
by Adam Hartung | Sep 23, 2016 | Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Television, Web/Tech
In early August Tesla announced it would be buying SolarCity. The New York Times discussed how this combination would help CEO Elon Musk move toward his aspirations for greater clean energy use. But the Los Angeles Times took the companies to task for merging in the face of tremendous capital needs at both, while Tesla was far short of hitting its goals for auto and battery production.
Since then the press has been almost wholly negative on the merger. Marketwatch’s Barry Randall wrote that the deal makes no sense. He argues the companies are in two very different businesses that are not synergistic – and he analogizes this deal to GM buying Chevron. He also makes the case that SolarCity will likely go bankrupt, so there is no good reason for Tesla shareholders to “bail out” the company. And he argues that the capital requirements of the combined entities are unlikely to be fundable, even for its visionary CEO.
 Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
But short-sellers are clearly not long-term investors. And there is a lot more ability for this deal to succeed and produce tremendous investor returns than anyone could ever glean from studying historical financial statements of both companies.
GM buying Chevron is entirely the wrong analogy to compare with Tesla buying SolarCity. Instead, compare this deal to what happened in the creation of television after General Sarnoff, who ran RCA, bought what he renamed NBC.
The world already had radio (just as we already have combustion powered cars.) The conundrum was that nobody needed a TV, especially when there were no TV programs. But nobody would create TV programs if there were no consumers with TVs. General Sarnoff realized that both had to happen simultaneously – the creation of both demand, and supply. It would only be by the creation, and promotion, of both that television could be a success. And it was General Sarnoff who used this experience to launch the first color televisions at the same time as NBC launched the first color programming – which fairly quickly pushed the industry into color.
Skeptics think Mr. Musk and his companies are in over their heads, because there are manufacturing issues for the batteries and the cars, and the solar panel business has yet to be profitable. Yet, the older among us can recall all the troubles with launching TV.
Early sets were not only expensive, they were often problematic, with frequent component failures causing owners to take the TV to a repairman. Often reception was poor, as people relied on poor antennas and weak network signals. It was common to turn on a set and have “snow” as we called it – images that were far from clear. And there was often that still image on the screen with the words “Technical Difficulties,” meaning that viewers just waited to see when programming would return. And programming was far from 24×7 – and quality could be sketchy. But all these problems have been overcome by innovation across the industry.
Yes, the evolution of electric cars will involve a lot of ongoing innovation. So judging its likely success on the basis of recent history would be foolhardy. Today Tesla sells 100% of its cars, with no discounts. The market has said it really, really wants its vehicles. And everybody who is offered electric panels with (a) the opportunity to sell excess power back to the grid and (b) financing, takes the offer. People enjoy the low cost, sustainable electricity, and want it to grow. But lacking a good storage device, or the inability to sell excess power, their personal economics are more difficult.
Electricity production, electricity storage (batteries) and electricity consumption are tightly linked technologies. Nobody will build charging stations if there are no electric cars. Nobody will build electric cars if there are not good batteries. Nobody will make better batteries if there are no electric cars. Nobody will install solar panels if they can’t use all the electricity, or store what they don’t immediately need (or sell it.)
This is not a world of an established marketplace, where GM and Chevron can stand alone. To grow the business requires a vision, business strategy and technical capability to put it all together. To make this work someone has to make progress in all the core technologies simultaneously – which will continue to improve the storage capability, quality and safety of the electric consuming automobiles, and the electric generating solar panels, as well as the storage capabilities associated with those panels and the creation of a new grid for distribution.
This is why Mr. Musk says that combining Tesla and SolarCity is obvious. Yes, he will have to raise huge sums of money. So did such early pioneers as Vanderbilt (railways,) Rockefeller (oil,) Ford (autos,) and Watson (computers.) More recently, Steve Jobs of Apple became heroic for figuring out how to simultaneously create an iPhone, get a network to support the phone (his much maligned exclusive deal with AT&T,) getting developers to write enough apps for the phone to make it valuable, and creating the retail store to distribute those apps (iTunes.) Without all those pieces, the ubiquitous iPhone would have been as successful as the Microsoft Zune.
