by Adam Hartung | Apr 5, 2016 | Disruptions, In the Rapids, Leadership, Web/Tech
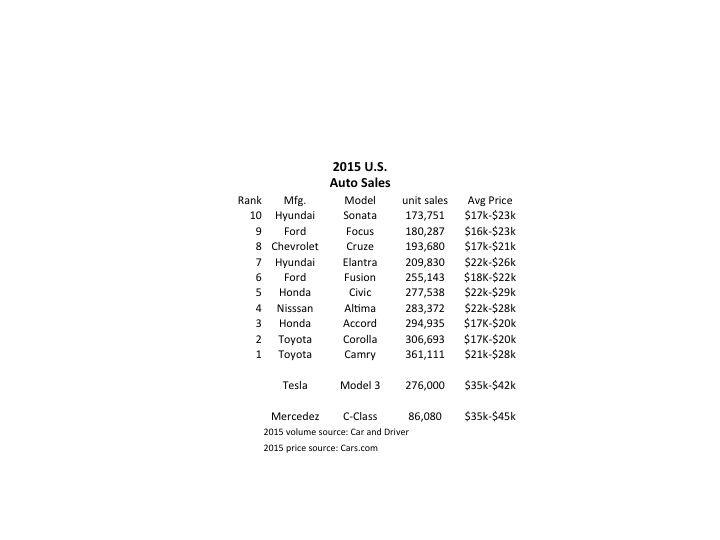
Tesla started taking orders for the Model 3 last week, and the results were remarkable. In 24 hours the company took $1,000 deposits for 198,000 vehicles. By end of Saturday the $1,000 deposits topped 276,000 units. And for a car not expected to be available in any sort of volume until 2017. Compare that with the top selling autos in the U.S. in 2015:
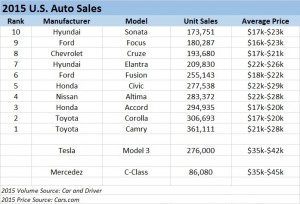 Remarkably, the Model 3 would rank as the 6th best selling vehicle all of last year! And with just a few more orders, it will likely make the top 5 – or possibly top 3! And those are orders placed in just one week, versus an entire year of sales for the other models. And every buyer is putting up a $1,000 deposit, something none of the buyers of top 10 cars did as they purchased product widely available in inventory. [Update 7 April – Tesla reports sales exceed 325,000, which would make the Model 3 the second best selling car in the USA for the entire year 2015 – accomplished in less than one week.]
Remarkably, the Model 3 would rank as the 6th best selling vehicle all of last year! And with just a few more orders, it will likely make the top 5 – or possibly top 3! And those are orders placed in just one week, versus an entire year of sales for the other models. And every buyer is putting up a $1,000 deposit, something none of the buyers of top 10 cars did as they purchased product widely available in inventory. [Update 7 April – Tesla reports sales exceed 325,000, which would make the Model 3 the second best selling car in the USA for the entire year 2015 – accomplished in less than one week.]
Even more astonishing is the average selling price. Note that top 10 cars are not highly priced, mostly in the $17,000 to $25,000 price range. But the Tesla is base priced at $35,000, and expected with options to sell closer to $42,000. That is almost twice as expensive as the typical top 10 selling auto in the U.S.
Tesla has historically been selling much more expensive cars, the Model S being its big seller in 2015. So if we classify Tesla as a “luxury” brand and compare it to like-priced Mercedes Benz C-Class autos we see the volumes are, again, remarkable. In under 1 week the Model 3 took orders for 3 times the volume of all C-Class vehicles sold in the U.S. in 2015.
[Car and Driver top 10 cars; Mercedes Benz 2015 unit sales; Tesla 2015 unit sales; Model 3 pricing]
Although this has surprised a large number of people, the signs were all pointing to something extraordinary happening. The Tesla Model S sold 50,000 vehicles in 2015 at an average price of $70,000 to $80,000. That is the same number of the Mercedes E-Class autos, which are priced much lower in the $50,000 range. And if you compare to the top line Mercedes S-Class, which is only slightly more expensive at an average $90,0000, the Model S sold over 2 times the 22,000 units Mercedes sold. And while other manufacturers are happy with single digit percentage volume growth, in Q4 Tesla shipments were 75% greater in 2015 than 2014.
