by Adam Hartung | Aug 2, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
eBay was once a game changer. When the internet was very young, and few businesses provided ecommerce, eBay was a pioneer. From humble beginnings selling Pez dispensers, eBay grew into a powerhouse. Things we used to sell via garage sale we could now list on eBay. Small businesses could create stores on eBay to sell goods to customers they otherwise would never reach. And collectors as well as designers suddenly discovered all kinds of products they formerly could not find. eBay sales exploded, as traditional retail started it slide downward.
To augment growth eBay realized those selling needed a simple way to collect money from people who lacked a credit card. Many customers simply had no card, or didn’t trust giving out the information across the web. So eBay bought fledgling PayPal for $1.5B in 2002, in order to grease the wheels for faster ecommerce growth. And it worked marvelously.
But times have surely changed. Now eBay and Paypal have roughly the same revenue. About $8B/year each. eBay has run into stiff competition, as CraigsList has grown to take over the “garage sale” and small local business ecommerce. Simultaneously, powerhouse Amazon has developed its storefront business to a level of sophistication, and ease of use, that makes it viable for businesses from smallest to largest to sell products on-line. And far more companies have learned they can go it alone with internet sales, using search engine optimization (SEO) techniques as well as social media to drive traffic directly to their stores, bypassing storefronts entirely.
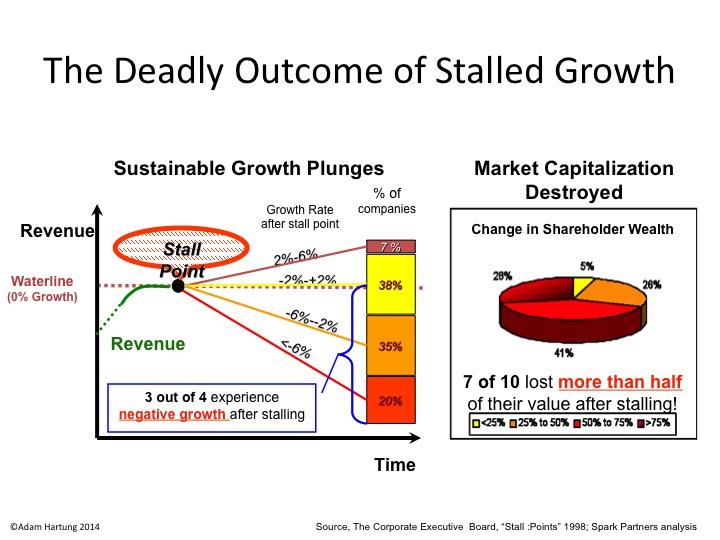
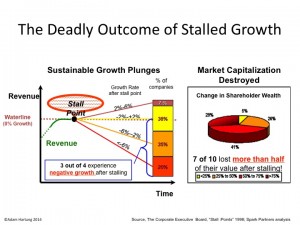 eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
On the other hand, Paypal has blossomed into a game changer in its own right. Not only does it support cash and credit card transactions for the growing legions of on-line shoppers, but it is providing full payment systems for providers like Uber and AirBnB. It’s tools support enterprise transactions in all currencies, including emerging bitcoin, and even provides international financial transactions as well as working capital for businesses.
Paypal is increasingly becoming a threat to traditional banks. Today most folks use a bank for depositing a pay check, and making payments. There are loans, but frequently that is shopped around irrespective of where you bank. Much like your credit cards, which most people acquire for their benefits rather than a relationship with the issuing bank. If customers increasingly make payments via Paypal, and borrow money via operations like Quicken Loans (a division of Intuit,) why do you need a bank? Discover Services, which now does offer cash deposits and loans on top of credit card services, has found that it can grow substantially by displacing traditional banks.
Paypal is today at the forefront of digital payments processing. It is a fast growing market, which will displace many traditional banks. And emerging competitors like Apple Pay and Google Wallet will surely change the market further – while aiding its growth. How it will shake out is unclear. But it is clear that Paypal is growing its revenue at 60% or greater since 2012, and at over 100%/quarter the last 2 quarters.
Paypal is now valued at about $47B. That is roughly the same as the #5 bank in America (according to assets) Bank of New York Mellon, and number 8 massive credit card issuer Capital One, as well as #9 PNC Bank – and over 50% higher valuation than #10 State Street. It is also about 50% higher than Intuit and Discover. Based on its current market leadership and position as likely game changer for the banking sector, Paypall is selling for about 8 times revenue. If its revenue continues to grow at 100%/quarter, however, revenues will reach over $38B in a year making the Price/Revenue multiple of today only 1.25.