It is fair for investors to worry if Tesla can raise enough money to pull this off. But, we don’t know how creative Mr. Musk may become in organizing the resources and identifying investors. So far, Tesla has beaten all the skeptics who predicted failure based on price of the cars (Tesla has sold 100% of its production,) lack of range (now up to nearly 300 miles,) lack of charging network (Tesla built one itself) and charging time (now only 20 minutes.) It would be shortsighted to think that the creativity which has made Tesla a success so far will suddenly disappear. And thus remarkably thoughtless to base an analysis on the industry as it exists today, rather than how it might well look in 3, 5 and 10 years.
The combination of Tesla and SolarCity allows Tesla to have all the components to pursue greater future success. Investors with sufficient risk appetite are justified in supporting this merger because they will be positioned to receive the future rewards of this pioneering change in the auto and electric utility industries.

by Adam Hartung | Apr 21, 2016 | In the Rapids, Leadership, Lifecycle, Television, Web/Tech
Netflix has been a remarkable company. Because it has accomplished something almost no company has ever done. It changed its business model, leading to new growth and higher profits.
Almost nobody pulls that off, because they remain stuck defending and extending their old model until they become irrelevant, or fail. Think about Blackberry, that gave us the smartphone business then lost it to Apple and its creation of the app market. Consider Circuit City, that lost enough customers to Amazon it could no longer survive. Sun Microsystems disappeared after PC servers caught up to Unix servers in capability. Remember the Bell companies and their land-line and long distance services, made obsolete by mobile phones and cable operators? These were some really big companies that saw their market shifts, but failed to “pivot” their strategy to remain competitive.
Netflix built a tremendous business delivering physical videos on tape and CD to homes, wiping out the brick-and-mortar stores like Blockbuster and Hollywood Video. By 2008 Netflix reached $1B revenues, reducing Blockbuster by a like amount. By 2010 Blockbuster was bankrupt. Netflix’ share price soared from $50/share to almost $300/share during 2011. By the end of 2012 CD shipments were dropping precipitously as streaming viewership was exploding. People thought Netflix was missing the wave, and the stock plummeted 75%. Most folks thought Netflix couldn’t pivot fast enough, or profitably, either.
But in 2013 Netflix proved the analysts wrong, and the company built a very successful – in fact market leading – streaming business. The shares soared, recovering all that lost value. By 2015 the company had more than doubled its previous high valuation.
But Netflix may be breaking entirely new ground in 2016. It is becoming a market leader in original programming. Something we long attributed to broadcasters and/or cable distributors like HBO and Showtime.
Today’s broadcast companies, like NBC, CBS and ABC, are offering less and less original programming. Overall there are 3 hours/night of prime time television which broadcasters used to “own” as original programming hours. Over the course of a year, allowing for holidays and one open night per week, that meant about 900 hours of programming for each network (including reruns as original programming.) But that was long ago.
 These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
Against that backdrop, Netflix has announced it will program 600 hours of original programming this year. That will approximately double any single large broadcast network. In a very real way, if you don’t want to watch sports or reality TV any more you probably will be watching some kind of “on demand” program. Either streamed from a cable service, or from a provider such as Netflix, Hulu or Amazon.
When it comes to original programming, the old broadcast networks are losing their relevancy to streaming technology, personal video devices and the customer’s ability to find what they want, when they want it – and increasingly at a quality they prefer – from streaming as opposed to broadcast media.
To complete this latest “pivot,” from a video streaming company to a true media company with its own content, Morgan Stanley has published that Netflix is now considered by customers as the #1 quality programming across streaming services. 29% of viewers said Netflix was #1, followed by long-time winner HBO now #2 with 21% of customers saying their programming is best. Amazon, Showtime and Hulu were seen as the best quality by 4%-5% of viewers.
So a decade ago Netflix was a CD distribution company. The largest customer of the U.S. Postal Service. Signing up folks to watch physical videos in their homes. Now they are the largest data streaming company on the planet, and one of the largest original programming producers and programmers in the USA – and possibly the world. And in this same decade we’ve watched the network broadcast companies become outlets for sports and reality TV, while cutting far back on their original shows. Sounds a lot like a market shift, and possibly Netflix could be the game changer, as it performs the first strategy double pivot in business history.
by Adam Hartung | Apr 15, 2015 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership
The money is not going into developing any new markets or new products. It is not being used to finance growth of GE at all. Rather, Mr. Immelt will immediately begin a massive $50B stock buyback program in order to prop up the stock price for investors.