In other words, people like this brand, like these cars and are buying them in unprecedented numbers. They are willing to plunk down deposits months, possibly years, in advance of delivery. And they are paying the highest prices ever for cars sold in these volumes. And demand clearly outstrips supply.
Yet, Tesla is not without detractors. From the beginning some analysts have said that high prices would relegate the brand to a small niche of customers. But by outselling all other manufacturers in its price point, Tesla has demonstrated its cars are clearly not a niche market. Likewise many analysts argued that electric cars were dependent on high gasoline prices so that “economic buyers” could justify higher prices. Yet, as gasoline prices have declined to prices not seen for nearly a decade Tesla sales keep going up. Clearly Tesla demand is based on more than just economic analysis of petroleum prices.
People really like, and want, Tesla cars. Even if the prices are higher, and if gasoline prices are low.
Emerging is a new group of detractors. They point to the volume of cars produced in 2015, and first quarter output of just under 15,000 vehicles, then note that Tesla has not “scaled up” manufacturing at anywhere near the necessary rate to keep customers happy. Meanwhile, constructing the “gigafactory” in Nevada to build batteries has slowed and won’t meet earlier expectations for 2016 construction and jobs. Even at 20,000 cars/quarter, current demand for Model S and Model 3 They project lots of order cancellations would take 4.5 years to fulfill.
Which leads us to the beauty of sales growth. When products tap an under- or unfilled need they frequently far outsell projections. Think about the iPod, iPhone and iPad. There is naturally concern about scaling up production. Will the money be there? Can the capacity come online fast enough?
Of course, of all the problems in business this is one every leader should want. It is certainly a lot more fun to worry about selling too much rather than selling too little. Especially when you are commanding a significant price premium for your product, and thus can be sure that demand is not an artificial, price-induced variance.
With rare exceptions, investors understand the value of high sales at high prices. When gross margins are good, and capacity is low, then it is time to expand capacity because good returns are in the future. The Model 3 release projects a backlog of almost $12B. Booked orders at that level are extremely rare. Further, short-term those orders have produced nearly $300million of short-term cash. Thus, it is a great time for an additional equity offering, possibly augmented with bond sales, to invest rapidly in expansion. Problematic, yes. Insolvable, highly unlikely.
On the face of it Tesla appears to be another car company. But something much more significant is afoot. This sales level, at these prices, when the underlying economics of use seem to be moving in the opposite direction indicates that Tesla has tapped into an unmet need. It’s products are impressing a large number of people, and they are buying at premium prices. Based on recent orders Tesla is vastly outselling competitive electric automobiles made by competitors, all of whom are much bigger and better resourced. And those are all the signs of a real Game Changer.
by Adam Hartung | Aug 2, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
eBay was once a game changer. When the internet was very young, and few businesses provided ecommerce, eBay was a pioneer. From humble beginnings selling Pez dispensers, eBay grew into a powerhouse. Things we used to sell via garage sale we could now list on eBay. Small businesses could create stores on eBay to sell goods to customers they otherwise would never reach. And collectors as well as designers suddenly discovered all kinds of products they formerly could not find. eBay sales exploded, as traditional retail started it slide downward.
To augment growth eBay realized those selling needed a simple way to collect money from people who lacked a credit card. Many customers simply had no card, or didn’t trust giving out the information across the web. So eBay bought fledgling PayPal for $1.5B in 2002, in order to grease the wheels for faster ecommerce growth. And it worked marvelously.
But times have surely changed. Now eBay and Paypal have roughly the same revenue. About $8B/year each. eBay has run into stiff competition, as CraigsList has grown to take over the “garage sale” and small local business ecommerce. Simultaneously, powerhouse Amazon has developed its storefront business to a level of sophistication, and ease of use, that makes it viable for businesses from smallest to largest to sell products on-line. And far more companies have learned they can go it alone with internet sales, using search engine optimization (SEO) techniques as well as social media to drive traffic directly to their stores, bypassing storefronts entirely.
