
by Adam Hartung | Mar 22, 2017 | In the Whirlpool, Investing, Retail
(Photo by Scott Olson/Getty Images)
Traditional retailers just keep providing more bad news. Payless Shoes said it plans to file bankruptcy next week, closing 500 of its 4,000 stores. Most likely it will follow the path of Radio Shack, which hasn’t made a profit since 2011. Radio Shack filed bankruptcy and shut a gob of stores as part of its “turnaround plan.” Then in February Radio Shack filed its second bankruptcy — most likely killing the chain entirely this time.
Sears Holdings finally admitted it probably can’t survive as a going concern this week. Sears has lost over $10 billion since 2010 — when it last showed a profit — and owes over $4 billion to its creditors. Retail stocks cratered Monday as the list of retailers closing stores accelerated: Sears, KMart, Macy’s, Radio Shack, JCPenney, American Apparel, Abercrombie & Fitch, The Limited, CVS, GNC, Office Depot, HHGregg, The Children’s Place and Crocs are just some of the household names that are slowly (or not so slowly) dying.
None of this should be surprising. By the time CEO Ed Lampert merged KMart with Sears the trend to e-commerce was already pronounced. Anyone could build an excel spreadsheet that would demonstrate as online retail grew, brick-and-mortar retail would decline. In the low margin world of retail, profits would evaporate. It would be a blood bath. Any retailer with any weakness simply would not survive this market shift — and that clearly included outdated store concepts like Sears, KMart and Radio Shack which long ago were outflanked by on-line shopping and trendier storefronts.
Yet, not everyone is ready to give up on some retailers. Walmart, for example, still trades at $70 per share, which is higher than it traded in 2015 and about where it traded back in 2012. Some investors still think that there are brick-and-mortar outfits that are either immune to the trends, or will survive the shake-out and have higher profits in the future.
And that is why we have to be very careful about business myths. There are a lot of people that believe as markets shrink the ultimate consolidation will leave one, or a few, competitors who will be very profitable. Capacity will go away, and profits will return. In the end, they believe if you are the last buggy whip maker you will be profitable — so investors just need to pick who will be the survivor and wait it out. And, if you believe this, then you have justified owning Walmart.
Only, markets don’t work that way. As industries consolidate they end up with competitors who either lose money or just barely eke out a small profit. Think about the auto industry, airlines or land-line telecom companies.
Two factors exist which effectively forces all the profits out of these businesses and therefore make it impossible for investors to make money long-term.
First, competitive capacity always remains just a bit too much for the market need. Management, and often investors, simply don’t want to give up in the face of industry consolidation. They keep hoping to reach a rainbow that will save them. So capacity lingers and lingers — always pushing prices down even as costs increase. Even after someone fails, and that capacity theoretically goes away, someone jumps in with great hopes for the future and boosts capacity again. Therefore, excess capacity overhangs the marketplace forcing prices down to break-even, or below, and never really goes away.
Given the amount of retail real estate out there and the bargains being offered to anyone who wants to open, or expand, stores this problem will persist for decades in retail.
Second, demand in most markets keeps declining. Hopefuls project that demand will “stabilize,” thus balancing the capacity and allowing for price increases. Because demand changes aren’t linear, there are often plateaus that make it appear as if demand won’t go down more. But then something changes — an innovation, regulatory change, taste change — and demand takes another hit. And all the hope goes away as profits drop, again.
It is not a successful strategy to try being the “last man standing” in any declining market. No competitor is immune to these forces when markets shift. No matter how big, when trends shift and new forms of competition start growing every old-line company will be negatively affected. Whether fast, or slow, the value of these companies will continue declining until they eventually become worthless.
Nor is it successful long-term to try and segment the business into small groupings which management thinks can be protected. When Xerox brought to market photocopying, small offset press manufacturers (ABDick and Multigraphics ) said not to worry. Xeroxing might be OK in some office installations, but there were customer segments that would forever use lithography. Even as demand shrunk, well into the 1990s, they said that big corporations, industrial users, government entities, schools and other segments would forever need the benefits of lithography, so investors were safe. Today the small offset press market is a tiny fraction of its size in the 1960s. ABDick and Multigraphics both went through rounds of bankruptcies before disappearing. Xerography, its child desktop publishing, and its grandchild electronic screens, killed offset for almost all applications.
So don’t be lured into false hopes by retailers who claim their segment is “protected.” Short-term things might not look bad. But the market has already shifted to e-commerce and this is just round one of change. More and more innovations are coming that will make the need for traditional stores increasingly unnecessary.