 When Mr. Immelt took the job of CEO GE sold for about $40/share. Last week it was trading for about $25/share. A decline of 37.5%. During that same time period the Dow Jones Industrial Average, of which GE is the oldest component, rose from 9,600 to 17,900. An increase of 86.5%. This has been a very, very long period of quite unsatisfactory performance for Mr. Immelt.
When Mr. Immelt took the job of CEO GE sold for about $40/share. Last week it was trading for about $25/share. A decline of 37.5%. During that same time period the Dow Jones Industrial Average, of which GE is the oldest component, rose from 9,600 to 17,900. An increase of 86.5%. This has been a very, very long period of quite unsatisfactory performance for Mr. Immelt.
Prior to Mr. Immelt GE was headed by Jack Welch. During his tenure at the top of GE the company created more wealth for its investors than any company ever in the recorded history of U.S. publicly traded companies. GE’s value increased 40-fold (4000%) from 1981 to 2001. He expanded GE into new businesses, often far removed from its industrial manufacturing roots, as market shifts created new opportunities for growing revenues and profits. From what was mostly a diversified manufacturing company Mr. Welch lead GE into real estate as those assets increased in value, then media as advertising revenues skyrocketed and finally financial services as deregulation opened the market for the greatest returns in banking history.
Jack Welch was the Steve Jobs of his era. Because he had the foresight to push GE into new markets, create new products and grow the company. Growth that was so substantial it kept GE constantly in the news, and investors thrilled.
But Mr. Immelt – not so much. During his tenure GE has not developed any new markets. He has not led the company into any growth areas. As the world of portable technology has exploded, making a fortune for Apple and Google investors, GE missed the entire movement into the Internet of Things. Rather than develop new products building on new technologies in wifi, portability, mobility and social Mr. Immelt’s GE sold the appliance division to Electrolux and spent the $3.3B on stock buybacks.
Mr. Immelt’s tenure has been lacked by a complete lack of vision. Rather than looking ahead and preparing for market shifts, Immelt’s GE has reacted to market changes – usually for the poorer. Unprepared for things going off-kilter in financial services, the company was rocked by the financial meltdown and was only saved by an infusion from Berkshire Hathaway. Now it is exiting the business which generates nearly half its profits, claiming it doesn’t want to deal with regulations, rather than figuring out how to make it a more successful enterprise. After accumulating massive real estate holdings, instead of selling them at the peak in the mid-2000s it is now exiting as fast as possible in a recovering economy – to let the fund managers capture gains from improving real estate.
GE is now repatriating some $36B in foreign profits, on which it will pay $6B in taxes. Investors should realize this is happening at the strongest value of the dollar since Mr. Immelt took office. If GE needed these funds, which have been in offshore currencies such as the Euro, it could have repatriated them anytime in the last 3 years and those funds would have been $50B instead of $36B! To say the timing of this transaction could not have been poorer ….
The only thing into which Mr. Immelt has invested has been GE stock. And even that has been a lousy spend, as the price has gone down rather than up! Smart investors have realized that there is no growth in Immelt’s GE, and they have dumped the stock faster than he could buy it. Mr. Immelt’s Harvard MBA gave him insight to financial engineering, but unfortunately not how to lead and grow a major corporation. After 15 years Immelt will leave GE a much smaller, and as he said in the press release, “simpler” business. Apparently it was too big and complicated for him to run.
In the GE statement Mr. Immelt states “This is a major step in our strategy to focus GE around its competitive advantage.” Sorry Mr. Immelt, but that is not a strategy. Identifying growing markets and technologies to create strong, high profit positions with long-term returns is a strategy. Using vague MBA-esque language to hide what is an obvious effort at salvaging a collapsing stock price for another 2 years has nothing to do with strategy. It is a financial tactic.
The Immelt era is the story of a GE which has reacted to events, rather than lead them. Where Steve Jobs took a broken, floundering company and used vision to guide it to great wealth, and Jack Welch used vision to build one of the world’s most resilient and strong corporations, Jeffrey Immelt and his team were overtaken by events at almost every turn. CEO Immelt took what was perhaps the leading corporation of the last century and will leave it in dire shape, lacking a plan for re-establishing its once great heritage. It is a story of utterly failed leadership.

