
by Adam Hartung | Nov 22, 2013 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Television
Do you really think in 2020 you’ll watch television the way people did in the 1960s? I would doubt it.
In today’s world if you want entertainment you have a plethora of ways to download or live stream exactly what you want, when you want, from companies like Netflix, Hulu, Pandora, Spotify, Streamhunter, Viewster and TVWeb. Why would you even want someone else to program you entertainment if you can get it yourself?
Additionally, we increasingly live in a world unaccepting of one-way communication. We want to not only receive what entertains us, but share it with others, comment on it and give real-time feedback. The days when we willingly accepted having information thrust at us are quickly dissipating as we demand interactivity with what comes across our screen – regardless of size.
These 2 big trends (what I want, when I want; and 2-way over 1-way) have already changed the way we accept entertaining. We use USB drives and smartphones to provide static information. DVDs are nearly obsolete. And we demand 24×7 mobile for everything dynamic.
Yet, the CEO of Charter Cable company wass surprised to learn that the growth in cable-only customers is greater than the growth of video customers. Really?
It was about 3 years ago when my college son said he needed broadband access to his apartment, but he didn’t want any TV. He commented that he and his 3 roommates didn’t have any televisions any more. They watched entertainment and gamed on screens around his apartment connected to various devices. He never watched live TV. Instead they downloaded their favorite programs to watch between (or along with) gaming sessions, picked up the news from live web sites (more current and accurate he said) and for sports they either bought live streams or went to a local bar.
To save money he contacted Comcast and said he wanted the premier internet broadband service. Even business-level service. But he didn’t want TV. Comcast told him it was impossible. If he wanted internet he had to buy TV. “That’s really, really stupid” was the way he explained it to me. “Why do I have to buy something I don’t want at all to get what I really, really want?”
Then, last year, I helped a friend move. As a favor I volunteered to return her cable box to Comcast, since there was a facility near my home. I dreaded my volunteerism when I arrived at Comcast, because there were about 30 people in line. But, I was committed, so I waited.
The next half-hour was amazingly instructive. One after another people walked up to the window and said they were having problems paying their bills, or that they had trouble with their devices, or wanted a change in service. And one after the other they said “I don’t really want TV, just internet, so how cheaply can I get it?”
These were not busy college students, or sophisticated managers. These were every day people, most of whom were having some sort of trouble coming up with the monthly money for their Comcast bill. They didn’t mind handing back the cable box with TV service, but they were loath to give up broadband internet access.
Again and again I listened as the patient Comcast people explained that internet-only service was not available in Chicagoland. People had to buy a TV package to obtain broad-band internet. It was force-feeding a product people really didn’t want. Sort of like making them buy an entree in order to buy desert.
As I retold this story my friends told me several stories about people who banned together in apartments to buy one Comcast service. They would buy a high-powered router, maybe with sub-routers, and spread that signal across several apartments. Sometimes this was done in dense housing divisions and condos. These folks cut the cost for internet to a fraction of what Comcast charged, and were happy to live without “TV.”
But that is just the beginning of the market shift which will likely gut cable companies. These customers will eventually hunt down internet service from an alternative supplier, like the old phone company or AT&T. Some will give up on old screens, and just use their mobile device, abandoning large monitors. Some will power entertainment to their larger screens (or speakers) by mobile bluetooth, or by turning their mobile device into a “hotspot.”
And, eventually, we will all have wireless for free – or nearly so. Google has started running fiber cable in cities including Austin, TX, Kansas City, MO and Provo, Utah. Anyone who doesn’t see this becoming city-wide wireless has their eyes very tightly closed. From Albuquerque, NM to Ponca City, OK to Mountain View, CA (courtesy of Google) cities already have free city-wide wireless broadband. And bigger cities like Los Angeles and Chicago are trying to set up free wireless infrastructure.
And if the USA ever invests in another big “public works infrastructure” program will it be to rebuild the old bridges and roads? Or is it inevitable that someone will push through a national bill to connect everyone wirelessly – like we did to build highways and the first broadcast TV.
