
by Adam Hartung | Jan 16, 2020 | Boards of Directors, Defend & Extend, Leadership, Software, Web/Tech
People who follow my speaking and writing – including my over 400 Forbes columns – know that I preach the importance of growth. Successful organizations are agile – and agility is the sum of learning + adaptability. Smart organizations are constantly looking externally, gathering data, learning about markets and shifts – then structured to adopt those learnings into their business model and adapt the organization to new market needs.
Steve Ballmer was the antithesis of agility. For his entire career he knew only that 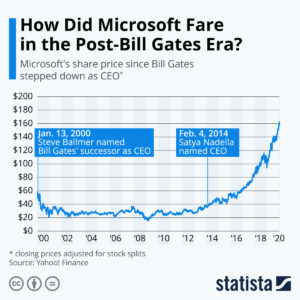 Windows and Office made all the money at Microsoft. So he kept investing in Windows and Office. He failed at everything else. False starts in phones, tablets, gaming – products came and went like ice cream cones on a hot August day. Ballmer laughed at the very notion of the iPhone ever being successful – while simultaneously throwing away $7.2B buying Nokia. Then there was $8.5B buying Skype. $400M buying the Borders Nook. Those were ridiculous acquisitions that just wasted shareholder money. To Ballmer, Microsoft’s future relied on maintaining Windows and Office.
Windows and Office made all the money at Microsoft. So he kept investing in Windows and Office. He failed at everything else. False starts in phones, tablets, gaming – products came and went like ice cream cones on a hot August day. Ballmer laughed at the very notion of the iPhone ever being successful – while simultaneously throwing away $7.2B buying Nokia. Then there was $8.5B buying Skype. $400M buying the Borders Nook. Those were ridiculous acquisitions that just wasted shareholder money. To Ballmer, Microsoft’s future relied on maintaining Windows and Office.
So as the market went mobile, Ballmer kept over-investing. He spent billions launching Windows 8, which I predicted was obviously going to fail at growing the Windows market as early as 2012. And it was easy to predict that Win8 tablets were going to be a bust when launched in 2012 as well. But Ballmer was “all-in” on Windows and Office. He was completely locked-in, and unwilling to even consider any data indicating that the PC market was dying – effectively driving Microsoft over a cliff.
It was not hard to identify Steve Ballmer as the worst CEO in America in 2012. When Ballmer took over Microsoft it was worth $60/share. He drove that value down to $20. And the company valuation was almost unchanged his entire 14 years as CEO. He remained locked-in to trying to Defend & Extend PC sales, and it did Microsoft no good. But when the Board replaced Ballmer with Nadella the company moved quickly into growth in gaming, and especially cloud services. In just 6 years Nadella has improved the company’s value by 400%!!!
Success is NOT about defending the past. Success IS about growth. Don’t be locked in to what worked before. Focus on what markets want and need – learn how to understand these needs – and then adapt to giving customers new solutions. Don’t make the mistakes of Ballmer – be a Nadella to lead your organization into growth opportunities!
by Adam Hartung | Jun 21, 2019 | Newsletter Post
The newsletters of Adam Hartung.
Keynote Speaker, Managing Partner, Author on Trends
Responding to Market Disruptions? Get Ahead of the Next One!
Market Threat Assessments
Recent studies of senior managers have shown that being blindsided by a disruption is the largest unresolved concern in strategy development today. That fear is too often real because disruption typically begins where it is least visible to management- on the fringes of the existing target markets. And, once the disruption “pirate ship” is sighted on the horizon, not only is it probably too late, but companies react poorly.
Research of corporate responses to disruption has shown that most companies ignore the threat, fortify existing positions or attempt to buy innovation. The first choice is not an option for an ongoing business. Fortification through distribution changes, product model proliferation and discounting only buys some additional time while wasting resources. Once a disruption enters the market, there’s little time for organic innovation efforts or “random acts of innovation” (Forbes) so companies often make acquisitions attempting to buy innovation.
Sadly, given the risk profile and limited experience in innovation, these are often sustaining innovations which are swept aside by the wave of disruption.
