
by Adam Hartung | Sep 14, 2016 | Immigration, In the Rapids, Innovation, Telecom, Trends
I’m amazed about Americans’ debate regarding immigration. And all the rhetoric from candidate Trump about the need to close America’s borders.
I was raised in Oklahoma, which prior to statehood was called The Indian Territory. I was raised around the only real Native Americans. All the rest of us are immigrants. Some voluntarily, some as slaves. But the fact that people want to debate whether we allow people to become Americans seems to me somewhat ridiculous, since 98% of Americans are immigrants. The majority within two generations.
 Throughout America’s history, being an immigrant has been tough. The first ones had to deal with bad weather, difficult farming techniques, hostile terrain, wild animals – it was very difficult. As time passed immigrants continued to face these issues, expanding westward. But they also faced horrible living conditions in major cities, poor food, bad pay, minimal medical care and often abuse by the people already that previously immigrated.
Throughout America’s history, being an immigrant has been tough. The first ones had to deal with bad weather, difficult farming techniques, hostile terrain, wild animals – it was very difficult. As time passed immigrants continued to face these issues, expanding westward. But they also faced horrible living conditions in major cities, poor food, bad pay, minimal medical care and often abuse by the people already that previously immigrated.
And almost since the beginning, immigrants have been not only abused but scammed. Those who have resources frequently took advantage of the newcomers that did not. And this persists. Immigrants that lack a social security card are unable to obtain a driver’s license, unable to open bank accounts, unable to apply for credit cards, unable to even sign up for phone service. Thus they remain at the will of others to help them, which creates the opportunity for scamming.
Take for example an immigrant trying to make a phone call to his relatives back home. For most immigrants this means using a calling card. Only these cards are often a maze of fees, charges and complex rules that result in much of the card’s value being lost. A 10-minute call to Ghana can range from $2.86 to $8.19 depending on which card you use. This problem is so bad that the FCC has fined six of the largest card companies for misleading consumers about calling cards. They continue to advise consumers about fraud. And even Congress has held hearings on the problem.
One outcome of immigrants’ difficulties has been the ingenuity and innovativeness of Americans. To this day around the world people marvel at how clever Americans are, and how often America leads the world in developing new things. As a young country, and due to the combination of resources and immigrants’ tough situation, America frequently is first at developing new solutions to solve problems – many of which are problems that clearly affect the immigrant population.
So, back to that phone call. Some immigrants can use Microsoft Skype to talk with their relatives, using the Internet rather than a phone. But this requires the people back home have a PC and an internet connection. Both of which could be dicey. Another option would be to use something like Facebook’s WhatsApp, but this requires the person back home have either a PC or mobile device, and either a wireless connection or mobile coverage. And, again, this is problematic.
But once again, ingenuity prevails. A Romanian immigrant named Daniel Popa saw this problem, and set out to make communications better for immigrants and their families back home. In 2014 he founded QuickCall.com to allow users to make a call over wireless technology, but which can then interface with the old-fashioned wired (or wireless) telecom systems around the world. No easy task, since telephone systems are a complex environment of different international, national and state players that use a raft of different technologies and have an even greater set of complicated charging systems.
But this new virtual phone network, which links the internet to the traditional telecom system, is a blessing for any immigrant who needs to contact someone in a rural, or poor, location that still depends on phone service. If the person on the other end can access a WiFi system, then the calls are free. If the connection is to a phone system then the WiFi interface on the American end makes the call much cheaper – and performs far, far better than any other technology. QuickCall has built the carrier relationships around the world to make the connections far more seamless, and the quality far higher.
But like all disruptive innovations, the initial market (immigrants) is just the early adopter with a huge need. Being able to lace together an internet call to a phone system is pretty powerful for a lot of other users. Travelers heading to a remote location, like Micronesia, Africa or much of South America — and even Eastern Europe – can lower the cost of planning their trip and connect with locals by using QuickCall.com. And for most Americans traveling in non-European locations their cell phone service from Sprint, Verizon, AT&T or another carrier simply does not work well (if at all) and is very expensive when they arrive. QuickCall.com solves that problem for these travelers.