So, what will Charter and Comcast sell customers then?
It is very, very easy today to end up with a $300/month bill from a major cable provider. Install 3 HD (high definition) sets in your home, buy into the premium movie packages, perhaps one sports network and high speed internet and before you know it you’ve agreed to spend more on cable service than you do on home insurance. Or your car payment. Once customers have the ability to bypass that “cable cost” the incentive is already intensive to “cut the cord” and set that supplier free.
Yet, the cable companies really don’t seem to see it. They remain unimpressed at how much customers dislike their service. And respond very slowly despite how much customers complain about slow internet speeds. And even worse, customer incredulous outcries when the cable company slows down access (or cuts it) to streaming entertainment or video downloads are left unheeded.
Cable companies say the problem is “content.” So they want better “programming.” And Comcast has gone so far as to buy NBC/Universal so they can spend a LOT more money on programming. Even as advertising dollars are dropping faster than the market share of old-fashioned broadcast channels.
Blaming content flies in the face of the major trends. There is no shortage of content today. We can find all the content we want globally, from millions of web sites. For entertainment we have thousands of options, from shows and movies we can buy to what is for free (don’t forget the hours of fun on YouTube!)
It’s not “quality programming” which cable needs. That just reflects industry deafness to the roar of a market shift. In short order, cable companies will lack a reason to exist. Like land-line phones, Philco radios and those old TV antennas outside, there simply won’t be a need for cable boxes in your home.
Too often business leaders become deaf to big trends. They are so busy executing on an old success formula, looking for reasons to defend & extend it, that they fail to evaluate its relevancy. Rather than listen to market shifts, and embrace the need for change, they turn a deaf ear and keep doing what they’ve always done – a little better, with a little more of the same product (do you really want 650 cable channels?,) perhaps a little faster and always seeking a way to do it cheaper – even if the monthly bill somehow keeps going up.
But execution makes no difference when you’re basic value proposition becomes obsolete. And that’s how companies end up like Kodak, Smith-Corona, Blackberry, Hostess, Continental Bus Lines and pretty soon Charter and Comcast.
by Adam Hartung | Aug 9, 2012 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in
McDonald’s is in a Growth Stall. Even though the stock is less than 10% off its recent 52 week high (which is about the same high it’s had since the start of 2012,) the odds of McDonald’s equity going down are nearly 10x the odds of it achieving new highs.
A Growth Stall occurs when a company has 2 consecutive quarters of declining sales or earnings, or 2 consecutive quarters of lower sales or earnings than the previous year. And our research, in conjunction with The Conference Board, proved that when this happens the future becomes fairly easy to predict.
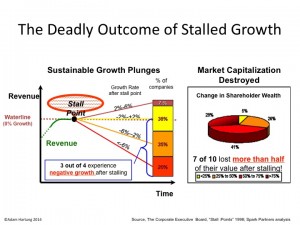
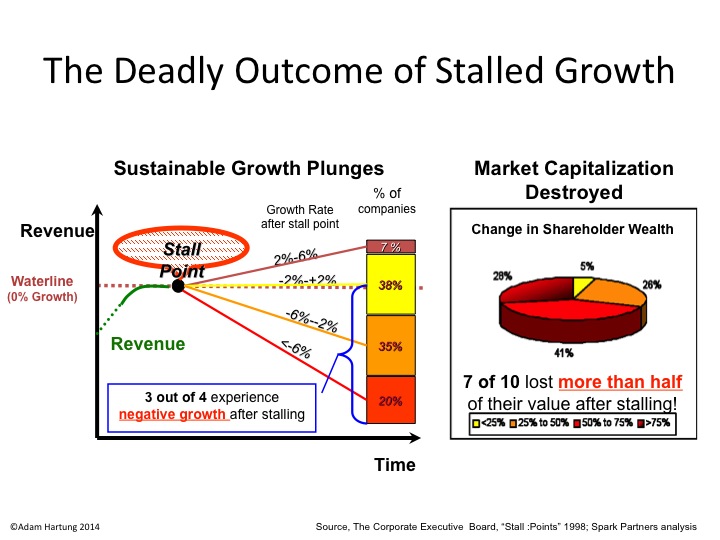
Growth Stalls are Deadly
When companies hit a growth Stall, 93% of the time they are unable to maintain even a 2% growth rate. 55% fall into a consistent revenue decline of more than 2%. 1 in 5 drop into a negative 6%/year revenue slide. 69% of Growth Stalled companies will lose at least half their market capitalization in just a few years. 95% will lose more than 25% of their market value.