A very large example is when Microsoft fell behind in the  mobile market in 2014 and purchased Nokia, a weak player in mobile phones to get access to this market. The joint project, the Lumia phone, failed to catch on and Microsoft’s share fell by 50%- fail. Cisco tried to catch up with the photography trend by acquiring Pure Digital, the maker of low cost Flip cameras. Unfortunately, shortly after the acquisition, the high-resolution sensors included in smartphones took photography to a new level. Bye, Flip! Trend monitoring would have predicted this natural evolution as a high risk threat.
mobile market in 2014 and purchased Nokia, a weak player in mobile phones to get access to this market. The joint project, the Lumia phone, failed to catch on and Microsoft’s share fell by 50%- fail. Cisco tried to catch up with the photography trend by acquiring Pure Digital, the maker of low cost Flip cameras. Unfortunately, shortly after the acquisition, the high-resolution sensors included in smartphones took photography to a new level. Bye, Flip! Trend monitoring would have predicted this natural evolution as a high risk threat.
Even in successful acquisitions, founders often leave the firm, losing the source of innovative ideas long term. (Time, Inc.)
To anticipate external changes, marketing departments have embraced big data as a powerful tool to help companies identify new markets and consumer preferences. These tools use the past to predict the short-term future which is reasonable in a steady market. The problem is that big data cannot accurately anticipate dynamic disruptions.
But, you and your staff can.
Uncovering market opportunities that can deliver improved returns at a manageable risk for the firm is the goal. New products will also generate an increasing percentage of revenue leading to continued growth. Companies that master this process have a long range radar to identify potential opportunities in a process called, “continuous innovation”.
What’s on your company’s radar today?
Spark Partners is here to help as your coach on trends and innovation. We bring years of experience studying trends, organizations, and how to implement. We bring nimbleness to your strategy, and help you maximize your ability to execute.
Let us do an opportunity assessment for your organization. For less than your annual gym cost, or auto insurance premium, we could likely identify some good opportunities your blinders are hiding. Read my Assessment Page to learn more.
“Don’t plan for what you know. Plan for what you don’t know.”
Adam Hartung, Create Marketplace Disruption
For more on how to include trends in your planning, I’ve created a “how-to” that you can adapt for your team. See my
Status Quo Risk Management Playbook.
Give us a
call today, or send an email, so we can talk about how you can be a leader, rather than follower. Or check out the rest of the
website to read up on what we do so we can create the right level of engagement for you.
Hartung Recent Blog Posts on Leadership, Investing, Trends
Adam's book reveals the truth about how to use strategy to outpace the competition.
Follow Adam's coverage in the press and in other media.
Follow Adam's column in Forbes.

by Adam Hartung | May 9, 2019 | Innovation, Marketing, Strategy, Trends
Market Threat Assessment
Recent studies of senior managers have shown that being blindsided by a disruption is the largest unresolved concern in strategy development today.
That fear is too often real because disruption typically begins where it is least visible to management- on the fringes of the existing target markets. And, once the disruption “pirate ship” is sighted on the horizon, not only is it probably too late, but companies react poorly.
Some research of corporate responses to disruption has shown that most companies ignore the threat, fortify existing positions or attempt to buy innovation. The first choice is not an option for an ongoing business. Fortification through distribution changes, product model proliferation and discounting only buys some additional time while wasting resources. Once a disruption enters the market, there’s little time for organic innovation efforts so companies often make acquisitions attempting to buy innovation. Sadly, given the risk profile and limited experience in innovation, these are often sustaining innovations which are swept aside by the wave of disruption.
A very large example is when Microsoft fell behind in the mobile market in 2014 and purchased Nokia, a weak player in mobile phones to get access to this market. The joint project, the Lumina phone, failed to catch on and Microsoft’s share fell by 50%- fail. Cisco tried to catch up with the photography trend by acquiring Pure Digital, the maker of low cost Flip cameras. Unfortunately, shortly after the acquisition, the high-resolution sensors included in smartphones took photography to a new level. Bye, Flip! Trend monitoring would have predicted this natural evolution as a high risk threat.
To anticipate external changes, marketing departments have embraced big data as a powerful tool to help companies identify new markets and consumer preferences. These tools use the past to predict the short-term future which is reasonable in a steady market. The problem is that big data cannot anticipate dynamic disruption.
But, you and your staff can.