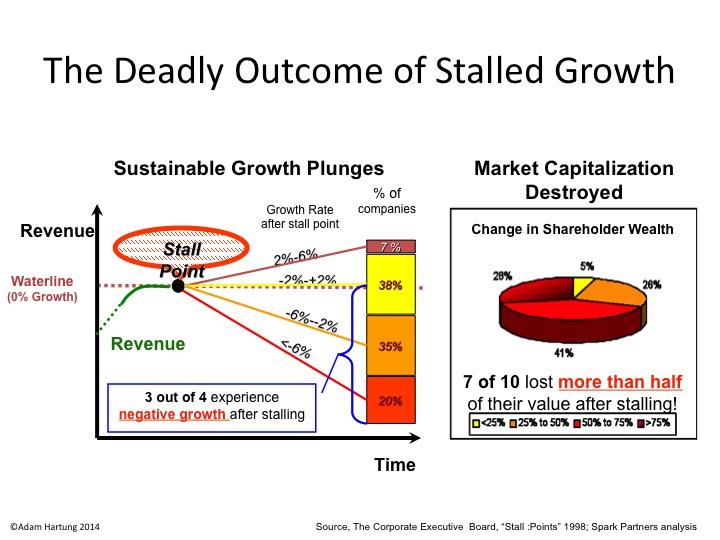
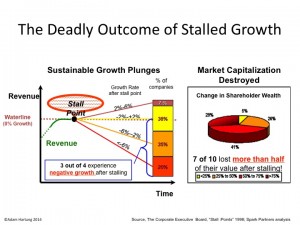 eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
On the other hand, Paypal has blossomed into a game changer in its own right. Not only does it support cash and credit card transactions for the growing legions of on-line shoppers, but it is providing full payment systems for providers like Uber and AirBnB. It’s tools support enterprise transactions in all currencies, including emerging bitcoin, and even provides international financial transactions as well as working capital for businesses.
Paypal is increasingly becoming a threat to traditional banks. Today most folks use a bank for depositing a pay check, and making payments. There are loans, but frequently that is shopped around irrespective of where you bank. Much like your credit cards, which most people acquire for their benefits rather than a relationship with the issuing bank. If customers increasingly make payments via Paypal, and borrow money via operations like Quicken Loans (a division of Intuit,) why do you need a bank? Discover Services, which now does offer cash deposits and loans on top of credit card services, has found that it can grow substantially by displacing traditional banks.
Paypal is today at the forefront of digital payments processing. It is a fast growing market, which will displace many traditional banks. And emerging competitors like Apple Pay and Google Wallet will surely change the market further – while aiding its growth. How it will shake out is unclear. But it is clear that Paypal is growing its revenue at 60% or greater since 2012, and at over 100%/quarter the last 2 quarters.
Paypal is now valued at about $47B. That is roughly the same as the #5 bank in America (according to assets) Bank of New York Mellon, and number 8 massive credit card issuer Capital One, as well as #9 PNC Bank – and over 50% higher valuation than #10 State Street. It is also about 50% higher than Intuit and Discover. Based on its current market leadership and position as likely game changer for the banking sector, Paypall is selling for about 8 times revenue. If its revenue continues to grow at 100%/quarter, however, revenues will reach over $38B in a year making the Price/Revenue multiple of today only 1.25.
Meanwhile, eBay is valued at about $34B. Given that all which is left in eBay is an outdated on-line ecommerce conglomerator, stuck in a growth stall, that valuation is far harder to justify. It is selling at about 4.25x revenue. But if revenues continue declining, as they have for 2 consecutive quarters, this multiple will expand. And values will be harder and harder to justify as investors rely on hope of a turnaround.
eBay was a game changer. But leadership became complacent, and now it is very likely overvalued. Just as Yahoo became when its value relied on its holdings of Alibaba rather as its organic business shrank. Meanwhile Paypal is the leader in a rapidly growing market that is likely to change the face of not just how we pay, but how we do personal and business finance. There is no doubt which is more valuable today, and likely to be in the future.

