 2014 | Current Affairs, Games, In the Swamp, Leadership
Microsoft has a new CEO. And a new Chairman. The new CEO says the company needs to focus on core markets. And analysts are making the same cry.
Amidst this organizational change, xBox continues its long history of losing money – as much as $2B/year. And early 2014 results show that xBox One is selling at only half the rate of Sony’s Playstation 4, with cumulative xBox One sales at under 70% of PS4, leading Motley Fool to call xBox One a “total failure.”
While calling xBox One a failure may be premature, Microsoft investors have plenty to worry about.
Firstly, the console game business has not been a profitable market for anyone for quite a while.
The old leader, Nintendo, watched sales crash in 2013, first quarter 2014 estimates reduced by 67% and the CEO now projecting the company will be unproftable for the year. Nintendo stock declined by 2/3 between 2010 and 2012, then after some recovery in 2013 lost 17% on the January day of its disappointing sales expectation. Not a great market indicator.
The new sales leader is Sony, but that should give no one reason to cheer. Sony lost money for 4 straight years (2008-2012), and was barely able to squeek out a 2013 profit only because it took a massive $4.6B 2012 loss which cleared the way to show something slightly better than break-even. Now S&P has downgraded Sony’s debt to near junk status. While PS4 sales are better than xBox One, in the fast shifting world of gaming this is no lock on future sales as game developers constantly jockey dollars between platforms.
Whether Sony will make money on PS4 in 2014 is far from proven. Especially since it sells for $100/unit (20%) less than xBox One – which compresses margins. What investors (and customers) can expect is an ongoing price war between Nintendo, Sony and Microsoft to attract sales. A competition which historically has left all competitors with losses – even when they win the market share war.
And on top of all of this is the threat that console market growth may stagnate as gamers migrate toward games on mobile devices. How this will affect sales is unknown. But given what happened to PC sales it’s not hard to imagine the market for consoles to become smaller each year, dominated by dedicated game players, while the majority of casual game players move to their convenient always-on device.
Due to its limited product range, Nintendo is in a “fight to the death” to win in gaming. Sony is now selling its PC business, and lacks strong offerings in most consumer products markets (like TVs) while facing extremely tough competition from Samsung and LG. Sony, likewise, cannot afford to abandon the Playstation business, and will be forced to engage in this profit killing battle to attract developers and end-use customers.
When businesses fall into profit-killing price wars the big winner is the one who figures out how to exit first. Back in the 1970s when IBM created domination in mainframes the CEO of GE realized it was a profit bloodbath to fight for sales against IBM, Sperry Rand and RCA. Thinking fast he made a deal to sell the GE mainframe business to RCA so the latter could strengthen its campaign as an IBM alternative, and in one step he stopped investing in a money-loser while strenghtening the balance sheet in alternative markets like locomotives and jet engines – which went on to high profits.
With calls to focus, Microsoft is now abandoning XP. It is working to force customers to upgrade to either Windows 7 or Windows 8. As PC sales continue declining, Microsoft faces an epic battle to shore up its position in cloud services and maintain its enterprise customers against competitors like Amazon.
After a decade in gaming, where it has never made money, now is the time for Microsoft to recognize it does not know how to profit from its technology – regardless how good. Microsoft could cleve off Kinect for use in its cloud services, and give its installed xBox base (and developer community) to Nintendo where the company could focus on lower cost machines and maintain its fight with Sony.
Analysts that love focus would cheer. They would cheer the benefit to Nintendo, and the additional “focus” to Microsoft. Microsoft would stop investing in the unprofitable game console market, and use resources in markets more likely to generate high returns. And, with some sharp investment bankers, Microsoft could also probably keep a piece of the business (in Nintendo stock) that it could sell at a future date if the “suicide” console business ever turns into something profitable.
Sometimes smart leadership is knowing when to “cut and run.”
Links:
2012 recognition that Sony was flailing without a profitable strategy
January, 2013 forecast that microsoft would abandon gaming

by Adam Hartung | Feb 9, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle, Lock-in
There is a definite trend to raising the minimum wage. Regardless your political beliefs, the pressure to increase the minimum wage keeps growing. The important question for business leaders is, “Are we prepared for a $12 or $15 minimum wage?”
