by Adam Hartung | Oct 10, 2012 | Books, Current Affairs, Leadership, Lock-in
There was a time, before primaries, when each party's platform was really important. Voters didn't pick a candidate, the party did. Then voters read what policies the party planned to implement should it control the executive branch, and possibly a legislative majority. It was the policies that drew the most attention – not the candidates.
Digging deeper than shortened debate-level headlines, there is a considerable difference in the recommended economic policies of the two dominant parties. The common viewpoint is that Republicans are good for business, which is good for the economy. Republican policies – and the more Adam Smith, invisible hand, limited regulation, lassaiz faire the better – are expected to create a robust, healthy, growing economy. Meanwhile, the common view of Democrat policies is that they too heavily favor regulation and higher taxes which are economy killers.
Right?
Well, for those who feel this way it may be time to review the last 80 years of economic history, as Bob Deitrick and Lew Godlfarb have done in a great, easy to read book titled "Bulls, Bears and the Ballot Box" (available at Amazon.com) Their heavily researched, and footnoted, text brings forth some serious inconsistency between the common viewpoint of America's dominant parties, and the reality of how America has performed since the start of the Great Depression.
Gary Hart recently wrote in The Huffington Post,
"Reason and facts are sacrificed to opinion and myth. Demonstrable
falsehoods are circulated and recycled as fact. Narrow minded opinion
refuses to be subjected to thought and analysis. Too many now subject
events to a prefabricated set of interpretations, usually provided by a
biased media source. The myth is more comfortable than the often
difficult search for truth."
Senator Daniel Patrick Moynihan is attributed with saying "everyone is
entitled to his own opinion, but not his own facts." So even though we
may hold very strong opinions about parties and politics, it is
worthwhile to look at facts. This book's authors are to be commended for spending several years, and many thousands of student research assistant man-days, sorting out economic performance from the common viewpoint – and the broad theories upon which much policy has been based. Their compendium of economic facts is the most illuminating document on economic performance during different administrations, and policies, than anything previously published.
Startling Results

Chart reproduced by permission of authors
The authors looked at a range of economic metrics including inflation, unemployment, growth in corporate profits, performance of the stock market, change in household income, growth in the economy, months in recession and others. To their surprise (I had the opportunity to interview Mr. Goldfarb) they discovered that laissez faire policies had far less benefits than expected, and in fact produced almost universal negative economic outcomes for the nation!
From this book loaded with statistical fact tidbits and comparative charts, here are just a few that caused me to realize that my long-term love affair with Milton Friedman's theories and recommended policies in "Free to Choose" were grounded in a theory I long admired, but that simply have proven to be myths when applied!
- Personal disposable income has grown nearly 6 times more under Democratic presidents
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has grown 7 times more under Democratic presidents
- Corporate profits have grown over 16% more per year under Democratic presidents (they actually declined under Republicans by an average of 4.53%/year)
- Average annual compound return on the stock market has been 18 times greater under Democratic presidents (If you invested $100k for 40 years of Republican administrations you had $126k at the end, if you invested $100k for 40 years of Democrat administrations you had $3.9M at the end)
- Republican presidents added 2.5 times more to the national debt than Democratic presidents
- The two times the economy steered into the ditch (Great Depression and Great Recession) were during Republican, laissez faire administrations
The "how and why" of these results is explained in the book. Not the least of which revolves around the velocity of money and how that changes as wealth moves between different economic classes.
The book is great at looking at today's economic myths, and using long forgotten facts to set the record straight. For example, in explaining President Reagan's great economic recovery of the 1980s it is often attributed to the stimulative impact of major tax cuts. But in reality the 1981 tax cuts backfired, leading to massive deficits and a weaker economy with a double dip recession as unemployment soared. So in 1982 Reagan signed (TEFRA) the largest peacetime tax increase in our nation's history. In his tenure Reagan signed 9 tax bills – 7 of which raised taxes!
The authors do not come down on the side of any specific economic policies. Rather, they make a strong case that a prosperous economy occurs when a president is adaptable to the needs of the country at that time. Adjusting to the results, rather than staunchly sticking to economic theory. And that economic policy does not stand alone, but must be integrated into the needs of society. As Dwight Eisenhower said in a New Yorker interview
"I despise people who go to the gutter on either the right or the left and hurl rocks at those in the center."
The book covers only Presidents Hoover through W. Bush. But as we near this election I asked Mr. Goldfarb his view on the incumbent Democrat's first 4 years. His response:
- "Obama at this time would rank on par with Reagan
- Corporate profits have risen under Obama more than any other president
- The stock market has soared 14.72%/year under Obama, second only to Clinton — which should be a big deal since 2/3 of people (not just the upper class) have a 401K or similar investment vehicle dependent upon corporate profits and stock market performance"
As to the challenging Republican party's platform, Mr. Goldfarb commented:
- "The platform is the inverse of what has actually worked to stimulate economic growth
- The recommended platform tax policy is bad for velocity, and will stagnate the economy
- Repealing the Affordable Care Act (Obamacare) will have a negative economic impact because it will force non-wealthy individuals to spend a higher percentage of income on health care rather than expansionary products and services
- Economic disaster happens in America when wealth is concentrated at the top, and we are at an all time high for wealth concentration. There is nothing in the platform which addresses this issue."