by Adam Hartung | Feb 12, 2015 | Current Affairs, Disruptions, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Despite huge fanfare at launch, after a few brief months Google Glass is no longer on the market. The Amazon Fire Phone was also launched to great hype, yet sales flopped and the company recently took a $170M write off on inventory.
Fortune mercilessly blamed Fire Phone’s failure on CEO Jeff Bezos. The magazine blamed him for micromanaging the design while overspending on development, manufacturing and marketing. To Fortune the product was fatally flawed, and had no chance of success according to the article.
Similarly, the New York Times blasted Google co-founder and company leader Sergie Brin for the failure of Glass. He was held responsible for over-exposing the product at launch while not listening to his own design team.

Both these articles make the common mistake of blaming failed new products on (1) the product itself, and (2) some high level leader that was a complete dunce. In these stories, like many others of failed products, a leader that had demonstrated keen insight, and was credited with brilliant work and decision-making, simply “went stupid” and blew it. Really?
Unfortunately there are a lot of new products that fail. Such simplistic explanations do not help business leaders avoid a future product flop. But there are common lessons to these stories from which innovators, and marketers, can learn in order to do better in the future. Especially when the new products are marketplace disrupters; or as they are often called, “game changers.”

Do you remember Segway? The two wheeled transportation device came on the market with incredible fanfare in 2002. It was heralded as a game changer in how we all would mobilize. Founders predicted sales would explode to 10,000 units per week, and the company would reach $1B in sales faster than ever in history. But that didn’t happen. Instead the company sold less than 10,000 units in its first 2 years, and less than 24,000 units in its first 4 years. What was initially a “really, really cool product” ended up a dud.
There were a lot of companies that experimented with Segways. The U.S. Postal Service tested Segways for letter carriers. Police tested using them in Chicago, Philadelphia and D.C., gas companies tested them for Pennsylvania meter readers, and Chicago’s fire department tested them for paramedics in congested city center. But none of these led to major sales. Segway became relegated to niche (like urban sightseeing) and absurd (like Segway polo) uses.
Segway tried to be a general purpose product. But no disruptive product ever succeeds with that sort of marketing. As famed innovation guru Clayton Christensen tells everyone, when you launch a new product you have to find a set of unmet needs, and position the new product to fulfill that unmet need better than anything else. You must have a very clear focus on the product’s initial use, and work extremely hard to make sure the product does the necessary job brilliantly to fulfill the unmet need.
Nobody inherently needed a Segway. Everyone was getting around by foot, bicycle, motorcycle and car just fine. Segway failed because it did not focus on any one application, and develop that market as it enhanced and improved the product. Selling 100 Segways to 20 different uses was an inherently bad decision. What Segway needed to do was sell 100 units to a single, or at most 2, applications.
Segway leadership should have studied the needs deeply, and focused all aspects of the product, distribution, promotion, training, communications and pricing for that single (or 2) markets. By winning over users in the initial market Segway could have made those initial users very loyal, outspoken customers who would recommend the product again and again – even at a $4,000 price.
Segway should have pioneered an initial application market that could grow. Only after that could Segway turn to a second market. The first market could have been using Segway as a golfer’s cart, or as a walking assist for the elderly/infirm, or as a transport device for meter readers. If Segway had really focused on one initial market, developed for those needs, and won that market it would have started a step-wise program toward more applications and success. By thinking the general market would figure out how to use its product, and someone else would develop applications for specific market needs, Segway’s leaders missed the opportunity to truly disrupt one market and start the path toward wider success.
 The Fire Phone had a great opportunity to grow which it missed. The Fire Phone had several features making it great for on-line shopping. But the launch team did not focus, focus, focus on this application. They did not keep developing apps, databases and ways of using the product for retailing so that avid shoppers found the Fire Phone superior for their needs. Instead the Fire Phone was launched as a mass-market device. Its retail attributes were largely lost in comparisons with other general purpose smartphones.