by Adam Hartung | Mar 9, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, Leadership, Television
The Netflix hit series “House of Cards” was released last night. Most media reviewers and analysts are expecting huge numbers of fans will watch the show, given its tremendous popularity the last 2 years. Simultaneously, there are already skeptics who think that releasing all episodes at once “is so last year” when it was a newsworthy event, and no longer will interest viewers, or generate subscribers, as it once did. Coupled with possible subscriber churn, some think that “House of Cards” may have played out its hand.
So, the success of this series may have a measurable impact on the valuation of Netflix. If the “House of Cards” download numbers, which are up to Netflix to report, aren’t what analysts forecast many may scream for the stock to tumble; especially since it is on the verge of reaching new all-time highs. The Netflix price to earnings (P/E) multiple is a lofty 107, and with a valuation of almost $29B it sells for just under 4x sales.
 But investors should ignore any, and in fact all, hype about “House of Cards” and whatever analysts say about Netflix. So far, they’ve been wildly wrong when making forecasts about the company. Especially when projecting its demise.
But investors should ignore any, and in fact all, hype about “House of Cards” and whatever analysts say about Netflix. So far, they’ve been wildly wrong when making forecasts about the company. Especially when projecting its demise.
Since Netflix started trading in 2002, it has risen from (all numbers adjusted) $8.5 to $485. That is a whopping 57x increase. That is approximately a 40% compounded rate of return, year after year, for 13 years!
But it has not been a smooth ride. After starting (all numbers rounded for easier reading) at $8.50 in May, 2002 the stock dropped to $3.25 in October – a loss of over 60% in just 5 months. But then it rallied, growing to $38.75, a whopping 12x jump, in just 14 months (1/04!) Only to fall back to $9.80, a 75% loss, by October, 2004 – a mere 9 months later. From there Netflix grew in value by about 5.5x – to $55/share – over the next 5 years (1/10.) When it proceeded to explode in value again, jumping to $295, an almost 6-fold increase, within 18 months (7/11). Only to get creamed, losing almost 80% of its value, back down to $63.85, in the next 4 months (11/11.) The next year it regained some loss, improving in value by 50% to $91.35 (12/12,) only to again explode upward to $445 by February, 2014 a nearly 5-fold increase, in 14 months. Two months later, a drop of 25% to $322 (4/14). But then in 4 months back up to $440 (8/14), and back down 4 months later to $341 (12/14) only to approach new highs reaching $480 last week – just 2 months later.
That is the definition of volatility.
Netflix is a disruptive innovator. And, simply put, stock analysts don’t know how to value disruptive innovators. Because their focus is all on historical numbers, and then projecting those historicals forward. As a result, analysts are heavily biased toward expecting incumbents to do well, and simultaneously being highly skeptical of any disruptive company. Disruptors challenge the old order, and invalidate the giant excel models which analysts create. Thus analysts are very prone to saying that incumbents will remain in charge, and that incumbents will overwhelm any smaller company trying to change the industry model. It is their bias, and they use all kinds of historical numbers to explain why the bigger, older company will project forward well, while the smaller, newer company will stumble and be overwhelmed by the entrenched competitor.
And that leads to volatility. As each quarter and year comes along, analysts make radically different assumptions about the business model they don’t understand, which is the disruptor. Constantly changing their assumptions about the newer kid on the block, they make mistake after mistake with their projections and generally caution people not to buy the disruptor’s stock. And, should the disruptor at any time not meet the expectations that these analysts invented, then they scream for shareholders to dump their holdings.
Netflix first competed in distribution of VHS tapes and DVDs. Netflix sent them to people’s homes, with no time limit on how long folks could keep them. This model was radically different from market leader Blockbuster Video, so analysts said Blockbuster would crush Netflix, which would never grow. Wrong. Not only did Blockbuster grow, but it eventually drove Blockbuster into bankruptcy because it was attuned to trends for convenience and shopping from home.
As it entered streaming video, analysts did not understand the model and predicted Netflix would cannibalize its historical, core DVD business thus undermining its own economics. And, further, much larger Amazon would kill Netflix in streaming. Analysts screamed to dump the stock, and folks did. Wrong. Netflix discovered it was a good outlet for syndication, created a huge library of not only movies but television programs, and grew much faster and more profitably than Amazon in streaming.