Many readers have expressed their disappointment in my chronic warnings about Walmart. But those warnings are no different than my warnings about Sears Holdings. It’s just that the timing may be different. Both companies have been over-investing in assets (brick-and-mortar stores) that are declining in value as they have attempted to defend and extend their old business model. Both radically under-invested in new markets which were cannibalizing their old business. And, in the end, both will end up with the same results.
And this is true for all retailers that depend on traditional brick-and-mortar sales for their revenues and profits — it’s only a matter of when things will go badly, not if. So traditional retail is nowhere that any investor wants to be.
by Adam Hartung | May 15, 2016 | In the Swamp, Investing, real estate, Retail
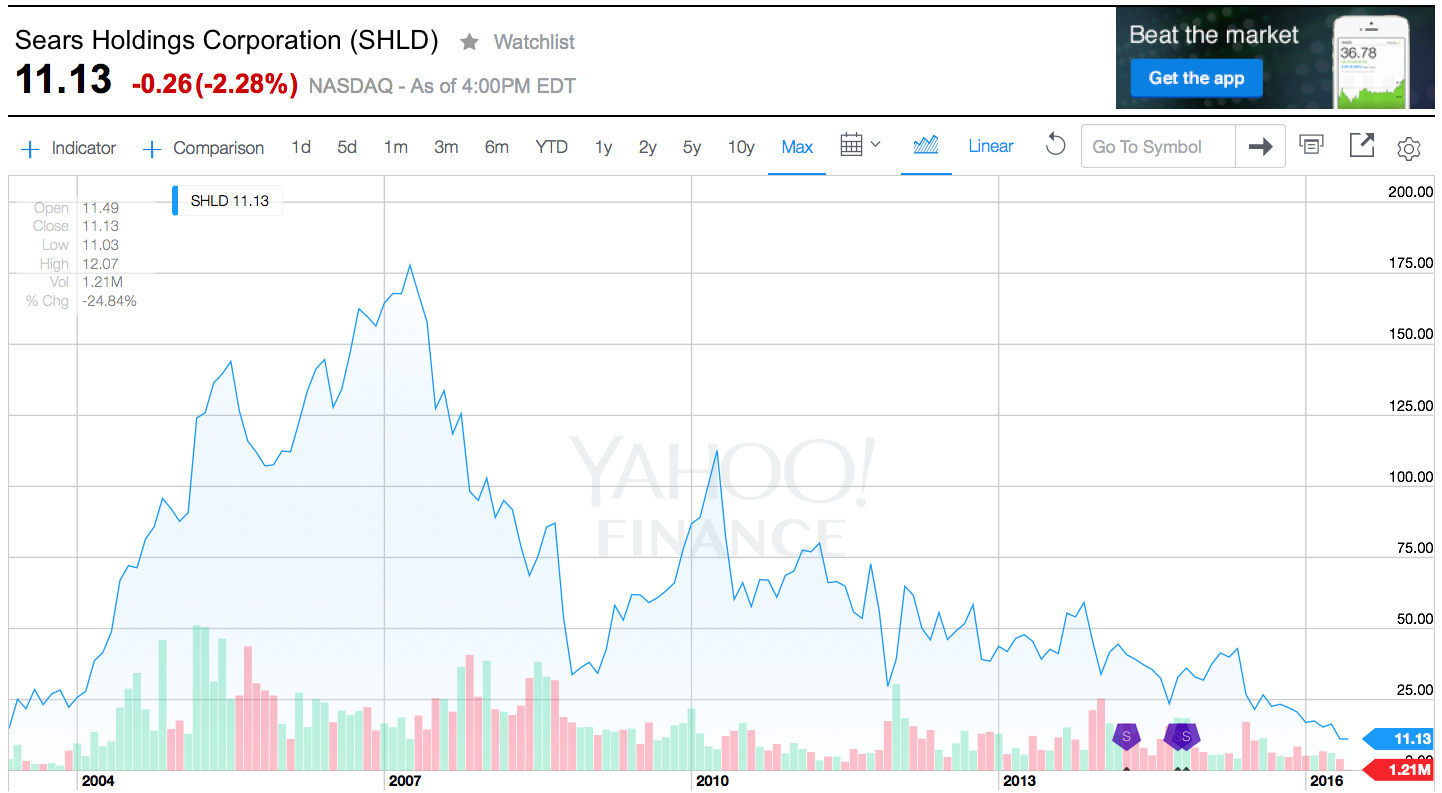
Last week Sears announced sales and earnings. And once again, the news was all bad. The stock closed at a record, all time low. One chart pretty much sums up the story, as investors are now realizing bankruptcy is the most likely outcome.