There are a lot of reasons to select the party for which you wish to vote. There is more to America than the economy. But, if you think like the Democrats did in 1992 and "it's about the economy" then you owe it to yourself to read this book. It may challenge your conventional wisdom as it presents – like Joe Friday said – "just the facts."
by Adam Hartung | Oct 4, 2012 | Defend & Extend, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lifecycle, Web/Tech
If you're still an investor in Hewlett Packard you must be new to this blog. But for those who remain optimistic, it is worth reveiwing why Ms. Whitman's forecast for HP yesterday won't happen. There are sound reasons why the company has lost 35% of its value since she took over as CEO, over 75% since just 2010 – and over $90B of value from its peak.
HP was dying before Whitman arrived
I recall my father pointing to a large elm tree when I was a boy and saying "that tree will be dead in under 2 years, we might as well cut it down now." "But it's huge, and has leaves" I said. "It doesn't look dead." "It's not dead yet, but the environmental wind damage has cost it too many branches, the changing creek direction created standing water rotting its roots, and neighboring trees have grown taking away its sunshine. That tree simply won't survive. I know it's more than 3 stories tall, with a giant trunk, and you can't tell it now – but it is already dead."
To teach me the lesson, he decided not to cut the tree. And the following spring it barely leafed out. By fall, it was clearly losing bark, and well into demise. We cut it for firewood.
Such is the situation at HP. Before she became CEO (but while she was a Director – so she doesn't escape culpability for the situation) previous leaders made bad decisions that pushed HP in the wrong direction:
- Carly Fiorina, alone, probably killed HP with the single decision to buy Compaq and gut the HP R&D budget to implement a cost-based, generic strategy for competing in Windows-based PCs. She sucked most of the money out of the wildly profitable printer business to subsidize the transition, and destroy any long-term HP value.
- Mark Hurd furthered this disaster by further investing in cost-cutting to promote "scale efficiencies" and price reductions in PCs. Instead of converting software products and data centers into profitable support products for clients shifting to software-as-a-service (SAAS) or cloud services he closed them – to "focus" on the stagnating, profit-eroding PC business.
- His ill-conceived notion of buying EDS to compete in traditional IT services long after the market had demonstrated a major shift offshore, and declining margins, created an $8B write-off last year; almost 60% of the purchase price. Giving HP another big, uncompetitive business unit in a lousy market.
- His purchase of Palm for $1.2B was a ridiculous price for a business that was once an early leader, but had nothing left to offer customers (sort of like RIM today.) HP used Palm to bring out a Touchpad tablet, but it was so late and lacking apps that the product was recalled from retailers after only 49 days. Another write-off.
- Leo Apotheker bought a small Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software company – only more than a decade after monster competitors Oracle, SAP and IBM had encircled the market. Further, customers are now looking past ERP for alternatives to the inflexible "enterprise apps" which hinder their ability to adjust quickly in today's rapidly changing marektplace. The ERP business is sure to shrink, not grow.
Whitman's "Turnaround Plan" simply won't work
Meg is projecting a classic "hockey stick" performance. She plans for revenues and profits to decline for another year or two, then magically start growing again in 3 years. There's a reason "hockey stick" projections don't happen. They imply the company is going to get a lot better, and competitors won't. And that's not how the world works.
Let's see, what will likely happen over the next 3 years from technology advances by industry leaders Apple, Android and others? They aren't standing still, and there's no reason to believe HP will suddenly develop some fantastic mojo to become a new product innovator, leapfrogging them for new markets.
- Meg's first action is cost cutting – to "fix" HP. Cutting 29,000 additional jobs won't fix anything. It just eliminates a bunch of potentially good idea generators who would like to grow the company. When Meg says this is sure to reduce the number of products, revenues and profits in 2013 we can believe that projection fully.
- Adding features like scanning and copying to printers will make no difference to sales. The proliferation of smart devices increasingly means people don't print. Just like we don't carry newspapers or magazines, we don't want to carry memos or presentations. The world is going digital (duh) and printing demand is not going to grow as we read things on smartphones and tablets instead of paper.
- HP is not going to chase the smartphone business. Although it is growing rapidly. Given how late HP is to market, this is probably not a bad idea. But it begs the question of how HP plans to grow.
- HP is going not going to exit PCs. Too bad. Maybe Lenovo or Dell would pay up for this dying business. Holding onto it will do HP no good, costing even more money when HP tries to remain competitive as sales fall and margins evaporate due to overcapacity leading to price wars.
- HP will launch a Windows8 tablet in January targeted at "enterprises." Given the success of the iPad, Samsung Galaxy and Amazon Kindle products exactly how HP will differentiate for enterprise success is far from clear. And entering the market so late, with an unproven operating system platform is betting the market on Microsoft making it a success. That is far, far from a low-risk bet. We could well see this new tablet about as successful as the ill-fated Touchpad.
