by Adam Hartung | Feb 9, 2011 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in, Weblogs
Summary:
- Start-ups that flourish give themselves permission to do whatever is necessary to succeed
- Most acquisitions kill that kind of permssion, forcing the acquired company to adopt the acquirers legacy
- AOL’s legacy business has been dying for several years
- AOL’s history of acquisitions has been horrible, because it doesn’t learn from the acquisitions.
- AOL’s acquisition, and announced integration, of Huffington Post will likely do nothing to turn around AOL, and probably leave HuffPo about as well off as AOL’s acquisition of Bebo
After the Super Bowl Sunday Night AOL announced it’s acquisition of The Huffington Post for $350M. Given that you can’t give away a newspaper company these days, the acquisition shows there is still value in “news” if you understand the right way to deliver it. HuffPo’s team of bloggers has shown that it’s possible to build a profitable news organization today – if you do it right. Something the folks at Tribune Corporation still don’t understand.
BusinessInsider.com headlined “AOL’s Huffington Post Acquisition Makes Sense for Both Sides.” For Arianna Huffington and her investors the big cash payout shows a clear win. They are receiving a pretty penny for their start-up. Beyond them, it’s less clear. AOL’s been losing subscribers, and site vistors for years. They’ve made a number of acquisitions to spark up interest including blogs Engadget, Joystiq, ad network Tacoda and social networking site Bebo. None of those have flourished – in fact the opposite has happened. AOL investors lost almost all the $850M spent on Bebo as Facebook crushed it. So far, the AOL track record has been horrible!
AOL clearly hopes HuffPo will bring it new visitors – but whether that works, and whether HuffPo continues growing, is now an open question. MediaPost.com reports “AOL Starts Mapping Plans for Huffington Post.” Unfortunately, it sounds much more as if AOL is trying to integrate HuffPo into its traditional organization – which will most likely do for HuffPo what integrating at News Corp did for MySpace – namely, layering it with “professional management,” additional systems, more overhead and rules for operating. Or, in other words, bury it in company legacy that strangles its abilitiy to innovate and shift with rapidly emerging market needs. The company that’s actually growing, winning in the marketplace, isn’t AOL. It’s HuffPo. If there’s any “integrating” needed it should be figuring out how to push AOL into HuffPo – not vice-versa.
As the New York Times headlined, this acquisition is “AOL’s Bet on Another Makeover.” And that’s what’s wrong. The acquisitions AOL made were pre-purchase successful because they were White Space endeavors that had close connection to the market. The founders gave their organization permission to do whatever it took to be successful, without artificial constraints based upon legacy. Their acquisitions have not used by AOL to create White Space with better market receptors – to teach AOL where growth lies. Rather, AOL has hoped they can use the acquisition to defend and extend their old success formula. AOL has hoped the acquisitions would allow them to slow the market shift, and preserve legacy operations.
As we’ve seen, that simply does not work. Markets shift for good reason, and the only way a business can thrive is to shift with them. At AOL the smart move would be to let Arianna run the show! A few months ago AOL purchased TechCrunch and ever since Michael Arrington, the founder, has been villifying AOL management for its bureaucracy and inability to adapt. What Mr. Armstrong, the relatively new CEO at AOL misses is that AOL’s business is dead. AOL needs to find an entirely new way of operating – and that’s what these acquisitions bring. AOL needs to get out of the way, let the acquisitions flourish, and learn something from them. AOL management needs to accept that the old AOL business model is rubbish, and what it must do is allow the acquisitions to operate in White Space, then learn from them! But that’s not been the history of AOL’s purchases, and doesn’t look like the case this time.
Mr. Armstrong could learn a lot from Sir Richard Branson. Virgin has made many acquisitions, and developed several new companies. He doesn’t try to integrate them, or drive them toward any particular business model From Virgin Airways to Virgin Money to Virgin Health Bank to Virgin Games (and all the other businesses) the requirement is that the business be tightly linked to market needs, operate in new ways and find out how to grow profitably. Virgin moves toward the new markets and businesses, it doesn’t expect the businesses to conform to the Virgin model.
I’d like to think AOL could learn from HuffPo and dramatically change. But from the announcements this week, it doesn’t look likely. AOL still looks like a management team desperately trying to save its old business, but without a clue how to do so. Too bad for AOL. Could be even worse for those who read HuffPo.
by Adam Hartung | Feb 3, 2011 | Defend & Extend, eBooks, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in, Openness
Summary:
- Company size is irrelevant to job creation
- New jobs are created by starting new businesses that create new demand
- Most leaders behave defensively, trying to preserve the old business
- But success comes from acting like a start-up and creating new opportunities
- Companies need to do more future-based planning that can change the competitive landscape and generate more growth, jobs and higher rates of return
A trio of economists just published "Who Creates Jobs? Small vs. Large vs. Young" at the National Bureau of Economic Research. For years businesspeople have said that the majority of jobs were created by small companies, therefore we should provide loans and other incentives for small business. At the same time, we all know that large companies employee millions of people, and therefore they have received benefits to keep their companies going even in tough times – like the recent bailouts of GM and Chrysler. But what these researchers discovered was that size was immaterial to job creation – and this ages-old debate is really irrelevant!
Digging deeper into the data, they discovered as reported in the New York Times, "To Create Jobs, Nurture Start-Ups." Regardless of size, most businesses over time get stuck defending their original success formula. What helped them initially grow becomes locked-in by behavioral norms, structural decision-making processes and a business model cost structure that may be tweaked, but rarely changed. Best practices serve to focus management on defending that business, even as market shifts lower the industry growth rate and profits. It doesn't take long before defensive tactics dominate, and as the leaders attempt to preserve historical practices there are no new jobs created. Usually quite the opposite happens as cost cutting dominates, leading to outsourcing and lay-offs reducing the workforce.
Look no further than most members of the Dow Jones Industrial Average to witness the lack of jobs created by older companies desperately trying to defend their historical business model. But what we've failed to realize is how the same management practices dominate small business as well! Most plumbing suppliers, window installers, insurance agencies, restaurants, car dealers, nurseries, tool rental shops, hair cutters and pet sitters spend all their time just trying to keep the business going. They look no further than what they did yesterday when making business decisions. Few think about growth, preferring instead to just keep the business the same – maybe by the owner/operator's father 3 decades ago! They don't create any new jobs, and are probably struggling to maintain existing employment as computers and other business aids reduce the need for labor – while competition keeps whacking away at historical margins.
So if you want to create jobs, throwing incentives at General Electric, General Motors or General Dynamics is not likely to get you very far. And asking the leaders of those companies what it takes to get them to create jobs is a wasted conversation. They don't know, and haven't really thought about the question. Leaders of almost all big organizations are just trying to make next quarter's profit projection any way they can – and that doesn't involve new hiring. After a lifetime of cutting costs and preservation behavior, how is Jeffrey Immelt of GE supposed to know anything about creating new businesses which leads to job creation?
Nor is offering loans or grants to the millions of existing small businesses who are just trying to keep the joint running going to make any difference. Their psychology is not about offering new products or services, and banks sure don't want to take the risk of investing in new experimental behaviors. They have little, if any, interest in figuring out how to grow when most of their attention is trying to preserve the storefront in the face of new competitors on-line, or from India, China or Vietnam!