President Obama began his push for raising the minimum wage above $10 a year ago in his 2013 State of the Union. Since then, several articles have been written on income inequality and raising the minimum wage. Although the case to raise it is not clear cut, there is no doubt it has increased the rhetoric against the top 1% of earners. And now the President is mandating an increase in the minimum wage for federal workers and contractors to $10.10/hour, despite lack of congressional support and flak from conservatives.
Whether the economic case is provable, it appears that public sentiment is greatly in favor of a much higher minimum wage. And it will not affect all companies the same. Those that depend upon low priced labor, such as retailers like Wal-Mart and fast food companies like McDonald’s have a much higher concern. As should their employees, suppliers and investors.
A recent Federal Reserve report took a specific look at what happens to fast food companies when the minimum wage goes up, such as happened in Illinois, California and New Jersey. And the results were interesting. Because they discovered that a higher minimum wage really did hurt McDonald’s, causing stores to close. But….. and this is a big but…. those closed stores were rapidly replaced by competitors that could pay the higher wages, leading to no loss of jobs (and an overall increase in pay for labor.)
The implications for businesses that use low-priced labor are clear. It is time to change the business model – to adapt for a different future. A higher minimum wage does not doom McDonald’s – but it will force the company to adapt. If McDonald’s (and Burger King, Wendy’s, Subway, Dominos, Pizza Hut, and others) doesn’t adapt the future will be very ugly for their customers and the company. But if these companies do adapt there is no reason the minimum wage will hurt them particularly hard.
The chains that replaced McDonald’s closed stores were Five Guys, Chick-fil-A and Chipotle. You might remember that in 1998 McDonald’s started investing in Chipotle, and by 2001 McDonald’s owned the chain. And Chipotle’s grew rapidly, from a handful of restaurants to over 500. But then in 2006 McDonald’s sold all its Chipotle stock as the company went IPO, and used the proceeds to invest in upgrading McDonald’s stores and streamlining the supply chain toward higher profits on the “core” business.
Now, McDonald’s is shrinking while Chipotle is growing. Bloomberg/BusinessWeek headlined “Chipotle: The One That Got Away From McDonalds” (Oct. 3, 2013.) Investors were well served to trade in McDonald’s stock for Chipotle’s. And franchisees have suffered through sales problems as they raised prices off the old “dollar menu” while suffering higher food costs creating shrinking margins. Meanwhile Chipotle’s franchisees have been able to charge more, while keeping customers very happy, and maintain margins while paying higher wages. In a nutshell, Chipotle’s (and similar competitors) has captured the lost McDonald’s business as trends favor their business.
So McDonald’s obviously made a mistake. But that does not mean “game over.” All McDonald’s, Burger King and Wendy’s need to do is adapt. Fighting the higher minimum wage will lead to a lot of grief. There is no doubt wages will go up. So the smart thing to do is figure out what these stores will look like when minimum wages double. What changes must happen to the menu, to the store look, to the brand image in order for the company to continue attracting customers profitably.
This will undoubtedly include changes to the existing brands. But, these companies also will benefit from revisiting the kind of strategy McDonald’s used in the 1990s when buying Chipotle’s. Namely, buying chains with a different brand and value proposition which can flourish in a higher wage economy. These old-line restaurants don’t have to forever remain dominated by the old brands, but rather can transition along with trends into companies with new brands and new products that are more desirable, and profitable, as trends change the game. Like The Limited did when selling its stores and converting into L Brands to remain a viable company.
Now is the time to take action. Waiting until forced to take action will be too late. If McDonald’s and its brethren (and Wal-Mart and its minimum-wage-paying retail brethren) remain locked-in to the old way of doing business, and do everything possible to defend-and-extend the old success formula, they will follow Howard Johnson’s, Bennigan’s, Circuit City, Sears and a plethora of other companies into brand, and profitability, failure. Fighting trends is a route to disaster.
However, by embracing the trend and taking action to be successful in a future scenario of higher labor these companies can be very successful. There is nothing which dictates they have to follow the road to irrelevance while smarter brands take their place. Rather, they need to begin extensive scenario planning, understand how these competitors succeed and take action to disrupt their old approach in order to create a new, more profitable business that will succeed.
