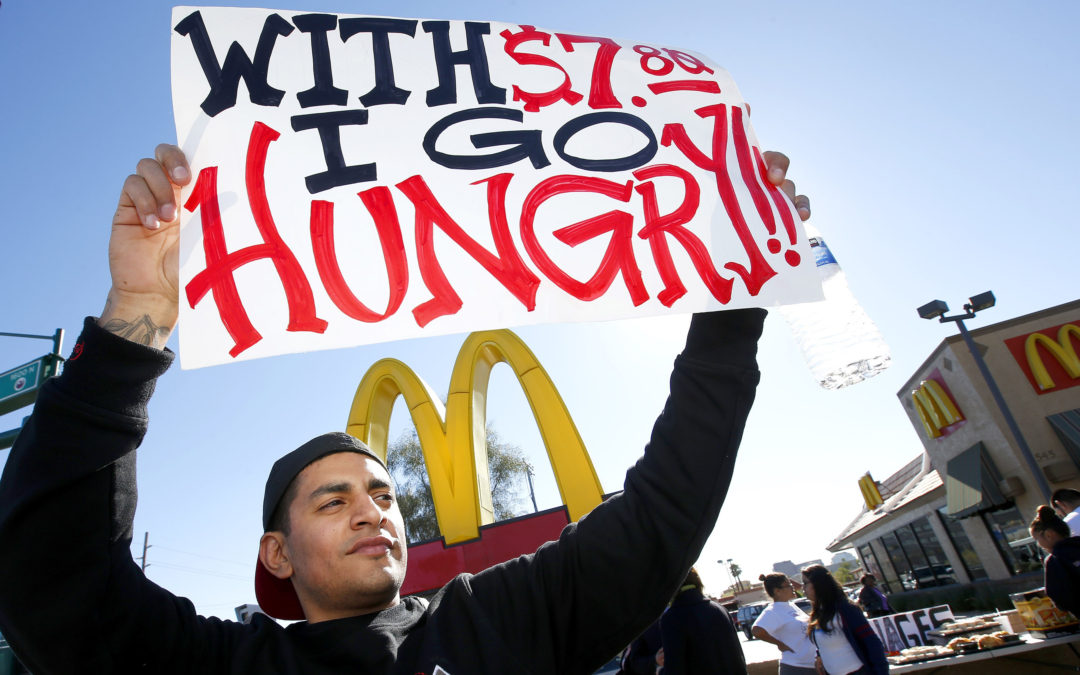by Adam Hartung | Nov 6, 2013 | Defend & Extend, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Can you believe it has been only 12 years since Apple introduced the iPod? Since then Apple’s value has risen from about $11 (January, 2001) to over $500 (today) – an astounding 45X increase.
With all that success it is easy to forget that it was not a “gimme” that the iPod would succeed. At that time Sony dominated the personal music world with its Walkman hardware products and massive distribution through consumer electronics chains such as Best Buy, and broad-line retailers like Wal-Mart. Additionally, Sony had its own CD label, from its acquisition of Columbia Records (renamed CBS Records,) producing music. Sony’s leadership looked impenetrable.
But, despite all the data pointing to Sony’s inevitable long-term domination, Apple launched the iPod. Derided as lacking CD quality, due to MP3’s compression algorithms, industry leaders felt that nobody wanted MP3 products. Sony said it tried MP3, but customers didn’t want it.
All the iPod had going for it was a trend. Millions of people had downloaded MP3 songs from Napster. Napster was illegal, and users knew it. Some heavy users were even prosecuted. But, worse, the site was riddled with viruses creating havoc with all users as they downloaded hundreds of millions of songs.
Eventually Napster was closed by the government for widespread copyright infreingement. Sony, et.al., felt the threat of low-priced MP3 music was gone, as people would keep buying $20 CDs. But Apple’s new iPod provided mobility in a way that was previously unattainable. Combined with legal downloads, including the emerging Apple Store, meant people could buy music at lower prices, buy only what they wanted and literally listen to it anywhere, remarkably conveniently.
The forecasted “numbers” did not predict Apple’s iPod success. If anything, good analysis led experts to expect the iPod to be a limited success, or possibly failure. (Interestingly, all predictions by experts such as IDC and Gartner for iPhone and iPad sales dramatically underestimated their success, as well – more later.) It was leadership at Apple (led by the returned Steve Jobs) that recognized the trend toward mobility was more important than historical sales analysis, and the new product would not only sell well but change the game on historical leaders.
Which takes us to the mistake Intel made by focusing on “the numbers” when given the opportunity to build chips for the iPhone. Intel was a very successful company, making key components for all Microsoft PCs (the famous WinTel [for Windows+Intel] platform) as well as the Macintosh. So when Apple asked Intel to make new processors for its mobile iPhone, Intel’s leaders looked at the history of what it cost to make chips, and the most likely future volumes. When told Apple’s price target, Intel’s leaders decided they would pass. “The numbers” said it didn’t make sense.
Uh oh. The cost and volume estimates were wrong. Intel made its assessments expecting PCs to remain strong indefinitely, and its costs and prices to remain consistent based on historical trends. Intel used hard, engineering and MBA-style analysis to build forecasts based on models of the past. Intel’s leaders did not anticipate that the new mobile trend, which had decimated Sony’s profits in music as the iPod took off, would have the same impact on future sales of new phones (and eventually tablets) running very thin apps.
Harvard innovation guru Clayton Christensen tells audiences that we have complete knowledge about the past. And absolutely no knowledge about the future. Those who love numbers and analysis can wallow in reams and reams of historical information. Today we love the “Big Data” movement which uses the world’s most powerful computers to rip through unbelievable quantities of historical data to look for links in an effort to more accurately predict the future. We take comfort in thinking the future will look like the past, and if we just study the past hard enough we can have a very predictible future.
But that isn’t the way the business world works. Business markets are incredibly dynamic, subject to multiple variables all changing simultaneously. Chaos Theory lecturers love telling us how a butterfly flapping its wings in China can cause severe thunderstorms in America’s midwest. In business, small trends can suddenly blossom, becoming major trends; trends which are easily missed, or overlooked, possibly as “rounding errors” by planners fixated on past markets and historical trends.
Markets shift – and do so much, much faster than we anticipate. Old winners can drop remarkably fast, while new competitors that adopt the trends become “game changers” that capture the market growth.
In 2000 Apple was the “Mac” company. Pretty much a one-product company in a niche market. And Apple could easily have kept trying to defend & extend that niche, with ever more problems as Wintel products improved.
But by understanding the emerging mobility trend leadership changed Apple’s investment portfolio to capture the new trend. First was the iPod, a product wholly outside the “core strengths” of Apple and requiring new engineering, new distribution and new branding. And a product few people wanted, and industry leaders rejected.
Then Apple’s leaders showed this talent again, by launching the iPhone in a market where it had no history, and was dominated by Motorola and RIMM/BlackBerry. Where, again, analysts and industry leaders felt the product was unlikely to succeed because it lacked a keyboard interface, was priced too high and had no “enterprise” resources. The incumbents focused on their past success to predict the future, rather than understanding trends and how they can change a market.
Too bad for Intel. And Blackberry, which this week failed in its effort to sell itself, and once again changed CEOs as the stock hit new lows.