Small businesspeople who have suppliers, or customers, in these locations can use QuickCall.com to connect with their business partners at far lower cost. Businesses can even have their local partners obtain a local phone number via QuickCall.com and they can drive the cost down further (potentially to zero). This makes it affordable to expand the offshore business, possibly even establishing small scale customer support centers at the local supplier, or distributor, location.
In The Innovator’s Dilemma Clayton Christensen makes the case that disruptive innovations develop by targeting a customer with an unmet need. Usually the innovation isn’t as good as the current “standard,” and is also more costly. Today, making an international call through the phone system is the standard, and it is fairly cheap. But this solution is often unavailable to immigrants, and thus QuickCall.com fills their unmet need, and at a cost substantially lower than the infamous calling cards, and with higher quality than a pure WiFi option.
But now that it is established, and expanding to more countries – including developed markets like the U.K. – the technology behind QuickCall.com is becoming more mainstream. And its uses are expanding. And it is reducing the need for people to have international calling service on their wired or wireless phone because the available market is expanding, the quality is going up, and the cost is going down. Exactly the way all disruptive innovations grow, and thus threaten the entrenched competition.
The end-game may be some form of Facebook in-app solution. But that depends on Facebook or one of its competitors seizing this opportunity quickly, and learning all QuickCall.com already knows about the technology and customers, and building out that network of carrier relationships. Notice that Skype was founded in 2003, and acquired by Microsoft in 2011, and it still doesn’t have a major presence as a telecom replacement. Will a social media company choose to make the investment and undertake developing this new solution?
As small as QuickCall.com is – and even though you may have never heard of it – it is an example of a disruptive innovation that has been successfully launched, and is successfully expanding. It may seem like an impossibility that this company, founded by an immigrant to solve an unmet need of immigrants, could actually change the way everyone makes international calls. But, then again, few of us thought the iPhone and its apps would cause us to give up Blackberries and quit carrying our PCs around.
America is known for its ingenuity and innovations. We can thank our heritage as immigrants for this, as well as the immigrant marketplace that spurs new innovation. America’s immigrants have the need to succeed, and the unmet needs that create new markets for launching new solutions. For all those conservatives who fear “European socialism,” they would be wise to realize the tremendous benefits we receive from our immigrant population. Perhaps these naysayers should use QuickCall.com to connect with a few more immigrants and understand the benefits they bring to America.
by Adam Hartung | May 10, 2016 | Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
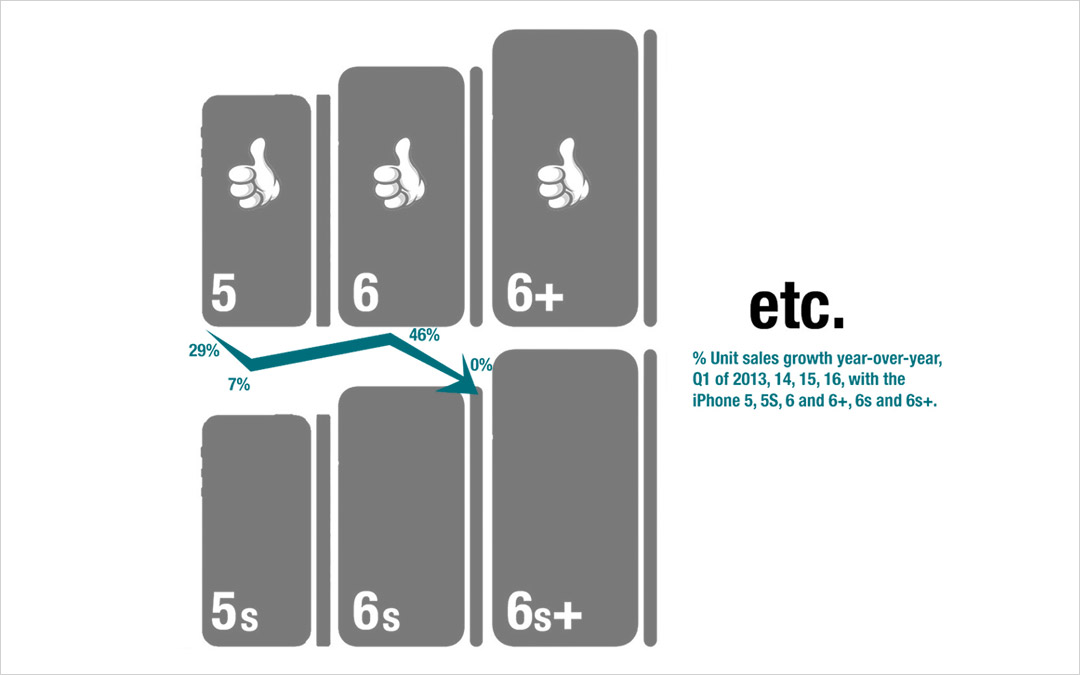
My last column focused on growth, and the risks inherent in a Growth stall. As I mentioned then, Apple will enter a Growth Stall if its revenue declines year-over-year in the current quarter. This forecasts Apple has only a 7% probability of consistently growing just 2%/year in the future.