Meanwhile, eBay is valued at about $34B. Given that all which is left in eBay is an outdated on-line ecommerce conglomerator, stuck in a growth stall, that valuation is far harder to justify. It is selling at about 4.25x revenue. But if revenues continue declining, as they have for 2 consecutive quarters, this multiple will expand. And values will be harder and harder to justify as investors rely on hope of a turnaround.
eBay was a game changer. But leadership became complacent, and now it is very likely overvalued. Just as Yahoo became when its value relied on its holdings of Alibaba rather as its organic business shrank. Meanwhile Paypal is the leader in a rapidly growing market that is likely to change the face of not just how we pay, but how we do personal and business finance. There is no doubt which is more valuable today, and likely to be in the future.

by Adam Hartung | Sep 30, 2014 | Current Affairs, Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Will the new Apple Pay product, revealed on iPhone 6 devices, succeed? There have been many entries into the digital mobile payments business, such as Google Wallet, Softcard (which had the unfortunate initial name of ISIS,) Square and Paypal. But so far, nobody has really cracked the market as Americans keep using credit cards, cash and checks.
But that looks like it might change, and Apple has a pretty good chance of making Apple Pay a success.
First, a look at some critical market changes. For decades we all thought credit card purchases were secure. But that changed in 2013, and picked up steam in 2014. With regularity we’ve heard about customer credit card data breaches at various retailers and restaurants. Smaller retailers like Shaw’s, Star Markets and Jewel caused some mild concern. But when top tier retailers like Target and Home Depot revealed security problems, across millions of accounts, people really started to notice. For the first time, some people are thinking an alternative might be a good idea, and they are considering a change.
In other words, there is now an underserved market. For a long time people were very happy using credit cards. But now, they aren’t as happy. There are people, still a minority, who are actively looking for an alternative to cash and credit cards. And those people now have a need that is not fully met. That means the market receptivity for a mobile payment product has changed.
Second let’s look at how Paypal became such a huge success fulfilling an underserved market. When people first began on-line buying transactions were almost wholly credit cards. But some customers lacked the ability to use credit cards. These folks had an underserved need, because they wanted to buy on-line but had no payment method (mailing checks or cash was risky, and COD shipments were costly and not often supported by on-line vendors.) Paypal jumped into that underserved market.
Quickly Paypal tied itself to on-line vendors, asking them to support their product. They went less to people who were underserved, and mostly to the infrastructure which needed to support the product. By encouraging the on-line retailers they could expand sales with Paypal adoption, Paypal gathered more and more sites. The 2002 acquisition by eBay was a boon, as it truly legitimized Paypal in minds of consumers and smaller on-line retailers.
After filling the underserved market, Paypal expanded as a real competitor for credit cards by adding people who simply preferred another option. Today Paypal accounts for $1 of every $6 spent on-line, a dramatic statistic. There are 153million Paypal digital wallets, and Paypal processes $203B of payments annually. Paypal supports 26 currencies, is in 203 markets, has 15,000 financial institution partners – all creating growth last year of 19%. A truly outstanding success story.
Back to traditional retail. As mentioned earlier, there is an underserved market for people who don’t want to use cash, checks or credit cards. They seek a solution. But just as Paypal had to obtain the on-line retailer backing to acquire the end-use customer, mobile payment company success relies on getting retailers to say they take that company’s digital mobile payment product.

Here is where Apple has created an advantage. Few end-use customers are terribly aware of retail beacons, the technology which has small (sometimes very small) devices placed in a store, fast food outlet, stadium or other environment which sends out signals to talk to smartphones which are in nearby proximity. These beacons are an “inside retail” product that most consumer don’t care about, just like they don’t really care about the shelving systems or price tag holders in the store.
Launched with iOS 7, Apple’s iBeacon has become the leader in this “recognize and push” technology. Since Apple installed Beacons in its own stores in December, 2013 tens of thousands of iBeacons have been installed in retailers and other venues. Macy’s alone installed 4,000 in 2014. Increasingly, iBeacons are being used by retailers in conjunction with consumer goods manufacturers to identify who is shopping, what they are buying, and assist them with product information, coupons and other purchase incentives.
Thus, over the last year Apple has successfully been courting the retailers, who are the infrastructure for mobile payments. Now, as the underserved payment issue comes to market it is natural for retailers to turn to the company with which they’ve been working on their “infrastructure” products.
Apple has an additional great benefit because it has by far the largest installed base of smartphones, and its products are very consistent. Even though Android is a huge market, and outsells iOS, the platform is not consistent because Android on Samsung is not like Android on Amazon’s Fire, for example. So when a retailer reaches out for the alternative to credit cards, Apple can deliver the largest number of users. Couple that with the internal iBeacon relationship, and Apple is really well positioned to be the first company major retailers and restaurants turn to for a solution – as we’ve already seen with Apple Pay’s acceptance by Macy’s, Bloomingdales, Duane Reed, McDonald’s Staples, Walgreen’s, Whole Foods and others.