The Fire Phone had a great opportunity to grow which it missed. The Fire Phone had several features making it great for on-line shopping. But the launch team did not focus, focus, focus on this application. They did not keep developing apps, databases and ways of using the product for retailing so that avid shoppers found the Fire Phone superior for their needs. Instead the Fire Phone was launched as a mass-market device. Its retail attributes were largely lost in comparisons with other general purpose smartphones.
People already had Apple iPhones, Samsung Galaxy phones and Google Nexus phones. Simultaneously, Microsoft was pushing for new customers to use Nokia and HTC Windows phones. There were plenty of smartphones on the market. Another smartphone wasn’t needed – unless it fulfilled the unmet needs of some select market so well that those specific users would say “if you do …. and you need…. then you MUST have a FirePhone.” By not focusing like a laser on some specific application – some specific set of unmet needs – the “cool” features of the Fire Phone simply weren’t very valuable and the product was easy for people to pass by. Which almost everyone did, waiting for the iPhone 6 launch.
This was the same problem launching Google Glass. Glass really caught the imagination of many tech reviewers. Everyone I knew who put on Glass said it was really cool. But there wasn’t any one thing Glass did so well that large numbers of folks said “I have to have Glass.” There wasn’t any need that Glass fulfilled so well that a segment bought Glass, used it and became religious about wearing Glass all the time. And Google didn’t improve the product in specific ways for a single market application so that users from that market would be attracted to buy Glass. In the end, by trying to be a “cool tool” for everyone Glass ended up being something nobody really needed. Exactly like Segway.
 Microsoft recently launched its Hololens. Again, a pretty cool gadget. But, exactly what is the target market for Hololens? If Microsoft proceeds down the road of “a cool tool that will redefine computing,” Hololens will likely end up with the same fate as Glass, Segway and Fire Phone. Hololens marketing and development teams have to find the ONE application (maybe 2) that will drive initial sales, cater to that application with enhancements and improvements to meet those specific needs, and create an initial loyal user base. Only after that can Hololens build future applications and markets to grow sales (perhaps explosively) and push Microsoft into a market leading position.
Microsoft recently launched its Hololens. Again, a pretty cool gadget. But, exactly what is the target market for Hololens? If Microsoft proceeds down the road of “a cool tool that will redefine computing,” Hololens will likely end up with the same fate as Glass, Segway and Fire Phone. Hololens marketing and development teams have to find the ONE application (maybe 2) that will drive initial sales, cater to that application with enhancements and improvements to meet those specific needs, and create an initial loyal user base. Only after that can Hololens build future applications and markets to grow sales (perhaps explosively) and push Microsoft into a market leading position.
All companies have opportunities to innovate and disrupt their markets. Most fail at this. Most innovations are thrown at customers hoping they will buy, and then simply dropped when sales don’t meet expectations. Most leaders forget that customers already have a way of getting their jobs done, so they aren’t running around asking for a new innovation. For an innovation to succeed launchers must identify the unmet needs of an application, and then dedicate their innovation to meeting those unmet needs. By building a base of customers (one at a time) upon which to grow the innovation’s sales you can position both the new product and the company as market leaders.

by Adam Hartung | Dec 24, 2014 | Defend & Extend, Disruptions
The Twelve Days of Christmas refers to an ancient festive season which begins on December 25. Colonial Americans modified this a bit by creating wreaths which they hung on neighbors’ doors on December 24 in anticipation of starting the festival of twelve days, which historically included feasts and celebrations.
Better known is the song “The Twelve Days of Christmas” which is believed to have started as a French folk rhyme, then later published in 1780 England. The song commemorates the twelve days of Christmas by offering ever grander gifts on each day of the holiday season.

So, it being Christmas Eve I am stealing this idea completely and offering my list of the 12 gifts investors would like to receive this holiday season from the companies into which they invest:
- Stop waxing eloquently about what you did last year or quarter. Yesterday has come and gone. Tell me about the future.
- Tell me about important trends that are going to impact your business. Is it demographics, aging population, the ecology movement, digitization, regulatory change, organic foods, mobility, mobile payments, nanotech, biotech… ? What are the critical trends that will impact your business going forward?