This usually happens when a company falls into Defend & Extend (D&E) management. D&E management is when the bulk of management attention, and resources, flow into protecting the “core” business by seeking ways to use sustaining innovations (rather than disruptive innovations) to defend current customers and extend into new markets. Unfortunately, this rarely leads to high growth rates, and more often leads to compressed margins as growth stalls. Instead of working on breakout performance products, efforts are focused on ways to make new versions of old products that are marginally better, faster or cheaper.
 Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
For example, Apple’s CEO has trumpeted the company’s installed base of 1B iPhones, and stated they will be a future money maker. He bragged about the 20% growth in “services,” which are iPhone users taking advantage of Apple Music, iCloud storage, Apps and iTunes. This shows management’s desire to extend sales to its “installed base” with sustaining software innovations. Unfortunately, this 20% growth was a whopping $1.2B last quarter, which was 2.4% of revenues. Not nearly enough to make up for the decline in “core” iPhone, iPad or Mac sales of approximately $9.5B.
Apple has also been talking a lot about selling in China and India. Unfortunately, plans for selling in India were at least delayed, if not thwarted, by a decision on the part of India’s regulators to not allow Apple to sell low cost refurbished iPhones in the country. Fearing this was a cheap way to dispose of e-waste they are pushing Apple to develop a low-cost new iPhone for their market. Either tactic, selling the refurbished products or creating a cheaper version, are efforts at extending the “core” product sales at lower margins, in an effort to defend the historical iPhone business. Neither creates a superior product with new features, functions or benefits – but rather sustains traditional product sales.
Of even greater note was last week’s announcement that Apple inked a partnership with SAP to develop uses for iPhones and iPads built on the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platform. This announcement revealed that SAP would ask developers on its platform to program in Swift in order to support iOS devices, rather than having a PC-first mentality.
This announcement builds on last year’s similar announcement with IBM. Now 2 very large enterprise players are building applications on iOS devices. This extends the iPhone, a product long thought of as great for consumers, deeply into enterprise sales. A market long dominated by Microsoft. With these partnerships Apple is growing its developer community, while circumventing Microsoft’s long-held domain, promoting sales to companies as well as individuals.
And Apple has shown a willingness to help grow this market by introducing the iPhone 6se which is smaller and cheaper in order to obtain more traction with corporate buyers and corporate employees who have been iPhone resistant. This is a classic market extension intended to sustain sales with more applications while making no significant improvements in the “core” product itself.
And Apple’s CEO has said he intends to make more acquisitions – which will surely be done to shore up weaknesses in existing products and extend into new markets. Although Apple has over $200M of cash it can use for acquisitions, unfortunately this tactic can be a very difficult way to actually find new growth. Each would be targeted at some sort of market extension, but like Beats the impact can be hard to find.