This does not guarantee Apple Pay will be the success of Paypal. The market is fledgling. Whether the need is strong or depth of being underserved is marked is unknown. How consumers will respond to credit card use and mobile payments long-term is impossible to gauge. How competitors will react is wildly unpredictable.
But, Apple is very well positioned to win with Apple Pay. It is being introduced at a good time when people are feeling their needs are underserved. The infrastructure is primed to support the product, and there is a large installed base of users who like Apple’s mobile products. The pieces are in place for Apple to disrupt how we pay for things, and possibly create another very, very large market. And Apple’s leadership has a history of successfully managing disruptive product launches, as we’ve seen in music (iPod,) mobile phones (iPhone) and personal technology tools (iPad.)
by Adam Hartung | Aug 26, 2010 | Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lifecycle
Summary:
- Trends happen much faster than we expect
- Old solutions disappear much faster than we anticipate
- Early adopters are big winners, suppliers who expect markets to last longer are killed in end-stage price wars
- We can anticipate the failure of land line phones in just a few years (as declining demand makes infrastructure maintenance too costly)
- There are a lot of other changes coming very quickly, more quickly than many of us anticipate – putting those who are late to change at risk of survival
How long do you think you’ll keep a land-line based telephone? From the looks of things, it may be only another year or two. They may be as popular as an old-fashioned printing press in just 5 years.

Source: Silicon Alley Insider from BusinessInsider.com
As the chart shows, already about a third of Americans have discontinued their land lines. And, we can see the trend is accelerating. This doesn’t count people that have one, but have quit using it. From about half of a percent dropping their line each quarter early in 2007, by 2009 the trend had increased to 1.2 to 1.5 percent dropping their land lines quarterly. And that’s normal – trends accelerate – much faster than incumbent technology suppliers predict.
Mobile phones started out with limited use. They were big, and had short battery life. It was sketchy if transmission quality would be good enough to hear or talk. They were expensive to use, and had limited service areas. In the early days, only people who had a big need used them. It took a few years before adoption grew to where most people had one. But then, in the last 5 years, it has become clear that almost everyone has one. Even the old and elderly. And many people have two – one for personal and one for business.
When trends begin they are easy to discount. Early versions are less good than the current solution. Costs are high. But early adopters have a reason to pick up the new solution. There is some kind of unmet need that the solution fits. From that small base, the products improve. Most incumbent suppliers plot out a linear curve adoption curve, and expect dropping of the old solution to be some time way out in the future.
But improvements to the “fringe” solution come faster than incumbents – and even big users of incumbent technologies – expect. Adoption starts growing faster. Yet, the incumbent supplier will listen to big customers and expect people to keep their solutions for a long time as they gradually adopt the new:
- People will have an automobile, but they’ll hang onto the horse and buggy because roads are so poor
- He may buy a new copier, but he’ll keep the mimeo machine “just in case”
- Folks will get a phone, and email, but they’ll keep writing letters and thus need a postman daily
- People may buy refrigerators, but they’ll keep the icebox and want weekly ice delivery
- Readers will skim the web for news, but they’ll want to keep reading a daily newspaper
- PCs will be popular, but folks will hang onto that old typewriter “maybe to type envelopes or something”
- Installing spreadsheets on company PC’s will not eliminate the need for adding machines “for when we need the tape”
- Digital cameras will be convenient, but users will want the film camera for picture prints
- Installing a DVR will not eliminate the videocassette player because people “still may want to watch old tapes some day”
- People will keep their cassette players, and DVD players, even as they buy a new MP3 player because they will want to listen to the purchased collections
Actually, once someone adopts the new solution, they rapidly find no need for the old solution. It goes to the closet, and then the trash, quickly. And from a market perspective, once a third to a half the customers quit using a product it will disappear from use almost overnight. From that perspective, those who depend upon traditional land line phones have plenty to worry about. Because we’re near a third. And smart phones keep adding more capability every month – the iPhone now has almost 300,000 apps, and Android phones have over 100,000! It’s easy to see where the functionality, ease of use and ubiquitousness of mobile phones could make the old land line a waste of money within just 24 months!
So, what will happen to bill collectors and political phone ads (robocalls), when we quit using land lines? Along with the loss of land lines is the loss of the traditional phone book to find people. When will the cost of maintaining the poles and lines become so high, relative to the number of users, that we simply take them down to recycle the material? Lots of things change when growth begins to decline for land-lines, causing the decline to happen more quickly. And changing how we all get things done – as consumers and as businesses. Are you prepared?
The tendency is to think change will happen slowly. It doesn’t. When markets shift it happens quickly. Much more quickly than the entrenched competitor expects. The “experts” always say the demand for the old will last much longer than happens. He hopes to have a long life, clipping coupons, across a “maturing” market. Instead, demand falls rapidly and remaining competitors go into price wars trying to stay alive – hoping the market will some day return to the old way of doing things. Those who didn’t anticipate the shift rapidly run out of cash, and fail.