Chart Source: Yahoo Finance 5/13/16
Quick Rundown: In January, 2002 Kmart is headed for bankruptcy. Ed Lampert, CEO of hedge fund ESL, starts buying the bonds. He takes control of the company, makes himself Chairman, and rapidly moves through proceedings. On May 1, 2003, KMart begins trading again. The shares trade for just under $15 (for this column all prices are adjusted for any equity transactions, as reflected in the chart.)
Lampert quickly starts hacking away costs and closing stores. Revenues tumble, but so do costs, and earnings rise. By November, 2004 the stock has risen to $90. Lampert owns 53% of Kmart, and 15% of Sears. Lampert hires a new CEO for Kmart, and quickly announces his intention to buy all of slow growing, financially troubled Sears.
In March, 2005 Sears shareholders approve the deal. The stock trades for $126. Analysts praise the deal, saying Lampert has “the Midas touch” for cutting costs. Pumped by most analysts, and none moreso than Jim Cramer of “Mad Money” fame (Lampert’s former roommate,) in 2 years the stock soars to $178 by April, 2007. So far Lampert has done nothing to create value but relentlessly cut costs via massive layoffs, big inventory reductions, delayed payments to suppliers and store closures.
Homebuilding falls off a cliff as real estate values tumble, and the Great Recession begins. Retailers are creamed by investors, and appliance sales dependent Sears crashes to $33.76 in 18 months. On hopes that a recovering economy will raise all boats, the stock recovers over the next 18 months to $113 by April, 2010. But sales per store keep declining, even as the number of stores shrinks. Revenues fall faster than costs, and the stock falls to $43.73 by January, 2013 when Lampert appoints himself CEO. In just under 2.5 years with Lampert as CEO and Chairman the company’s sales keep falling, more stores are closed or sold, and the stock finds an all-time low of $11.13 – 25% lower than when Lampert took KMart public almost exactly 13 years ago – and 94% off its highs.
What happened?
Sears became a retailing juggernaut via innovation. When general stores were small and often far between, and stocking inventory was precious, Sears invented mail order catalogues. Over time almost every home in America was receiving 1, or several, catalogues every year. They were a major source of purchases, especially by people living in non-urban communities. Then Sears realized it could open massive stores to sell all those things in its catalogue, and the company pioneered very large, well stocked stores where customers could buy everything from clothes to tools to appliances to guns. As malls came along, Sears was again a pioneer “anchoring” many malls and obtaining lower cost space due to the company’s ability to draw in customers for other retailers.
To help customers buy more Sears created customer installment loans. If a young couple couldn’t afford a stove for their new home they could buy it on terms, paying $10 or $15 a month, long before credit cards existed. The more people bought on their revolving credit line, and the more they paid Sears, the more Sears increased their credit limit. Sears was the “go to” place for cash strapped consumers. (Eventually, this became what we now call the Discover card.)
In 1930 Sears expanded the Allstate tire line to include selling auto insurance – and consumers could not only maintain their car at Sears they could insure it as well. As its customers grew older and more wealthy, many needed help with financia advice so in 1981 Sears bought Dean Witter and made it possible for customers to figure out a retirement plan while waiting for their tires to be replaced and their car insurance to update.
To put it mildly, Sears was the most innovative retailer of all time. Until the internet came along. Focused on its big stores, and its breadth of products and services, Sears kept trying to sell more stuff through those stores, and to those same customers. Internet retailing seemed insignificantly small, and unappealing. Heck, leadership had discontinued the famous catalogues in 1993 to stop store cannibalization and push people into locations where the company could promote more products and services. Focusing on its core customers shopping in its core retail locations, Sears leadership simply ignored upstarts like Amazon.com and figured its old success formula would last forever.
But they were wrong. The traditional Sears market was niched up across big box retailers like Best Buy, clothiers like Kohls, tool stores like Home Depot, parts retailers like AutoZone, and soft goods stores like Bed, Bath & Beyond. The original need for “one stop shopping” had been overtaken by specialty retailers with wider selection, and often better pricing. And customers now had credit cards that worked in all stores. Meanwhile, for those who wanted to shop for many things from home the internet had taken over where the catalogue once began. Leaving Sears’ market “hollowed out.” While KMart was simply overwhelmed by the vast expansion of WalMart.
What should Lampert have done?
There was no way a cost cutting strategy would save KMart or Sears. All the trends were going against the company. Sears was destined to keep losing customers, and sales, unless it moved onto trends. Lampert needed to innovate. He needed to rapidly adopt the trends. Instead, he kept cutting costs. But revenues fell even faster, and the result was huge paper losses and an outpouring of cash.