Back in February, McDonalds sales in USA stores open at least 13 months fell 1.4%. By May these same stores reported reported their 7th consecutive month (now more than 2 quarters) of declining revenues. And in July McDonald’s reported the worst sales decline in over a decade – with stores globally selling 2.5% less (USA stores were down 3.2% for the month.) McDonald’s leadership is now warning that annual sales will be weaker than forecast – and could well be a reported decline.
While McDonald’s has been saying that Asian store revenue growth had offset the USA declines, we now can see that the USA drop is the key signal of a stall. There was no specific program in Asia to indicate that offshore revenues could create a renewed uptick in USA sales. Now with offshore sales plummeting we can see that McDonald’s American performance is the lead indicator of a company with serious performance issues.
Growth Stalls are a great forecasting tool because they indicate when a company has become “out of step” with its marketplace. While management, and in fact many analysts, will claim that this performance deficit is a short term aberration which will be repaired in coming months, historical evidence — and a plethora of case stories – tell us that in fact by the time a Growth Stall shows itself (especially in a company as large as McDonald’s) the situation is far more dire (and systemic) than management would like investors to believe.
Something fundamental has happened in the marketplace, and company leadership is busy trying to defend its historical business in the face of a major change that is pulling customers toward substitute solutions. Frequently this defend & extend approach exacerbates the problems as retrenchment efforts further hurt revenues.
McDonald’s has reached this inflection point as the result of a long string of leadership decisions which have worked to submarine long-term value.
Back in 2006 McDonald’s sold its fast growing Chipotle chain in order to raise additional funds to close some McDonald’s stores, and undertake an overhaul of the supply chain as well as many remaining stores. This one-time event was initially good for McDonald’s, but it hurt shareholders by letting go of an enormously successful revenue growth machine.
Since that sale Chipotle has outperformed McDonalds by 3x, and it was clear in 2011 that investors were better off with the faster growing Chipotle than the operationally focused McDonald’s. Desperate for revenues as its products lagged changing customer tastes, by December, 2012 McDonald’s was urging franchisees to stay open on Christmas Day in order to add just a bit more to the top line. However, such operational tactics cannot overcome a product line that is fat-and-carb-heavy and off current customer food trends, and by this July was ranked the worst burger in the marketplace. Meanwhile McDonald’s customer service this June ranked dead last in the industry. All telltale signs of the problems creating the emergent Growth Stall.
Meanwhile, McDonald’s is facing a significant attack on its business model as trends turn toward higher minimum wages. By August, 2013 the first signs of the trend were clear – and the impact on McDonald’s long-term fortunes were put in question. By February, 2014 the trend was accelerating, yet McDonald’s continued ignoring the situation. And this month the issue has become a front-and-center problem for McDonald’s investors as the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) has said it will not separate McDonald’s from its franchisees in pay and hours disputes – something which opens McDonald’s deep pockets to litigants looking to build on the living wage trend.
The McDonald’s CEO is somewhat “under seige” due to the poor revenue and earnings reports. Yet, the company continues to ascribe its Growth Stall to short-term problems such as a meat processing scandal in China. But this inverts the real situation. Such scandals are not the cause of current poor results. Rather, they are the outcome of actions taken to meet goals set by leadership pushing too hard, trying to achieve too much, by defending and extending an outdated success formula desperately in need of change to meet new competitive market conditions.