Then Apple did it again. Years after Microsoft attempted to launch a tablet, and gave up, Apple built on the mobility trend to launch the iPad. Analysts again said the product would have limited acceptance. Looking at history, market leaders claimed the iPad was a product lacking usability due to insufficient office productivity software and enterprise integration. The numbers just did not support the notion of investing in a tablet.
Anyone can analyze numbers. And today, we have more numbers than ever. But, numbers analysis without insight can be devastating. Understanding the past, in grave detail, and with insight as to what used to work, can lead to incredibly bad decisions. Because what really matters is vision. Vision to understand how trends – even small trends – can make an enormous difference leading to major market shifts — often before there is much, if any, data.
by Adam Hartung | Oct 23, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, Leadership, Lifecycle
On 11 October Safeway announced it was going to either sell or close its 79 Dominick's brand grocery stores in Chicago. After 80 years in Chicago, San Francisco based Safeway leadership felt it was simply time for Dominick's to call it quits.
The grocery industry is truly global, because everyone eats and almost nobody grows their own food. It moves like a giant crude oil carrier, much slower than technology, so identifying trends takes more patience than, say, monitoring annual smartphone cycles. Yet, there are clearly pronounced trends which make a huge difference in performance.
Good for those who recognize them. Bad for those who don't.
Safeway, like a lot of the dominant grocers from the 1970s-1990s, clearly missed the trends.
Coming out of WWII large grocers replaced independent neighborhood corner grocers by partnering with emerging consumer goods giants (Kraft, P&G, Coke, etc.) to bring customers an enormous range of products very efficiently. They offered a larger selection at lower prices. Even though margins were under 10% (think 2% often) volume helped these new grocery chains make good returns on their assets. Dillon's (originally of Hutchinson, Kansas and later purchased by Kroger) became a 1970s textbook, case study model of effective financial management for superior returns by Harvard Business School guru William Fruhan.
But times changed.
Looking at the trend toward low prices, Aldi from Germany came to the U.S. market with a strategy that defines the ultimate in low cost. Often there is only one brand of any product in the store, and that is likely to be the chain's private label. And often it is only available in one size. And customers must be ready to use a quarter to borrow the shopping cart (returned if you replace the cart.) And customers pay for their sacks. Stores are remarkably small and efficient, frequently with only 2 or 3 employees. And with execution so well done that the Aldi brand became #1 in "simple brands" according to a study by brand consultancy Seigal+Gale.
Of course, we also know that big discount chains like WalMart and Target started cherry picking the traditional grocer's enormous SKU (stock keeping units) list, limiting selection but offering lower prices due to lower cost.
Looking at the quality trend, Whole Foods and its brethren demonstrated that people would pay more for better perceived quality. Even though filling the aisles with organic
products and the ultimate in freshness led to higher prices, and someone nicknaming the chain
"whole paycheck," customers payed up to shop there, leading to superior
returns.
Connected to quality has been the trend, which began 30 years ago, to "artisanal" products. Shoppers pay more to buy what are considered limited edition products that are perceived as superior due to a range of "artisanal quality" features; from ingredients used to age of product (or "freshness,") location of manufacture ("local,") extent to which it is considered "organic," quantity of added ingredients for preservation or vitamin enhancement ("less is more,") ecological friendliness of packaging and even producer policies regarding corporate social and ecological responsibility.
But after decades of partnership, traditional grocers today remain dependant on large consumer goods companies to survive. Large CPGs supply a massive number of SKUs in a limited number of contracts, making life easy for grocery store buyers. Big CPGs pay grocers for shelf space, coupons to promote customer purchases, rebates, ads in local store circulars, discounts for local market promotions, sales volumes exceeding commitments and even planograms which instruct employees how to place products on shelves — all saving money for the traditional grocer. In some cases payments and rebates equalling more than total grocer profits.
Additionally, in some cases big CPG firms even deliver their products into the store and stock shelves at no charge to the grocer (called store-door-delivery as a substitute for grocer warehouse and distribution.) And the big CPG firms spend billions of dollars on product advertising to seemingly assure sales for the traditional grocer.
These practices emerged to support the bi-directionally beneficial historically which tied the traditional grocer to the large CPG companies. For decades they made money for both the CPG suppliers and their distributors. Customers were happy.
But the market shifted, and Safeway (including its employees, customers, suppliers and investors) is the loser.
The old retail adage "location, location, location" is no longer enough in grocery. Traditional grocery stores can be located next to good neighborhoods, and execute that old business model really well, and, unfortunately, not make any money. New trends gutted the old Safeway/Dominick's business model (and most of the other traditional grocers) even though that model was based on decades of successful history.
The trend to low price for customers with the least funds led them to shop at the new low-price leaders. And companies that followed this trend, like Aldi, WalMart and Target are the winners.
The trend to higher perceived quality and artisanal products led other customers to retailers offering a different range of products. In Chicago the winners include fast growing Whole Foods, but additionally the highly successful Marianno's division of Roundy's (out of Milwaukee.) And even some independents have become astutely profitable competitors. Such as Joe Caputo & Sons, with only 3 stores in suburban Chicago, which packs its parking lots daily by offering products appealing to these trendy shoppers.
And then there's the Trader Joe's brand. Instead of being all things to all people, Aldi created a new store chain designed to appeal to customers desiring upscale products, and named it Trader Joe's. It bares scance resemblance to an Aldi store. Because it is focused on the other trend toward artisinal and quality. And it too brings in more customers, at higher margin, than Dominick's.
When you miss a trend, it is very, very painful. Even if your model worked for 75 years, and is tightly linked to other giant corporations, new trends lead to market shifts making your old success formula obsolete.
Simultaneously, new trends create opportunities. Even in enormous industries with historically razor-thin margins – or even losses. Building on trends allows even small start-up companies to compete, and make good profits, in cutthroat industries – like groceries.
Trends really matter. Leaders who ignore the trends will have companies that suffer. Meanwhile, leaders who identify and build on trends become the new winners.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 30, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Leadership, Lock-in
Last week we learned that there is no doubt, the world is warming. A U.N. report affirmed by some 1,000 scientists asserted 95% confidence as to the likely outcomes, as well as the cause. We must expect more volatility in weather, and that the oceans will continue rising.
Yet, most people really could have cared less. And a vocal minority still clings to the notion that because the prior decade saw a slower heating, perhaps this will all just go away.
Incredibly, for those of us who don't live and work in Florida, there was CNN news footage of daily flooding in Miami's streets due to current sea levels which have risen over last 50 years. Given that we can now predict the oceans will rise between 1 and 6 feet in the next 50 years, it is possible to map the large areas of Miami streets which are certain to be flooded.
There is just no escaping the fact that the long-term trend of global warming will have a remarkable impact on everyone. It will affect transportation, living locations, working locations, electricity generation and distribution, agriculture production, textile production – everything will be affected. And because it is happening so slowly, we actually can do lots of modeling about what will happen.
Yet, I never hear any business leaders talk about how they are planning for global warning. No comments about how they are making changes to keep their business successful. Nor comments about the new opportunities this will create. Even though the long-term impacts will be substantial, the weather and how it affects us is treated like the status quo.
What does this have in common with the government shutdown?
America has known for decades that its healthcare system was dysfunctional; to be polite. It was incredibly expensive (by all standards) and yet had no better outcomes for citizens than other modern countries. For over 20 years efforts were attempted to restructure health care. Yet as the morass of regulations ballooned, there was no effective overhaul that addressed basic problems built into the system. Costs continued to soar, and more people joined the ranks of those without health care, while other families were bankrupted by illness.
Finally, amidst enormous debate, the Affordable Care Act was passed. Despite wide ranging opinions from medical doctors, nurses, hospital and clinic administrators, patient advocacy groups, pharmaceutical companies, medical device companies and insurance companies (to name just some of those with a vested interest and loud, competing, viewpoints) Congress passed the Affordable Care Act which the President signed.
Like most such things in America, almost nobody was happy. No one got what they wanted. It was one of those enormous, uniquely American, compromises. So, like unhappy people do in America, we sued! And it took a few years before finally the Supreme Court ruled that the legislation was constitutional. The Affordable Care Act would be law.
But, people remain who simply do not want to accept the need for health care change. So, in a last ditch effort to preserve the status quo, they are basically trying to kidnap the government budget process and hold it hostage until they get their way. They have no alternative plan to replace the Affordable Care Act. They simply want to stop it from moving forward.
What global warming and the government shut down have in common are:
- Very long-term problems
- No quick solution for the problem
- No easy solution for the problem
- If you do nothing about the problem today, you have no immediate calamity
- Doing anything about the problem affects almost everyone
- Doing anything causes serious change
So, in both cases, people have emerged as the Status Quo Police. They take on the role of stopping change. They will do pretty much anything to defend & extend the status quo:
- Ignore data that is contradictory to the best analytical views
- Claim that small probability outcomes (that change may not be necessary) justifies doing nothing
- Delay, delay, delay taking any action until a disaster requires action
- Constantly claim that the cost of change is not justified
- Claim that the short-term impact of change is more deleterious than the long-term benefits
- Assume that the status quo will somehow resolve itself favorably – with no supporting evidence or analysis
- Undertake any action that preserves the status quo
- Threaten a "scorched earth policy" (that they will create big, immediate problems if forced to change the status quo)
The earth is going to become warmer. The oceans will rise, and other changes will happen. If you don't incorporate this in your plans, and take action, you can expect this trend will harm you.
U.S. health care is going to be reformed. How it will happen is just starting. How it will evolve is still unclear. Those who create various scenarios in their plans to prepare for this change will benefit. Those who do nothing, hoping it goes away, will find themselves struggling.
The Status Quo Police, trying their best to encourage people to ignore the need for change – the major, important trends – are helping nobody. By trying to preserve the status quo they inhibit effective planning, and action, to prepare for a different (better) future.
Does your organization have Status Quo Police? Are their functions, groups or individuals who are driven to defend and extend the status quo – even in the face of trends that demonstrate change is necessary? Can they stop conversations around substantial change? Are they allowed to stop future planning for scenarios that are very different from the past? Can they enforce cultural norms that stop considering new alternatives? Can they control resources resulting in less innovation and change?
Let's learn from these 2 big issues. Change is inevitable. It is even necessary. Trying to preserve the status quo is costly, and inhibits taking long-term effective action. Status Quo Police are obstructionists who keep us from facing, and solving, difficult problems. They don't help our organizations create a new, more successful future. Only by overcoming them can we reach our full potential, and create opportunities out of change.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 4, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Just over a week after Microsoft announces plans to replace CEO Steve Ballmer the company announced it will spend $7.2B to buy the Nokia phone/tablet business. For those looking forward to big changes at Microsoft this was like sticking a pin in the big party balloon!
Everyone knows that Microsoft's future is at risk now that PC sales are declining globally at nearly 10% – with developing markets shifting even faster to mobile devices than the USA. And Microsoft has been the perpetual loser in mobile devices; late to market and with a product that is not a game changer and has only 3% share in the USA.
But, despite this grim reality, Microsoft has doubled-down (that's doubled its bet for non-gamblers) on its Windows 8 OS strategy, and continues to play "bet the company". Nokia's global market share has shriveled to 15% (from 40%) since former Microsoft exec-turned-Nokia-CEO Stephen Elop committed the company to Windows 8. Because other Microsoft ecosystem companies like HP, Acer and HP have been slow to bring out Win 8 devices, Nokia has 90% of the miniscule market that is Win 8 phones. So this acquisition brings in-house a much deeper commitment to spending on an effort to defend & extend Microsoft's declining O/S products.
As I predicted in January, the #1 action we could expect from a Ballmer-led Microsoft is pouring more resources into fighting market leaders iOS and Android – an unwinnable war. Previously there was the $8.5B Skype and the $400M Nook, and now a $7.2B Nokia. And as 32,000 Nokia employees join Microsoft losses will surely continue to rise. While Microsoft has a lot of cash – spending it at this rate, it won't last long!
Some folks think this acquisition will make Microsoft more like Apple, because it now will have both hardware and software which in some ways is like Apple's iPhone. The hope is for Apple-like sales and margins soon. But, unfortunately, Google bought Motorola months ago and we've seen that such revenue and profit growth are much harder to achieve than simply making an acquisition. And Android products are much more popular than Win8. Simply combining Microsoft and Nokia does not change the fact that Win8 products are very late to market, and not very desirable.
Some have postulated that buying Nokia was a way to solve the Microsoft CEO succession question, positioning Mr. Elop for Mr. Ballmer's job. While that outcome does seem likely, it would be one of the most expensive recruiting efforts of all time. The only reason for Mr. Elop to be made Microsoft CEO is his historical company relationship, not performance. And that makes Mr. Elop is exactly the wrong person for the Microsoft CEO job!
In October, 2010 when Mr. Elop took over Nokia I pointed out that he was the wrong person for that job – and he would destroy Nokia by making it a "Microsoft shop" with a Microsoft strategy. Since then sales are down, profits have evaporated, shareholders are in revolt and the only good news has been selling the dying company to Microsoft! That's not exactly the best CEO legacy.
Mr. Elop's job today is to sell more Win8 mobile devices. Were he to be made Microsoft CEO it is likely he would continue to think that is his primary job – just as Mr. Ballmer has believed. Neither CEO has shown any ability to realize that the market has already shifted, that there are two leaders far, far in front with brand image, products, apps, developers, partners, distribution, market share, sales and profits. And it is impossible for Microsoft to now catch up.
It is for good reason that short-term traders pushed down Microsoft's share value after the acquisition was announced. It is clear that current CEO Ballmer and Microsoft's Board are still stuck fighting the last war. Still trying to resurrect the Windows and Office businesses to previous glory. Many market anallysts see this as the last great effort to make Ballmer's bet-the-company on Windows 8 pay off. But that's a bet which every month is showing longer and longer odds.
Microsoft is not dead. And Microsoft is not without the ability to turn around. But it won't happen unless the Board recognizes it needs to steer Microsoft in a vastly different direction, reduce (rather than increase) investments in Win8 (and its devices,) and create a vision for 2020 where Microsoft is highly relevant to customers. So far, we're seeing all the wrong moves.
by Adam Hartung | Aug 6, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership
Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon worth $25.2B just paid $250 million to become sole owner of The Washington Post.
Some think the recent rash of of billionaires buying newspapers is simply rich folks buying themselves trophies. Probably true in some instances – and that benefits no one. Just look at how Sam Zell ruined The Chicago Tribune and Los Angeles Times. Or Rupert Murdoch's less than stellar performance owning The Wall Street Journal. It's hard to be excited about a financially astute commodities manager, like John Henry, buying The Boston Globe – as it has all the earmarks of someone simply jumping in where angels fear to tread.
These companies lost their way long ago. For decades they defined themselves as newspaper companies. They linked everything about what they did to printing a daily paper. The service they provided, which was a mix of hard news and entertainment reporting, was lost in the productization of that service into a print deliverable.
So when people started to look for news and entertainment on-line, these companies chose to ignore the trend. They continued to believe that readers would always want the product – the paper – rather than the service. And they allowed themselves to remain fixated on old processes and outdated business models long after the market shifted.
The leaders ignored the fact that advertisers could obtain much more directed placement at targets, at far lower cost, on-line than through the broad-based, general ads placed in newspapers. And that consumers could get a much faster, and cheaper, sale via eBay, CraigsList or Vehix.com than via overpriced classified ads.
Newspaper leadership kept trying to defend their "core" business of collecting news for daily publication in a paper format. They kept trying to defend their local advertising base. Even though every month more people abandoned them for an on-line format. Not one major newspaper headmast made a strong commitment to go on-line. None tried to be #1 in news dissemination via the web, or take a leadership role in associating ad placement with news and entertainment.
They could have addressed the market shift, and changed their approach and delivery. But they did not.
Money manager Mr. Henry has done a good job of turning the Boston Red Sox into a profitable institution. But there is nothing in common between the Red Sox, for which you can grow the fan base, bring people to the ballpark and sell viewing rights, and The Boston Globe. The former is unique. The latter is obsolete. Yes, the New York Times company paid $1.1B for the Globe in 1993, but that doesn't mean it's worth $70M today. Given its revenue and cost structure, as a newspaper it is probably worth nothing.
But, we all still want news. Nobody wants the information infrastructure collecting what we need to know to crumble. Nobody wants journalism to die. But it is unreasonable to expect business people to keep investing in newspapers just to fulfill a public good. Even Mr. Zell abandoned that idea.
Thus, we need the news, as a service, to be transformed into a new, profitable enterprise. Somehow these organizations have to abandon the old ways of doing things, including print and paper distribution, and transform to meet modern needs. The 6 year revenue slide at Washington Post has to stop, and instead of thinking about survival company leadership needs to focus on how to thrive with a new, profitable business model.
And that's why we all should be glad Jeff Bezos bought The Washington Post. As head of Amazon.com The Harvard Business Review ranked him the second best performing CEO of the last decade. CNNMoney.com named him Business Person of the Year 2012, and called him "the ultimate disruptor."
By not doing what everyone else did, breaking all the rules of traditional retail, Mr. Bezos built Amazon.com into a $61B general merchandise retailer in 20 years. When publishers refused to create electronic books he led Amazon into competing with its suppliers by becoming a publisher. When Microsoft wouldn't produce an e-reader, retailer and publisher Amazon.com jumped into the intensely competitive world of personal electroncs creating and launching Kindle. And then upped the stakes against competitors by enhancing that into Kindle Fire. And when traditional IT suppliers like HP and Dell were slow to help small (or any) business move toward cloud computing Amazon launched its own network services to help the market shift.
Mr. Bezos' language regarding his intentions post acquisition are quite telling, "change… is essential… with or without new ownership….need to invent…need to experiment."
And that is exactly what the news industry needs today. Today's leaders are HuffingtonPost.com, Marketwatch.com and other web sites with wildly different business models than traditional paper media. WaPo success will require transforming a dying company, tied to an old success formula, into a trend-aligned organization that give people what they want, when they want it, at a profit.
And it's hard to think of someone better experienced, or skilled, than Jeff Bezos to provide that kind of leadership. With just a little imagination we can imagine some rapid moves:
- distribution of all content via Kindle style eReaders, rather than print. Along with dramatically increasing the cost of paper subscriptions and daily paper delivery
- Instead of a "one size fits all" general purpose daily paper, packaging news into more fitting targeted products. Sports stories on sports sites. Business stories on business sites. Deeper, longer stories into ebooks available for $.99 purchase. And repackaging of stories that cover longer time spans into electronic short-books for purchase.
- Packaging content into Facebook locations for targeted readers. Tying ads into these social media sites, and promoting ad sales for small, local businesses to the Facebook sites.
- Or creating an ala carte approach to buying various news and entertainment in an iTunes or Netflix style environment (or on those sites)
- Robustly attracting readers via connecting content with social media, including Twitter, to meet modern needs for immediacy, headline knowledge and links to deeper stories — with sales of ads onto social media
- Tying electronic coupons, and buy-it-now capabilities to ads linked to appropriate content
- Retargeting advertising sales from general purpose to targeted delivery at specific readers, with robust packages of on-line coupons, links to specials and fast, impulse purchase capability
- Increased use of bloggers and ad hoc writers to supplement staff in order to offer opinions and insights quickly, but at lower cost.
- Changes in compensation linked to page views and readership, just as revenue is linked to same.
We've watched a raft of newspapers and magazines disappear. This has not been a failure of journalism, but rather a failure of business leaders to address shifting markets and transform old organizations to meet modern needs. It's not a quality problem, but rather a failure of strategy to adapt to shifting markets. And that's a lesson every business leaders needs to note, because today, as I wrote in April, 2012, every company has to behave like a tech company!
Doing more of the same, cutting costs and rich egos won't fix a newspaper. Only the willingness to experiment and find new solutions which transform these organizations into something very different, well beyond print, will work. Let's hope Mr. Bezos brings the same zest for addressing these challenges and aligning with market needs he brought to Amazon. To a large extent, the future of news and "freedom of the press" may well depend upon it.
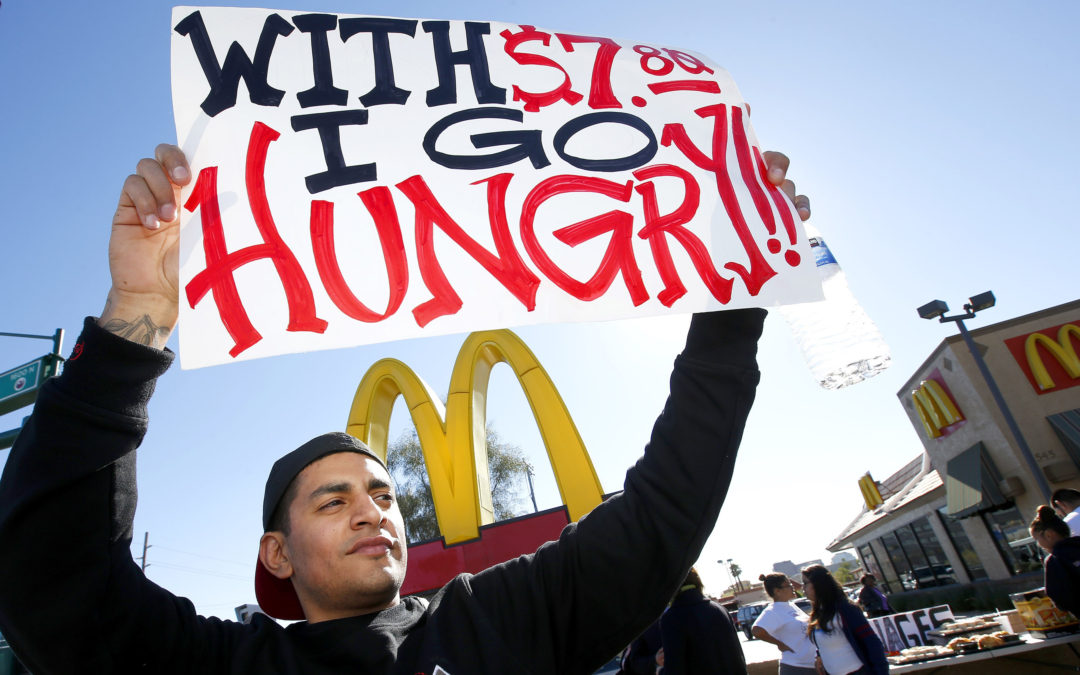
by Adam Hartung | Aug 1, 2013 | Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, In the Swamp, Leadership
Alex Robles protests in front of a McDonald’s in 2013, in Phoenix. (AP Photo/Ross D. Franklin)
Horatio Alger wrote books in the 1800s about young poor boys who became wealthy via clean living and hard work. Americans loved the idea that anyone can become rich, and loved those stories. We love them as much today as then, clinging to the non-rich roots of successes like Steve Jobs.
Unfortunately, such possibilities have been growing tougher in America. Today U.S. income inequality is among the highest in the world, while income mobility is among the lowest. You are more likely to go from rags to riches in France or Germany than the USA. Net/net – in current circumstances your most important decision is who will be your parents, because if you are born rich you will likely live a rich life, while if you are born poor you’ll probably die poor.
Organizations like Occupy Wall Street have tried to bring the problem of inequality and jobs to the face of America – with mixed results. But the truth is that 80% of Americans will face poverty and unemployment in their lifetimes. And the biggest growth in poverty, declining marriage rates and single mother households all belong to white Americans today. These poverty related issues are no longer tied to skin color or immigration they way they once were.
It’s safe to say that a lot of Americans are sounding like the famous Howard Beale phrase from the 1976 movie “Network” and starting to say “I’m mad as hell, and I’m not going to take this any more!”
This situation has given birth to a new trend – frequently referred to as the “living wage.” A living wage allows one parent to earn enough money from a single 40 hour per week job to feed, cloth, educate, transport and otherwise lead a decent life for a family of 4. Today in America this is in the range of $13.50-$15.00 per hour.
This, of course, should not be confused with the minimum wage which is a federally (or state) mandate to pay a specific minimum hourly wage. Because the minimum wage is lower than living wage, a movement has been started to match the two numbers – something which would roughly double today’s $7.25 federal minimum wage.
This concept would have been heresy just 40 years ago. America’s Chamber of Commerce and other pro-business groups have long attempted to abolish the minimum wage, and have fought hard against any and every increase.
As the income inequality gap has widened popularity has grown for this movement, however, and now 70% of Americans support higher minimum wages, almost 3 times those who don’t. Whether effective or not, this week fast food employees took to old fashioned strikes and picket lines in New York City, Chicago, St. Louis, Milwaukee and Detroit for higher wages.
Regardless of your opinion about the economics (or politics) of such a move, the trend is definitely building for taking action.
The biggest industries affected by such an increase would be fast food and retail. And if these companies don’t do something to adapt to this trend the results could be pretty severe.
McDonald’s is the largest fast food company. And it definitely does not pay a living wage. The company recently published for employees a budget for trying to live on a McDonald’s income, and it translated into requiring employees work 2 full-time jobs. Rancor about the posted budget was widespread, as even pro-business folks found it amazing a company could put out such a document while its CEO (and other execs) make many multiples of what most employees earn.
Estimates are that a wage increase to $15/hour for employees would cost McDonald’s $8B. McDonald’s showed $10B of Gross Income in 2012, and $8B of Pre-Tax Income. Obviously, should the living wage movement pass nationally McDonald’s investors would see a devastating impact. Simultaneously, prices would have to increase hurting customers and suppliers would likely be pinched to the point of losses.
Couple this with McDonald’s laissez-faire attitude about obesity trends, and you have two big trends that don’t bode well for rising returns for shareholders. Yet, other than opposing regulations and government action on these matters McDonald’s has shown no ability to adapt to these rather important, and impactful, trends. Hoping there will be no legislation is a bad strategy. Fighting against any change, given the public health and economic situation, is as silly as fighting against regulations on tobacco was in the 1960s. But so far there has been no proposed adaptation to McDonald’s 50 year old success formula offered to investors, employees, customers or legislators.
WalMart is America’s largest retailer. And the most vitriolic opposing higher wages. Even though a living wage increase would cost customers only $12/year. When Washington, DC passed a requirement retailers pay a living wage WalMart refused to build and open 4 proposed new stores. Even though the impact would be only $.46/customer visit (estimated at $12.50/customer/year.)
It would seem such harsh action, given the small impact, is a bit illogical. Given that WalMart is already out of step with the trend toward on-line shopping, why would the company want to take such an additional action fighting against a trend that affects not only its profits, but most of its customers — who would benefit from a rise in income and buying power?
In 1914 Henry Ford was suffering from high turnover and a generally unhappy workforce. He reacted by doubling pay – with his famous “$5 day”. Not only did he reduce turnover, he became the perferred employer in his industry – and rather quickly it became clear that employees who formerly could not afford an automobile were able to now become customers at the new, higher pay scale. Apparently nobody at WalMart is familiar with this story. Or they lack the will to apply it.
Fighting trends is expensive. Yet, most leadership teams become stuck defending & extending an old strategy – an old success formula – even after it is out of date. Most companies don’t fail because the leadership is incompetent, but rather because they fail to adapt to trends and changing circumstances. Long-lived companies are those which build for future scenarios, rather than trying to keep the world from changing by spending on lobbyists, advertising and other efforts to halt (or reverse) a trend.
McDonald’s and WalMart (and for that matter Yum Brands, Wendy’s, JCPenney, Sears, Best Buy and a whole host of other companies) are largely unwilling to admit that the future is likely to look different than the past. Will that kill them? It sure won’t help them. But investors could feel a lot more comfortable (as would employees, suppliers and customers) if they would develop and tell us about their strategies to adapt to changing circumstances.
Are you looking at trends, developing scenarios about the future and figuring out how to adapt in ways that will help you profitably grow? Or are you stuck defending and extending an old success formula even as markets shift and trends move customers in different directions?
Follow Adam's coverage in press and other media
by Adam Hartung | Jul 18, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in
Sears has performed horribly since acquired by Fast Eddie Lampert's KMart in 2005. Revenues are down 25%, same store sales have declined persistently, store margins have eroded and the company has recently taken to reporting losses. There really hasn't been any good news for Sears since the acquisition.
Bloomberg Businessweek made a frontal assault on CEO Edward Lampert's leadership at Sears this week. Over several pages the article details how a "free market" organization installed by Mr. Lampert led to rampant internal warfare and an inability for the company to move forward effectively with programs to improve sales or profits. Meanwhile customer satisfaction has declined, and formerly valuable brands such as Kenmore and Craftsman have become industry also-rans.
Because the Lampert controlled hedge fund ESL Investments is the largest investor in Sears, Mr. Lampert has no risk of being fired. Even if Nobel winner Paul Krugman blasts away at him. But, if performance has been so bad – for so long – why does the embattled Mr. Lampert continue to lead in the same way? Why doesn't he "fire" himself?
By all accounts Mr. Lampert is a very smart man. Yale summa cum laude and Phi Beta Kappa, he was a protege of former Treasury Secretay Robert Rubin at Goldman Sach before convincing billionaire Richard Rainwater to fund his start-up hedge fund – and quickly make himself the wealthiest citizen in Connecticut.
If the problems at Sears are so obvious to investors, industry analysts, economics professors, management gurus and journalists why doesn't he simply change?
Mr. Lampert, largely because of his success, is a victim of BIAS. Deep within his decision making are his closely held Beliefs, Interpretations, Assumptions and Strategies. These were created during his formative years in college and business. This BIAS was part of what drove his early success in Goldman, and ESL. This BIAS is now part of his success formula – an entire set of deeply held convictions about what works, and what doesn't, that are not addressed, discussed or even considered when Mr. Lampert and his team grind away daily trying to "fix" declining Sears Holdings.
This BIAS is so strong that not even failure challenges them. Mr. Lampert believes there is deep value in conventional retail, and real estate. He believes strongly in using "free market competition" to allocate resources. He believes in himself, and he believes he is adding value, even if nobody else can see it.
Mr. Lampert assumes that if he allows his managers to fight for resources, the best programs will reach the top (him) for resourcing. He assumes that the historical value in Sears and its house brands will remain, and he merely needs to unleash that value to a free market system for it to be captured. He assumes that because revenues remain around $35B Sears is not irrelevant to the retail landscape, and the company will be revitalized if just the right ideas bubble up from management.
Mr. Lampert inteprets the results very different from analysts. Where outsiders complain about revenue reductions overall and same store, he interprets this as an acceptable part of streamlining. When outsiders say that store closings and reduced labor hurt the brand, he interprets this as value-added cost savings. When losses appear as a result of downsizing he interprets this as short-term accounting that will not matter long-term. While most investors and analysts fret about the overall decline in sales and brands Mr. Lampert interprets growing sales of a small integrated retail program as a success that can turn around the sinking behemoth.
Mr. Lampert's strategy is to identify "deep value" and then tenaciously cut costs, including micro-managing senior staff with daily calls. He believes this worked for Warren Buffett, so he believes it will continue to be a successful strategy. Whether such deep value continues to exist – especially in conventional retail – can be challenged by outsiders (don't forget Buffett lost money on Pier 1,) but it is part of his core strategy and will not be challenged. Whether cost cutting does more harm than good is an unchallenged strategy. Whether micro-managing staff eats up precious resources and leads to unproductive behavior is a leadership strategy that will not change. Hiring younger employees, who resemble Mr. Lampert in quick thinking and intellect (if not industry knowledge or proven leadership skills) is a strategy that will be applied even as the revolving door at headquarters spins.
The retail market has changed dramatically, and incredibly quickly. Advances in internet shopping, technology for on-line shopping (from mobile devices to mobile payments) and rapid delivery have forever altered the economics of retailing. Customer ease of showrooming, and desire to shop remotely means conventional retail has shrunk, and will continue to shrink for several years. This means the real challenge for Sears is not to be a better Sears as it was in 2000 — but to become something very different that can compete with both WalMart and Amazon – and consumer goods manufacturers like GE (appliances) and Exide (car batteries.)
There is no doubt Mr. Lampert is a very smart person. He has made a fortune. But, he and Sears are a victim of his BIAS. Poor results, bad magazine articles and even customer complaints are no match for the BIAS so firmly underlying early success. Even though the market has changed, Mr. Lampert's BIAS has him (and his company) in internal turmoil, year after year, even though long ago outsiders gave up on expecting a better result.
Even if Sears Holdings someday finds itself in bankruptcy court, expect Mr. Lampert to interpret this as something other than a failure – as he defends his BIAS better than he defends its shareholders, employees, suppliers and customers.
What is your BIAS? Are you managing for the needs of changing markets, or working hard to defend doing more of what worked in a bygone era? As a leader, are you targeting the future, or trying to recapture the past? Have market shifts made your beliefs outdated, your interpretations of what happens around you faulty, your assumptions inaccurate and your strategies hurting results? If any of this is true, it may be time you address (and change) your BIAS, rather than continuing to invest in more of the same. Or you may well end up like Sears.
by Adam Hartung | Jul 10, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Television
Tribune Corporation finally emerged from a 4 year bankruptcy on the last day of 2012. Before the ink hardly dried on the documents, leadership has decided to triple company debt to double up the number of TV stations. Oh my, some people just never learn.
The media industry is now over a decade into a significant shift. Since the 1990s internet access has changed expectations for how fast, easily and flexibly we acquire entertainment and news. The result has been a dramatic decline in printed magazine and newspaper reading, while on-line reading has skyrocketed. Simultaneously, we're now seeing that on-line streaming is making a change in how people acquire what they listen to (formerly radio based) and watch (formerly television-based.)
Unfortunately, Tribune – like most media industry companies – consistently missed these shifts and underestimated both the speed of the shift and its impact. And leadership still seems unable to understand future scenarios that will be far different from today.
In 2000 newspaper people thought they had "moats" around their markets. The big newspaper in most towns controlled the market for classified ads for things like job postings and used car sales. Classified ads represented about a third of newspaper revenues, and 40% of profits. Simultaneously display advertising for newspapers was considered a cash cow. Every theatre would advertise their movies, every car dealer their cars and every realtor their home listings. Tribune leadership felt like this was "untouchable" profitability for the LA Times and Chicago Tribune that had no competition and unending revenue growth.
So in 2000 Tribune spent $8B to buy Times-Mirror, owner of the Los
Angeles Times. Unfortunately, this huge investment (75% over market
price at the time, by the way) was made just as people were preparing to
shift away from newspapers. Craigslist, eBay and other user sites killed the market for classified ads. Simultaneously movie companies, auto companies and realtors all realized they could reach more people, with more information, cheaper on-line than by paying for newspaper ads.
These web sites all existed before the acquisition, but Tribune leadership ignored the trend. As one company executive said to me "CraigsList!! You think that's competition for a newspaper? Craigslist is for hookers! Nobody would ever put a job listing on Craigslist." Like his compadres running newspapers nationwide, the new competitors and trends toward on-line were dismissed with simplistic statements and broad generalizations that things would never change.
The floor fell out from under advertising revenues in newspapers in the 2000s. There was no way Times-Mirror would ever be worth a fraction of what Tribune paid. Debt used to help pay for the acquisition limited the options for Tribune as cost cutting gutted the organization.
Then, in 2007 Sam Zell bailed out management by putting together a leveraged buyout to acquire Tribune company. Saying that he read 3 newspapers every day, he believed people would never stop reading newspapers. Like a lot of leaders, Mr. Zell had more money than understanding of trends and shifting markets. He added a few billion dollars more debt to Tribune. By the end of 2008 Tribune was unable to meet its debt obligations, and filed for bankruptcy.
Now, new leadership has control of Tribune. They are splitting the company in two, seperating the print and broadcast businesses. The hope is to sell the newspapers, for which they believe there are 40 potential buyers. Even though profits continued falling, from $156M to $89M, in just the last year. Why anyone would buy newspaper companies, which are clearly buggy whip manufacturers, is wholly unclear. But hope springs eternal!
The new stand-alone Tribune Broadcasting company has decided to go all-in on a deal to borrow $2.7B and buy 19 additional local television stations raising total under their control to 42.
Let's see, what's the market trend in entertainment and news? Where once we were limited to local radio and television stations for most content, now we can acquire almost anything we want – from music to TV, movies, documentaries or news – via the internet. Rather than being subjected to what some programming executive decides to give us, we can select what we want, when we want it, and simply stream it to our laptop, tablet, smartphone, or even our large-screen TV.
A long time ago content was controlled by distribution. There was no reason to create news stories or radio programs or video unless you had access to distribution. Obviously, that made distribution – owning newspapers, radio and TV stations – valuable.
But today distribution is free, and everywhere. Almost every American has access to all the news and entertainment they want from the internet. Either free, or for bite-size prices that aren't too high. Today the value is in the content, not distribution.
In the last 2 years the number of homes without a classical TV connection (the cable) has doubled. Sure, it's only 5% of homes now. But the trend is pretty clear. Even homes that have cable are increasingly not watching it as they turn to more and more streaming video. Instead of watching a 30 minute program once per week, people are starting to watch 8 or 10 half hour episodes back to back. And when they want to watch those episodes, where they want to watch them.
While it might be easy for Tribune to ignore Hulu, Netflix and Amazon, the trend is very clear. The need for broadcast stations like NBC or WGN or Food Network to create content is declining as we access content more directly, from more sources. And the need to have content delivered to our home by a local affiliate station is becoming, well, an anachronism.
Yet, Tribune's new TV-oriented leadership is doubling down on its bet for local TV's future. Ignoring all the trends, they are borrowing more money to buy more assets that show all signs of becoming about as valuable whaling ships. It's a big, dumb bet. Similar to overpaying for Times-Mirror. Some leaders just seem destined to never learn.
by Adam Hartung | Jun 28, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, In the Whirlpool, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
The last 12 months Tesla Motors stock has been on a tear. From $25 it has more than quadrupled to over $100. And most analysts still recommend owning the stock, even though the company has never made a net profit.
There is no doubt that each of the major car companies has more money, engineers, other resources and industry experience than Tesla. Yet, Tesla has been able to capture the attention of more buyers. Through May of 2013 the Tesla Model S has outsold every other electric car – even though at $70,000 it is over twice the price of competitors!
During the Bush administration the Department of Energy awarded loans via the Advanced Technology Vehicle Manufacturing Program to Ford ($5.9B), Nissan ($1.4B), Fiskar ($529M) and Tesla ($465M.) And even though the most recent Republican Presidential candidate, Mitt Romney, called Tesla a "loser," it is the only auto company to have repaid its loan. And did so some 9 years early! Even paying a $26M early payment penalty!
How could a start-up company do so well competing against companies with much greater resources?
Firstly, never underestimate the ability of a large, entrenched competitor to ignore a profitable new opportunity. Especially when that opportunity is outside its "core."
A year ago when auto companies were giving huge discounts to sell cars in a weak market I pointed out that Tesla had a significant backlog and was changing the industry. Long-time, outspoken industry executive Bob Lutz – who personally shepharded the Chevy Volt electric into the market – was so incensed that he wrote his own blog saying that it was nonsense to consider Tesla an industry changer. He predicted Tesla would make little difference, and eventually fail.
For the big car companies electric cars, at 32,700 units January thru May, represent less than 2% of the market. To them these cars are simply not seen as important. So what if the Tesla Model S (8.8k units) outsold the Nissan Leaf (7.6k units) and Chevy Volt (7.1k units)? These bigger companies are focusing on their core petroleum powered car business. Electric cars are an unimportant "niche" that doesn't even make any money for the leading company with cars that are very expensive!
This is the kind of thinking that drove Kodak. Early digital cameras had lots of limitations. They were expensive. They didn't have the resolution of film. Very few people wanted them. And the early manufacturers didn't make any money. For Kodak it was obvious that the company needed to remain focused on its core film and camera business, as digital cameras just weren't important.
Of course we know how that story ended. With Kodak filing bankruptcy in 2012. Because what initially looked like a limited market, with problematic products, eventually shifted. The products became better, and other technologies came along making digital cameras a better fit for user needs.
Tesla, smartly, has not tried to make a gasoline car into an electric car – like, say, the Ford Focus Electric. Instead Tesla set out to make the best car possible. And the company used electricity as the power source. By starting early, and putting its resources into the best possible solution, in 2013 Consumer Reports gave the Model S 99 out of 100 points. That made it not just the highest rated electric car, but the highest rated car EVER REVIEWED!
As the big car companies point out limits to electric vehicles, Tesla keeps making them better and addresses market limitations. Worries about how far an owner can drive on a charge creates "range anxiety." To cope with this Tesla not only works on battery technology, but has launched a program to build charging stations across the USA and Canada. Initially focused on the Los-Angeles to San Franciso and Boston to Washington corridors, Tesla is opening supercharger stations so owners are never less than 200 miles from a 30 minute fast charge. And for those who can't wait Tesla is creating a 90 second battery swap program to put drivers back on the road quickly.
This is how the classic "Innovator's Dilemma" develops. The existing competitors focus on their core business, even though big sales produce ever declining profits. An upstart takes on a small segment, which the big companies don't care about. The big companies say the upstart products are pretty much irrelevant, and the sales are immaterial. The big companies choose to keep focusing on defending and extending their "core" even as competition drives down results and customer satisfaction wanes.
Meanwhile, the upstart keeps plugging away at solving problems. Each month, quarter and year the new entrant learns how to make its products better. It learns from the initial customers – who were easy for big companies to deride as oddballs – and identifies early limits to market growth. It then invests in product improvements, and market enhancements, which enlarge the market.
Eventually these improvements lead to a market shift. Customers move from one solution to the other. Not gradually, but instead quite quickly. In what's called a "punctuated equilibrium" demand for one solution tapers off quickly, killing many competitors, while the new market suppliers flourish. The "old guard" companies are simply too late, lack product knowledge and market savvy, and cannot catch up.
- The integrated steel companies were killed by upstart mini-mill manufacturers like Nucor Steel.
- Healthier snacks and baked goods killed the market for Hostess Twinkies and Wonder Bread.
- Minolta and Canon digital cameras destroyed sales of Kodak film – even though Kodak created the technology and licensed it to them.
- Cell phones are destroying demand for land line phones.
- Digital movie downloads from Netflix killed the DVD business and Blockbuster Video.
- CraigsList plus Google stole the ad revenue from newspapers and magazines.
- Amazon killed bookstore profits, and Borders, and now has its sites set on WalMart.
- IBM mainframes and DEC mini-computers were made obsolete by PCs from companies like Dell.
- And now Android and iOS mobile devices are killing the market for PCs.
There is no doubt that GM, Ford, Nissan, et. al., with their vast resources and well educated leadership, could do what Tesla is doing. Probably better. All they need is to set up white space companies (like GM did once with Saturn to compete with small Japanese cars) that have resources and free reign to be disruptive and aggressively grow the emerging new marketplace. But they won't, because they are busy focusing on their core business, trying to defend & extend it as long as possible. Even though returns are highly problematic.
Tesla is a very, very good car. That's why it has a long backlog. And it is innovating the market for charging stations. Tesla leadership, with Elon Musk thought to be the next Steve Jobs by some, is demonstrating it can listen to customers and create solutions that meet their needs, wants and wishes. By focusing on developing the new marketplace Tesla has taken the lead in the new marketplace. And smart investors can see that long-term the odds are better to buy into the lead horse before the market shifts, rather than ride the old horse until it drops.
by Adam Hartung | Jun 5, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Web/Tech
Microsoft CEO Steve Ballmer appears to be planning a major reorganization. The apparent objective is to help the company move toward becoming a "devices and services company" as presented in the company's annual shareholder letter last October.
But, the question for investors is whether this is a crafty move that will help Microsoft launch renewed profitable growth, or is it leadership further confusing customers and analysts while leaving Microsoft languishing in stalled markets? After all, the shares are up some 31% the last 6 months and it is a good time to decide if an investor should buy, hold or sell.
There are a lot of things not going well for Microsoft right now.
Everyone knows PC sales have started dropping. IDC recently lowered its forecast for 2013 from a decline of 1.3% to negative 7.8%. The mobile market is already larger than PC sales, and IDC now expects tablet sales (excluding smartphones) will surpass PCs in 2015. Because the PC is Microsoft's "core" market – producing almost all the company's profitability – declining sales are not a good thing.
Microsoft hoped Windows 8 would reverse the trend. That has not happened. Unfortunately, ever since being launched Windows 8 has underperformed the horrific sales of Vista. Eight months into the new product it is selling at about half the rate Vista did back in 2007 – which was the worst launch in company history. Win8 still has fewer users than Vista, and at 4% share 1/10th the share of market leaders Windows 7 and XP.
Microsoft is launching an update to Windows 8, called Windows 8.1 or "blue." But rather than offering a slew of new features to please an admiring audience the release looks more like an early "fix" of things users simply don't like, such as bringing back the old "start" button. Reviewers aren't talking about how exciting the update is, but rather wondering if these admissions of poor initial design will slow conversion to tablets.
And tablets are still the market where Microsoft isn't – even if it did pioneer the product years before the iPad. Bloomberg reported that Microsoft has been forced to cut the price of RT. So far historical partners such as HP and HTC have shunned Windows tablets, leaving Acer the lone company putting out Windows a mini-tab, and Dell (itself struggling with its efforts to go private) the only company declaring a commitment to future products.
And whether it's too late for mobile Windows is very much a real question. At the last shareholder meeting Nokia's investors cried loud and hard for management to abandon its commitment to Microsoft in favor of returning to old operating systems or moving forward with Android. This many years into the game, and with the Google and Apple ecosystems so far in the lead, Microsoft needed a game changer if it was to grab substantial share. But Win 8 has not proven to be a game changer.
In an effort to develop its own e-reader market Microsoft dumped some $300million into Barnes & Noble's Nook last year. But the e-reader market is fast disappearing as it is overtaken by more general-purpose tablets such as the Kindle Fire. Yet, Microsoft appears to be pushing good money after bad by upping its investment by another $1B to buy the rest of Nook, apparently hoping to obtain enough content to keep the market alive when Barnes & Noble goes the way of Borders. But chasing content this late, behind Amazon, Apple and Google, is going to be much more costly than $1B – and an even lower probability than winning in hardware or software.
Then there's the new Microsoft Office. In late May Microsoft leadership hoped investors would be charmed to hear that 1M $99 subscriptions had been sold in 3.5 months. However, that was to an installed base of hundreds of millions of PCs – a less than thrilling adoption rate for such a widely used product. Companies that reached 1M subscribers from a standing (no installed base) start include Instagram in 2.5 months, Spotify in 5 months, Dropbox in 7 months and Facebook (which pioneered an entire new marketplace in Social) in only 10 months. One could have easily expected a much better launch for a product already so widely used, and offered at about a third the price of previous licenses.
A new xBox was launched on May 21st. Unfortunately, like all digital markets gaming is moving increasingly mobile, and consoles show all the signs of going the way of desktop computers. Microsoft hopes xBox can become the hub of the family room, but we're now in a market where a quarter of homes lead by people under 50 don't really use "the family room" any longer.
xBox might have had a future as an enterprise networking hub, but so far Kinnect has not even been marketed as a tool for business, and it has not yet incorporated the full network functionality (such as Skype) necessary to succeed at creating this new market against competitors like Cisco.
Thankfully, after more than a decade losing money, xBox reached break-even recently. However, margins are only 15%, compared to historical Microsoft margins of 60% in "core" products. It would take a major growth in gaming, plus a big market share gain, for Microsoft to hope to replace lost PC profits with xBox sales. Microsoft has alluded to xBox being the next iTunes, but lacking mobility, or any other game changer, it is very hard to see how that claim holds water.
The Microsoft re-org has highlighted 3 new divisions focused on servers and tools, Skype/Lync and xBox. What is to happen with the business which has driven three decades of Microsoft growth – operating systems and office software – is, well, unclear. How upping the focus on these three businesses, so late in the market cycle, and with such low profitability will re-invigorate Microsoft's value is, well, unclear.
In fact, given how Microsoft has historically made money it is wholly unclear what being a "devices and services" company means. And this re-organization does nothing to make it clear.
My past columns on Microsoft have led some commenters to call me a "Microsoft hater." That is not true. More apt would be to say I am a Microsoft bear. Its historical core market is shrinking, and Microsoft's leadership invested far too much developing new products for that market in hopes the decline would be delayed – which did not work. By trying to defend and extend the PC world Microsoft's leaders chose to ignore the growing mobile market (smartphones and tablets) until far too late – and with products which were not game changers.
Although Microsoft's leaders invested heavily in acquisitions and other markets (Skype, Nook, xBox recently) those very large investments came far too late, and did little to change markets in Microsoft's favor. None of these have created much excitement, and recently Rick Sherland at Nomura securities came out with a prediction that Microsoft might well sell the xBox division (a call I made in this column back in January.)
As consumers, suppliers and investors we like the idea of a near-monopoly. It gives us comfort to believe we can trust in a market leader to bring out new products upon which we can rely – and which will continue to make long-term profits. But, good as this feels, it has rarely been successful. Markets shift, and historical leaders fall as new competitors emerge; largely because the old leadership continues investing in what they know rather than shifting investments early into new markets.
This Microsoft reorganization appears to be rearranging the chairs on the Titanic. The mobile iceberg has slashed a huge gash in Microsoft's PC hull. Leadership keeps playing familiar songs, but the boat cannot float without those historical PC profits. Investors would be smart to flee in the lifeboat of recent share price gains.