Then Netflix turned to original programming. Again, analysts said this would be a huge investment that would kill the company’s financials. And besides that people already had original programming from historical market leaders HBO and Showtime. Wrong. By using analysis of what people liked from its archive, Netflix leadership hedged its bets and its original shows, especially “House of Cards” have been big hits that brought in more subscribers. HBO and Showtime, which have depended on cable companies to distribute their programming, are now increasingly becoming additional programming on the Netflix distribution channel.
Investors should own Netflix because the company’s leadership, including CEO Reed Hastings, are great at disruptive innovation. They identify unmet customer needs and then fulfill those needs. Netflix time and again has demonstrated it can figure out a better way to give certain user segments what they want, and then expand their offering to eat away at the traditional market. Once it was retail movie distribution, increasingly it is becoming cable distribution via companies like ComCast, AT&T and Time Warner.
And investors must be long-term. Netflix is an example of why trading is a bad idea – unless you do it for a living. Most of us who have full time day jobs cannot try timing the ups and downs of stock movements. For us, it is better to buy and hold. When you’re ready to buy, buy. Don’t wait, because in the short term there is no way to predict if a stock will go up or down. You have to buy because you are ready to invest, and you expect that over the next 3, 5, 7 years this company will continue to drive growth in revenues and profits, thus expanding its valuation.
Netflix, like Apple, is a company that has mastered the skills of disruptive innovation. While the competition is trying to figure out how to sustain its historical position by doing the same thing better, faster and cheaper Netflix is figuring out “the next big thing” and then delivering it. As the market shifts, Netflix is there delivering on trends with new products – and new business models – which push revenues and profits higher.
That’s why it would have been smart to buy Netflix any time the last 13 years and simply held it. And odds are it will continue to drive higher valuations for investors for many years to come. Not only are HBO, Showtime and Comcast in its sites, but the broadcast networks (ABC, CBS, NBC) are not far behind. It’s a very big media market, which is shifting dramatically, and Netflix is clearly the leader. Not unlike Apple has been in personal technology.
by Adam Hartung | Dec 11, 2014 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lifecycle, Television, Web/Tech
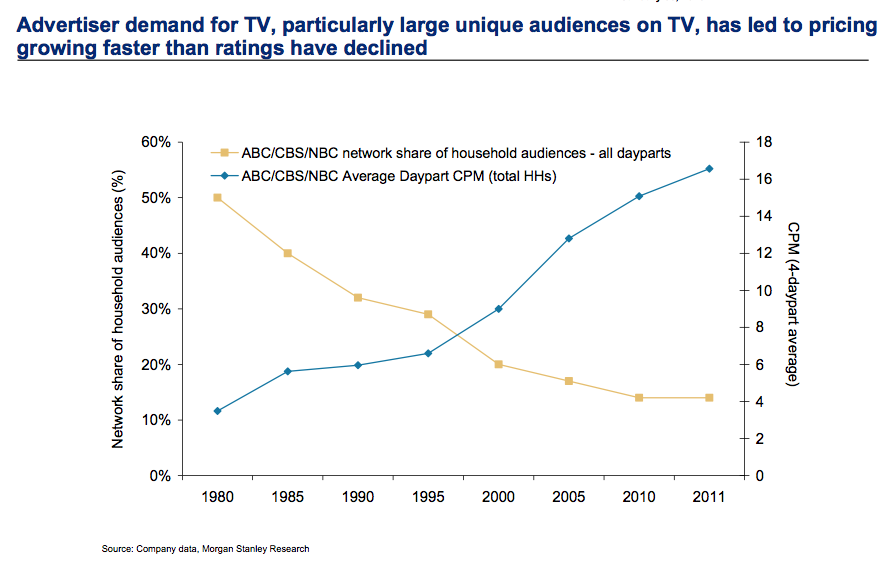
The trend toward the death of broadcast TV as we’ve known it keeps moving forward. This trend may not happen as fast as the death of desktop computers, but it is a lot faster than glacier melting.
This television season (through October) Magna Global has reported that even the oldest viewers (the TV Generation 55-64) watched 3% less TV. Those 35-54 watched 5% less. Gen Xers (25-34) watched 8% less, and Millenials (18-24) watched a whopping 14% less TV. Live sports viewing is not even able to maintain its TV audience, with NFL viewership across all networks down 10-19%.
Everyone knows what is happening. People are turning to downloaded entertainment, mostly on their mobile devices. With a trend this obvious, you’d think everyone in the media/TV and consumer goods industries would be rethinking strategy and retooling for a new future.