Application of Growth Stall analysis has historically been very valuable. In May, 2009 I reported on the Growth Stall at Motorola which threatened to dramatically lower company value. Subsequently Motorola spun off its money losing phone business, sold other assets and businesses, and is now a very small remnant of the business prior to its Growth Stall; which was brought on by an overwhelming market shift to smartphones from 2-way radios and traditional cell phones.
In February, 2008 a Growth Stall at General Electric indicated the company would struggle to reach historical performance for long-term investors. The stock peaked at $57.80 in 2000, then at $41.40 in July, 2007. By January, 2009 (post Stall) the company had crashed to only $10, and even recent higher valuations ($28 in 10/2013) are still far from the all-time highs – or even highs in the last decade.
In May, 2008 the Growth Stall at AIG portended big problems for the Dow Jones Industrial (DJIA) giant as financial markets continued to shift radically and quickly. By the end of 2008 AIG stock cratered and the company was forced to wipe out shareholders completely in a government-backed restructuring.
Perhaps the most compelling case has been Microsoft. By February, 2010 a Growth Stall was impending (and confirmed by May, 2011) warning of big changes for the tech giant. Mobile device sales exploded, sending Apple and Google stocks soaring, while Microsoft’s primary, core market for PCs (and software for PCs) has fallen into decline. Windows 8 subsequently had a tepid market acceptance, and gained no traction in mobile devices, causing Microsoft to write-off its investment in the Surface tablet. Recent announcements about enormous lay-offs, with vast cuts in the acquired Nokia handheld unit, do not bode well for long-term revenue growth at the decaying (yet cash rich) giant.
As the Dow has surged to record highs, it has lifted all boats. Including those companies which are showing serious problems. It is easy to look at the ubiquity of McDonald’s stores and expect the chain to remain forever dominant. But, the company is facing serious strategic problems with its products, service and business model which leadership has shown no sign of addressing. The recent Growth Stall serves as a key long-term indicator that McDonald’s is facing serious problems which will most likely seriously jeopardize investors’ (as well as employees’, suppliers’ and supporting communities’) potential returns.

by Adam Hartung | May 3, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
For the first time in 20 years, Apple’s quarterly profit exceeded Microsoft’s (see BusinessWeek.com “Microsoft’s Net Falls Below Apple As iPad Eats Into Sales.) Thus, on the face of things, the companies should be roughly equally valued. But they aren’t. This week Microsoft’s market capitalization is about $215B, while Apple’s is about $365B – about 70% higher. The difference is, of course, growth – and how a lack of it changes management!
According to the Conference Board, growth stalls are deadly.

When companies hit a growth stall, 93% of the time they are unable to maintain even a 2% growth rate. 75% fall into a no growth, or declining revenue environment, and 70% of them will lose at least half their market capitalization. That’s because the market has shifted, and the business is no longer selling what customers really want.
At Microsoft, we see a company that has been completely unable to deal with the market shift toward smartphones and tablets:
- Consumer PC shipments dropped 8% last quarter
- Netbook sales plunged 40%
Quite simply, when revenues stall earnings become meaningless. Even though Microsoft earnings were up, it wasn’t because they are selling what customers really want to buy. In stalled companies, executives cut costs in sales, marketing, new product development and outsource like crazy in order to prop up earnings. They can outsource many functions. And they go to the reservoir of accounting rules to restate depreciation and expenses, delaying expenses while working to accelerate revenue recognition.
Stalled company management will tout earnings growth, even though revenues are flat or declining. But smart investors know this effort to “manufacture earnings” does not create long-term value. They want “real” earnings created by selling products customers desire; that create incremental, new demand. Success doesn’t come from wringing a few coins out of a declining market – but rather from being in markets where people prefer the new solutions.