To gain more insight, take a look at Jeff Bezos. But rather than harp on Amazon.com’s growth, look instead at the leadership he has provided to The Washington Post since acquiring it just over 2 years ago. Mr. Bezos did not try to be a better newspaper operator. He didn’t involve himself in editorial decisions. Nor did he focus on how to drive more subscriptions, or sell more advertising to traditional customers. None of those initiatives had helped any newspaper the last decade, and they wouldn’t help The Washington Post to become a more relevant, viable and profitable company. Newspapers are a dying business, and Bezos could not change that fact.
Mr. Bezos focused on trends, and what was needed to make The Washington Post grow. Media is under change, and that change is being created by technology. Streaming content, live content, user generated content, 24×7 content posting (vs. deadlines,) user response tracking, readers interactivity, social media connectivity, mobile access and mobile content — these are the trends impacting media today. So that was where he had leadership focus. The Washington Post had to transition from a “newspaper” company to a “media and technology company.”
So Mr. Bezos pushed for hiring more engineers – a lot more engineers – to build apps and tools for readers to interact with the company. And the use of modern media tools like headline testing. As a result, in October, 2015 The Washington Post had more unique web visitors than the vaunted New York Times. And its lead is growing. And while other newspapers are cutting staff, or going out of business, the Post is adding writers, editors and engineers. In a declining newspaper market The Washington Post is growing because it is using trends to transform itself into a company readers (and advertisers) value.
CEO Lampert could have chosen to transform Sears Holdings. But he did not. He became a very, very active “hands on” manager. He micro-managed costs, with no sense of important trends in retail. He kept trying to take cash out, when he needed to invest in transformation. He should have sold the real estate very early, sensing that retail was moving on-line. He should have sold outdated brands under intense competitive pressure, such as Kenmore, to a segment supplier like Best Buy. He then should have invested that money in technology. Sears should have been a leader in shopping apps, supplier storefronts, and direct-to-customer distribution. Focused entirely on defending Sears’ core, Lampert missed the market shift and destroyed all the value which initially existed in the great retail merger he created.
Impact?
Every company must understand critical trends, and how they will apply to their business. Nobody can hope to succeed by just protecting the core business, as it can be made obsolete very, very quickly. And nobody can hope to change a trend. It is more important than ever that organizations spend far less time focused on what they did, and spend a lot more time thinking about what they need to do next. Planning needs to shift from deep numerical analysis of the past, and a lot more in-depth discussion about technology trends and how they will impact their business in the next 1, 3 and 5 years.
Sears Holdings was a 13 year ride. Investor hope that Lampert could cut costs enough to make Sears and KMart profitable again drove the stock very high. But the reality that this strategy was impossible finally drove the value lower than when the journey started. The debacle has ruined 2 companies, thousands of employees’ careers, many shopping mall operators, many suppliers, many communities, and since 2007 thousands of investor’s gains. Four years up, then 9 years down. It happened a lot faster than anyone would have imagined in 2003 or 2004. But it did.
And it could happen to you. Invert your strategic planning time. Spend 80% on trends and scenario planning, and 20% on historical analysis. It might save your business.

by Adam Hartung | Feb 11, 2016 | Current Affairs, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in
USAToday alerted investors that when Sears Holdings reports results 2/25/16 they will be horrible. Revenues down another 8.7% vs. last year. Same store sales down 7.1%. To deal with ongoing losses the company plans to close another 50 stores, and sell another $300million of assets. For most investors, employees and suppliers this report could easily be confused with many others the last few years, as the story is always the same. Back in January, 2014 CNBC headlined “Tracking the Slow Death of an Icon” as it listed all the things that went wrong for Sears in 2013 – and they have not changed two years later. The brand is now so tarnished that Sears Holdings is writing down the value of the Sears name by another $200million – reducing intangible value from the $4B at origination in 2004 to under $2B.
This has been quite the fall for Sears. When Chairman Ed Lampert fashioned the deal that had formerly bankrupt Kmart buying Sears in November, 2004 the company was valued at $11billion and 3,500 stores. Today the company is valued at $1.6billion (a decline of over 85%) and according to Reuters has just under 1,700 stores (a decline of 51%.) According to Bloomberg almost no analysts cover SHLD these days, but one who does (Greg Melich at Evercore ISI) says the company is no longer a viable business, and expects bankruptcy. Long-term Sears investors have suffered a horrible loss.