But, you would be wrong. Because despite the obviousness of the trend, emotional ties to hoping the old business sticks around are stronger than logic when it comes to forecasting.
CBS predicted at the beginning of 2014 TV ad revenue would grow 4%. Oops. Now CBS’s lead forecaster is admitting he was way off, and adjusted revenues were down 1% for the year. But, despite the trend in viewer behavior and ad expenditures in 2014, he now predicts a growth of 2% for 2015.
That, my young friends, is how “hockey stick” forecasts are created. A lot of old assumptions, combined with a willingness to hope trends will be delayed, and you can ignore real data while promising people that the future will indeed look like the past – even when it defies common sense.
To compensate for fewer ads the networks have raised prices on all ads. But how long can that continue? This requires a really committed buyer (read more about CMO weaknesses below) who simply refuses to acknowledge the market has shifted and the dollars need to shift with it. That cannot last forever.
Meanwhile, us old folks can remember the days when Nielsen ratings determined what was programmed on TV, as well as what advertisers paid. Nielsen had a lock on measuring TV audience viewing, and wielded tremendous power in the media and CPG world.
But now AC Nielsen is struggling to remain relevant. With TV viewership down, time shifting of shows common and streaming growing like the proverbial weed Nielsen has no idea what entertainment the public watches. They don’t know what, nor when, nor where. Unwilling to move quickly to develop tools for catching all the second screen viewing, Nielsen has no plan for telling advertisers what the market really looks like – and the company looks to become a victim of changing markets.
Which then takes us to looking at those folks who actually buy ads that drive media companies. The Chief Marketing Officers (CMOs) of CPG companies. Surely these titans of industry are on top of these trends, and rapidly shifting their spending to catch the viewers with the most ads placed for the lowest cost.
You would wish.
Unfortunately, because these senior executives are in the oldest age groups, they are a victim of their own behavior. They still watch TV, so assume others must as well. If there is cyber-data saying they are wrong, well they simply discount that data. The Nielsen’s aren’t accurate, but these execs still watch the ratings “because it’s the best info we have” – a blatant untruth by the way. But Nielsen does conveniently reinforce their built in assumptions, and their hope that they won’t have to change their media spend plans any time soon.
Further, very few of these CMOs actually use social media. The vast majority watch their children, grandchildren and young employees use mobile devices constantly – and they bemoan all the activity on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram and Twitter – or for the most part even Linked-in. But they don’t actually USE these products. They don’t post information. They don’t set up and follow channels. They don’t connect with people, share information, exchange photos or tell stories on social media. Truthfully, they ignore these trends in their own lives. Which leaves them woefully inept at figuring out how to change their company marketing so it can be more relevant.
The trend is obvious. The answer, equally so. Any modern marketer should be an avid user of social media. Most network heads and media leaders are farther removed from social media than the Pope! They don’t constantly download entertainment, and exchanging with others on all the platforms. They can’t manage the use of these channels when they don’t have a clue how they work, or how other people use them, or understand why they are actually really valuable tools.
Are you using these modern tools? Are you actually living, breathing, participating in the trends? Or are you, like these outdated execs, biding your time wasting money on old programs while you look forward to retirement? And likely killing your company.
When trends emerge it is imperative we become part of that trend. You can’t simply observe it, because your biases will lead you to hope the trend reverts as you continue doing more of the same. A leader has to adopt the trend as a leader, be a practicing participant, and learn how that trend will make a substantial difference in the business. And then apply some vision to remain relevant and successful.

 Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.
Fortune quotes legendary short seller Jim Chanos as saying the deal is “crazy.” He argues that SolarCity has an uneconomic business model based on his analysis of historical financial statements. And now Fortune is reporting that shareholder lawsuits to block the deal could delay, or kill, the merger.

 These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.
These days most of those hours are filled with sports – think evening games of football, basketball, baseball including playoffs and “March Madness” events. Sports are far cheaper to program, and can fill a lot of hours. Next think reality programming. Showing people race across countries, or compete to survive a political battlefield on an island, or even dancing or dieting, uses no expensive actors or directors or sets. It is far, far less expensive than writing, casting, shooting and programming a drama (like Blacklist) or comedy (like Big Bang Theory.) Plan on showing every show twice in reruns, plus intermixing with the sports and reality shows, and most networks get away with around 200-250 hours of original programming per year.