To create jobs you have to focus on growth – not defense. And that takes an entirely different way of thinking. Instead of thinking about the past you have to be obsessive about the future, and how you can do things differently! Most of the time, business leaders don't think this way until their backs are up against the wall, looking at potential failure! For example, how Mr. Gerstner turned around IBM when he moved the company away from mainframe obsession and pointed the company toward services. Or when Steve Jobs redirected Apple away from its Mac obsession and pushed the company into new markets for music/entertainment and smartphones. Unfortunately, these stories are so rare that we tend to use them for a decade (or even 2 decades)!
For years Cisco said it would obsolete its own products, and by implementing that direction Cisco has grown year after year in the tech world, where flame-outs abound (just look at what happened to Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, AOL and rapidly Yahoo!) Look at how Netflix has pushed Blockbuster aside by expanding its business from snail-mail to downloads. Or how Amazon.com has found explosive growth by changing the way we read books, now selling more Kindle products than printed. Rather than thinking about how each could do more of what they always did, fearing cannibalization of the "core business," they are aiding destruction of their historical business by implementing the newest technology and solution before some start-up beats them to the punch!
As you enter 2011 and prepare for 2012, is your planning based upon doing more of what your business has always done? A start up has no last year, so its planning is based entirely on views of the future. Are you fixated on improving your operations? A start up has no operations, so it is fixated on competitors to figure out how it can meet market needs better, and use "fringe" solutions in new ways that competitors have not yet adopted. Are you hoping that market shifts slow, or stop, so revenue, market share and profit slides abate? A start up is looking for ways to disrupt the marketplace to it can grab high growth from existing solutions while generating new demand by meeting unmet needs. Are you trying to preserve resources in order to defend your business from competitors? A start up is looking for places to experiment with new solutions and figure out how to change the competitive landscape while growing revenues and profits.
If you want to thrive you have to grow. To grow, you have to think young! Be willing to plan for the future, like Apple did when it moved into new markets for music downloads. Be willing to find competitive holes and fill them with new technology, like Netflix. Don't fear market changes – create them like Cisco does with new solutions that obsolete previous generations. And keep testing new ways to expand the market, even as you see intense competition in historical markets being attacked by new competitors. That is the only way to create value, and generate new jobs!
by Adam Hartung | Jan 10, 2011 | Defend & Extend, Disruptions, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Summary:
- Communication is now global, instantaneous and free
- As a result people, and businesses, now adopt innovation more quickly than ever
- Competitors adapt much quicker, and react much stronger than ever in history
- Profits are squeezed by competitors rapidly adopting innovations
- But many business leaders avoid disruptions, leading to slower growth and declining returns
- To maintain, and grow, revenues and profits you must be willing to implement disruptions in order to stay ahead of fast moving competitors
- Amidst fast shifting markets, greatest value (P/E multiple and market cap) is given to those companies that create disruptions (like Facebook, Groupon, Twitter)
All business leaders know the pace of competitive change has increased.
It took decades for everyone to obtain an old-fashioned land line telephone. Decades for everyone to buy a TV. And likewise, decades for color TV adoption. Microwave ovens took more than a decade. Thirty years ago the words “long distance” implied a very big cost, even if it was a call from just a single interchange away (not even an area code away – just a different set of “prefix” numbers.) People actually wrote letters, and waited days for responses! Social change, and technology adoption, took a lot longer – and was considered expensive.
Now we assume communications at no cost with colleagues, peers, even competitors not only across town state, or nation, but across the globe! Communication – whether email, or texting, or old fashioned voice calls – has become free and immediate. (Consider Skype if you want free phone calls [including video no less] and use a PC at your local library or school building if you don’t own one.) Factoring inflation, it is possible to provide every member of a family of 5 with instant phone, email and text communication real-time, wirelessly, 24×7, globally for less than my parents paid for a single land-line, local-exchange only (no long distance) phone 50 years ago! And these mobile devices can send pictures!
As a result, competitors know more about each other a whole lot faster, and take action much more quickly, than ever in history. Facebook, for example, is now connecting hundreds of millions of people with billions of communications every day. According to statistics published on Facebook.com, every 20 minutes the Facebook website produces:
- 1,000,000 shared links
- 1,323,000 tagged photos
- 1,484,000 event invitations
- 1,587,000 Wall posts
- 1,851,000 Status updates
- 1,972,000 Friend requests accepted
- 2,716,000 photos uploaded
- 4,632,000 messages
- 10,208,000 comments
Multiply those numbers by 3 to get hourly. By 72 to get daily. Big numbers! Alexander Graham Bell had to invent the hardware and string thousands of miles of cable to help people communicate with his disruption. His early “software” were thousands of “operators” connecting calls through central switchboards. Mark Zuckerberg and friends only had to create a web site using existing infrastructure and existing tools to create theirs. Rapidly adopting, and using, existing innovations allowed Facebook’s founders to create a disruptive innovation of their own! Disruption has allowed Facebook to thrive!
Facebook has disrupted the way we communicate, learn, buy and sell. “Word of mouth” referrals are now possible from friends – and total strangers. Product benefits and problems are known instantaneously. Networks of people arguably have more influence that TV networks! Many employees are likely to make more facebook communications in a day than have conversations with co-workers! Facebook (or twitter) is rapidly becoming the new “water cooler.” Only it is global and has inputs from anyone. Yet only a fraction of businesses have any plans for using Facebook – internally or to be more competitive!
Far too many business leaders are unwilling to accept, adopt, invest in or implement disruptions.
InnovateOnPurpose.com highlights why in “Why Innovation Makes Executives Uncomfortable:”
- Innovation is part art, and not all science. Many execs would like to think they can run a business like engineering a bridge. They ignore the fact that businesses implement in society, and innovation is where we use the social sciences to help us gain insight into the future. Success requires more than just extending the past – because market shifts happen. If you can’t move beyond engineering principles you can’t lead or manage effectively in a fast-changing world where the rules are not fixed.
- Innovation requires qualitative insights not just quantitative statistics. Somewhere in the last 50 years the finance pros, and a lot of expensive strategy consultants, led business leaders to believe that if they simply did enough number crunching they could eliminate all risk and plan a guaranteed great future. Despite hundreds of math PhDs, that approach did not work out so well for derivative investors – and killed Lehman Brothers (and would have killed AIG insurance had the government not bailed it out.) Math is a great science, and numbers are cool, but they are insufficient for success when the premises keep changing.
- Innovation requires hunches, not facts. Well, let’s say more than a hunch. Innovation requires we do more scenario planning about the future, rather than just pouring over historical numbers and expecting projections to come true. We don’t need crystal balls to recognize there will be change, and to develop scenario plans that help us prepare for change. Innovation helps us succeed in a dynamic world, and implementation requires a willingness to understand that change is inevitable, and opportunistic.
