by Adam Hartung | Jul 19, 2021 | Entertainment, Entrepreneurship, Innovation, Strategy, Trends
Netflix Redefines The Pivot
Last week Netflix announced it was going to enter gaming . Interestingly, the analyst reaction was, at best, mixed. Most didn’t think it was a great idea. My favorite is this quote in AdAge came from a pair of Bernstein analysts.
“Bernstein analysts Todd Juenger and Gini Zhang said in a note that they were “tepid” about Netflix getting into gaming, partly because it would mean a lesser focus on the core business. They worry about creating a distraction.”
These untalented analysts went on to say:
“It’s hard not to imagine that if Netflix were to launch its own video games, the majority of the company’s energy would be focused on the success of that new, different, exciting thing (even among employees who aren’t involved in it),” according to the note. It’s also unclear how the company can capitalize on the video-game content without raising prices—and potentially turning away some users unwilling to pay extra, they said.”
A History of Pivoting to Meet Customer Needs
Wow, I’ve heard that before. Remember how Netflix started? Back when we all went to Blockbuster or another video store to rent a tape or dvd overnight, Netflix offered to send them to our house. And let us keep them as long as we wanted. This convenience was so powerful Netflix drove Blockbuster, Family Video and all other traditional video rental stores bankrupt.
After this big win analysts thought that Netflix should take on Amazon in general merchandise e-commerce. After all, Netflix was the largest customer of UPS, USPS and Fedex at the time. Most analysts thought Netflix had the infrastructure to ship things, so they wanted to build on that infrastructure. But Netflix didn’t to that at all. Keeping its eyes on its Value Proposition of “Delivering Entertainment” Netflix instead went headlong into video streaming. And the stock tumbled dramatically as analysts said streaming wasn’t the “core” of Netflix. Netflix wasn’t a tech company, or a telecom or cable company and streaming would be a huge distraction for people lacking proper skills. Netflix’ Value Delivery System was dominated by logistics expertise, and the analysts were focused on milking more out of the Value Delivery System.
Of course Netflix knew its value was in keeping customers happy, not milking its invested assets. Netflix’ “core” was in knowing entertainment, so it had to develop the skills in streaming, or its customers would drift away. Further, Netflix knew it had nowhere near the savvy of Amazon for general merchandise marketing and sales. If it followed Amazon it would fritter away its Value Proposition, and probably never make any money chasing Amazon by trying to devote more energy to its logistics Value Delivery System.
Of course, Netflix was right. Leadership jettisoned the physical distribution Value Delivery System and built a new one around streaming technology. Just as the Bernstein analysts feared, Netflix had to raise prices. Which it did on physical distribution in order to raise the money to invest in streaming, which turned out to be the shot allowing Netflix to dominate globally, not just in the USA. It was enormous win for gaining customers, selling more stuff, and making more money.
About 5 years ago, Netflix realized it yet again had to change its Value Delivery System if it was to maintain its customer Value Proposition. So it scaled back investing in streaming, as that technology was becoming available to everyone. And it invested heavily in content production. Even though it had long distributed other people’s content, Netflix saw that to be a leader in “Delivering Entertainment” it had to create its own. So the money was shifted into making “House of Cards,” which was a huge hit, and “Orange is the New Black.” Now Netflix is the most prolific video content creator in North America. So much good content Netflix has jeopardized the future of TV networks, major movie studios and even entire theatre chains.
Where once the big employment center, and resource hog, in Netflix was logistics, Netflix leadership pivoted its Value Delivery System into streaming technology. Then it pivoted again into content creation. And now, as gaming has become “the next big thing” Netflix is once again pivoting its resources — into fast growing gaming.
Given this is the third pivot, and 4th Value Delivery System, in Netflix, would you bet against CEO Reed Hastings and his leadership team? The negative analysts are as dead wrong now as they were before. Netflix has demonstrated a keen understanding of their Value Proposition, and demonstrated the skill set to adapt their Value Delivery System to meeting emerging customer needs. I believe it is almost a certainty Netflix will find its way in on-line gaming as the trend keeps growing exponentially. And like all the other pivots, they’ll attract even more customers, and sell more product, and make more money.
Are you adaptable to new Value Delivery Systems as technology makes them available?