Disruptions happen all the time. In the 1970s and 1980s gasoline prices skyrocketed, allowing offshore competitors to upend the locked-in Detroit companies that refused to adapt. On-line services allowed Google Maps to wipe out Rand-McNally, Travelocity to kill OAG and Wikipedia to kill bury Encyclopedia Britannica. These outcomes were not dictated by events. Rather, they reflect an inability of an existing leader to adapt to market changes. An inability to embrace disruptions killed the old competitors, while opening doors for new competitors which embraced the trend.
Now is the time to embrace a higher minimum wage. Every business will be impacted. Those who wait to see the impact will struggle. But those who embrace the trend, develop future scenarios that incorporate the trend and design new business opportunities can turn this disruption into a big win.

by Adam Hartung | Jan 24, 2014 | Current Affairs, In the Swamp, Leadership
JPMorganChase Board of Directors this week voted to double CEO Jamie Dimon’s pay to something north of $20million. That he received such a big raise after the bank was forced to pay out more than $20B in fines for illegal activity has raised a number of eyebrows among analysts and shareholders. That he is receiving this raise after the bank laid off some 7,5000 employees in 2013, and recently announced it would not give employees raises due to the large fines, shows a distinct callousness toward employees, while raising questions about company leadership.
The Wall Street Journal reported that there was a lot of Board discourse about CEO Dimon’s pay package. But in the byzantine world of large company governance, apparently the Board felt compelled to pay Mr. Dimon tremendously well in order to send a message to Washington that the Board thought the regulators were wrong in pursuing malfeasance at JPMC. A show of support for the CEO who claimed this week he felt the bank had been treated unfairly.
Did that last paragraph leave you a bit confused? Because the logic, to be honest, is far from straightforward. The Board of a troubled bank with long-term leadership issues creating billions in trading losses and billions in fines for illegal behavior decided to withhold employee pay raises but double the CEO compensation in order to snub the nose of the regulators who have been pointing out years of unethical, if not illegal, behavior? The same regulators who might well see this very action as a good reason to heighten their investigations?
I’m not trying to oversimply the complexities of corporate governance, but this is some pretty tortured logic. When so many things have gone wrong, and it can be traced to leadership, rewarding that leader handsomely has the clear appearance of supporting his behavior, while punishing employees for the results of that leader’s actions.
Mr. Dimon is a media darling, and has been most of his career. He has also been outspoken on many issues during his career, drawing the attention of friends and foes. He is unabashed in his opinions, and even when he’s dead wrong – as when he referred to massive London trading losses as “a tempest in a teapot” he always speaks with total confidence. Mr. Dimon shows complete faith in his ability to be smarter than everyone else, and complete faith in his decisions, and he has no problem making sure everyone is fully aware of his absolute trust in himself.
But people are able to see trends. Although his defenders would like to say that the fines were related to issues which predated Mr. Dimon’s leadership, there are clear markers that differ. For example, it was the desperate search for higher profits under Mr. Dimon which led to the creation of the London trading desk, and giving it lattitude for big bets, that created some $7B in losses. Mr. Dimon’s final reaction was akin to “we make mistakes. Sorry. Time to move on.”
Oh yeah, and he fired the employees while claiming no personal responsibility.
And in January we learned that the bank was paying a $2.6B fine for aiding and abetting the ponzi scheme operated by Mr. Bernie Madoff. This behavior was something which had gone on for decades, without any oversight or reporting at the bank. This had continued while Mr. Dimon was CEO.
Why did these things happen? Because there was a huge desire to make more money.
Mr. Dimon is known for being as blunt with executives and employees as he is with the media. His “take no prisoners” style has been seen as crippling by many. Mr. Dimon focuses on results, and he is known for being brutal when he doesn’t receive the results he wants. For executives and employees that created a culture where delivering results to Mr. Dimon was paramount. And if that required taking big risks, or looking the other way about troubling behavior, well, people did what they had to do to make things happen at JPMC. If you had to bend the rules, or look the other way, to get results that was better than having to deal with the wrath of Mr. Dimon.
“The person at the top” sets the tone by which the organization behaves. And the more we learn about JPMC the more we see a company where the CEO loves to flash his POTUS cufflinks at the Congress and press, claim he’s taking the high road, and blame employees or predecessors when things go wrong. And that’s not a healthy environment.
Across the river from Wall Street Chris Christie, Governor of New Jersey, has become embroiled in controversy. His staff created an enormous traffic debacle in Fort Lee as retaliation against a mayor who did not support the Governor’s re-election bid. Mr. Christie fired the staffer, and claimed he knew nothing about it. But the majority of people in New Jersey aren’t buying the Governer’s ignorance.