- Innovation requires risks, not certainties. Unfortunately, there are NO certainties in business. Even the status quo plan is filled with risk. It’s not that innovation is risky, but rather that planning systems (ERP systems, CRM systems, all systems) are heavily biased toward doing more of the same – not something new! Markets can shift incredibly fast, and make any success formula obsolete. But most executives would rather fail doing the same thing faster, working harder, doing what used to work, than implement changes targeted at future market needs. Leaders perceive following the old strategy is less risky, when in reality it’s loaded with risk too! Too many businesses have failed at the hands of low-risk, certainty seeking leadership unable to shift with changing markets (GM, Chrysler, Circuit City, Fannie Mae, Brach’s, Sun Microsystems, Quest, the old AT&T, Lucent, AOL, Silicon Graphics, Yahoo, to name a few.)
Markets are shifting all around us. Faster than imaginable just 2 decades ago. Leaders, strategists and planners that enter 2011 hoping they can win by doing more, better, faster, cheaper will have a very tough time. That is the world of execution, and modern communication makes execution incredibly easy to copy, incredibly fast. Even Wal-Mart, ostensibly one of the best execution-oriented companies of all time, has struggled to grow revenue and profit for a decade. Today, companies that thrive embrace disruption. They are willing to disrupt within their organizations to create new ideas, and they are willing to take disruptive opportunities to market. Compare Apple to Dell, or Netflix to Blockbuster.
Recent investments have valued Facebook at $50B, Groupon at $6B and Twitter at almost $4B. Apple is now the second most valuable company (measured by market capitalization). Why? Because they are disrupting the way we do things. To thrive (perhaps survive by 2015) requires moving beyond the status quo, overcoming the perceived risk of innovation (and change) and taking the actions necessary to provide customers what they want in the future! Any company can thrive if it embraces the disruptions around it, and uses them to create a few disruptions of its own.
by Adam Hartung | Jan 5, 2011 | Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in, Openness
Summary:
- Business planning systems are designed to defend historical markets
- Rapidly shifting markets makes it impossible to grow by defense alone
- Growth requires understanding what customers want, and creating new solutions that most likely aren’t part of the current business
- You can’t grow if you don’t plan to grow, but to plan for growth you have to shift resources from traditional planning into scenario planning
- High growth companies like Virgin, Apple and Google plan to fulfill future needs, not defend & extend past practicess
Imagine you see a pile of hay. Above it is a sign flashing “find the needle.” That achievement would be hard. Change the sign to “find the hay” and suddenly achieving the goal becomes much easier. So, as the comedian Bill Engvall might ask, what’s your sign? Unfortunately, most businesses plan for 2011, and beyond, using the first sign. Very few do planning using the latter. Most businesses won’t grow, because they simply don’t know how to plan for growth!!
Most businesses start planning with “I’m in the horseshoe (for example) business. My market isn’t growing, and there is more capacity than demand. How can I grow?” For these people, their sign is “find the needle.”
Take for example Earthlink. The company’s growth looked like a rocket ship in the early internet days as people by the millions signed up for dial-up service. But along came broadband, and the market for dial up died – never to return. Earthlink has no hope of growing as long as it thinks of itself as a dial-up company
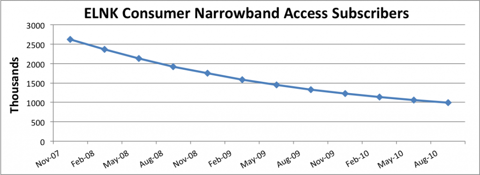
Chart at SeekingAlpha.com author Ananthan Thangavel
Despite the absolute certainty that the market is shrinking, at this point almost all business planners will develop plans to defend this dying business as long as possible. Despite the impossibility of achieving good returns, there will be a plethora of actions to try and keep serving all the way to the very last customer. Just look at how AOL has invested millions trying to defend its dying internet access busiuness. Reality is, the company that walks away – gives up- is the smartest. There’s no way to make money as oversupply keeps too many companies spending too much to service too few customers.
The next step for most planners is to attempt extending the business into something adjacent. For example, Earthlink would say “let’s invest in Broadband. We’ll hang onto customers as they want to switch, and maybe pick up a few customers.” But this completely ignores the fact that competitors already have a substantial lead. Competitors have learned the technology, and the marketplace. They are growing, and have no intention of giving up any room to a new competitor.
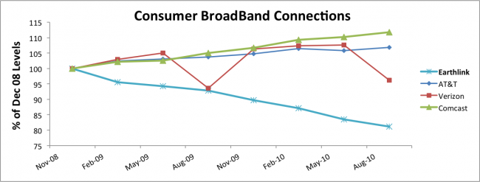
Chart at SeekingAlpha.com author Ananthan Thangavel
Planning systems are designed to keep the business doing more of what it always did, or possibly extending the business into adjacent markets after returns have faltered. Planning systems have no way of recognizing when a business, or market, has become obsolete. And practically never do they recognize the power of exsting competitors when looking at adjacent markets. As a result, the planning system produces no growth plans, leading 2011 to end with the self-fulfilling prophecy that the plan predicted – little or no growth.
The future for Earthlink is pretty grim. As it is for most companies that plan based upon history, trying to Defend & Extend their historical markets. In the highly dynamic, global marketplaces of 2011 trying to find growth by remaining focused on the past is like looking for the needle in a haystack. Maybe there’s something in there – but it’s not likely – and it’s even a lot less likely you’ll find it – and if you did, the cost of finding it will almost assuredly be greater than the value.
Alternatively, why not use planning resources to find, and develop, growth markets. Instead of looking at what you did (as in the past tense) try to figure out what you should do. Rather than studying past products, customers and markets, why not develop scenarios about the future that give you insight to what people will want to buy in 2011, 2012 and beyond? Rather than looking for needles, why not go explore the hay?
Newspapers kept focusing on declining subscriptions, when they should have been studying Craig’s List, eBay, Vehix.com and other on-line environments to learn the future of advertising. Had Tribune company poured its resources into its early internet investments, such as cars.com and careerbuilder.com, rather than trying to defend its traditional newspapers, it may well have avoided bankruptcy. But rather than looking to the future when doing its planning, and understanding that on-line news was going to explode, Tribune kept looking for the needle (cost cuts, layoffs, outsourcing, etc.) to save the old success formula.
Direct mail companies and Sunday insert printers have continued looking for ways to defend & extend their coupon printing business – despite the fact that nobody reads junk mail or uses printed coupons. Several have failed, and larger companies have merged trying to find “synergies” and more cost cuts. Simultaneously a 28 year old music major from Nothwestern university starts figuring out how to help companies acquire new customers by offering email coupons, and within 2 years his company, Groupon, is valued at around $6B. There’s nothing that stopped coupon powerhouse Advo from being Groupon, except that its planning system was devoted to finding the needle, while Groupon’s leaders decided to go play in the hay.
Hallmark and American Greetings want us to buy birthday and holiday cards for various occasions – in a world where almost nobody mails cards any longer. As they keep trying to defend their old business, and extend it into a few new opportunities for on-line cards, Twitter captures the wave of instant communications by offering everyone 140 character ways to communicate. Because Twitter is out where the growth is, the company raises $200M giving it a value of $3.7B.
Nothing stops any business from being anything it wants to be. But as most enter 2011 they will use their planning resources, including all those management meetings and hours of forms completion, to do nothing more than re-examine the historical business. Most will devolve into trying to figure out how to do more with less. As future forecasts look grim, or perhaps cautiously optimistic (based on a lot of things going right – like a mysterious pick-up in demand) there will be much nashing of teeth – and meetings looking for a needle that can be offered to employees and investors as a hope for rising future value.