- Tell me your future scenarios. How will these trends change the way your customers and your company will behave? What are your most likely scenarios (and don’t try to be creative in an effort to preserve the status quo!)
- Tell me how the game will change for your industry over the next 1, 3, and 5 years. How will things be different for the industry, based on the trends and scenarios. The world is a fast changing place, and I want to know how this will change your industry.
- Tell me about the customers you lost last year. I gain no value from hearing about, or from, your favorite customers that love what currently do. Instead, bring me info on the customers who are buying alternative products, changing their behaviors, in ways that might impact sales. Even if these changes are only a small percentage of revenue.
- Tell me who the competitors are that are trying to change the game. Don’t tell me that these companies will fail. Tell me who the folks are that are really trying to do something new and different.
- Tell me about the fringe competitors. The ones you constantly say do not matter because they are small, or not part of the historical industry, or from some distant location where you don’t now compete. Tell me about the companies doing the new things which are seen as remote and immaterial, but are nibbling at the edges of the market.
- Tell me how you are reacting to potential game changers in your market. What are your plans to deal with disruptive competitors and disruptive innovations affecting your way of doing business? Other than working harder, faster, cheaper and planning to do better, what are you planning to do differently?
- Tell me how you intend to be a market game changer. Tell me what you intend to do that aligns with trends and leads the company toward fulfilling future scenarios as a market leader.
- Tell me what projects you are undertaking to experiment with new forms of competition, attracting new customers and creating new markets. Tell me about your teams that are working in white space to discover new opportunities.
- Tell me how you will disrupt your own organization so the constant effort to enhance the old success formula doesn’t kill any effort to do something new and different. How will you keep these experimental white space teams from being killed, or simply starved of resources, by the organizational inertia to defend and extend the status quo.
- Tell me the goals of these project teams, and how they will be nurtured and supplemented, as well as evaluated, to lead the company in new directions. Don’t just tell me that you will measure sales or profits, but rather real goals that measure market learning and ability to understand new customer behaviors.
If investors had this transparency, rather than merely reams and reams of historical data, just imagine how much smarter we could all invest.
Happy Holidays!

by Adam Hartung | Sep 30, 2014 | Current Affairs, Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Will the new Apple Pay product, revealed on iPhone 6 devices, succeed? There have been many entries into the digital mobile payments business, such as Google Wallet, Softcard (which had the unfortunate initial name of ISIS,) Square and Paypal. But so far, nobody has really cracked the market as Americans keep using credit cards, cash and checks.
But that looks like it might change, and Apple has a pretty good chance of making Apple Pay a success.
First, a look at some critical market changes. For decades we all thought credit card purchases were secure. But that changed in 2013, and picked up steam in 2014. With regularity we’ve heard about customer credit card data breaches at various retailers and restaurants. Smaller retailers like Shaw’s, Star Markets and Jewel caused some mild concern. But when top tier retailers like Target and Home Depot revealed security problems, across millions of accounts, people really started to notice. For the first time, some people are thinking an alternative might be a good idea, and they are considering a change.
In other words, there is now an underserved market. For a long time people were very happy using credit cards. But now, they aren’t as happy. There are people, still a minority, who are actively looking for an alternative to cash and credit cards. And those people now have a need that is not fully met. That means the market receptivity for a mobile payment product has changed.
Second let’s look at how Paypal became such a huge success fulfilling an underserved market. When people first began on-line buying transactions were almost wholly credit cards. But some customers lacked the ability to use credit cards. These folks had an underserved need, because they wanted to buy on-line but had no payment method (mailing checks or cash was risky, and COD shipments were costly and not often supported by on-line vendors.) Paypal jumped into that underserved market.
Quickly Paypal tied itself to on-line vendors, asking them to support their product. They went less to people who were underserved, and mostly to the infrastructure which needed to support the product. By encouraging the on-line retailers they could expand sales with Paypal adoption, Paypal gathered more and more sites. The 2002 acquisition by eBay was a boon, as it truly legitimized Paypal in minds of consumers and smaller on-line retailers.