As a key input to your next strategy workshop, use trends! As a start, gather info from the people closest to your market and further using Porter’s five force model. See my articles on Scenarios to expand these trends to actionable goals.
What’s on your company’s radar today?
We are here to help as your coach on trends and innovation. We bring years of experience studying trends, organizations, and how to implement. We bring nimbleness to your strategy, and help you maximize your ability to execute.
Go the www.adamhartung.com and view the Assessment Page. Send me a reply to this email, or call me today, and let’s start talking about what trends will impact your organization and what you’ll need to do to pivot toward greater success.
by Adam Hartung | Jun 14, 2016 | Defend & Extend, Investing, Leadership, Web/Tech
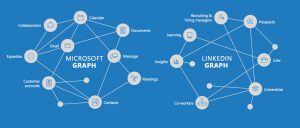
Microsoft is buying Linked-In, and we should expect this to be a disaster.
It is clear why Linked-in agreed to be purchased. As revenues have grown, gross margins have dropped precipitously, and the company is losing money. And LInked-in still receives 2/3 of its revenue from recruiting ads (the balance is almost wholly subscription fees,) unable to find a wider advertiser base to support growth. Although membership is rising, monthly active users (MAUs, the most important gauge of social media growth) is only 9% – like Twitter, far below the 40% plus rate of Facebook and upcoming networks. With only 106M MAUs, Linked in is 1/3 the size of Twitter, and 1/15th the size of Facebook. And its $1.5B Lynda acquisition is far, far, far from recovering its investment – or even demonstrating viability as a business.
Even though the price is below the all-time highs for LNKD investors, Microsoft’s offer is far above recent trading prices and a big windfall for them.
But for Microsoft investors, this is a repeat of the pattern that continues to whittle away at their equity value.
 Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.
Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.
But the world changed. Today PC sales continue their multi-year, accelerating decline, while some markets (such as education) are shifting to Chromebooks for low cost desktop/laptop computing, growing their sales and share. Meanwhile, mobile devices have been the growth market for years. Networks are largely public (rather than private) and storage is primarily in the cloud – and supplied by Amazon. Solutions are spread all around, from Google Drive to apps of every flavor and variety. People spend less computing cycles creating documents, spreadsheets and presentations, and a lot more cycles either searching the web or on Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, YouTube and Snapchat.
But Microsoft’s leadership still would like to capture that old world. They still hope to put the genie back in the bottle, and have everyone live and work entirely on Microsoft. And somehow they have deluded themselves into thinking that buying Linked-in will allow them to return to the “good old days.”
Microsoft has not done a good job of integrating its own solutions like Office 365, Skype, Sharepoint and Dynamics into a coherent, easy to use, and to some extent mobile, solution. Yet, somehow, investors are expected to believe that after buying Linked-in the two companies will integrate these solutions into the LInked-in social platform, enabling vastly greater adoption/use of Office 365 and Dynamics as they are tied to Linked-in Sales Navigator. Users will be thrilled to have their personal information analyzed by Microsoft big data tools, then sold to advertisers and recruiters. Meanwhile, corporations will come back to Microsoft in droves as they convert Linked-in into a comprehensive project management tool that uses Lynda to educate employees, and 365 to push materials to employees – and allow document collaboration – all across their mobile devices.
Do you really believe this? It might run on the Powerpoint operating system, but this vision will take an enormous amount of code integration. And with Linked-in operated as separate company within Microsoft, who is going to do this integration? This will involve a lot of technical capability, and based on previous performance it appears both companies lack the skills necessary to pull it off. How this mysterious, magical integration will happen is far, far from obvious, or explained in the announcement documents. Sounds a lot more like vaporware than a straightforward software project.
And who thinks that today’s users, from individuals to corporations, have a need for this vision? While it may sound good to Microsoft, have you heard Linked-in users saying they want to use 365 on Linked in? Or that they’ll continue to use Linked-in if forced to buy 365? Or that they want their personal information data mined for advertisers? Or that they desire integration with Dynamics to perform Linked-in based CRM? Or that they see a need for a social-network based project management tool that feeds up training documents or collaborative documents? Are people asking for an integrated, holistic solution from one vendor to replace their current mobile devices and mobile solutions that are upgraded by multiple vendors almost weekly?
And, who really thinks Microsoft is good at acquisition integration? Remember aQuantive? In 2007 Microsoft spent $6B (an 85% premium to market price) to purchase this digital ad agency in order to build its business in the fast growing digital ad space. Don’t feel bad if you don’t remember, because in 2012 Microsoft wrote it off. Of course, there was the buy-it-and-write-it-off pattern repeated with Nokia. Microsoft’s success at taking “bold moves” to expand beyond its core business has been nothing less than horrible. Even the $1.2B acquisition of Yammer in 2012 to make Sharepoint more collaborative and usable has been unsuccessful, even though rolled out for free to 365 users. Yammer is adding nothing to Microsoft’s sales or value as competitor Slack has reaped the growth in corporate messaging.
The only good news story about Microsoft acquisitions is that they missed spending $44B to buy Yahoo – which is now on the market for $5B. Whew, thank goodness that one got away!
Microsoft’s leadership primed the pump for this week’s announcement by having the Chairman talk about investing outside of the company’s core a couple of weeks ago. But the vast majority of analysts are now questioning this giant bet, at a price so high it will lower Microsoft’s earnings for 2 years. Analysts are projecting about a $2B revenue drop for $90B Microsoft next year, and this $26B acquisition will deliver only a $3B bump. Very, very expensive revenue replacement.
Despite all the lingo, Microsoft simply cannot seem to escape its past. Its acquisitions have all been designed to defend and extend its once great history – but now outdated. Customers don’t want the past, they are looking to the future. And no matter how hard they try, Microsoft’s leaders simply appear unable to define a future that is not tightly linked to the company’s past. So investors should expect Linked-In’s future to look a lot like aQuantive. Only this one is going to be the most painful yet in the long list of value transfer from Microsoft investors to the investors of acquired companies.
by Adam Hartung | Jun 9, 2016 | Innovation, Investing, Software, Teamwork
Last week Bloomberg broke a story about how Microsoft’s Chairman, John Thompson, was pushing company management for a faster transition to cloud products and services. He even recommended changes in spending might be in order.
Really? This is news?
Let’s see, how long has the move to mobile been around? It’s over a decade since Blackberry’s started the conversion to mobile. It was 10 years ago Amazon launched AWS. Heck, end of this month it will be 9 years since the iPhone was released – and CEO Steve Ballmer infamously laughed it would be a failure (due to lacking a keyboard.) It’s now been 2 years since Microsoft closed the Nokia acquisition, and just about a year since admitting failure on that one and writing off $7.5B And having failed to achieve even 3% market share with Windows phones, not a single analyst expects Microsoft to be a market player going forward.
So just now, after all this time, the Board is waking up to the need to change the resource allocation? That does seem a bit like looking into barn lock acquisition long after the horses are gone, doesn’t it?
The problem is that historically Boards receive almost all their information from management. Meetings are tightly scheduled affairs, and there isn’t a lot of time set aside for brainstorming new ideas. Or even for arguing with management assumptions. The work of governance has a lot of procedures related to compliance reporting, compensation, financial filings, senior executive hiring and firing – there’s a lot of rote stuff. And in many cases, surprisingly to many non-Directors, the company’s strategy may only be a topic once a year. And that is usually the result of a year long management controlled planning process, where results are reviewed and few challenges are expected. Board reviews of resource allocation are at the very, very tail end of management’s process, and commitments have often already been made – making it very, very hard for the Board to change anything.
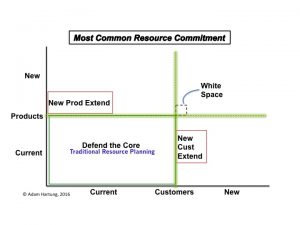
And these planning processes are backward-oriented tools, designed to defend and extend existing products and services, not predict changes in markets. These processes originated out of financial planning, which used almost exclusively historical accounting information. In later years these programs were expanded via ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems (such as SAP and Oracle) to include other information from sales, logistics, manufacturing and procurement. But, again, these numbers are almost wholly historical data. Because all the data is historical, the process is fixated on projecting, and thus defending, the old core of historical products sold to historical customers.