Smart companies get out of that rut. They focus their planning on the future. What do customers want, and how can we give them what they want? How can we create whole new markets. Apple was a PC company, but by exploring mobility it became a provider of MP3 consumer electronics, downloadable music, a mobile device and app supplier and the early winner in cloud accessing tablets. Google has moved from a search engine to a powerhouse ad placement company and is pushing the edges of growth in mobile computing as well as several other markets. Virgin started as a distributor of long-playing vinyl record albums, but by exploring what customers really wanted it has become an international airline, cell phone company, international lender and space travel pioneer (to mention just a few of its businesses.)
You can grow in 2011, but to do so you need to shed the old planning system (and its resource wasting processes) and get serious about scenario planning. Focus on the future, not the past.
by Adam Hartung | Dec 23, 2010 | Defend & Extend, General, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Openness
“Goodbye 2010, the Year of Austerity” is the headline from Mediapost.com‘s Marketing Daily. And that could be the mantra for many, many companies. Nobody is winning today by trying to save their way to prosperity! As we move into this decade, it is important business leaders realize that the only way to create a strong bottom line (profit) is to develop a strong top line (revenue.) Recommendations:
- Never be desperate. Go to where the growth is, and where you can make money. Don’t chase any business, chase the business where you can profitably growth. Be somewhat selective.
- Focus efforts on markets you know best. I add that it’s important you understand not to do just what you like, but learn to do what customers VALUE.
- Let go of crap, traditions and “playing it safe” actions. Growth is all about learning to do what the market wants, not trying to protect the past – whether processes, products or even customers.
- More lemonade making. You can’t grow unless you’re willing to learn from everything around you. We constantly find ourselves holding lemons, but those who prosper don’t give up – they look for how to turn those into desirable lemonade. What is your willingness to learn from the market?
- Austerity measures are counterproductive 99% of the time. Efficiency is the biggest obstacle to innovation. You don’t have to be a spendthrift to succeed, but you can’t be a miser investing in only the things you know, and have done before.
- Communicate, communicate, communicate. We don’t learn if we don’t share. Developing insight from the environment happens when all inputs are shared, and lots of people contribute to the process.
- Get off the downbeat buss. There’s more to success than the power of positive thinking, but it is very hard to gain insight and push innovation when you’re a pessimist. Growth is an opportunity to learn, and do exciting things. That should be a positive for everybody – except the status quo police.
Realizing that you can’t beat the cost-cutting horse forever (in fact, most are about ready for the proverbial glue factory), it’s time to realize that businesses have been under-investing in innovation for the last decade. While GM, Circuit City, Blockbuster, Silicon Graphics and Sun Microsystems have been failing, Apple, Google, Cisco, Netflix, Facebook and Twitter have maintained double-digit growth! Those who keep innovating realize that markets aren’t dead, they’re just shifting! Growth is there for businesses who are willing to innovate new solutions that attract customers and their dollars! For every dead DVD store there’s somebody making money streaming downloads. Businesses simply have to work harder at innovating.
Fast Company gives us “Five Innovative New Year’s Resolutions:”
- Associate. Work harder at trying to “connect the dots.” Pick up on weak signals, before others, and build scenarios to help understand the impact of these signals as they become stronger. For example, 24x7WallStreet.com clues us in that greater use of mobile devices will wipe out some businesses in “The Ten Businesses The Smartphone Has Destroyed.” But for each of these (and hundreds others over the next few years) there will be a large number of new business opportunities emerging. Just look at the efforts of Foursquare and Groupon and the direction those growth businesses are headed.
- Observe. Pay attention to what’s happening in the world, and think about what it means for your (and every other) business. $100/barrel oil has an impact; what opportunity does it create? Declining network TV watching has an impact – how will you leverage this shift? Don’t just wander through the market, and reacting. Figure out what’s happening and learn to recognize the signs of growth opportunities. Use market events to drive being proactive.
- Experiment. If you don’t have White Space teams trying figure out new business models, how will you be a future winner? Nobody “lucks” into a growth market. It takes lots of trial and learning – and that means the willingness to experiment. A lot. Plan on experimenting. Invest in it. And then plan on the positive results.
- Question. Keep asking “why” until the market participants are so tired they throw you out of the room. Then, invent scenarios and ask “why not” until they throw you out again. Markets won’t tell you what the next big thing is, but if you ask a lot of questions your scenarios about the future will be a whole lot better – and your experimentation will be significantly more productive.
- Network. You can’t cast your net too wide in the effort to obtain multiple points of view. Nothing is narrower than our own convictions. Only by actively soliciting input from wide-ranging sources can you develop alternative solutions that have higher value. We become so comfortable talking to the same people, inside our companies and outside, that we don’t realize how we start hearing only reinforcement for our biases. Develop, and expand, your network as fast as possible. Oil and water may be hard to mix, but it blending inputs creates a good salad dressing.
ChiefExecutive.net headlined “2010 CEO Wealth Creation Index Shows a Few Surprises.” Who creates wealth? Included in thte Top 10 list are the CEOs of Priceline.com, Apple, Amazon, Colgate-Palmolive and DeVry. These CEOs are driving industry innovation, and through that growth. This has produced above-average cash flow, and higher valuations for their shareholders. As well as more, and better quality jobs for employees. Meanwhile suppliers are in a position to offer their own insights for ways to grow, rather than constantly battling price discussions.
Who destroys wealth? In the Top 10 list are the CEOs of Dean Foods, Kraft, Computer Sciences (CSC) and Washington Post. These companies have long eschewed innovation. None have introduced any important innovations for over a decade. Their efforts to defend & extend old practices has hurt revenue growth, providing ample opportunity for competitors to enter their markets and drive down margins through price wars. Penny-pinching has not improved returns as revenues faltered, and investors have watched value languish. Employees are constantly in turmoil, wondering what future opportunities may ever exist. Suppliers never discuss anything but price. These are not fun companies to work in, or with, and have not produced jobs to grow our economy.
Any company can grow in 2011. Will you? If you choose to keep doing what you’ve always done – well you shouldn’t plan on improved performance. On the other hand, embracing market shifts and creating an adaptive organization that identifies and launches innovation could well make you into a big winner. Next holiday season when you look at performance results for 2011 they will have more to do with management’s decisions about how to manage than any other factor. Any company can grow, if it does the right things.
by Adam Hartung | Dec 17, 2010 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
Summary:
- Many people think it is OK for large companies to grow slowly
- Many people admire caretaker CEOs
- In dynamic markets, low-growth companies fail
- It is harder to generate $1B of new revenue, than grow a $100B company by $10B
- Large companies have vastly more resources, but they squander them badly
- We allow large company CEOs too much room for mediocrity and failure
- Good CEOs never lose a growth agenda, and everyone wins!
“I may just be your little rent collector Mr. Potter, but that George Bailey is making quite a bit happen in that new development of his. If he keeps going it may just be time for this smart young man to go asking George Bailey for a job.” From “It’s a Wonderful Life“ an employee of the biggest employer in mythical Beford Falls talks about the growth of a smaller competitor.
My last post gathered a lot of reads, and a lot of feedback. Most of it centered on how GE should not be compared to Facebook, largely because of size differences, and therefore how it was ridiculous to compare Jeff Immelt with Mark Zuckerberg. Many readers felt that I overstated the good qualities of Mr. Zuckerberg, while not giving Mr. Immelt enough credit for his skills managing “lower growth businesses” in a “tough economy.” Many viewed Mr. Immelt’s task as incomparably more difficult than that of managing a high growth, smaller tech company from nothing to several billion revenue in a few years. One frequent claim was that it is enough to maintain revenue in a giant company, growth was less important.
Why do so many people give the CEOs of big companies a break? Given that they make huge salaries and bonuses, have fantastic perquesites (private jets, etc.), phenominal benefits and pensions, and receive remarkable payouts whether they succeed or fail I would think we’d have very high standards for these leaders – and be incensed when their performance is sub-par.
Facebook started with almost no resources (as did Twitter and Groupon). Most leaders of start-ups fail. It is remarkably difficult to marshal resources – both enough of them and productively – to grow a company at double digit rates, produce higher revenue, generate cash flow (or loans) and keep employees happy. Growing to a billion dollars revenue from nothing is inexplicably harder than adding $10B to a $100B company. Compared to Facebook, GE has massive resources. Mr. Immelt entered the millenium with huge cash flow, huge revenues, and an army of very smart employees. Mr. Zuckerberg had to come out of the blocks from a standing start and create ALL his company’s momentum, while comparatively Mr. Immelt took on his job riding a bullet out of a gun! GE had huge momentum, a low cost of capital, and enough resources to do anything it wanted.
Yet somehow we should think that we don’t have as high expectations from Mr. Immelt as we do Mr. Zuckerberg? That would seem, at the least, distorted.
In business school I read the story of how American steel manufacturers were eclipsed by the Japanese. Ending WWII America had almost all the steel capacity. Manufacturers raked in the profits. Japanese and German companies that were destroyed had to rebuild, which they progressively did with more efficient assets. By the 1960s American companies were no longer competitive. Were we to believe that having their industrial capacity destroyed somehow was a good thing for the foreign competitors? That if you want to improve your competitiveness (say in autos) you should drop a nuclear bomb on the facilities (some may like that idea – but not many who live in Detroit I dare say.) In reality the American leaders simply refused to invest in new technologies and growth markets, allowing competitors to end-run them. The American leaders were busy acting as caretakers, and bragging about their success, instead of paying attention to market shifts and keeping their companies successful!
Big companies, like GE, are highly advantaged. They not only have brand, and market position, but cash, assets, employees and vendors in position to help them be even more successful! A smart CEO uses those resources to take the company into growth markets where it can grow revenues, and profits, faster than the marketplace. For example Steve Jobs at Apple, and Eric Schmidt at Google have found new markets, revenues and cash flow beyond their original “core” markets. That’s what Mr. Welch did as predecessor to Mr. Immelt. He didn’t so much take advantage of a growth economy as help create it! Unfortunately, far too many large company CEOs squander their resources on low rate of return projects, trying to defend their existing business rather than push forward.
Most big companies over-invest in known markets, or technologies, that have low growth rates, rather than invest in growth markets, or technologies they don’t know as well. Think about how Motorola invented the smart phone technology, but kept investing in traditional cellular phones. Or Sears, the inventor of “at home shopping” with catalogues closed that division to chase real-estate based retail, allowing Amazon to take industry leadership and market growth. Circuit City ended up investing in its approach to retail until it went bankrupt in 2010 – even though it was a darling of “Good to Great.” Or Microsoft, which launched a tablet and a smart phone, under leader Ballmer re-focused on its “core” operating system and office automation markets letting Apple grab the growth markets with R&D investments 1/8th of Microsoft’s. These management decisions are not something we should accept as “natural.” Leaders of big companies have the ability to maintain, even accelerate, growth. Or not.
Why give leaders in big companies a break just because their historical markets have slower growth? Singer’s leadership realized women weren’t going to sew at home much longer, and converted the company into a defense contractor to maintain growth. Netflix converted from a physical product company (DVDs) into a streaming download company in order to remain vital and grow while Blockbuster filed bankruptcy. Apple transformed from a PC company into a multi-media company to create explosive growth generating enough cash to buy Dell outright – although who wants a distributor of yesterday’s technology (remember Circuit City.) Any company can move forward to be anything it wants to be. Excusing low growth due to industry, or economic, weakness merely gives the incumbent a pass. Good CEOs don’t sit in a foxhole waiting to see if they survive, blaming a tough battleground, they develop strategies to change the battle and win, taking on new ground while the competition is making excuses.
GM was the world’s largest auto company when it went broke. So how did size benefit GM? In the 1980s Roger Smith moved GM into aerospace by acquiring Hughes electronics, and IT services by purchasing EDS – two remarkable growth businesses. He “greenfielded” a new approach to auto manufucturing by opening the wildly successful Saturn division. For his foresight, he was widely chastised. But “caretaker” leadership sold off Hughes and EDS, then forced Saturn to “conform” to GM practices gutting the upstart division of its value. Where one leader recognized the need to advance the company, followers drove GM to bankruptcy by selling out of growth businesses to re-invest in “core” but highly unprofitable traditional auto manufacturing and sales. Meanwhile, as the giant failed, much smaller Kia, Tesla and Tata are reshaping the auto industry in ways most likely to make sure GM’s comeback is short-lived.
CEOs of big companies are paid a lot of money. A LOT of money. Much more than Mr. Zuckerberg at Facebook, or the leaders of Groupon and Netflix (for example). So shouldn’t we expect more from them? (Marketwatch.com “Top CEO Bonuses of 2010“) They control vast piles of cash and other resources, shouldn’t we expect them to be aggressively investing those resources in order to keep their companies growing, rather than blaming tax strategies for their unwillingness to invest? (Wall Street Journal “Obama Pushes CEOs on Job Creation“) It’s precisely because they are so large that we should have high expectations of big companies investing in growth – because they can afford to, and need to!
At the end of the day, everyone wins when CEOs push for growth. Investors obtain higher valuation (Apple is worth more than Microsoft, and almost more than 10x larger Exxon!,) employees receive more pay (see Google’s recent 10% across the board pay raise,) employees have more advancement opportunities as well as personal growth, suppliers have the opportunity to earn profits and bring forward new innovation – creating more jobs and their own growth – rather than constantly cutting price. Answering the Economist in “Why Do Firms Exist?” it is to deliver to people what they want. When companies do that, they grow. When they start looking inward, and try being caretakers of historical assets, products and markets then their value declines.
Can Mr. Zuckerberg run GE? Probably. I’d sure rather have him at the helm of GM, Chrysler, Kraft, Sara Lee, Motorola, AT&T or any of a host of other large companies that are going nowhere the caretaker CEOs currently making excuses for their lousy performance. Think what the world would be like if the aggressive leaders in those smaller companies were in such positions? Why, it might just be like having all of American business run the way Steve Jobs, Jeff Bezos and John Chambers have led their big companies. I struggle to see how that would be a bad thing.
by Adam Hartung | Dec 7, 2010 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
Today’s guest blog is provided by Mike Meikle, hope you enjoy:
Summary
- Oracle is at the top of the heap in the Traditional Software market.