Mobile phone sales increased 20% (according to IDC), and Apple achieved 14% market share – #3 – in USA (according to MediaPost.com) last quarter. And in this business, Apple is taking the lion’s share of the profits:

Image provided by BusinessInsider.com
When companies are growing, investors like that they pump earnings (and cash) back into growth opportunities. Investors benefit because their value compounds. In a stalled company investors would be better off if the company paid out all their earnings in dividends – so investors could invest in the growth markets.
But, of course, stalled companies like Microsoft and Research in Motion, don’t do that. Because they spend their cash trying to defend the old business. Trying to fight off the market shift. At Microsoft, money is poured into trying to protect the PC business, even as the trend to new solutions is obvious. Microsoft spent 8 times as much on R&D in 2009 as Apple – and all investors received was updates to the old operating system and office automation products. That generated almost no incremental demand. While revenue is stalling, costs are rising.
At Gurufocus.com the argument is made “Microsoft Q3 2011: Priced for Failure“. Author Alex Morris contends that because Microsoft is unlikely to fail this year, it is underpriced. Actually, all we need to know is that Microsoft is unlikely to grow. Its cost to defend the old business is too high in the face of market shifts, and the money being spent to defend Microsoft will not go to investors – will not yield a positive rate of return – so investors are smart to get out now!
Additionally, Microsoft’s cost to extend its business into other markets where it enters far too late is wildly unprofitable. Take for example search and other on-line products: 
Chart source BusinessInsider.com
While much has been made of the ballyhooed relationship between Nokia and Microsoft to help the latter enter the smartphone and tablet businesses, it is really far too late. Customer solutions are now in the market, and the early leaders – Apple and Google Android – are far, far in front. The costs to “catch up” – like in on-line – are impossibly huge. Especially since both Apple and Google are going to keep advancing their solutions and raising the competitive challenge. What we’ll see are more huge losses, bleeding out the remaining cash from Microsoft as its “core” PC business continues declining.
Many analysts will examine a company’s earnings and make the case for a “value play” after growth slows. Only, that’s a mythical bet. When a leader misses a market shift, by investing too long trying to defend its historical business, the late-stage earnings often contain a goodly measure of “adjustments” and other machinations. To the extent earnings do exist, they are wasted away in defensive efforts to pretend the market shift will not make the company obsolete. Late investments to catch the market shift cost far too much, and are impossibly late to catch the leading new market players. The company is well on its way to failure, even if on the surface it looks reasonably healthy. It’s a sucker’s bet to buy these stocks.
Rarely do we see such a stark example as the shift Apple has created, and the defend & extend management that has completely obsessed Microsoft. But it has happened several times. Small printing press manufacturers went bankrupt as customers shifted to xerography, and Xerox waned as customers shifted on to desktop publishing. Kodak declined as customers moved on to film-less digital photography. CALMA and DEC disappeared as CAD/CAM customers shifted to PC-based Autocad. Woolworths was crushed by discount retailers like KMart and WalMart. B.Dalton and other booksellers disappeared in the market shift to Amazon.com. And even mighty GM faltered and went bankrupt after decades of defend behavior, as customers shifted to different products from new competitors.
Not all earnings are equal. A dollar of earnings in a growth company is worth a multiple. Earnings in a declining company are, well, often worthless. Those who see this early get out while they can – before the company collapses.
Update 5/10/11 – Regarding announced Skype acquisition by Microsoft
That Microsoft has apparently agreed to buy Skype does not change the above article. It just proves Microsoft has a lot of cash, and can find places to spend it. It doesn’t mean Microsoft is changing its business approach.
Skype provides PC-to-PC video conferencing. In other words, a product that defends and extends the PC product. Exactly what I predicted Microsoft would do. Spend money on outdated products and efforts to (hopefully) keep people buying PCs.
But smartphones and tablets will soon support video chat from the device; built in. And these devices are already connected to networks – telecom and wifi – when sold. The future for Skype does not look rosy. To the contrary, we can expect Skype to become one of those features we recall, but don’t need, in about 24 to 36 months. Why boot up a PC to do a video chat you can do right from your hand-held, always-on, device?