Remember, after all revenue gains and losses were summed, Apple’s revenue fell $7.6B last quarter. Let’s look at some favorite analyst acquisition targets to explain:
- Box could be a great acquisition to help bring more enterprise developers to Apple. Box is widely used by enterprises today, and would help grow where iCloud is weak. IBM has already partnered with Box, and is working on applications in areas like financial services. Box is valued at $1.45B, so easily affordable. But it also has only $300M of annual revenue. Clearly Apple would have to unleash an enormous development program to have Box make any meaningful impact in a company with over $500B of revenue. Something akin of Instagram’s growth for Facebook would be required. But where Instagram made Facebook a pic (versus words) site, it is unclear what major change Box would bring to Apple’s product lines.
- Fitbit is considered a good buy in order to put some glamour and growth onto iWatch. Of course, iWatch already had first year sales that exceeded iPhone sales in its first year. But Apple is now so big that all numbers have to be much bigger in order to make any difference. With a valuation of $3.7B Apple could easily afford FitBit. But FitBit has only $1.9B revenue. Given that they are different technologies, it is unclear how FitBit drives iWatch growth in any meaningful way – even if Apple converted 100% of Fitbit users to the iWatch. There would need to be a “killer app” in development at FitBit that would drive $10B-$20B additional annual revenue very quickly for it to have any meaningful impact on Apple.
- GoPro is seen as a way to kick up Apple’s photography capabilities in order to make the iPhone more valuable – or perhaps developing product extensions to drive greater revenue. At a $1.45B valuation, again easily affordable. But with only $1.6B revenue there’s just not much oomph to the Apple top line. Even maximum Apple Store distribution would probably not make an enormous impact. It would take finding some new markets in industry (enterprise) to build on things like IoT to make this a growth engine – but nobody has said GoPro or Apple have any innovations in that direction. And when Amazon tried to build on fancy photography capability with its FirePhone the product was a flop.
- Tesla is seen as the savior for the Apple Car – even though nobody really knows what the latter is supposed to be. Never mind the actual business proposition, some just think Elon Musk is the perfect replacement for the late Steve Jobs. After all the excitement for its products, Tesla is valued at only $28.4B, so again easily affordable by Apple. And the thinking is that Apple would have plenty of cash to invest in much faster growth — although Apple doesn’t invest in manufacturing and has been the king of outsourcing when it comes to actually making its products. But unfortunately, Tesla has only $4B revenue – so even a rapid doubling of Tesla shipments would yield a mere 1.6% increase in Apple’s revenues.
- In a spree, Apple could buy all 4 companies! Current market value is $35B, so even including a market premium $55B-$60B should bring in the lot. There would still be plenty of cash in the bank for growth. But, realize this would add only $8B of annual revenue to the current run rate – barely 25% of what was needed to cover the gap last quarter – and less than 2% incremental growth to the new lower run rate (that magic growth percentage to pull out of a Growth Stall mentioned earlier in this column.)
Such acquisitions would also be problematic because all have P/E (price/earnings) ratios far higher than Apple’s 10.4. FitBit is 24, GoPro is 43, and both Box and Tesla are infinite because they lose money. So all would have a negative impact on earnings per share, which theoretically should lower Apple’s P/E even more.
Acquisitions get the blood pumping for investment bankers and media folks alike – but, truthfully, it is very hard to see an acquisition path that solves Apple’s revenue problem.
All of Apple’s efforts big efforts today are around sustaining innovations to defend & extend current products. No longer do we hear about gee whiz innovations, nor do we hear about growth in market changing products like iBeacons or ApplePay. Today’s discussions are how to rejuvenate sales of products that are several versions old. This may work. Sales may recover via growth in India, or a big pick-up in enterprise as people leave their PCs behind. It could happen, and Apple could avoid its Growth Stall.