When I started business school in 1980 finance Professor Bill Fruhan introduced me to a concept that had never before occurred to me. Value Destruction. Through case analysis the good professor taught us that leadership could make decisions that increased company valuation. Or, they could make decisions that destroyed shareholder value. As obvious as this seems, at the time I could not imagine CEOs and their teams destroying shareholder value. It seemed anathema to the entire concept of business education. Yet, he quickly made it clear how easily misguided leaders could create really bad outcomes that seriously damaged investors.
 As a case study in bad leadership, Sears under Chairman Lampert offers great lessons in Value Destruction that would serve Professor Fruhan’s teachings well:
As a case study in bad leadership, Sears under Chairman Lampert offers great lessons in Value Destruction that would serve Professor Fruhan’s teachings well:
1 – Micro-management in lieu of strategy. Mr. Lampert has been merciless in his tenacity to manage every detail at Sears. Daily morning phone calls with staff, and ridiculously tight controls that eliminate decision making by anyone other than the top officers. Additionally, every decision by the officers was questioned again and again. Explanations took precedent over action as micro-management ate up management’s time, rather than trying to run a successful company. While store employees and low- to mid-level managers could see competition – both traditional and on-line – eating away at Sears customers and core sales, they were helpless to do anything about it. Instead they were forced to follow orders given by people completely out of touch with retail trends and customer needs. Whatever chance Sears and Kmart had to grow the chain against intense competition it was lost by the Chairman’s need to micro-manage.
2 – Manage-by-the-numbers rather than trends. Mr. Lampert was a finance expert and former analyst turned hedge fund manager and investor. He truly believed that if he had enough numbers, and he studied them long enough, company success would ensue. Unfortunately, trends often are not reflected in “the numbers” until it is far, far too late to react. The trend to stores that were cleaner, and more hip with classier goods goes back before Lampert’s era, but he completely missed the trend that drove up sales at Target, H&M and even Kohl’s because he could not see that trend reflected in category sales or cost ratios. Merchandising – from buying to store layout and shelf positioning – are skills that go beyond numerical analysis but are critical to retail success. Additionally, the trend to on-line shopping goes back 20 years, but the direct impact on store sales was not obvious until customers had long ago converted. By focusing on numbers, rather than trends, Sears was constantly reacting rather than being proactive, and thus constantly retreating, cutting stores and cutting product lines.
3 – Seeking confirmation rather than disagreement. Mr. Lampert had no time for staff who did not see things his way. Mr. Lampert wanted his management team to agree with him – to confirm his Beliefs, Interpretations, Assumptions and Strategies — to believe his BIAS. By seeking managers who would confirm his views, and execute, rather than disagree Mr. Lampert had no one offering alternative data, interpretations, strategies or tactics. And, as Mr. Lampert’s plans kept faltering it led to a revolving door of managers. Leaders came and went in a year or two, blamed for failures that originated at the Chairman’s doorstep. By forcing agreement, rather than disagreement and dialogue, Sears lacked options or alternatives, and the company had no chance of turning around.
4 – Holding assets too long. In 2004 Sears had a LOT of assets. Many that could likely be redeployed at a gain for shareholders. Sears had many owned and leased store locations that were highly valuable with real estate prices climbing from then through 2008. But Mr. Lampert did not spin out that real estate in a REIT, capturing the value for SHLD shareholders while the timing was good. Instead he held those assets as real estate in general plummeted, and as retail real estate fell even further as more revenue shifted to e-commerce. By the time he was ready to sell his REIT much of the value was depleted.
Additionally, Sears had great brands in 2004. DieHard batteries, Craftsman tools, Kenmore appliances and Lands End apparel were just 4 household brands that still had high customer appeal and tremendous value. Mr. Lampert could have sold those brands to another retailer (such as selling DieHard to WalMart, for example) as their house brands, capturing that value. Or he could have mass marketd the brand beyond the Sears store to increase sales and value. Or he could have taken one or more brands on-line as a product leader and “category killer” for ecommerce customers. But he did not act on those options, and as Sears and Kmart stores faded, so did these brands – which largely no longer have any value. Had he sold when value was high there were profits to be made for investors.
5 – Hubris – unfailingly believing in oneself regardless the outcomes. In May, 2012 I wrote that Mr. Lampert was the 2nd worst CEO in America and should fire himself. This was not a comment made in jest. His initial plans had all panned out very badly, and he had no strategy for a turnaround. All results, from all programs implemented during his reign as Chairman had ended badly. Yet, despite these terrible numbers Mr. Lampert refused to recognize he was the wrong person in the wrong job. While it wasn’t clear if anyone could turn around the problems at Sears at such a late date, it was clear Mr. Lampert was not the person to do it. If Mr. Lampert had been as self-analytical as he was critical of others he would have long before replaced himself as the leader at Sears. But hubris would not allow him to do this, he remained blind to his own failings and the terrible outcome of a failed company was pretty much sealed.