Are you ready for impending market shifts? How prepared are you for a world where
- We don’t print anything, because everyone has some kind of on-line digital document reader. Not just books and magazines, but user instructions, warranty info, etc.
- We don’t need cash because we can Paypal transact anything using our smartphone
- Doctors can monitor all your vital statistics real time, remotely, 24x7x365. Manufacturers can monitor use of their products 24x7x365
- So much retail is on-line that the amount of retail floor space declines 40%
- You can regrow a finger, or organ, if it is damaged
- Television and radio aren’t serially broadcast, you organize what you want when you want it. There are no “commercials” in content delivery
- The primary way of communicating with friends and colleagues is Facebook and Twitter – forget text except for only very private communications
by Adam Hartung | Aug 19, 2010 | Current Affairs, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Summary:
- By 2015 or 2020 cash, checks, debit and credit cards could disappear
- Smartphones are positioned to eliminate old financial transaction tools, as well as land line phone service and PCs
- All businesses will have to make changes to deal with new forms of payment processing, and early adopters will likely gain an advantage with customes
- There will likely be some big winners and big losers from this transition
Can you imagine a world with no cash? It could happen soon, and how will it affect your business?
Bloomberg.com headlined “AT&T, Verizon to Target Visa, Mastercard with Smartphones.” The business idea is to replace your Visa and Mastercard with a smartphone app that acts as your debit and/or credit card. Doing this makes it faster and easier for smartphone users to place transactions – online or in person – without even bothering with a card or any other physical artifact.
This is a big deal, because according to Mediapost.com “Smartphones Nearly 20% of All Phones Sold.” So smartphones are starting to be everywhere, and at current rates will replace old mobile phones in just a couple of years. They are increasingly replacing traditional land-line service as headlined in DailyMarkets.com, “Cell Phone Only Use Hits New High of 24.5% in U.S.” People are abandoning the historical land-line telephone.
The traditional “phone company” and its services are rapidly disappearing. After all the effort Southwestern Bell put in to recreating the old “ma bell” of AT&T, it now looks like that entire business is in decline and likely to become about as common as CB or portable AM radios. What is the future of AT&T and Verizon if they front-end Discover as the payment processor? Will these companies transition to become something very different than their past, and if so what will that be? Or will they be an early proponent for change but let the business value go to others – as they did in mobile phones, ISDN and other internet connectivity as well as cable entertainment?
Mediapost.com also reports “PayPal Making Micropayments a Reality.” Which gives us the last piece of the puzzle to just about guarantee old payment methods are likely to be gone by 2020 (possibly earlier – 2015?). People are giving up old land-line telecom for mobile, and mobile is rapidly becoming all smartphones. Smartphones are getting apps allowing them to conduct financial transactions without the need of a credit card, debit card or (going ultra low-tech) check (no printer needed – lol – which has to be a concern for companies like Zebra that make the printers). In fact, you can even make all kinds of payments, even really small ones under $1 – not just big ones – using your cell phone by opening a Paypal account. What you can easily see is a future where you don’t need a wallet at all. Everything you’ll need for financial transactions will be on your smartphone. (How much you want to bet somebody will figure out how to put your driver’s license on the smartphone too?)
Ultra convenient, don’t you think? You won’t need a credit card, or any other card. You won’t need a PC to do your on-line banking. You won’t need cash for small purchases – you can even do garage sale transactions or buy gum using your smartphone. And there’s sure to be an app that will consolidate all your payments and set up to automatically do transactions (like your mortgage or car lease) without you even having to do anything. And all from your smartphone. No more wallet, no more PC, no more coins or bills in your pocket.
So, what happens to cash registers, and the folks that make them? No registers in restaurants or hotels? What happens to desk clerks in hotels – will they be necessary? What about cashiers in retail stores – any need? Will banks have any need for a local branch? Why would ATMs exist? Quite literally a raft of companies would be affected that deal in the handling of transactions – from Visa and Mastercard to IBM and Diebold. Even those little printers in cabs could disappear as your phone now pays the cabbie directly what the meter requires. You could even pay modern parking meters with your smartphone!! What happens to companies that make mens and women’s wallets? Will purses and clutches disappear from style? How much easier will it be for the IRS to track the income of people that have historically been in cash jobs?
Do your scenarios of 2015 include this kind of change in payments? Should it? What will be the impact on your bank? On your credit card supplier? Will your customers want to change how they pay? How will you need to change your order-to-cash process? Are you ready to be an early adopter, thus aiding revenue generation? Or will you let others steal sales by moving quickly to these modern payment systems?
There’s precious little that’s more important in business than collecting the money. A new set of technologies are sure to be changing how that happens. Will you leverage this to your advantage, or will your competitors?

 eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.