But investors have the right to be concerned. Apple can grow by defending and extending the iPhone market only so long. This strategy will certainly affect future margins as prices, on average, decline. In short, investors need to know what will be Apple’s next “big thing,” and when it is likely to emerge. It will take something quite significant for Apple to maintain it’s revenue, and profit, growth.
The good news is that Apple does sell for a lowly P/E of 10 today. That is incredibly low for a company as profitable as Apple, with such a large installed base and so many market extensions – even if its growth has stalled. Even if Apple is caught in the Innovator’s Dilemma (i.e. Clayton Christensen) and shifting its strategy to defending and extending, it is very lowly valued. So the stock could continue to perform well. It just may never reach the P/E of 15 or 20 that is common for its industry peers, and investors envisioned 2 or 3 years ago. Unless there is some new, disruptive innovation in the pipeline not yet revealed to investors.
by Adam Hartung | Oct 26, 2012 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
This is an exciting time of year for tech users – which is now all of us. The biggest show is the battle between smartphone and tablet leader Apple – which has announced new products with the iPhone 5 and iPad Mini – and the now flailing, old industry leader Microsoft which is trying to re-ignite its sales with a new tablet, operating system and office productivity suite.
I’m reminded of an old joke. Steve the trucker drives with his pal Alex. Someone at the diner says “Steve, imagine you’re going 60 miles an hour when you start down a hill. You keep gaining speed, nearing 90. Then you realize your brakes are out. Now, you see one quarter mile ahead a turn in the road, because there’s a barricade and beyond that a monster cliff. What do you do?”
Steve smiles and says “Well, I wake up Alex.”
“What? Why?” asks the questioner.
“Because Alex has never seen a wreck like the one we’re about to have.”
Microsoft has played “bet the company” on its Windows 8 launch, updated office suite and accompanied Surface tablet. (More on why it didn’t have to do this later.) Now Microsoft has to do something almost never done in business. The company has to overcome a 3 year lateness to market and upend a multi-billion dollar revenue and brand leader. It must overcome two very successful market pioneers, both of which have massive sales, high growth, very good margins, great cash flow and enormous war chests (Apple has over $100B cash.)
Just on the face of it, the daunting task sounds unlikely to succeed.
But there is far more reason to be skeptical. Apple created these markets with new products about which people had few, if any conceptions. But today customers have strong viewpoints on both what a smartphone and tablet should be like to use – and what they expect from Microsoft. And these two viewpoints are almost diametrically opposed.
Yet Microsoft has tried bridging them in the new product – and in doing so guaranteed the products will do poorly. By trying to please everyone Microsoft, like the Ford Edsel, is going to please almost no one:
- Since the initial product viewing, almost all professional reviewers have said the Surface is neat, but not fantastically so. It is different from iOS and Google’s Android products, but not superior. It has generated very little enthusiasm.
- Tests by average users have shown the products to be non-intuitive. Especially when told they are Microsoft products. So the Apple-based interface intuition doesn’t come through for easy use, nor does historical Microsoft experience. Average users have been confused, and realize they now must learn a 3rd interface – the iOS or Android they have, the old Microsoft they have, and now this new thing. It might as well be Linux for all its similarity to Microsoft.
- For those who were excited about having native office products on a tablet, the products aren’t the same as before – in feel or function. And the question becomes, if you really want the office suite do you really want a tablet or should you be using a laptop? The very issue of trying to use Office on the Surface easily makes people rethink the question, and start to realize that they may have said they wanted this, but it really isn’t the big deal they thought it would be. The tablet and laptop have different uses, and between Surface and Win8 they are seeing learning curve cost maybe isn’t worth it.
- The new Win8 – especially on the tablet – does not support a lot of the “professional” applications written on older Windows versions. Those developers now have to redevelop their code for a new platform – and many won’t work on the new tablet processors.
- Many have been banking on Microsoft winning the “enterprise” market. Selling to CIOs who want to preserve legacy code by offering a Microsoft solution. But they run into two problems. (1) Users now have to learn this 3rd, new interface. If they have a Galaxy tab or iPad they will have to carry another device, and learn how to use it. Do not expect happy employees, or executives, who expressly desire avoiding both these ideas. (2) Not all those old applications (drivers, code, etc) will port to the new platform so easily. This is not a “drop in” solution. It will take IT time and money – while CEOs keep asking “why aren’t you doing this for my iPad?”
All of this adds up to a new product set that is very late to market, yet doesn’t offer anything really new. By trying to defend and extend its Windows and Office history, Microsoft missed the market shift. It has spent several billion dollars trying to come up with something that will excite people. But instead of offering something new to change the market, it has given people something old in a new package. Microsoft they pretty much missed the market altogether.
Everyone knows that PC sales are going to decline. Unfortunately, this launch may well accelerate that decline. Remember how slowly people were willing to switch to Vista? How slowly they adopted Microsoft 7 and Office 2010? There are still millions of users running XP – and even Office XP (Office Professional 2003.) These new products may convince customers that the time and effort to “upgrade” simply means its time to switch.
Microsoft has fallen into a classic problem the Dean of innovation Clayton Christensen discusses. Microsoft long ago overshot the user need for PCs and office automation tools. But instead of focusing on developing new solutions – like Apple did by introducing greater mobility with its i products – Microsoft has diligently, for a decade, continued to dump money into overshooting the user needs for its basic products. They can’t admit to themselves that very, very, very few people are looking for a new spreadsheet or word processing application update. Or a new operating system for their laptop.
These new Microsoft products will NOT cause people to quit the trend to mobile devices. They will not change the trend of corporate users supplying their own devices for work (there’s now even an IT acronym for this movement [BYOD,] and a Wikipedia page.) It will not find a ready, excited market of people wanting to learn yet another interface, especially to use old applications they thought they already new!
It did not have to be this way.
Years ago Microsoft started pouring money into xBox. And although investors can complain about the historical cost, the xBox (and Kinect) are now market leaders in the family room. Honestly, Microsoft already has – especially with new products released this week – what people are hoping they can soon buy from AppleTV or GoogleTV; products that are at best vaporware.
Long-term, there is yet another great battle to be fought. What will be the role of monitors, scattered in homes and bars, and in train stations, lobbies and everywhere else? Who will control the access to monitors which will be used for everything from entertainment (video/music,) to research and gaming. The tablet and smartphones may well die, or mutate dramatically, as the ability to connect via monitors located nearly everywhere using —- xBox?
But, this week all discussion of the new xBox Live and music applications were overshadowed by the CEO’s determination to promote the dying product line around Windows8.
This was simply stupid. Ballmer should be fired.
The PC products should be managed for a cash hoarding transition into a smaller market. Investments should be maximized into the new products that support the next market transition. xBox and Kinect should be held up as game changers, and Microsoft should be repositioned as a leader in the family and conference room; an indespensible product line in an ever-more-connected world.
But that didn’t happen this week. And the CEO keeps heading straight for the cliff. Maybe when he takes the truck over the guard rail he’ll finally be replaced. Investors can only wake up and watch – and hope it happens sooner, rather than later.
UPDATE 16 April, 2019 – Android TV is a new emerging tech that could have a big impact on the overall marketplace. Read more about Android TV here.
by Adam Hartung | Apr 1, 2009 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, In the Whirlpool, Lifecycle, Lock-in, Web/Tech
How many of these company names do you remember — Sperry Rand? Burroughs? Univac? NCR? Control Data? Wang? Lanier? DataPoint? Data General? Digital Equipment/DEC? Gateway? Cray? Novell? Banyan? Netscape?
I'm only 50, yet most of these companies were originated, became major successes, and failed within my lifetime. Now, prepare to add a couple more. In the 1980s Silicon Graphics set the standard for high-speed computing, using their breakthrough technology to open the door on graphics. There never would have been a PS3 or Wii were it not for the pioneering work at SGI. The company invented high speed graphics calculating methods that allowed for "real-time" animation on a computer, as well as "color fill" and "texture mapping" – all capabilities we take for granted on our computer screen today but that were merely dreams to early GUI users. But now SGI has disappeared according to the Cnet.com article "First GM, Now Silicon Graphics. Lessons Learned?" The company that expanded the high-speed computing market most on SGI's early lead was Sun Microsystems, building the boxes upon which the first all-computer animated movie was made – Toy Story. But 2 weeks ago we learned Sun will most likely soon disappear into the bowels of IBM ("Final Chapter for Sun Micro Could be Written by IBM" at WSJ.com)
When Clayton Christensen wrote The Innovator's Dilemma he said academics like to talk about the tech industry because the product life cycles are so short. Actually, he would have been equally accurate to say their company life cycles were so short. For business academics, looking at tech companies is like cancer researchers looking at white lab mice. Their lifespan is so short you can rapidly see the impact of business decisions – almost like having a business lab.
What we see at these companies was an inability to shift with changes in their markets. They all Locked-in on some assumptions, and when the market shifted these companies stayed with their old assumptions – not shifting with market needs. Like Jim Collins' proverbial "hedgehog" they claimed to be the world's best at something, only to learn that the world put less and less value in what they claimed as #1. Either the technology shifted, or the application, or the user requirements. In the end, we can look back and their lives are like a short roller coaster – up and then crashing down. Lots of money put in, lots spent, not much left for investors, vendors or employees at the end. They were #1, very good (in fact, exceptional), and met a market need. Yet they were unable to thrive and even survive – because a market shift emerged which they did not follow, did not meet and eventually made them obsolete.
Today we can see the same problem emerging in some of the even larger tech companies we've grown to admire. Dell taught everyone how to operate the world's best supply chain. Yet, they've been copied and are seeing their market weaken to new products supplied by different channels. Microsoft monopolized the "desktop", but today less and less computing is done on desktops. Computing today is moving from the extremes of your hand (in your telephone) to "clouds" accessed so serrendipituously that you aren't even sure where the computing cycles are, much less how they are supplied. And software is provided in distributed ways between devices and servers such that an internet search engine provider (Google) is beginning to provide operating systems (Android) for new platforms where there is no "desktop." As behemoth as these two companies became, as invincible as they looked, they are equally vulnerable to the fate of those mentioned at the beginning of this blog.
Of course, their fate is not sealed. Apple and IBM both are tech companies that came perilously close to the Whirlpool before finding their way back into the Rapids. When businesses decide their best future is to Defend & Extend past strengths they get themselves into trouble. To break out of this rut they have to spend less time thinking about their strengths, and more about market needs. Instead of looking at similar competitors and figuring out how to be better, they have to look at fringe competitors and figure out how to change with emerging market requirements. And just like they disrupted the marketplace once with their excellence, they must be willing to disrupt their internal processes in order to find White Space where they can create new market disruptions.
Today, with change affecting all companies, it is important that leaders look at the "lab results" from tech. It's important to recognize past Lock-ins, and assumptions about continuation (or return to) past markets. Markets are changing, and only those that take the lead with customers will quickly return to profitability and emerge market leaders. It's those new leading companies that will get the economy growing again, so waiting is really not an option.

 Throughout America’s history, being an immigrant has been tough. The first ones had to deal with bad weather, difficult farming techniques, hostile terrain, wild animals – it was very difficult. As time passed immigrants continued to face these issues, expanding westward. But they also faced horrible living conditions in major cities, poor food, bad pay, minimal medical care and often abuse by the people already that previously immigrated.
Throughout America’s history, being an immigrant has been tough. The first ones had to deal with bad weather, difficult farming techniques, hostile terrain, wild animals – it was very difficult. As time passed immigrants continued to face these issues, expanding westward. But they also faced horrible living conditions in major cities, poor food, bad pay, minimal medical care and often abuse by the people already that previously immigrated.