Instead most Americans see a negative pattern in the governor’s behavior. His “take no prisoners” attitude has created accomplishments, but simultaneously he’s shown he thinks its OK to take off the gloves and fight bare knuckle – and not stop before taking some pretty sketchy shots at people in his quest to come out on top. Now regulators are digging even deeper to see if his bullying behavior set the stage for problems, even if he didn’t do the dastardly deed himself. And, as for governance, it will be up to voters to decide if Mr. Christie’s leadership is what they want, or not.
But at JPMC the governance is up to the Board. And this Board is, unfortunately, controlled by Mr. Dimon. He is not just CEO, but also Chairman of the Board. He holds the “bully gavel” when it comes to Board matters. He is able to set the agenda, and control the data the Board receives. He is able to call the Board members, and strong arm them to see things his way. Although it is clear the bank would benefit from a seperation of the roles of CEO and Chairman, Mr. Dimon has stopped this from happening. And the big winner has been – Mr. Dimon.
The signal this sends for JPMC employees, customers and investors is not good. While the stock is up some 22% the last year, governance and the CEO should have a long-term vision and not be influenced by short-term price changes. In the case of JPMC the culture appears to be one where seeking results is primary. Even if it leads to taking inordinate risks (which can create huge losses,) or taking and supporting questionable clients (Bernie Madoff,) or operating on the edge of financial industry legality. And if things go wrong – look for a scapegoat. Primarily someone below you who you can blame, while you claim you either didn’t know about it or didn’t support their behavior.
At JPMC the important question now is less about CEO pay and more about governance. The Board clearly has lost its ability to control a CEO + Chairman able to push his will, even when the logic of some actions appears hard to follow. The Board should be addressing who should be the Chairman, what should be the strategy, is the bank doing the right things, are the right compliance tools in place, and then – after all of that – is compensation being set correctly. That Mr. Dimon received such an undeserved raise simply points to much bigger problems in governance – and raises questions about the future of JPMC.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 19, 2013 | Current Affairs, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Television, Web/Tech
Apple announced the new iPhones recently. And mostly, nobody cared.
Remember when users waited anxiously for new products from Apple? Even the media became addicted to a new round of Apple products every few months. Apple announcements seemed a sure-fire way to excite folks with new possibilities for getting things done in a fast changing world.
But the new iPhones, and the underlying new iPhone software called iOS7, has almost nobody excited.
Instead of the product launches speaking for themselves, the CEO (Tim Cook) and his top product development lieutenants (Jony Ive and Craig Federighi) have been making the media rounds at BloombergBusinessWeek and USAToday telling us that Apple is still a really innovative place. Unfortunately, their words aren't that convincing. Not nearly as convincing as former product launches.
CEO Cook is trying to convince us that Apple's big loss of market share should not be troubling. iPhone owners still use their smartphones more than Android owners, and that's all we should care about. Unfortunately, Apple profits come from unit sales (and app sales) rather than minutes used. So the chronic share loss is quite concerning.
Especially since unit sales are now growing barely in single digits, and revenue growth quarter-over-quarter, which sailed through 2012 in the 50-75% range, have suddenly gone completely flat (less than 1% last quarter.) And margins have plunged from nearly 50% to about 35% – more like 2009 (and briefly in 2010) than what investors had grown accustomed to during Apple's great value rise. The numbers do not align with executive optimism.
For industry aficianados iOS7 is a big deal. Forbes Haydn Shaughnessy does a great job of laying out why Apple will benefit from giving its ecosystem of suppliers a new operating system on which to build enhanced features and functionality. Such product updates will keep many developers writing for the iOS devices, and keep the battle tight with Samsung and others using Google's Android OS while making it ever more difficult for Microsoft to gain Windows8 traction in mobile.
And that is good for Apple. It insures ongoing sales, and ongoing profits. In the slog-through-the-tech-trench-warfare Apple is continuing to bring new guns to the battle, making sure it doesn't get blown up.
But that isn't why Apple became the most valuable publicly traded company in America.