Copyright Adam Hartung
Efforts to enhance the process by including extensions to new products or new customers are very, very difficult to implement. The “owners” of the planning processes are inherent skeptics, inclined to base all forecasts on past performance. They have little interest in unproven ideas. Trying to plan for products not yet sold, or for sales to customers not yet in the fold, is considered far dicier – and therefore not worthy of planning. Those extensions are considered speculation – unable to be forecasted with any precision – and therefore completely ignored or deeply discounted.
And the more they are discounted, the less likely they receive any resource funding. If you can’t plan on it, you can’t forecast it, and therefore, you can’t really fund it. And heaven help some employee has a really novel idea for a new product sold to entirely new customers. This is so “white space” oriented that it is completely outside the system, and impossible to build into any future model for revenue, cost or – therefore – investing.
Take for example Microsoft’s recent deal to sell a bunch of patent rights to Xiaomi in order to have Xiaomi load Office and Skype on all their phones. It is a classic example of taking known products, and extending them to very nearby customers. Basically, a deal to sell current software to customers in new markets via a 3rd party. Rather than develop these markets on their own, Microsoft is retrenching out of phones and limiting its investments in China in order to have Xiaomi build the markets – and keeping Microsoft in its safe zone of existing products to known customers.
The result is companies consistently over-investment in their “core” business of current products to current customers. There is a wealth of information on those two groups, and the historical info is unassailable. So it is considered good practice, and prudent business, to invest in defending that core. A few small bets on extensions might be OK – but not many. And as a result the company investment portfolio becomes entirely skewed toward defending the old business rather than reaching out for future growth opportunities.
This can be disastrous if the market shifts, collapsing the old core business as customers move to different solutions. Such as, say, customers buying fewer PCs as they shift to mobile devices, and fewer servers as they shift to cloud services. These planning systems have no way to integrate trend analysis, and therefore no way to forecast major market changes – especially negative ones. And they lack any mechanism for planning on big changes to the product or customer portfolio. All future scenarios are based on business as it has been – a continuation of the status quo primarily – rather than honest scenarios based on trends.
How can you avoid falling into this dilemma, and avoiding the Microsoft trap? To break this cycle, reverse the inputs. Rather than basing resource allocation on financial planning and historical performance, resource allocation should be based on trend analysis, scenario planning and forecasts built from the future backward. If more time were spent on these plans, and engaging external experts like Board Directors in discussions about the future, then companies would be less likely to become so overly-invested in outdated products and tired customers. Less likely to “stay at the party too long” before finding another market to develop.
If your planning is future-oriented, rather than historically driven, you are far more likely to identify risks to your base business, and reduce investments earlier. Simultaneously you will identify new opportunities worthy of more resources, thus dramatically improving the balance in your investment portfolio. And you will be far less likely to end up like the Chairman of a huge, formerly market leading company who sounds like he slept through the last decade before recognizing that his company’s resource allocation just might need some change.

 Windows and Office made all the money at Microsoft. So he kept investing in Windows and Office. He failed at everything else. False starts in phones, tablets, gaming – products came and went like ice cream cones on a hot August day. Ballmer laughed at the very notion of the iPhone ever being successful – while simultaneously throwing away $7.2B buying Nokia. Then there was $8.5B buying Skype. $400M buying the Borders Nook. Those were ridiculous acquisitions that just wasted shareholder money. To Ballmer, Microsoft’s future relied on maintaining Windows and Office.
Windows and Office made all the money at Microsoft. So he kept investing in Windows and Office. He failed at everything else. False starts in phones, tablets, gaming – products came and went like ice cream cones on a hot August day. Ballmer laughed at the very notion of the iPhone ever being successful – while simultaneously throwing away $7.2B buying Nokia. Then there was $8.5B buying Skype. $400M buying the Borders Nook. Those were ridiculous acquisitions that just wasted shareholder money. To Ballmer, Microsoft’s future relied on maintaining Windows and Office.





 Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.
Once upon a time, in a land far away, and barely remembered by young people, Microsoft OWNED the tech marketplace. Individuals and companies purchased PCs preloaded with Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer and a handful of other tools and trinkets. And as companies built networks they used PC servers loaded with Microsoft products. Computing was a Microsoft solution, beginning to end, for the vast majority of users.