After filling the underserved market, Paypal expanded as a real competitor for credit cards by adding people who simply preferred another option. Today Paypal accounts for $1 of every $6 spent on-line, a dramatic statistic. There are 153million Paypal digital wallets, and Paypal processes $203B of payments annually. Paypal supports 26 currencies, is in 203 markets, has 15,000 financial institution partners – all creating growth last year of 19%. A truly outstanding success story.
Back to traditional retail. As mentioned earlier, there is an underserved market for people who don’t want to use cash, checks or credit cards. They seek a solution. But just as Paypal had to obtain the on-line retailer backing to acquire the end-use customer, mobile payment company success relies on getting retailers to say they take that company’s digital mobile payment product.

Here is where Apple has created an advantage. Few end-use customers are terribly aware of retail beacons, the technology which has small (sometimes very small) devices placed in a store, fast food outlet, stadium or other environment which sends out signals to talk to smartphones which are in nearby proximity. These beacons are an “inside retail” product that most consumer don’t care about, just like they don’t really care about the shelving systems or price tag holders in the store.
Launched with iOS 7, Apple’s iBeacon has become the leader in this “recognize and push” technology. Since Apple installed Beacons in its own stores in December, 2013 tens of thousands of iBeacons have been installed in retailers and other venues. Macy’s alone installed 4,000 in 2014. Increasingly, iBeacons are being used by retailers in conjunction with consumer goods manufacturers to identify who is shopping, what they are buying, and assist them with product information, coupons and other purchase incentives.
Thus, over the last year Apple has successfully been courting the retailers, who are the infrastructure for mobile payments. Now, as the underserved payment issue comes to market it is natural for retailers to turn to the company with which they’ve been working on their “infrastructure” products.
Apple has an additional great benefit because it has by far the largest installed base of smartphones, and its products are very consistent. Even though Android is a huge market, and outsells iOS, the platform is not consistent because Android on Samsung is not like Android on Amazon’s Fire, for example. So when a retailer reaches out for the alternative to credit cards, Apple can deliver the largest number of users. Couple that with the internal iBeacon relationship, and Apple is really well positioned to be the first company major retailers and restaurants turn to for a solution – as we’ve already seen with Apple Pay’s acceptance by Macy’s, Bloomingdales, Duane Reed, McDonald’s Staples, Walgreen’s, Whole Foods and others.
This does not guarantee Apple Pay will be the success of Paypal. The market is fledgling. Whether the need is strong or depth of being underserved is marked is unknown. How consumers will respond to credit card use and mobile payments long-term is impossible to gauge. How competitors will react is wildly unpredictable.
But, Apple is very well positioned to win with Apple Pay. It is being introduced at a good time when people are feeling their needs are underserved. The infrastructure is primed to support the product, and there is a large installed base of users who like Apple’s mobile products. The pieces are in place for Apple to disrupt how we pay for things, and possibly create another very, very large market. And Apple’s leadership has a history of successfully managing disruptive product launches, as we’ve seen in music (iPod,) mobile phones (iPhone) and personal technology tools (iPad.)

 Remarkably, the Model 3 would rank as the 6th best selling vehicle all of last year! And with just a few more orders, it will likely make the top 5 – or possibly top 3! And those are orders placed in just one week, versus an entire year of sales for the other models. And every buyer is putting up a $1,000 deposit, something none of the buyers of top 10 cars did as they purchased product widely available in inventory. [Update 7 April – Tesla reports sales exceed 325,000, which would make the Model 3 the second best selling car in the USA for the entire year 2015 – accomplished in less than one week.]
Remarkably, the Model 3 would rank as the 6th best selling vehicle all of last year! And with just a few more orders, it will likely make the top 5 – or possibly top 3! And those are orders placed in just one week, versus an entire year of sales for the other models. And every buyer is putting up a $1,000 deposit, something none of the buyers of top 10 cars did as they purchased product widely available in inventory. [Update 7 April – Tesla reports sales exceed 325,000, which would make the Model 3 the second best selling car in the USA for the entire year 2015 – accomplished in less than one week.]