From $11B valuation and a $92/share stock price at time of merging KMart and Sears, to a $1.6B valuation and a $15/share stock price. A loss of $9.4B (that’s BILLION DOLLARS). That is amazing value destruction. In a world where employees are fired every day for making mistakes that cost $1,000, $100 or even $10 it is a staggering loss created by Mr. Lampert. At the very least we should learn from his mistakes in order to educate better, value creating leaders.
by Adam Hartung | Oct 16, 2015 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Lifecycle
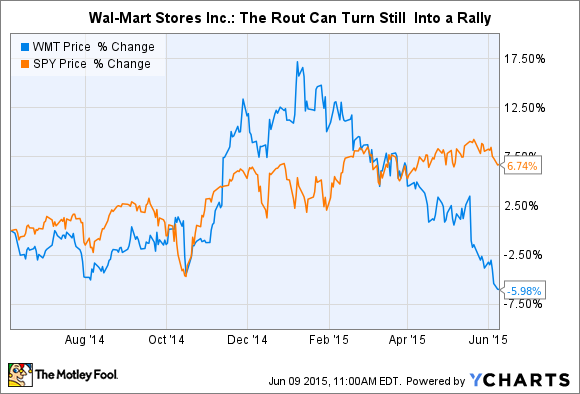
Wal-Mart market value took a huge drop on Wednesday. In fact, the worst valuation decline in its history. That decline continued on Thursday. Since the beginning of 2015 Wal-Mart has lost 1/3 of its value. That is an enormous ouch.
 But, if you were surprised, you should not have been. The telltale signs that this was going to happen have been there for years. Like most stock market moves, this one just happened really fast. The “herd behavior” of investors means that most people don’t move until some event happens, and then everyone moves at once carrying out the implications of a sea change in thinking about a company’s future.
But, if you were surprised, you should not have been. The telltale signs that this was going to happen have been there for years. Like most stock market moves, this one just happened really fast. The “herd behavior” of investors means that most people don’t move until some event happens, and then everyone moves at once carrying out the implications of a sea change in thinking about a company’s future.
All the way back in October, 2010 I wrote about “The Wal-Mart Disease.” This is the disease of constantly focusing on improving your “core” business, while market shifts around you increasingly make that “core” less relevant, and less valuable. In the case of Wal-Mart I pointed out that an absolute maniacal focus on retail stores and low-cost operations, in an effort to be the low price retailer, was being made obsolete by on-line retailers who had costs that are a fraction of Wal-Mart’s expensive real estate and armies of employees.
At that time WMT was about $54/share. I recommended nobody own the stock.
In May, 2011 I reiterated this problem at Wal-Mart in a column that paralleled the retailer with software giant Microsoft, and pointed out that because of financial machinations not all earnings are equal. I continued to say that this disease would cripple Wal-Mart. Six months had passed, and the stock was about $55.
By February, 2012 I pointed out that the big reorganization at Wal-Mart was akin to re-arranging deck chairs on a sinking ship and said nobody should own the stock. It was up, however, trading at $61.
At the end of April, 2012 the Wal-Mart Mexican bribery scandal made the press, and I warned investors that this was a telltale sign of a company scrambling to make its numbers – and pushing the ethical (if not legal) envelope in trying to defend and extend its worn out success formula. The stock was $59.
Then in July, 2014 a lawsuit was filed after an overworked Wal-Mart truck driver ran into a car killing James McNair and seriously injuring comedian Tracy Morgan. Again, I pointed out that this was a telltale sign of an organization stretching to try and make money out of a business model that was losing its ability to sustain profits. Market shifts were making it ever harder to keep up with emerging on-line competitors, and accidents like this were visible cracks in the business model. But the stock was now $77. Most investors focused on short-term numbers rather than the telltale signs of distress.
In January, 2015 I pointed out that retail sales were actually down 1% for December, 2014. But Amazon.com had grown considerably. The telltale indication of a rotting traditional retail brick-and-mortar approach was showing itself clearly. Wal-Mart was hitting all time highs of around $87, but I reiterated my recommendation that investors escape the stock.
By July, 2015 we learned that the market cap of Amazon now exceeded that of Wal-Mart. Traditional retail struggles were apparent on several fronts, while on-line growth remained strong. Bigger was not better in the case of Wal-Mart vs. Amazon, because bigger blinded Wal-Mart to the absolute necessity for changing its business model. The stock had fallen back to $72.