- Traditional Software market is deflating with $7 billion less profit than 2009
- Software as a Service, a component of Cloud Computing, has a forecasted 26% annual growth rate over the next five years.
- Oracle Cloud Computing strategy is muddled with bi-polar corporate marketing and platform dependency.
- Customers feel trapped with Oracle and are looking for alternatives.
- Oracle is trapped in a classic Defend and Extend situation.
- Oracle seems to be following Microsoft in using 1990’s corporate strategy in 2011.
Throughout the 1990’s Microsoft held the dominant position in software. Firmly ensconced in Corporate and Consumer arenas, Microsoft generated enormous profits. With an overflowing war chest, MSFT aggressively quashed or bought out the competition – which eventually attracted the attention of the United States Justice Department.
After a little less than 10 years, Microsoft now fights to stay relevant as multiple challengers have exposed gaping holes in its armor. The tech giant’s senior leadership appears rudderless as product lines fail to get off the mark (Windows Phone 7) or flounder (Vista).
With this in mind let us turn toward Oracle. Long viewed as the top Database Management System (DBMS) for the corporate world, its database software underpins much of the global information economy. It has a large war chest stuffed with the profits created by costly traditional software licensing deals with locked-in customers. It has used that cash to acquire new lines of business (PeopleSoft, Sun) and competitors (ATG, MySQL).
However there are some dark clouds on the horizon. The advent of Cloud Computing is a threat to its current licensing model. How will Oracle adapt to corporations implementing virtual servers and databases in the Cloud? Traditional software licensing is down $7 billion industry-wide from 2009. Meanwhile “software as a service” (SaaS) is seeing explosive growth, with a forecasted 26% annual growth rate over the next five years as a natural component of Cloud Computing.
Oracle has made some efforts to delve into the Cloud Computing fray with the Oracle Exalogic Elastic Cloud, or “Cloud-In-a-Box”, leveraging their SUN and ATG acquisitions. However this arrives several years behind the Amazon, Google, and Microsoft triumvirate of Cloud Computing products. Oracle’s Cloud offering will also have to overcome Oracle’s own negative statements about Cloud Computing. CEO Larry Ellison called Cloud Computing “complete gibberish” in late 2008.
Oracle also has problems with its customers. Chafing under the steep licensing costs and sub-standard support, nearly half are looking to shift to lower cost alternatives as they become available. Many have felt trapped by lack of suitable replacements. MySQL was one such competitor, but with Oracle purchasing SUN and getting MySQL in the bargain, that option disappeared. So customers have continued to (reluctantly) fork over licensing and maintenance fees to Oracle, creating the bulk of the organization’s profit stream.
Sound familiar?
Also, the champions of Oracle software offerings, developers, are dissatisfied with the company. The founders of MySQL and the creator of Java, now key software offerings of Oracle, have jumped ship as a result of disagreements with Oracle’s corporate direction.
Now Oracle finds itself in is a classic Defend & Extend situation. Nearly all their profits rely on historical licensing and maintenance for traditional software, a market that is rapidly shrinking. Current customers are unhappy with cost and service; hungry for alternatives and ready to embrace new solutions. But Oracle has arrived late and timidly to the Cloud Computing maketplace, attempting to leverage recently acquired assets where key personnel have left (and taking who knows how much vital market and product knowledge.) Not only will Oracle have to struggle to differentiate itself from other Cloud offerings going forward, it will have to incorporate their newly acquired assets (including technologies) into a cohesive offering while trying to ramp up top notch service.
Oracle will have to break out of the “consistency trap” if it is to drive profits toward new growth. New services that provide value to the customer will have to be developed and aggressively marketed. To grow future revenue and profits Oracle cannot rely on shoehorning customers into poorly fitting licensing and support models based on the fading market of yesteryear.
Or Oracle could choose to not change its old Success Formula. For advice on that approach Oracle’s Mr. Ellison talk to Microsoft’s Mr. Ballmer to see how well his 1990’s corporate strategy is working as Microsoft stumbles into 2011.
Thanks Mike! Mike Meikle shares his insights at “Musings of a Corporate Consigliere” (http://mikemeikle.wordpress.com/). I hope you read more of his thoughts on innovation and corporate change at his blog site. I thank Mike for contributing this blog for readers of The Phoenix Principle today, and hope you’ve enjoyed his contribution to the discussion about innovation, strategy and market shifts.
If you would like to contribute a guest blog please send me an email. I’d be pleased to pass along additional viewpoints on wide ranging topics.
by Adam Hartung | Dec 6, 2010 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Disruptions, Food and Drink, Leadership, Lock-in
Summary:
- Business leaders like consistency
- Consistency leads to repetition, sameness, and lower rates of return
- Kraft's product lines are consistent, but without growth
- Kraft's value has been stagnant for 10 years
- Disruptive competitors make higher rates of return, and grow
- Disruptive competitors have higher valuations – just look at Groupon
"Needless consistency is the hobgoblin of small minds" – Ralph Waldo Emerson
That was my first thought when I read the MediaPost.com Marketing Daily article "Kraft Mac & Cheese Gets New, Unified Look." Whether this 80-something year old brand has a "unified" look is wholly uninteresting. I don't care if all varieties have the same picture – and if they do it doesn't make me want to eat more powdered cheese and curved noodles.
In fact, I'm not at all interested in anything about this product line. It is kind of amusing, in an historical way, to note that people (largely children) still eat the stuff which fueled my no-cash college years (much like ramen noodles does for today's college kids.) While there's nothing I particularly dislike about the product, as an investor or marketer there's nothing really to like about it either. Pasta products always do better in a recession, as people look for cheaper belly-fillers (especially for the kid,) so that more is being sold the last couple of years doesn't tell me anything I would not have guessed on my own. That the entire category has grown to only $800M revenue across this 8 decade period only shows that it's a relatively small business with no excitement! Once people feel their finances are on firm footing sales will soon taper off.
Kraft's Mac & Cheese is emblematic of management teams that lock-in on defending and extending old businesses – even though the lack of growth leaves them struggling to grow cash flow and create a decent valuation. Introducing multiple varieties of this product has not produced growth that even matched inflation across the years. Primarily, marketing programs have been designed to try keeping existing customers from buying something else. This most recent Kraft program is designed to encourage adults to try a product they gave up eating many years ago. This is, at best, "foxhole" marketing. Spending money largely just to keep the brand from going away, rather than really expecting any growth. Truly, does anyone think this kind of spending will generate a billion dollar product line in 2011 – or even 2012?
What's wrong with defensive marketing, creating consistency across the product line – across the brand – and across history? It doesn't produce high rates of return. There are lots of pasta products, even lots of brands of mac & cheese. While Kraft's product surely produces a positive margin, multiple competitors and lack of growth means increased spending over time merely leaves the brand producing a marginal rate of return. Incremental ad spending doesn't generate real growth, just a hope of not losing ground. We know people aren't flocking to the store to buy more of the product. New customers aren't being identified, and short-term growth in revenues does not yield the kinds of returns that would enhance valuation and make the world a better place for investors – or employees.