Do you clearly know your Value Proposition, and are you focused on it — or are you focused on running your Value Delivery System. Are you trying to maximize your old business, or are you seeing how emerging trends are creating new opportunities to grow by entering new businesses, with new Value Delivery Systems? Netflix has demonstrated how to grow very large, very fast. Are your eyes open to Trends and Market Shifts – and are you adaptable to take advantage of emerging market needs? Now is a good time to learn from Netflix.
My calls on Netflix have historically been quite good. Check out these links to previous articles:
How Netflix became the King of Strategic Pivots, 4/2018
Predicting Netflix Would Dominate Entertainment Content, 4/2016
Explaining Why and How Netflix content creation would be good for investors, 3/2015
Explaining why investors should buy Netflix stock when it crashed after announcing its move into streaming, 10/2011
Explaining why you should buy Netflix, predicting it would be the next Apple or Google, 11/2010
Netflix ended last week at $530/share. Had you bought it when I recommended in 11/2010 the stock was $25. You would have had a 25X gain. Had you added to your position in October, 2011 the stock was $16.75. You would have a gain of 31.6X. Had you added in 3/2015 when I recommended higher valuation for investors from content you would have bought at $62, for a gain of 8.5X in 6 years.
Did you see the trends, and were you expecting the changes that would happen to your demand? It IS possible to use trends to make good forecasts, and prepare for big market shifts. If you don’t have time to do it, perhaps you should contact us, Spark Partners. We track hundreds of trends, and are experts at developing scenarios applied to your business to help you make better decisions.
TRENDS MATTER. If you align with trends your business can do GREAT! Are you aligned with trends? What are the threats and opportunities in your strategy and markets? Do you need an outsider to assess what you don’t know you don’t know? You’ll be surprised how valuable an inexpensive assessment can be for your future business. Click for Assessment info. Or, to keep up on trends, subscribe to our weekly podcasts and posts on trends and how they will affect the world of business at www.SparkPartners.com
Give us a call or send an email. Adam@sparkpartners.com 847-726-8465.

by Adam Hartung | Dec 15, 2020 | eBooks, Investing, Strategy, Trends

Thrive to the Future – the 4 top trends for 2021 and beyond.
In February, Disney appointed a new CEO from inside the company. I was not a fan. He came from the traditional,old Disney businesses – studio movies and theme parks. Both of those businesses are historical artifacts, not growing, and clobbered by the acceleration of trends due to the pandemic. But…… after crashing almost 50% shortly after changing CEOs (and the pandemic hitting the USA) the stock just reached a new all time high – recovering all those losses and pushing ahead an additional 16%.
A lot of companies are complaining about how bad the pandemic has affected them. They were tied to their historical value delivery system, and working hard to keep optimizing that business model. They weren’t following trends, so when the pandemic accelerated trends to more mobile, more asynchronous work, greater use of gig resources and ever greater expectations for AI (artificial intelligence) they simply were not prepared.
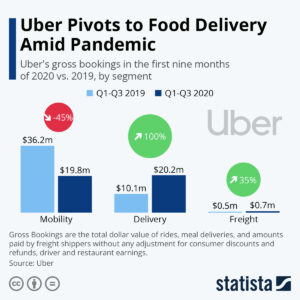
But smart companies moved really fast to implement their plans for new business based on trends. For example, while everyone thought of Uber as an alternative to taxis, leadership had already been looking at changes in package distribution. They could see problems in the post office, limitations (and pricing) to UPS and Fedex, and the “last mile” delivery problem everyone local had — as well as alternatives being tested by Amazon.com. So when demand for local deliveries picked up, Uber was ready to change. In a year demand for taxi type services fell 45%, but deliveries rose 100%!! And even though it was small, freight jumped 35%. The net was that in an extremely fast changing marketplace, gross bookings for the first 3 quarters of 2020 were $40.7M vs. $46.8M in 2019. In a terrible year, Uber was ready (and able) to move fast to implement changes to keep revenues moving forward.
And Disney is another great example. Theme parks and studio entertainment seemed to be relics of a bygone era, and in 2020, demand was hit hard. Theme parks fell 37% and studio movies fell 13%. I thought Disney would go into cost cutting mode exclusively and start down the road to irrelevancy.
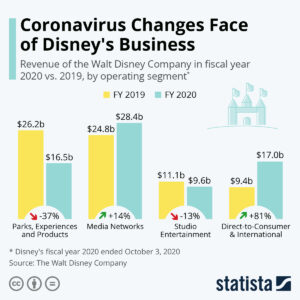
But I was wrong. Yes, Disney did cut employment in those two divisions. Extensively. But that was an acceleration of something bound to happen. Those businesses were shrinking and outdated. However, simultaneously, Disney poured resources into Media Networks and Direct-to-Customer, two business units highly aligned with trends! Basically, Disney went from that old-line movie and parks company to a very well positioned e-commerce vendor and competitor to Netflix!! In just 9 months. Already, Disney has 80M subscribers for Disney+, compared to Netflix 200M, and is targeting 260M by 2024!!! Disney has demonstrated it is ready to launch first run movies, at much higher prices, on its network – building out new pricing schemes as well as new business models for streaming content!
The lesson here is to be prepared for change! Don’t build your plans just on the past – past products and customers. Instead, look hard at trends and build scenarios for the future based on trends. Be ready for those trends to accelerate. And then TAKE ACTION. Don’t wait. Don’t stall. Go to the future by implementing those plans.
If you are planning based on trends you will be prepared for big changes in your “base” or “core” business. And you’ll develop plans for new solutions that meet emerging trends. So when the opportunity presents itself, like in a pandemic – or something a lot less dramatic – you’ll be ready to implement a new business. You can shift your value delivery system quickly to continue meeting the Value Proposition that you offer your customers.
Congratulations to Uber and Disney for doing good trend planning and being ready. Are you properly planning? Are you ready for change?
Did you see the trends, and were you expecting the changes that would happen to your demand? It IS possible to use trends to make good forecasts, and prepare for big market shifts. If you don’t have time to do it, perhaps you should contact us, Spark Partners. We track hundreds of trends, and are experts at developing scenarios applied to your business to help you make better decisions.
TRENDS MATTER. If you align with trends your business can do GREAT! Are you aligned with trends? What are the threats and opportunities in your strategy and markets? Do you need an outsider to assess what you don’t know you don’t know? You’ll be surprised how valuable an inexpensive assessment can be for your future business. Click for Assessment info. Or, to keep up on trends, subscribe to our weekly podcasts and posts on trends and how they will affect the world of business at www.SparkPartners.com
Give us a call or send an email. Adam@sparkpartners.com 847-331-6384

by Adam Hartung | May 2, 2018 | Entrepreneurship, Food and Drink, Innovation, Marketing, Strategy
Execution – Implementation – Delivering — These are table stakes today. If you can’t do them you don’t get a seat at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
Take for example a small company named NakedWine.com that created a potential death trap for its business by implementing one crucial execution mis-step.
The NakedWine value proposition is simple. They will find wines you never heard of and skip the costs of distributors and retailers by matching the customer and winemaker. Customers ostensibly get wines far cheaper because the winemaker’s cost of marketing and sales are avoided. Decent value proposition for both the customer, and the manufacturer.
The NakedWine strategy is to convince people that the NakedWine wines will be good, month after month. The NakedWine brand is crucial, as customer trust is now not in the hands of the winemaker, nor wine aficionados that rate known wines on a point scale, or even the local retail shop owner or employee. Customers must trust NakedWine to put a good product in their hands. Customers who most likely know little or nothing about wines. NakedWines wants customers to trust them so much they will buy the company’s boxed selections month after month, delivered to their home. These customers likely don’t know what they are getting, and don’t much care, because they trust NakedWine to give them a pleasurable product at a price point which makes them happy. When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
But, NakedWines blew the whole strategy with one simple execution mistake.
Not everyone lives where they can accept a case of wine, due to weather. As northern Californians, maybe NakedWine leaders just forget how cold it is in Minneapolis, Chicago, Buffalo and Boston. Or how hot it is in Tucson, Phoenix, Houston, Palm Springs and Las Vegas. In these climates a case of wine left on a truck for a day – or 2 if the first delivery is missed – spells the end of that wine. Ruined by the temperature. Especially heat, as everyone who drinks beer or wine knows that a couple of hours at 90 degrees can kill those products completely.
The only time the customer finally connects with NakedWine is when that wine enters the house, and over the lips. But that step, that final step of getting the perishable wine to the customer safely, in good quality, and aligned with customer expectations was not viewed as part of the brand-building strategy. Instead, leadership decided at this step NakedWines should instead focus on costs. They would view delivery as completely generic – divorced from the brand-building effort. They would use the low–cost vendor, regardless of the service provided.
NakedWine decided to use Fedex Ground, even though Fedex has a terrible package tracking system. Fedex is unwilling to make sure (say, by drivers using a cell phone) that customers will be there to receive a shipment. The driver rings a bell – no answer and he’s on the run in seconds to make sure he’s meeting Fedex efficiency standards, even if the customer was delayed to the door by a phone call or other issue. When the customer requests Fedex send the driver back around again, Fedex is unwilling to attempt a second delivery within short time, or even any time that same day, after delivery fails. If a customer calls about a missed delivery, Fedex is unwilling to route a failed delivery to a temperature local Fedex Office location for customer pick-up. Or to tell the customer where they can meet the driver along his route to accept delivery. Despite a range of good options, the NakedWine product is forced to sit on that Fedex truck, bouncing around all day in the heat, or cold, being ruined. Fedex uses its lowest cost approach to delivery to offer the lowest cost bid, regardless of the impact on the product and/or customer experience, and NakedWine didn’t think about the impact choosing that bid would have on its brand building.
Brand Building at Every Step
Simply put, in addition to flyers, advertising and product discounts, NakedWine should have followed through on its brand building strategy at every step. It must source wines its customers will enjoy. And it must deliver that perishable product in a way that builds the brand – not put it at risk. For example, NakedWine should screen all orders for delivery location, in order to make sure there are no delivery concerns. If there are, someone at NakedWine should contact the customer to discuss with them issues related to shipping, such as temperature. If it is to be too hot or cold, they could highly recommend using a temperature controlled pick-up location so as not to put the product at risk. And they should build in fail-safe’s with the shipping company to handle delivery problems. That is implementing a brand building strategy all the way from value-proposition to delivery.
Leaders Execute Plans
Too often leaders will work hard on a strategy, and create a good value proposition. But then, for some unknown reason, they turn over “execution” to people who don’t really understand the strategy. Worse, leadership often makes the egregious error of pushing those who create the value delivery system to largely to focus on costs, or other wrong metrics, with little concern for the value proposition and strategy. The result is a great idea that goes off the rails. Because the value delivery system simply does not live up to expectations of the value proposition.
by Adam Hartung | Dec 6, 2011 | Current Affairs, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Transparency
There are few organizations as efficient as the U.S. Postal Service. Really. But it is still going out of business.
Think about the Post Office’s value proposition. They send someone to almost every single home and business in the entire United States 6 days/week on the hope that there will be a demand for their service – sold at a starting price of 44 cents! For that mere $.44 they will deliver your hand crafted, signed message anywhere else in the entire United States! And, if you want it delivered fairly close they will actually deliver your physical document the very next day! All for 44 cents! And, if you are a large volume customer rates can be even cheaper.
And the Post Office has been a remarkably operationally innovative organizations. Literally billions of items are processed every week (about 700million/day😉 picked up, sorted and distributed across one of the physically largest countries in the world. The distance from Anchorage to Miami (let’s ignore Hawaii for now) is a staggering 5,100 miles, which works out to a miniscule .009 cent/mile for a first class letter! Compare that to the Pony Express cost (in 1860 $10/oz and 10 days Missouri to California,) and adjusted for inflation you’ll be hard pressed to find any business that has continually improved its service, at ever lower (constantly declining when adjusted for inflation) prices.
And while AMR is filing bankruptcy largely to force a new union contract, the Post Office has accomplished its record improvements wtih an almost entirely union workforce.
Executive compensation is surprisingly low. The CEO makes about $800,000/year. Competitor CEOs make much more. At Fedex (the Post Office delivers more items every day that Fedex does in a whole year) the CEO made over $7,400,000, and at UPS (the Post Office delivers more items each week than UPS does annually) the CEO made $9,500,000. So, despite this remarkable effectiveness, the CEO makes only about 1/10th CEOs of much smaller organizations.
The Post Office understands what it must do, and does it extremely efficiently. It knows its “hedgehog concept” and relentlessly pursues it to unparalleled performance. Yet, it is barred from raising prices, is losing money, and is now planning to close 3,700 locations and dramatically curtail services – such as overnight and Saturday delivery in a radical cost reduction effort.
Simply put, the U.S. Postal Service is becoming irrelevant. In the 1980s faxing was the first attack on the mail, but the big market shift began 15 years ago with the advent of email. Now with mobile devices, texting and social media the shift away from physical letters is accelerating. Fewer people write letters, send bills or even pay bills via physical mail. Are you mailing any physical holiday cards this year? How many?
Even the veritable “junk mail” is far less viable these days. Coupons are used less and less – and to the extent they are used they have to be much more immediate and compelling – such as offerings from GroupOn and FourSquare et.al. which arrive at consumers by email and social media usually through a smartphone or tablet mobile device.
The Post Office didn’t really do anything wrong. The market shifted. The Post Office value proposition simply isn’t as valuable. We don’t really care if the mail delivery comes daily, in fact many people forget to check their mailbox for several consecutive day. We don’t much care that a physical letter can transit the continent overnight, because we usually want to communicate immediately. And we don’t need a physical legacy for 99.99% of our communications.
The Post Office is really good at what it does, we just don’t need it. Not any more than we need a good horse shoe or small offset printing press.
The Post Office saw this coming. Over a decade ago the Post Office asked if it could enter new businesses in record retention (medical, income, taxation), automated bill payment, social security check administration and a raft of other opportunities that would provide government delivery and storage services to various agencies and to under-served users such as low-income and the elderly. But its mandate did not include these services, and expansion into new markets required a change in charter which was not approved by Congress. Thus, USPS was stuck doing what it has always done, as market shift pushed the Post Office increasingly into irrelevancy.
And that’s what happens to most failed businesses. They don’t fail because they are lousy at execution. Or because of lousy, inattentive managers. Or even because of unions and high variable costs such as energy. They fall into trouble because they either don’t recognize, or for some other reason don’t move to take advantage of market shifts. It’s not a lack of focus, management laziness or worker intransigence that kills the business. It’s an inability to do what customers really want and value, and spending too much time and money trying to ever optimize something customers increasingly don’t care about.
To their credit, both FedEx and UPS have shifted their businesses along with the market. Both do much, much more than deliver packages. Fedex bought Kinko’s and offers people their “office away from the office” globally, as well as multiple small business solutions. UPS offers a vast array of corporate transportation and logistics services, including e-commerce solutions for businesses of all sizes. Their ability to move with markets, and meet emerging needs has helped both companies justify higher prices and earn substantially better profitability.
The U.S. Post Office is the poster child for what goes wrong when all a company does is focus on efficiency. More, better, faster, cheaper is NOT enough to compete. Being operationally efficient, even low-cost, is not enough to succeed in fast shifting markets where customers have ever-growing and changing needs. Leadership has to be able to recognize market shifts early, and invest in new growth opportunities allowing the company to remain viable in changing markets.
My generation will wax nostalgic about the post office. We’ll weave in “mail” stories with others about days before ubiquitious air conditioning, when all we had was AM radio in the car and 3 stations of black & white television stations at home. They will be fun to reminisce.
But our children, and certainly grandchildren, simply won’t care. Not at all. And we better remember to keep the stories short, so they can be related in 140 characters or less if we want them saved for posterity!







 at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition.
at the table, much less a chance to play the game. But, unfortunately, all too often tactical implementation decisions are made by tactical “experts” without proper consideration of the strategy. And one bad tactical decision can kill the entire business by not living up to the value proposition. When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.
When implementing this value proposition NakedWines doesn’t target wine enthusiasts, because those customers already have their wine sources, and they are varietal, geography and brand picky. Instead NakedWine pays on-line retailers like Saks Off 5th, and others, to put flyers into customer packages of semi-luxury goods. NakedWine provides deep discounts for initial purchases to entice someone to take that first purchase risk. NakedWine incurs big costs finding potential buyers, and hooking them to make an initial purchase so they can bring them into the brand-building cocoon. NakedWine wants to build a brand which keeps the allure of good wine, a sophisticated idea, for a customer who would rather trust NakedWine than become a wine expert. Or experiment with a local retailer.