Now Wal-Mart is back to $60/share. Where it was in January, 2012 and only 10% higher than when I first said to avoid the stock in 2010. Five years up, then down the roller coaster.
From October of 2010 through January, 2015 I looked dead wrong on Wal-Mart. And the folks who commented on my columns here at this journal and on my web site, or emailed me, were profuse in pointing out that my warnings seemed misguided. Wal-Mart was huge, it was strong and it would dominate was the feedback.
But I kept reiterating the point that long-term investors must look beyond short-term reported sales and earnings. Those numbers are subject to considerable manipulation by management. Further, short-term operating actions, like shorter hours, lower pay, reduced benefits, layoffs and gouging suppliers can all prop up short-term financials at the expense of recognizing the devaluation of the company’s long-term strategy.
Investors buy and hold. They hold until they see telltale signs of a company not adjusting to market shifts. Short-term traders will say you could have bought in 2010, or 2012, and held into 2014, and then jumped out and made a profit. But, who really can do that with forethought? Market timing is a fools game. The herd will always stay too long, then run out too late. Timers get trampled in the stampede more often than book gains.
In this week’s announcement Wal-Mart executives provided more telltale signs of their problems, and the fact that they don’t know how to fix them, and therefore won’t.
- Wal-Mart is going to spend $20B to buy back stock in order to prop up the price. This is the most obvious sign of a company that doesn’t know how to keep up its valuation by growing profits.
- Wal-Mart will spend $11B on sprucing up and opening stores. Really. The demand for retail space has been declining at 4-6%/year for a decade, and retail business growth is all on-line, yet Wal-Mart is still massively investing in its old “core” business.
- Wal-Mart will spend $1.1B on e-commerce. That is the proverbial “drop in the competitors bucket.” Amazon.com alone spent $8.9B in 2014 growing its on-line business.
- Wal-Mart admits profits will decline in the next year. It is planning for a growth stall. Yet, we know that statistically only 7% of companies that have a growth stall ever go on to maintain a consistent growth rate of a mere 2%. In other words, Wal-Mart is projecting the classic “hockey stick” forecast. And investors are to believe it?
The telltale signs of an obsolete business model have been present at Wal-Mart for years, and continue.
In 2003 Sears Holdings was $25/share. In 2004 Sears bought K-Mart, and the stock was $40. I said don’t go near it, as all the signs were bad and the merger was ill-conceived. Despite revenue declines, consistent losses, a revolving door at the executive offices and no sign of any plan to transform the battered, outdated retail giant against growing on-line competition investors believed in CEO Ed Lampert and bid the stock up to $77 in early 2011. (I consistently pointed out the telltale signs of trouble and recommended selling the stock.)
By the end of 2012 it was clear Sears was irrelevant to holiday shoppers, and the stock was trading again at $40. Now, SHLD is $25 – where it was 12 years ago when Mr. Lampert started his machinations. Again, only a market timer could have made money in this company. For long-term investors, the signs were all there that this was not a place to put your money if you want to have capital growth for retirement.
There will be plenty who will call Wal-Mart a “value” stock and recommend investors “buy on weakness.” But Wal-Mart is no value. It is becoming obsolete, irrelevant – increasingly looking like Sears. The likelihood of Wal-Mart falling to $20 (where it was at the beginning of 1998 before it made an 18 month run to $50 more than doubling its value) is far higher than ever trading anywhere near its 2015 highs.

by Adam Hartung | Jun 30, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Leadership
24×7 Wall Street just released its fourth annual analysis of the worst companies to work for in America. By looking across all four reports it is possible to identify likely problems which will be valuable for investors, employees (current and prospective,) suppliers and communities to know.
 Trend 1- Low minimum wages & “Wage gap” issues remain a big deal
Trend 1- Low minimum wages & “Wage gap” issues remain a big deal
The lists are dominated by retailers. Of the 30 unique companies identified, exactly half (15) were retailers. A handful were on the list 2 or more years. Consistently these employees complained about low wages.
By paying minimum wage, and often refusing to hire employees full time, the companies keep costs of brick and mortar store operations lower.
However, this takes a toll on employee morale as overall pay does not meet minimum living standards. Further employees feel heavily overworked and stressed, while having no job security. Often this leads to employee unhappiness with senior management, frequently offering low evaluations of the CEO – who makes 1,000 times their annual earnings.