The Skype acquisition is a predictable Defend & Extend management move. It gives the illusion of excitement and growth, when it’s really “so much ado about nothing.” And now there are $8.5B fewer dollars to pay investors to invest in REAL growth opportunities in growth markets. The ongoing wasting of cash resources in an effort to defend & extend, when the market trends are in another direction.
by Adam Hartung | Apr 11, 2011 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership
Today’s Guest Blog is provided by Mike Meikle. He offers some great insight to the declining value of manufacturing as producitivity continues to skyrocket, pushing all of us toward understanding and competing in markets where greater value lies in digital products rather than physical.
Summary
- Hyperdigitization is the economic shift toward “virtual” goods and services
- Manufacturing jobs have dropped 31 percent but output is at a near record $1.7 trillion.
- Economic output of Hyperdigitization is $2.9 trillion.
- Google, Facebook and GroupOn all have large revenue streams/valuations yet no physical product.
- Industrial Age economic model of static business models is rapidly fading.
- Organizations must release their innovative capabilities to survive and thrive.
Recently, I was engaged by ExecSense to give a Risk Management & Outsourcing Trends for 2011 webinar targeted for Risk Management executives. Since I only had an hour to cover a vast amount material, I could only briefly touch on some interesting topics. One of these was Hyperdigitization, a jargon-laden term that means economic output is moving toward “virtual” goods and services.
So how does hyperdigitization tie into outsourcing trends? As companies continue shift their business processes to outside service providers, firms will have to develop ways to protect their intellectual property and virtual output. Since intellectual property is data, risk managers will have to develop and monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPI) and Key Risk Indicators (KRI) to ensure their firm does not sacrifice their long-term competitive advantage for short-term cost savings. This penny-wise, pound-foolish strategy has been discussed previously by Mr. Hartung.
But before we dig further into explaining hyperdigitization, let us review an example of the current fading Industrial economic model. One of the chief laments heard throughout the Great Recession is that America doesn’t “make” anything anymore. Manufacturing jobs have left primarily to cheaper labor, less regulation, lower tax countries. Without construction jobs to fall back on, this has left a broad swath of the population unemployed. Unfortunately this high unemployment fallout is a result of our economic model shifting away from Industrial Age practices.
While the jobs may have left (down 31%) productivity boosts have pushed the U.S. manufacturing output to near record highs of 1.7 trillion dollars. We make more goods with less people due to technological advances. Contrary to the economic doomsayers this is a positive trend, one that has happened before (agrarian-based economy) and will undoubtedly happen again.
What does this hyperdigitization of economic output mean in real terms? Well, based on a Gartner report, about 20 percent of U.S. economic output in 2009 or 2.9 trillion dollars. That’s nearly double the U.S. manufacturing output. We are awash in virtual products and services. Think about Google alone. The company is worth $163 billion at last estimate and does not have one physical product.
Other examples are Facebook and GroupOn. Both are projected to be worth $65 billion and $25 billion respectively. Yet again, neither has a physical product. These three companies have based their business models on information arbitrage; the process of mining available data for new opportunities.
So where does all this intellectual property (data) that generates billions in profit come from? People, who are supported by a corporate culture that values innovation and measured risk taking.
As the global economy gets exponentially more competitive, organizations need to be fast, flexible and innovative; a near polar opposite of the Industrial Age business model. A large percentage of companies are still mired in outdated business practices that protect the status-quo (Extend & Defend), squash risk taking and stifle innovation. This has especially become prevalent in the era of downsizing culminating in the practices of the Great Recession.
In order to compete in an economy driven by hyperdigitization, the human capital of an organization has to be made a priority. Developed nation’s economies are shifting away from static business models that produce generic widgets and services. To thrive in the hyper competitive, constantly shifting global economy, organizations will have to create and promote a culture that emphasizes and values the Information Age success triumvirate of risk taking, innovation and rapid-execution.
Thanks Mike! Mike Meikle shares his insights at “Musings of a Corporate Consigliere” (http://mikemeikle.wordpress.com/). I hope you read more of his thoughts on innovation and corporate change at his blog site. I thank Mike for contributing this blog for readers of The Phoenix Principle today, and hope you’ve enjoyed his contribution to the discussion about innovation, strategy and market shifts.
If you would like to contribute a guest blog please send me an email. I’d be pleased to pass along additional viewpoints on wide ranging topics.
by Adam Hartung | Feb 15, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
Summary:
- Nokia agreed to develop smartphones with Microsoft software
- But Microsoft’s product is without users, developers or apps
- Apple and Google Android dominate developers, app base and users
- Apple and Google Android have extensive distribution, and customer acceptance
- Microsoft brings Nokia very little
- Nokia hopes it can succeed simply by ramming Microsoft product through distribution. This will be no more successful than its efforts with Symbian
- Apple is the winner, because Nokia didn’t select Google Android
“For First Time Ever, Smartphones Outsell PCs in Q4 of 2010” headlined BGR.com. This is a big deal, as it creates something of an inflection point – possibly what some would call a “tipping point” – in the digital technology market. For over 2 years some of us, using IDC data such as reported in ReadWriteWeb, have been predicting that PCs are on the way to extinction – much like mainframes and mini-computers went. Smartphone sales last quarter jumped 87.2% year-over-year to about 101M units. Meanwhile PC sales, a market manufacturers hoped would recover as “enterprises” resumed buying post-recession, grew only 5.5% in the like period, to 92.1M units. No doubt the installed base of the latter product is multiples of the former, but we can see that increasingly people are ready to use the newer, alternative technology.
This week Mediapost.com reported “Tablet Sales to Hit 242M by 2015.” Both NPD Group and iSuppli are projecting a 10-fold increase wtihin 5 years in the volume of these new devices, which is sure to devastate PC sales. Between smartphones and tablets, as well as the rapid development of cloud-based apps and data storage solutions, it’s becoming quite clear that the life-span of PC technology has its limits. Soon we’ll be able to do more, cheaper, better and faster with these new products than we ever could on a PC.
This is really bad news for Microsoft. Apple and Google dominate both these mobile markets. As Microsoft has fought to defend its PC business by re-investing in Vista, then Windows 7 and Office 2010, the market has been shifting away from the PC platform entirely. It’s common now to hear about corporations considering iPads and other tablets for field workers. And it’s impossible to walk through an airport, or sit in a meeting these days without seeing people use their smartphones and tablets, purchased individually at retail, while leaving their PCs at the office. Most corporate Blackberry users now have either an Apple or Android smartphone or tablet as they eschew their RIM product for anything other than required corporate uses.
Nokia has largely missed the smartphone market, choosing, like Microsoft, to continue investing in defending its traditional business. Long the largest cell phone supplier, Nokia did not develop the application base or developer network for Symbian (it’s proprietary smartphone technology) as it kept pumping out older devices. Nokia is reminiscent of the Ed Zander led Motorola disaster, where the company kept pumping out Razr phones until demand collapsed, nearly killing the company.
So the Board replaced the Nokia CEO. As discussed in Forbes on 5 October, 2010 in “HP and Nokia’s Bad CEO Selections” Nokia put in place a Microsoft executive. Given that Microsoft had missed the smartphone market entirely, as well as the tablet market, moving the Microsoft Defend & Extend way of thinking into Nokia didn’t look like it would bring much help for the equally locked-in Nokia. Exchanging one defensive management approach for another doesn’t create an offense – or new products.
It wasn’t much of a surprise last week when the 5-month tenured CEO, Stephen Elop, announced he thought Nokia’s business was in horrible shape via an internal email as reported in the Wall Street Journal, “Nokia, Microsoft Talk Cellphones.” Rather quickly, a deal was struck in which Nokia would not only pick up the Microsoft mobile operating system, but would use their products to promote other extremely poorly performing Microsoft products. “Nokia to Adopt Microsoft Bing, Adcenter” was another headline at MediaPost.com. Bing and adCenter were very late to market, and even with adoption by early market leader Yahoo! have been unable to make much inroad into the search and on-line ad placement markets dominated by Google.
Mr Elop went with what he knew, selecting Microsoft. I guess he’s the new “chief decider” at Nokia. His decision caused a break out of optimism amongst long-suffering Microsoft investors and customers who’ve gotten very little from the giant PC near-monopolist the last decade. Mediapost told us “Study: Surge of Support for Windows Phone 7” as developers who long ignored the product entirely were starting to consider writing apps for the device. After all this time, new hope beats within the breast of those still stuck on Microsoft.
But if ever there was a case of too little, and way, way too late, this has to be it. Two companies long known for weak product innovation, and success driven by market domination and distribution control strategies, are partnering to take on the two most innovative companies in digital technology as they create entirely new markets with new technologies.
RIM, the smartphone market originator, has seen its fortunes disintegrate as Blackberry sales fell below iPhones – even with over 10,000 apps. Today Microsoft has virtually NO apps, and NO developer base as it just now enters this market, “Google Searches for Mobile App Experts” (Wall Street Journal) as its effort continues to expand its 100,000+ apps base as it chases the 350,000+ apps already existing for the iPhone. Where Microsoft and Nokia hope to build an app base, and a user base, Apple and Google already have both, which theyt are aggressively growing.
Exactly what going to happen to slow Apple and Google’s growth in order to allow Microsoft + Nokia to catch up? In what fairy tale will the early hare take a nap so the awakened tortoise will be allowed to somehow, miraculously get back into the race?
Being late to market is never good. Look at how Sony, and everyone else, were late to digitally downloaded music. iPad and iTunes not only took off but continue to hold well over 50% of the market almost a decade later. Over the same decade Apple has held onto 2/3 of the download video market, while Microsoft’s Zune has struggled to capture less than 1/4 of Apple’s share (about 18% according to WinRumors.com).
Apple (and Google) aren’t going to slow down the pace of innovation to give Microsoft and Nokia a chance to catch up. Today (15 Feb., 2010) ITProPortal.com breaks news “Apple iPhone 5 to have 4 Inch Screen,” an upgrade designed to bring yet more users to its mobile device platform – away from PCs and competitive smarphones. The same article discusses how Google Android manufacturers are bringing out 4.3 inch screens in their effort to keep growing.
So, amidst the “big announcement” of Microsoft and Nokia agreeing to work together on a new platform, where’s the product announcement? Where’s the app base? And exactly what is the strategy to be competitive in 2012 and 2015? Does anyone really think throwing money at this will create the products (hardware and software) fast enough to let either catch up with existing leaders? Does anyone think Microsoft products dependent upon Nokia’s distribution can save either’s mobile business – while Apple has just expanded to Verizon for distribution? And Google is already on almost all networks? And where is Microsoft or Nokia in the tablet business, which is closely associated with smartphone market for obvious issues of mobility and use of cloud-based computing architectures?
The good news here is for Apple fans. Nokia clearly should have chosen Android. This would give the laggard a chance of leveraging the base of technology at Google – including advances being made to the Chrome operating system and its advantages for the cloud. No matter what the price, it’s the only chance Nokia has. With this decision the most likely outcome is big investments by both Microsoft and Nokia to play catch-up, but limited success. Results will not likely cover investment rates, leading Nokia to a Motorola-like outcome. And Microsoft will remain a bit player in the fastest growing digital markets. Both have billions of dollars to throw away in this desperate effort. But the outcome is almost certain. It’s doubtful between the two of them they can buy enough developers, network agreements and users to succeed against the 2 growth leaders and the desperately defensive RIM.
Like I said last month in this blog “Buy Apple, Sell Microsoft.” It’s still the easiest money-making trade of 2011. Now thankfully reinforced by the former Microsoft exec running Nokia.