While Kraft is trying to create headlines with more spending in a very tired product, across town in Chicago Groupon has created a $500M revenue business in just 2 years! And new reports from the failed acquisition attempt by Google indicate revenues are likely to reach $2B in 2011 (CNNMoney.com, Fortune, "Google's Groupon Groping Reveals the Shifting Power of the Web World.") Where's Kraft in this kind of growth market? After all, coupons for Kraft products have been in mailers and Sunday inserts for 50 years. Why isn't Kraft putting money into a real growth business, which is producing enormous value while cash flow grows in multiples? While Groupon has created somewhere around $6B of value in 2 years, Kraft's value has only gone sideways for the last decade (chart at Marketwatch.com.)
Kraft has not introduced a new product since — well — DiGiorno. And that's been more than a decade. While the company has big revenues – so did General Motors. The longer a company plays defense, regardless of size, trying to extend its outdated products (and business model) the riskier that business becomes. While big revenues appear to offer some kind of security, we all know that's not true. Not only does competition drive down margins in these older businesses, but newer products make it harder and harder for the old products to compete at all. Eventually, the effort to maintain historical consistency simply allows competitors to completely steal the business away with new products, creating a big revenue drop, or producing such low returns that failure is inevitable.
Lots of business people like consistency. They like consistency in how the brand is executed, or how products are aligned. They like consistency in the technology base, or production capabilities. They like consistency in customers, and markets. They like being consistent with company history – doing what "made the company famous." They like the similarity of doing something again, and again, hoping that consistency will produce good returns.
But consistency is the hobgoblin of small minds. And those who are more clever find ways to change the game. Xerox figured out how to let everyone be a one-button printer, and killed the small printing press manufacturers. HP's desktop printers knocked the growth out of Xerox. Google figured out a better way to find information, and place ads, just about killing newspapers (and magazines.) Apple found a better way to use mobile minutes, taking a big bite out of cell phone manufacturers. Amazon found a better way to sell things, killing off bookstores and putting a world of hurt on many retailers. Netflix found a better way of distributing DVDs and digital movies, sending Blockbuster to bankruptcy. Infosys and Tata found a better way of doing IT services, wiping out PWC and nearly EDS. Hulu (and soon Netflix, Google and Apple) has found a better way of delivering television programming, killing the growth in cable TV. Groupon is finding a better way of delivering coupons, creating huge concerns for direct mail companies. Now tablet makers (like Apple) are demonstrating a better way of working remotely, sending shivers of worry down the valuation of Microsoft. These companies, failed or in jeapardy, were very consistent.
Those who create disruptions show again and again that they can generate growth and above average returns, even in a recession. While those who keep trying to defend and extend their old business are letting consistency drive their behavior – leading to intense competition, genericization, and lower rates of return. Maybe Kraft should spend more money looking for the next food we would all like, rather than consistently trying to convince us we want more Mac & Cheese (or Velveeta).
by Adam Hartung | Nov 23, 2010 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Lock-in, Web/Tech
Summary:
- Most planning systems rely on extending past performance to predict the future
- But markets are shifting too fast, making such forecasts wildly unreliable
- To compete effectively, companies must anticipate future market shifts
- Planning needs to incorporate a lot more scenario development, and competitor information in order to overcome biases to existing customers and historical products
- Apple and Google have taken over the mobile phone business, while the original leaders have fallen far behind
- Historical mobile phone leaders Nokia, Samsung, Motorola, RIM and Microsoft had the technologies and products to remain leaders, but they lacked scenarios of the future enticing them to develop new markets. Thus they allowed new competitors to overtake them
- Lacking scenarios and deep competitor understanding, companies react to market events – which is slow, costly and ineffective.
“Apple, Android Help Smartphone Sales Double Over Last Year” is the Los Angeles Times headline. Google-supplied Android phones jumped from 3% of the market to 26% versus the same quarter last year. iPhones remained at 17% of the market. Blackberry is now just under 15%, compared to about 21% last year. What’s clear is people are no longer buying traditional mobile phones, as #1 Nokia share fell from 38% to 27%. Like many market changes, the shift has come fast – in only a matter of a few months. And it has been dramatic, as companies not even in the market 5 years ago are now the leaders. Former leaders are struggling to stay in the game as the market shifts.
The lesson Google and Apple are teaching us is that companies must have a good idea of the future, and then send their product development and marketing in that direction. Although traditional cell phone manufacturers, such as Motorola and Samsung, had smartphone technology many years prior to Apple, they were so focused on their traditional markets they failed to look into the future. Busy selling to existing customers an existing technology, they didn’t develop scenarios about 2010 and beyond that would describe how the market could expand – far beyond where traditional phone sales would take it. Both famously said “so what” to the new technology, and used existing customer focus groups of people who had no idea the potential benefit of a smart phone to justify their willingness to remain fixated on the existing business. Lacking a forward planning process based on scenario development, and lacking a good market sensing system that would pick up on the early market shift as novice competitor Apple started to really change the market, these companies are now falling rapidly to the wayside.
Even smartphone pioneer Research in Motion (RIM) was so focused on meeting the needs of its existing “enterprise” customers that it failed to develop scenarios about how to expand the smartphone business into the hands of everyone. RIM missed the value of mobile apps, and the opportunity to build an enormous app database. Now RIM has been surpassed, and is showing no signs of providing effective competition for the market leaders. While the Apple and Android app base continues to explode, based upon 3rd and 4th generation product inducing more developers to sign up, and more customers to buy in, RIM has not effectively built a developer base or app set – causing it to fall further behind quarter by quarter.
Even software giant Microsoft missed the market. Fixated upon putting out an updated operating system for personal computers (Vista then later Windows 7) it let its 45% market share in smart phones circa 2007 disappear. Now approaching 2011 Microsoft has largely missed the market. Again, focused clearly upon its primary goal of defending its existing business in O/S and office automation software, Microsoft did not have a forward focused planning group that was able to warn the company that its new products might well arrive in a market that was stagnating, and on the precipice of a likely decline, because of new technology which could make the PC platform obsolete (a combination of smart mobile devices and cloud computing architecture.) Microsoft’s product development was being driven by its historical products, and market position, rather than an understanding of future markets and how it should develop for them.
We can see this lack of future scenario development and close competitor tracking has confused Microsoft. Desperately trying to recover from a market stall in 2009 when revenues and profits fell, Microsoft has no idea what to do in the rapidly expanding smartphone market today. Its first product, Kin, was dropped only two months after launch, which industry analysts saw as necessary given the product’s lack of advantages. But now Mediapost.com informs us in “Return of the Kin?” Microsoft is considering a re-launch in order to clear out old inventory.
This amidst a launch of the Windows Phone 7 that has gone nowhere. Firstly, there was insufficient advertising to gain any public awareness of the product launch earlier in November (Mediapost “Where’s the Windows Phone 7 Ad Barrage?“) Initial sales have gone nowhere “Windows Phone 7 Lands Without a Sound” [Mediapost], with many stores lacking inventory, very few promoting the product and Microsoft keeping surprisingly mum about initial sales. This has raised the question “Is Windows Phone 7 Dead On Arrival?” [Mediapost] as sales barely achieving 40,000 initial unit sales at launch, compared to daily sales of 200,000 Android phones and 270,000 iphones!
Companies, like Apple and Google, that have clear views of the future, based upon careful analysis of what can be done and tracking market trends, create scenarios that allow them to break out of the pack. Scenario development helps them to understand what the future can be like, and drive their product development toward creating new markets with more customers, more unit sales, higher revenues and improved cash flow. By studying early competitors, especially fringe ones, they create new products which are more highly desired, breaking them out of price competition (remember the Motorola Razr fiasco that nearly bankrupted the company?) and into higher price points and better earnings. Creating and updating future scenarios becomes central to planning – using scenarios to guide investments rather than merely projections based upon past performance.
Companies that base future planning on historical trends find themselves rapidly in trouble. Market shifts leave them struggling to compete, as customers quickly move to new solutions (old fashioned notions of “exit costs” are now dead). Instead of heading for the money, they are confused – lost in a sea of options but with no clear direction. Nokia, Samsung, RIM and Microsoft all have lots of resources, and great historical experience in the market. But lacking good scenario planning they are lost. Unable to chart a course forward, reacting to market leaders, and hoping customers will seek them out because they were once great.
Far too many companies do their planning off of past projections. One could say “planning by looking in the rear view mirror.” In a dynamic, global world this is not sufficient. When monster companies like these can be upset so fast, by someone they didn’t even think of as a traditional competitor (someone likely not even on the radar screen recently) how vulnerable is your company? Do you plan on 2015 looking like 2005? If not, how can future projections based on past actuals be valuable? it’s time more companies change their approach to planning to put an emphasis on scenario development with more competitive (rather than existing customer) input. That’s the only way to get rich, instead of getting lost.
by Adam Hartung | Nov 16, 2010 | Defend & Extend, General, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Summary:
- Many companies block employee access to Facebook and other social network applications
- But these environments actually improve performance
- Social networks like Facebook allow people to be more productive, and are very inexpensive
- Facebook’s new email client is an example of how these environments can provide companies better services at lower cost – supplanting existing email, for example
- Those who embrace advances early gain an information advantage, as well as a cost advantage
- The new Facebook email client is a big deal for business, and should be explored by everyone
A year ago I was on a panel at the Indian Institute of Technology global conference. My fellow panelists were mostly IT heads from major corporations. When it came to Twitter, Linked-in, MySpace and Facebook – the world of social networking – universally they all blocked access. The reasons given were primarily data confidentiality (fear company information would escape) and productivity (fear employees would unproductively apply their time to personal efforts.) They saw no advantages to social network applications, only risk. Most of those companies – from pharmaceuticals to airlines – still deny access.
This follows a long list of things denied employees by large employers on the grounds of confidentiality and productivity
- employees don’t need a phone at their desk, who could they need to talk to and what do they need to say at work? They can write letters or memos.
- employees don’t need a personal computer. All data should be kept on secured tapes and accessed by productive data center professionals when it makes sense.
- employees don’t need a hard disk in their personal computer. We must keep all data away from employees and keep them focused on using applications tied to central data repositories for productivity
- employees don’t need laptops. Who knows where they will go, and what employees will do with them. They could let data escape, or spend time on personal letters and spreadsheets.
- employees don’t need their own printers. Send all jobs to a central printer location so we can control what is printed for confidentiality and to make sure somebody isn’t printing more than is necessary
- employees don’t need their own cell phones. What in the world do they need to say that can’t wait until they are in the office? How will we keep them from wasting time on personal calls?
- employees don’t need internet access at work. There’s nothing on the web that is important for their work, and it opens a security hole in our operations. If we give them internet access they’ll waste hours and hours browsing instead of working.
This list could go on for a long time, as I’m sure you can now imagine. Confidentiality and productivity are merely excuses for those who fear new tools. Reality is that all these new products improved productivity dramatically, helping employees get more done faster – and making them smarter on the job as well. Organizations that rapidly adopted these (and other) technologies actually achieved superior performance, and rapidly saw their costs decline as these lower cost solutions gave more productivity at lower prices. In most cases, something formerly proprietary and costly became available from an outside source much, much cheaper that worked a whole lot better. Like how the Post Office displaced private messenger services – even though it did have security risks and made it possible for anyone to send a letter (see what I mean, you can go back in time forever with these examples.)
Today social media is the next “big thing” to improve productivity. Facebook, Twitter and its counterparts offer full multi-media, real time interaction with people you know, and don’t know that well, globally. You can find out about everything remarkably fast, and often quite accurately, at practically no cost. No server need be bought – and you don’t even need a PC. A cheap smartphone or tablet will give you all you want – soon to include conferencing and video chat. And you don’t have to buy any software. And you can connect to everyone – not just the people in your company, or on your server, or even on your network or your network service provider. According to Gartner, at MediaPost.com “Implications of a Facebook email Client” will be noticable by 2012, and universal by 2014!
And that’s why “Facebooks Not email Announcement” (as reported in LiveBlog Twitter style on ReadWriteWeb.com) is important for business. Facebook email is going to be better, faster and cheaper than existing email – especially if you’re still using 2 decades out-of-date products like Lotus Notes! Something Facebook doesn’t even want to call email because of its advancements.
An email client for Facebook goes far beyond the value of a Microsoft Live server (think Hotmail+ if you’re not IT oriented). Even GMail, for all its great features, doesn’t offer everything you get in Facebook, due to how Facebook provides integration into everything else that makes its network wildly productive for those of us who realize we live in networks. You even have an archive, searchability – and the capability of creating multiple virtual private networks for doing all kinds of business activities in different markets! And practically free! Using incredibly cheap devices, in multiple varieties and platforms, that employees might well purchase themselves!
For use by everyone from execs to salespeople, businesses will soon be able to stop buying and handing out laptops. Even PCWorld addressed the opportunity in “Social Networks to Supplant email in Business?” Businesses will soon quit operating server farms for most communications. Even quit supporting networks for things like printing sales documents, or creating document-loaded USB drives to hand out. With everyone on tablets and smartphones, and connected over social networks, in a couple of years “leave behinds” will be unnecessary. Those in sales and purchasing will be able to obtain competitive reviews, and prices, and configurations almost instantaneously by asking people on their network for input and feedback. Email will become slow, and a siloed application less useful than products that sit on the network.
With each advance, new opportunities emerge. Doctors have long been notoriously unwilling to carry laptops, or email patients. From the operating room to test results, finding out from an M.D. what’s going on has been problematic. Now MediaPost tells us in “Doctors Without Social Media Borders” how patient communication is rising dramatically from adoption of social media. It lets the physician, and others in medicine, communicate faster, more productively and cheaper than anything before. And this is just one example of how behavior changes when new capabilities arise. Formerly unmet needs are satisfied, and people shift to where they achieve greatest satisfaction.
Once email was considered the “killer app” that made everyone need a PC – and access to the web. Social media takes email into entirely new orbits. Getting more done, faster, with more people, using more current data, verified by more access points, across multiple media creates competitive advantage. Those who ignore this trend will fall behind. Those who adopt it have the opportunity to beat their competition. Everyone knows that those who know the most, first, and are able to apply it have a big first mover advantage. If you’re not promoting this in your company – if you are in fact blocking it – you’ll soon have no chance of remaining competitive. You’ll just start falling behind – and the gap will widen.