We became addicted to a company that brought us things which were great, even when we didn't know we wanted them – much less think we needed them. We were happy with CDs and Walkmen until we discovered much smaller, lighter iPods and 99cent iTunes. We were happy with our Blackberries until we learned the great benefits of apps, and all the things we could do with a simple smartphone. We were happy working on laptops until we discovered smaller, lighter tablets could accomplish almost everything we couldn't do on our iPhone, while keeping us 24×7 connected to the cloud (that we didn't even know or care about before,) allowing us to leave the laptop at the office.
Now we hear about upgrades. A better operating system (sort of sounds like Microsoft talking, to be honest.) Great for hard core techies, but what do users care? A better Siri; which we aren't yet sure we really like, or trust. A new fingerprint reader which may be better security, but leaves us wondering if it will have Siri-like problems actually working. New cheaper color cases – which don't matter at all unless you are trying to downgrade your product (sounds sort of like P&G trying to convince us that cheaper, less good "Basic" Bounty was an innovation.)
More (upgrades) Better (voice interface, camera capability, security) and Cheaper (plastic cases) is not innovation. It is defending and extending your past success. There's nothing wrong with that, but it doesn't excite us. And it doesn't make your brand something people can't live without. And, while it keeps the battle for sales going, it doesn't grow your margin, or dramatically grow your sales (it has declining marginal returns, in fact.)
And it won't get your stock price from $450-$475/share back to $700.
We all know what we want from Apple. We long for the days when the old CEO would have said "You like Google Glass? Look at this……. This will change the way you work forever!!"
We've been waiting for an Apple TV that let's us bypass clunky remote controls, rapidly find favorite shows and helps us avoid unwanted ads and clutter. But we've been getting a tease of Dick Tracy-esque smart watches.
From the world's #1 tech brand (in market cap – and probably user opinion) we want something disruptive! Something that changes the game on old companies we less than love like Comcast and DirecTV. Something that helps us get rid of annoying problems like expensive and bad electric service, or routers in our basements and bedrooms, or navigation devices in our cars, or thumb drives hooked up to our flat screen TVs —- or doctor visits. We want something Game Changing!
Apple's new CEO seems to be great at the Sustaining Innovation game. And that pretty much assures Apple of at least a few more years of nicely profitable sales. But it won't keep Apple on top of the tech, or market cap, heap. For that Apple needs to bring the market something big. We've waited 2 years, which is an eternity in tech and financial markets. If something doesn't happen soon, Apple investors deserve to be worried, and wary.
by Adam Hartung | Aug 23, 2013 | In the Swamp, Leadership, Software, Web/Tech
Steve Ballmer announced he would be retiring as CEO of Microsoft within the next 12 months. This extended timing, rather than immediately, shows clear the Board is ready for him to go but there is nobody ready to replace him.
The big question is, who would want Ballmer's job? It will be very tough to make Microsoft an industry leader again. What would his replacement propose to do? The fuse for a turnaround is short, and the options faint.
Microsoft has been on a downhill trajectory for at least 4 years. Although the company has introduced innovations in gaming (xBox and Kinect) as well as on-line (games and Bing), those divisions perpetually lose money. Stiff competitors Sony, Nintendo and Google have made these forays intellectually interesting, but of no value for investors or customers. The end-game for Microsoft has remained Windows – and as PC sales decline that's very bad news.
Microsoft viability has been firmly tied to Windows and Office sales. Historically these have been unassailable products, creating over 100% of the profits at Microsoft (covering losses in other divisions.) But, these products have lost growth, and relevancy. Windows 8 and Office 365 are product nobody really cares about, while they keep looking for updates from Apple, Google, Amazon and Samsung.
The market started going mobile 10 years ago. As Apple and Google promoted increased mobility, Microsoft tried to defend & extend its PC stronghold. It was a classic business inflection point in the making. Everyone knew at some point mobile devices would be more important than PCs. But most industry insiders (including Microsoft) kept thinking it would be later rather than sooner.
They were wrong. The shift came a lot faster than expected. Like in sailboat racing, suddenly the wind was taken out of Microsoft's sails as competitors shot to the lead in customer interest. While people were excited for new smartphones and tablets, Microsoft tried to re-engineer its historical product as an extension into the new market.
Windows 8 tablets and Surface tablets were ill-fated from the beginning. They did not appeal to the huge installed base of Windows customers, because changes like touch screens and tiles simply were too expensive and too behaviorally different. And they offered no advantage for people to switch that had already started buying iOS and Android products. Not to mention an app availability about 10% of the market leaders. Simply put, investing in Windows 8 and its own tablet was like adding bricks to a downhill runaway truck (end-of-life for PCs) – it sped up the time to an inevitable crash.
And spending money on poorly thought out investments like the Barnes & Noble Nook merely demonstrated Microsoft had money to burn, rather than a strategy for competing. Skype cost some $8B, but how has that helped Microsoft become more competive? It's not just an overspending on internal projects that failed to achieve any market success, but a series of wasted investments in bad acquisitions that showed Microsoft had no idea how it was going to regain industry leadership in a changing marketplace going more mobile and into the cloud every month.
Now the situation is pretty dire, and now is the time for Microsoft to give up on its defend and extend strategy for Windows/Office. Customers are openly uninterested in new laptops running Windows 8. And Win 8.1 will not change this lackadaisical attitude. Nobody is interested in Windows 8 phones, or tablets. This has left companies in the Microsoft ecosystem like HP, Dell and Nokia gasping for air as sales tumble, profits evaporate and customers flock to new solutions from Apple and Samsung. Instead of seeking out an update to Office for a new PC, people are using much lighter (and cheaper) cloud services from Amazon and office solutions like Google docs. And most of those old add-on product sales, like printers and servers, are disappearing into the cloud and mobile displays.
So now, after being forced to write off Surface and report a horrible quarter, the Board has pushed Ballmer out the door. Pretty remarkable. But, incredibly late. Just like the leaders at RIM stayed too long, leaving the company with no future options as Blackberry sales plummeted, Ballmer is taking leave as sales, profits and cash flow are taking a turn for the worst. And only months after a reorganization that simply made the whole situation a lot more confusing for not only investors, but internal managers and employees.
Microsoft has a big cash hoard, but how long will that last? As its distribution system falters, and sales drop, the costs will rapidly catch up with cash flow. Big layoffs are a certainty; think half the workforce in 2 years. Equally certain are sales of divisions (who can buy xBox market share and turn it competitively profitable?) or shut-downs (how long will Bing stay alive when it is utterly unnecessary and expensive to maintain?)
But, there is a better option. Without the cash from
Windows/Office, you can't keep much of the rest of Microsoft walking. So
now is the time to cut investments in Windows/Office and put money into the
best things Microsoft has going – primarily Kinect and cloud services. A radical restructuring of its spending and investments.
Kinect is an incredible product. It has found multiple applications Microsoft fails to capitalize upon. Kinect has the possibility of becoming the centerpiece for managing how we connect to data, how we store data, how we find data. It can bring together our smartphone, tablet and historical laptop worlds – and possibly even connect this to traditional TV and radio. It can be the centerpiece for two-way communications (think telephone or skype via all your devices.) Coupled with the right hardware, it can leapfrog iTV (which we still are waiting to see) and Cisco simultaneously.
In cloud services it will take a lot to compete with leaders Amazon, IBM, Apple and Google. They have made big investments, and are far in front. But, this is the bread-and-butter market for Microsoft. Millions of small businesses that want easy to use BYOD (bring your own device) environment, and easy access to data, documents and functionality for IT, like guaranteed data back-up and uptime, and user functionality like all those apps. These customers have relied on Microsoft for these kind of services for years, and would enjoy a services provider with an off-the-shelf product they can implement easily and cheaply that supports all their needs. Expensive to develop, but a growing market where Microsoft has a chance to leapfrog competitors.
As for Bing, give it to Yahoo – if Marissa Mayer will take it. Stop the bloodletting and get out of a market where Microsoft has never succeeded. Bing is core to Yahoo's business. If you can trade for some Yahoo stock, go for it. Let Yahoo figure out how to sell content and ads, while Microsoft refocuses on the new platform for 2017; from the user to the infrastructure services.
Strong leaders have their benefits. But, when they don't understand market shifts, and spend far too long trying to defend & extend past markets, they can put their organizations in terrible jeopardy of total failure. Ballmer leaves no with clear replacement, nor with any vision in place for leapfrogging competitors and revitalizing Microsoft.
So it is imperative the new leader provide this kind of new thinking. There are trends developing that create future scenarios where Microsoft can once again be a market leader. And it will be the role of the new CEO to identify that vision and point Microsoft's investments in the right direction to regain viability by changing the game on the current winners.