As employees fight for higher wages, and a reduction in the “wage gap,” it will apply pressure to the sustainability of these retailers who rely on very low pay to maintain (or enhance) profits. The trend to a higher minimum wage will challenge profit growth – or maintenance – in these companies.
Trend 2 – Employees often “see change coming” and become negatively vocal
Jos. A Banks jumped onto the list as #4 in 2013. Just before a major shake-up and being acquired by Men’s Wearhouse. Family Dollar also appeared on the list in 2014 (#9,) only to be embroiled in a takeover battle with Dollar General, and finally aquired by Dollar Tree within 7 months. Office Max appeared on the list (#5) in 2012, and was acquired by Office Depot 8 months later. And, of course, Radio Shack made the list in 2012 (#3,) 2013 (#5) and 2014 (#11) only to file bankruptcy in 2015.
Employees can see when something bad is impending, likely jeopardizing their livelihoods, and start talking about it.
Similarly, growing internet threats are often picked-up by employees. hh Gregg employees started complaining loudly in 2014 (#8) as their 100% commission compensation became threatened by a growing Amazon.com. And that same year Books-A-Million was #1 on the list, as part time staffers saw the same advancing Amazon. And in 2012 Game Stop (#10) employees could see how the advancing Netflix and Hulu threatened the “core business” and started to light up the complaint section.
Trend 3 – Ignoring employee unhappiness while focusing on earnings can portend a disaster
Sears and KMart (collectively Sears Holdings) made the list in 3 of the 4 years. The stock was $66 in June, 2011, and $55 in 6/12 when it made #6. By 6/13 it had declined to $39, and made the list at #7. Starting 6/14 the stock was reasonably flat, and missed the list. But then in 6/17 the stock fell to 27 and reappeared twice – as both Sears and KMart.
Employees have consistently expressed their dismay with CEO Ed Lampert, and 80% actively dislike his leadership. After the Radio Shack experience, there is ample reason to listen more to these employees than the CEO who keeps promising a turnaround – amidst a long string of large quarterly losses and declining sales.
But this also opens the door for looking at some stocks that have defied employee unrest. Dillard’s made the list all 4 years. In 2012 the stock rose from $54 to $66, yet appeared #2 on the list. In 2013 the stock rose to $85 as it made the list #3. 2014 the stock made it to $119, and was sixth. In 2015 the stock peaked at $149, but has recently declined to $111 as it made the list #2.
Similarly Express Scripts rose from $53 in 2012 to $62 in 2013 when it appeared on the list in position #2. In 2014 it rose to $71 as it remained #2. And it 2015 the stock is at $85 as it topped the list #1.
It would be worthwhile to look at the clues employees are sending. Express Scripts employees are loudly complaining (louder than literally any other company) across multiple years of being overworked, overstressed, underpaid and without any job security. As are Dillard’s employees, who are the most outspoken in retail. How long will profit improvements be sustainable in these companies?
While the data is less clear on Dollar General, it appeared on the list as #4 in 2013. Then Family Dollar appeared on the list as #9 in 2014. Dollar General subsequently tried buying Family Dollar, and reappeared on the list as #10 in 2015. What are employees saying about the sustainability of the “dollar store” segment in a very tough retail market with growing internet competitors?
Any CEO can slash employee costs and payroll for a few years, but at some point the model simply collapses – aka, Sears Holdings and Radio Shack. Or there is a loss of identity as suffered by Office Max, Jos. A Banks and Family Dollar. It would be worthwhile for anyone to listen carefully to the feedback of these employees before investing in company equity, investing one’s livelihood as an employee, investing one’s resources to be a supplier, or investing one’s tax base as a community official.
There are a number of “one off” issues on the list. Companies appear once primarily due to bad CEO performance (Xerox, #5 this year, HP #8 in 2012 as the revolving door on the CEO office reached a high pitch.) Or due to some change in market competition.
But it is possible to look through these issues – which could become future trends but show limited insight today – to see that an aggregated employee view of leadership offers insights not always found in the P&L or management’s discussion of earnings. If you choose to put your resources into these companies, be aware of the risks warnings being sent by employees!
Please refer to the 24x7WallStreet.com site for deeper information on how the list was compiled, who is on each list, and their editor’s opinions of employee comments. 24×7 list in 2015 – 24×7 list in 2014 – 24×7 list in 2013 – 24×7 list in 2012





 As a case study in bad leadership, Sears under Chairman Lampert offers great lessons in Value Destruction that would serve Professor Fruhan’s teachings well:
As a case study in bad leadership, Sears under Chairman Lampert offers great lessons in Value Destruction that would serve Professor Fruhan’s teachings well:
