by Adam Hartung | Aug 2, 2015 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, In the Swamp, Leadership, Web/Tech
eBay was once a game changer. When the internet was very young, and few businesses provided ecommerce, eBay was a pioneer. From humble beginnings selling Pez dispensers, eBay grew into a powerhouse. Things we used to sell via garage sale we could now list on eBay. Small businesses could create stores on eBay to sell goods to customers they otherwise would never reach. And collectors as well as designers suddenly discovered all kinds of products they formerly could not find. eBay sales exploded, as traditional retail started it slide downward.
To augment growth eBay realized those selling needed a simple way to collect money from people who lacked a credit card. Many customers simply had no card, or didn’t trust giving out the information across the web. So eBay bought fledgling PayPal for $1.5B in 2002, in order to grease the wheels for faster ecommerce growth. And it worked marvelously.
But times have surely changed. Now eBay and Paypal have roughly the same revenue. About $8B/year each. eBay has run into stiff competition, as CraigsList has grown to take over the “garage sale” and small local business ecommerce. Simultaneously, powerhouse Amazon has developed its storefront business to a level of sophistication, and ease of use, that makes it viable for businesses from smallest to largest to sell products on-line. And far more companies have learned they can go it alone with internet sales, using search engine optimization (SEO) techniques as well as social media to drive traffic directly to their stores, bypassing storefronts entirely.
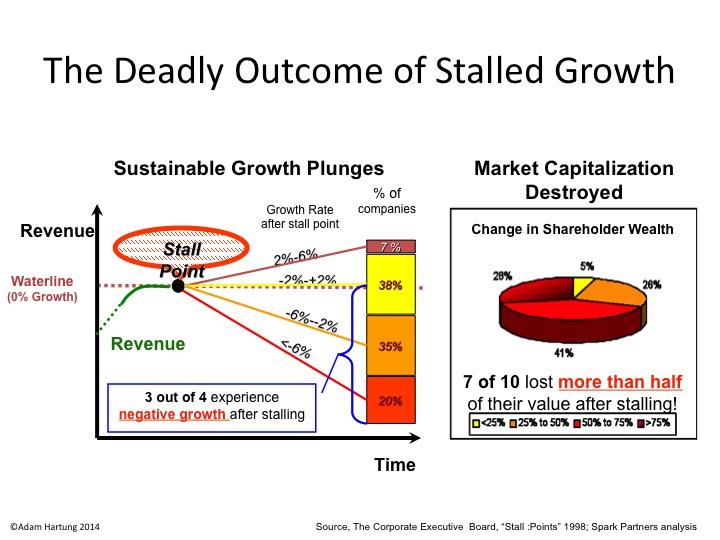
 eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
On the other hand, Paypal has blossomed into a game changer in its own right. Not only does it support cash and credit card transactions for the growing legions of on-line shoppers, but it is providing full payment systems for providers like Uber and AirBnB. It’s tools support enterprise transactions in all currencies, including emerging bitcoin, and even provides international financial transactions as well as working capital for businesses.
Paypal is increasingly becoming a threat to traditional banks. Today most folks use a bank for depositing a pay check, and making payments. There are loans, but frequently that is shopped around irrespective of where you bank. Much like your credit cards, which most people acquire for their benefits rather than a relationship with the issuing bank. If customers increasingly make payments via Paypal, and borrow money via operations like Quicken Loans (a division of Intuit,) why do you need a bank? Discover Services, which now does offer cash deposits and loans on top of credit card services, has found that it can grow substantially by displacing traditional banks.
Paypal is today at the forefront of digital payments processing. It is a fast growing market, which will displace many traditional banks. And emerging competitors like Apple Pay and Google Wallet will surely change the market further – while aiding its growth. How it will shake out is unclear. But it is clear that Paypal is growing its revenue at 60% or greater since 2012, and at over 100%/quarter the last 2 quarters.
Paypal is now valued at about $47B. That is roughly the same as the #5 bank in America (according to assets) Bank of New York Mellon, and number 8 massive credit card issuer Capital One, as well as #9 PNC Bank – and over 50% higher valuation than #10 State Street. It is also about 50% higher than Intuit and Discover. Based on its current market leadership and position as likely game changer for the banking sector, Paypall is selling for about 8 times revenue. If its revenue continues to grow at 100%/quarter, however, revenues will reach over $38B in a year making the Price/Revenue multiple of today only 1.25.
Meanwhile, eBay is valued at about $34B. Given that all which is left in eBay is an outdated on-line ecommerce conglomerator, stuck in a growth stall, that valuation is far harder to justify. It is selling at about 4.25x revenue. But if revenues continue declining, as they have for 2 consecutive quarters, this multiple will expand. And values will be harder and harder to justify as investors rely on hope of a turnaround.
eBay was a game changer. But leadership became complacent, and now it is very likely overvalued. Just as Yahoo became when its value relied on its holdings of Alibaba rather as its organic business shrank. Meanwhile Paypal is the leader in a rapidly growing market that is likely to change the face of not just how we pay, but how we do personal and business finance. There is no doubt which is more valuable today, and likely to be in the future.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 12, 2013 | General, In the Whirlpool, Leadership
This week the people who decide what composes the Dow Jones Industrial Average booted off 3 companies and added 3 others. What's remarkable is how little most people cared!
"The Dow," as it is often called, is intended to represent the core of America's economy. "As the Dow goes, so goes America" is the theory. It is one of the most watched indices of all markets, with many people tracking how much it goes up, or down, every trading day. So being a component of the DJIA is a pretty big deal.
It's not a good day when you find out your company has been removed from the index. Because it is a very public statement that your company simply isn't all that important any more. Certainly not as important as it once was! Your relevance, once considered core to representing the economy, has dissipated. And, unfortunately, most companies that fall off the DJIA slip away into oblivion.
I have a simple test. Do like Jay Leno, of Tonight Show fame, and simply ask a dozen college graduates that are between 26 and 31 about a company. If they know that company, and are positively influenced by it, you have relevancy. If they don't care about that company then the CEO and Board should take note, because it is an early indicator that the company may well have lost relevancy and is probably in more trouble than the leaders want to admit.
Ask these folks about Alcoa (AA) and what do you imagine the typical response? "Alcoa?" It is a rare person under 40 who knows that Alcoa was once the king of aluminum — back when we wrapped food in "tin foil" and before we all drank sodas and beer from a can. To most, "Alcoa" is a random set of letters with no meaning – like Altria – rather than its origin as ALuminum COrporation of America.
But, its not even the largest aluminum company any more. Alcoa is now 3rd. In a world where we live on smartphones and tablets, who really cares about a mining company that deals in commodities? Especially the third largest with no growth prospects?
Speaking of smartphones, Hewlett Packard (HPQ) was recently considered a bellweather of the tech industry. An early innovator in test equipment, it was one of the original "Silicon Valley" companies. But its commitment to printers has left people caring little about the company's products, since everyone prints less and less as we read more and more off digital screens.
Past-CEO Fiorina's huge investment in PCs by buying Compaq (which previously bought minicomputer maker DEC,) committed the rest of HP into what is now one of the fastest shrinking markets. And in PCs, HP doesn't even have any technology roots. HP is just an assembler, mostly offshore, as its products are all based on outsourced chip and software technology.
What a few years ago was considered a leader in technology has become a company that the younger crowd identifies with technology products they rarely use, and never buy. And lacking any sort of exciting pipeline, nobody really cares about HP.
Bank of America (BAC) was one of the 2 leaders in financial services when it entered the DJIA. It was a powerhouse in all things banking. But, as the mortgage market disintegrated B of A rapidly fell into trouble. It's shotgun wedding with Merrill Lynch to save the investment bank from failure made the B of A bigger, but not stronger.
Now racked with concerns about any part of the institution having long-term success against larger, and better capitalized, banks in America and offshore has left B of A with a lot of branches, but no market leadership. What innovations B of A may have had in lending or derivatives are now considered headaches most people either don't understand, or largely despise.
These 3 companies were once great lions of their industries. And they were rewarded with placement on the DJIA as icons of the economy. But they now leave with a whimper. Their values so shredded that their departure makes almost no impact on calculating the DJIA using the remaining companies. (Note: the DJIA calculation was significantly impacted by the addition of much higher valued companies Nike, Goldman Sachs and Visa.)
If we look at some past examples of other companies removed from the DJIA, one should be skeptical about the long-term future for these three:
- 2009 – GM removed due to bankruptcy
- 2004 – AT&T and Kodak removed (both ended up in bankruptcy)
- 1999 – Goodyear, Union Carbide, Sears
- 1997 – Westinghouse, Woolworths
- 1991 – American Can, Navistar/International Harvester
Any company can lose relevancy. Markets shift. There is risk incurred by focusing on the status quo (Status Quo Risk.) New technology, regulations, competitors, business practices — innovations of all sorts — enter the market daily. Being really good at something, in fact being the worlds BEST at something, does not insure success or longevity (despite the popularity of In Search of Excellence).
When markets shift, and your company doesn't, you can find yourself without relevancy. And with a fast declining value. Whether you are iconic – or not.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 15, 2009 | Current Affairs, General, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in
The Real Blindness Behind The Collapse
Adam Hartung,
09.14.09, 05:00 PM EDT
The exact same failing brought down Wall Street, Detroit and Main Street's real estate speculators.
"Too big to fail" is a new phrase in the American lexicon, born in the economic crisis that gave us a bankrupt Lehman Brothers and the shotgun marriage of Merrill Lynch with Bank of America.
Nobody really knows what it means, except that somehow in the banking
world, central bankers can decide that some institutions–like AIG, Citigroup, JPMorgan Chase and BofA–are so big they simply have to be kept alive.
This is the first paragraph in my latest column for Forbes. There is much EVERY business leader can learn from the collapse of Lehman. Learn about risk, and about how to succeed in a shifting marketplace. Please give the Forbes article a read – and put on a comment! Everybody enjoys reading what others think!
by Adam Hartung | May 7, 2009 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in
Good public policy and good management don't always align. And the banking crisis is a good example. We now hear "Banks must raise $75billion" if they are to be prepared for ongoing write-downs in a struggling economy. This is after all the billions already loaned to keep them afloat the last year.
But the bankers are claiming they will have no problem raising this money as reported in "The rush to raise Capital." "AIG narrows loss" tells how one of the primary contributors to the banking crisis now thinks it will survive. And as a result of this news, "Bank shares largely higher" is another headline reporting how financial stocks surged today post-announcements.
So regulators are feeling better. They won't have to pony up as much money as they might have. And politicians feel better, hoping that the bank crisis is over. And a lot of businesses feel better, hearing that the banks which they've long worked with, and are important to their operations, won't be going under. Generally, this is all considered good news. Especially for those worried about how a soft economy was teetering on the brink of getting even worse.
But the problem is we've just extended the life of some pretty seriously ill patients that will probably continue their bad practices. The bail out probably saved America, and the world, from an economic calamity that would have pushed millions more into unemployment and exacerbated falling asset values. A global "Great Depression II" would have plunged millions of working poor into horrible circumstances, and dramatically damaged the ability of many blue and white collar workers in developed countries to maintain their homes. It would have been a calamity.
But this all happened because of bad practices on the part of most of these financial institutions. They pushed their Success Formulas beyond their capabilities, causing failure. Only because of the bailout were these organizations, and their unhealthy Success Formulas saved. And that sows the seeds of the next problem. In evolution, when your Success Formula fails due to an environomental shift you are wiped out. To be replaced by a stronger, more adaptable and better suited competitor. Thus, evolution allows those who are best suited to thrive while weeding out the less well suited. But, the bailout just kept a set of very weak competitors alive – disallowing a change to stronger and better competitors.
These bailed out banks will continue forward mostly as they behaved in the past. And thus we can expect them to continue to do poorly at servicing "main street" while trying to create risk pass through products that largely create fees rather than economic growth. These banks that led the economic plunge are now repositioned to be ongoing leaders. Which almost assures a continuing weak economy. Newly "saved" from failure, they will Defend & Extend their old Success Formula in the name of "conservative management" when in fact they will perpetuate the behavior that put money into the wrong places and kept money from where it would be most productive.
Free market economists have long discussed how markets have no "brakes". They move to excess before violently reacting. Like a swing that goes all one direction until violently turning the opposite direction. Leaving those at the top and bottom with very upset stomachs and dramatic vertigo. The only way to avert the excessive tops is market intervention – which is what the government bail-out was. It intervened in a process that would have wiped out most of the largest U.S. banks. But, in the wake of that intervention we're left with, well, those same U.S. banks. And mostly the same leaders.
What's needed now are Disruptions inside these banks which will force a change in their Success Formula. This includes leadership changes, like the ousting of Bank of America's Chairman/CEO. But it takes more than changing one man, and more than one bank. It takes Disruption across the industry which will force it to change. Force it to open White Space in which it redefines the Success Formula to meet the needs of a shifted market – which almost pushed them over the edge – before those same shifts do crush the banks and the economy.
And that is now going to be up to the regulators. The poor Secretary of Treasury is already eyeball deep in complaints about his policies and practices. I'm sure he'd love to stand back and avoid more controversy. But, unless the regulatory apparatus now pushes those leading these banks to behave differently, to Disrupt and implement White Space to redefine their value for a changed marketplace, we can expect a protracted period of bickering and very weak returns for these banks. We can expect them to walk a line of ups and downs, but with returns that overall are neutral to declining. And that they will stand in the way of newer competitors who have a better approach to global banking from taking the lead.
So, if you didn't like government intervention to save the banks – you're really going to hate the government intervention intended to change how they operate. If you are glad the government intervened, then you'll find yourself arguing about why the regulators are just doing what they must do in order to get the banks, and the economy, operating the way it needs to in a shifted, information age.
by Adam Hartung | Mar 26, 2009 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Innovation, Leadership, Quotes
Clayton Christensen is a Harvard Business School professor who first described in detail how "disruptive" innovations shift markets, allowing upstart competitors to overtake existing companies that appear invulnerable. I just found a 4 minute video clip "Clay Christensen's Advice for Jamie Dimon" at BigThink.com. In this clip the famous professor tells the story about how the big "banks" allowed themselves to be overtaken by "non-banks" – and then he offers advice on what the big banks should do (Jamie Dimon is the Chairman and CEO of J.P.MorganChase, and an HBS alumni.)
Dr. Christensen lays out succinctly how banks relied on loan officers to find good loan candidates, and make good loans. But increasingly, borrowers were classified by a computer program, not by loan officers. Once the qualification process was turned into a computer-based Q&A, anybody with money could get into the lending business – whether for credit cards, or car loans, or mortgages, or small business loans, or commercial loans. Losing control of each of these lower-end markets, the bankers had to bid up their willingness to take on more risk to remain in business while also chasing fewer and fewer high-quality borrowers. The result was greater risk being taken by banks to compete with non-banks (like GMAC, GE Credit, Discover Card, etc.) What should they do? Dr. Christensen says go buy an Indian or Chinese phone company!!!
Hand it to Dr. Christensen to make the quick and cogent case for how Lock-in by the banks got them into so much trouble. By trying to do more of the same in the face of a radically shifting market (people going to non-banks for loans and to make deposits), they found themselves taking on considerably more risk than they originally intended. Rather than finding businesses with good rates of return, they kept taking on slightly more risk in the business they knew. They favored "the devil you know" over the "the devil you don't know." In reality, they were taking on considerably more risk than if they had diversified into other businesses that were on far less shaky ground than unbacked mortgages.
This is Strategic Bias. We all like to remain "close to core" when investing resources. So we keep taking on more and more risk to remain in our "core" — and for little reason other than it's the market and business we know. Because we know the business, we convince ourselves it's not as risky as doing something else. In truth, markets determine risk – not us. Because we assess risk from our personal perspective, we keep convincing ourselves to do more of what we've done — even when the marketplace makes the risk of doing what we've done incredibly risky —- like happened to Citbank, Bank of America and a host of other banks.
And in great form, the professor offers a solution almost nobody would consider. His argument is that (1) these banks need to go where demand is great, go to new and growing markets, not old markets, and loan demand cannot be greater than in emerging markets. (2) To succeed in the future (not the past) banks have to learn to compete in emerging markets because of growth and because so many winning competitors are already there, and (3) you want to enter businesses that are growing, not what necessarily your traditional business or what you are used to doing. He points out that the traditional "banking" infrastructure is nascent in emerging markets, and well may not develop as it did in the western world. But everyone in these places has phones, so phones are becoming the tool for transactions and the handling of money. When people start doing everything on their phone (remember the rapidly escalating capabilities of phones – like the iPhone and Pre) it may well be that the "phone company" becomes more of a bank than a bank!!
Who knows if Clayton is right about the Indian phone company? But his point that you have to consider competitors you never thought about before is spot on. When markets shift they don't return to old ways. It's all about the future, and banking has changed, so don't expect it to return to old methods. Secondly, you have to be willing to Disrupt old Lock-ins about your business. If the "loaning" of money is now automated, banking becomes about transaction management – not making loans. You have to consider entirely different ways of competing, and that means Disrupting your Lock-ins so you can consider new ways of competing. Thirdly, you don't just sit and wait to see what happens. Get out there and participate! Open White Space projects in which you experiment and LEARN what works. You can't develop a new Success Formula by thinking about it, you have to DO IT in the marketplace.
Big American banks have tilted on the edge of failure. More will likely fail – although we don't yet know which the regulators will put under or keep afloat. What we can be sure of is that the market conditions that put them on the edge will not revert. To be successful in the future these organizations have to change. Probably radically so. So if they want to use the TARP money effectively, they had better take action quickly to begin experimenting in new markets with new solutions.
Gotta hand it to Professor Clayton Christensen, he's made a huge improvement in the way we think about innovation and strategy the last few years. His ideas on banking are well worth consideration by the CEOs trying to bring their shareholders, employees and customers back from brink.

 eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.
eBay was a game changer, but now is stuck in practices that have become far less relevant. The result has been 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. By definition that puts eBay in a growth stall, and fewer than 7% of companies ever recover from a growth stall to consistently increase revenue by a mere 2%/year. Why not? Because once in a growth stall the company has already missed the market shift, and competition is taking customers quickly in new directions. The old leader, like eBay, keeps setting aggressive targets for its business, and tells everyone it will find new customers in remote geographies or vertical markets. But it almost never happens – because the market shift is making their offering obsolete.