- Ms. Whitman is betting HP's future (remember, 3 years from now) on "cloud" computing. Oh boy. That is sort of like when WalMart told us their future growth would be "China." She did not describe what HP was going to do differently, or far superior, to unseat companies already providing a raft of successful, growing, profitable cloud services. "Cloud" is not an untapped market, with companies like Oracle, IBM, VMWare, Salesforce.com, NetApp and EMC (not to mention Apple and Amazon) already well entrenched, investing heavily, launching new products and gathering customers.
HPs problems are far deeper than who is CEO
Ms. Whitman said that the biggest problem at HP has been executive turnover. That is not quite right. The problem is HP has had a string of really TERRIBLE CEOs that have moved the company in the wrong direction, invested horribly in outdated strategies, ignored market shifts and assumed that size alone would keep HP successful. In a bygone era all of them – from Carly Fiorina to Mark Hurd to Leo Apotheker – would have been flogged in the Palo Alto public center then placed in stocks so employees (former and current) could hurl fruit and vegetables, or shout obscenities, at them!
Unfortately, Ms. Whitman is sure to join this ignominious list. Her hockey stick projection will not occur; cannot given her strategy.
HP's only hope is to sell the PC business, radically de-invest in printers and move rapidly into entirely new markets. Like Steve Jobs did a dozen years ago when he cut Mac spending to invest in mobile technologies and transform Apple. Meg's faith in operational improvement, commitment to existing "enterprise" markets and Microsoft technology assures HP, and its investors, a decidedly unpleasant future.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 25, 2012 | Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Transparency, Web/Tech
I like writing about tech companies, such as Apple and Facebook, because they show how fast you can apply innovation and grow – whether it is technology, business process or new best practices. But many people aren't in the tech industry, and think innovation applies a lot less to them.
Whoa there cowboy, innovation is important to you too!
Few industries are as mired in outdated practices and slow to adopt technology than construction. Whether times are good, or not, contractors and tradespeople generally do things the way they've been done for decades. Even customers like to see bids where the practices are traditional and time-worn, often eschewing innovations simply because they like the status quo.
Skanska, a $19B construction firm headquarted in Stockholm, Sweden with $6B of U.S. revenue managed from the New York regional HQ refused to accept this. When Bill Flemming, President of the Building Group recognized that construction industry productivity had not improved for 40 years, he reckoned that perhaps the weak market wasn't going to get better if he just waited for the economy to improve. He was sure that field-based ideas could allow Skanska to be better than competitors, and open new revenue sources.
Skanska USA CEO Mike McNally agreed instantly. In 2009 he brought together his management team to see if they would buy into investing in innovation. He met the usual objections
- We're too busy
- I have too much on my plate
- Business is already too difficult, I don't need something new
- Customers aren't asking for it, they want lower prices
- Who's going to pay for it? My budget is already too thin!
But, he also recognized that nobody said "this is crazy." Everyone knew there were good things happening in the organization, but the learning wasn't being replicated across projects to create any leverage. Ideas were too often tried once, then dropped, or not really tried in earnest. Mike and Bill intuitively believed innovation would be a game changer. As he discussed implementing innovation with his team he came to saying "If Apple can do this, we can too!"
Even though this wasn't a Sweden (or headquarters) based project, Mike decided to create a dedicated innovation group, with its own leader and an initial budget of $500K – about .5% of the Building Group total overhead.
The team started with a Director of innovation, plus a staff of 2. They were given the white space to find field based ideas that would work, and push them. Then build a process for identifying field innovations, testing them, investing and implementing. From the outset they envisaged a "grant" program where HQ would provide field-based teams with money to test, develop and create roll-out processes for innovations.
Key to success was finding the right first project. And quickly the team knew they had one in one of their initial field projects called Digital Resource Center, which could be used at all construction sites. This low-cost, rugged PC-based product allowed sub-contractors around the site to view plans and all documentation relevant for their part of the project without having to make frequent trips back to the central construction trailer.
This saved a lot of time for them, and for Skanska, helping keep the project moving quickly with less time wasted talking. And at a few thousand dollars per station, the payback was literally measured in days. Other projects were quick to adopt this "no-brainer." And soon Skanska was not only seeing faster project completion, but subcontractors willing to bake in better performance on their bids knowing they would be able to track work and identify key information on these field-based rugged PCs.
As Skanska's Innovation Group started making grants for additional projects they set up a process for receiving, reviewing and making grants. They decided to have a Skansa project leader on each grant, with local Skansa support. But also each grant would team with a local university which would use student and faculty to help with planning, development, implementation and generate return-on-investment analysis to demonstrate the innovation's efficacy. This allowed Skansa to bring in outside expertise for better project development and implementation, while also managing cost effectively.
With less than 2 years of Innovation Group effort, Skanska has now invested $1.5M in field-based projects. The focus has been on low-cost productivity improvements, rather than high-cost, big bets. Changing the game in construction is a process of winning through lots of innovations that prove themselves to customers and suppliers rather than trying to change a skeptical group overnight. Payback has been almost immediate for each grant, with ROI literally in the hundreds of percent.
You likely never heard of Skanska, despite its size. And that's because its in the business of building bridges, subway stations and other massive projects that we see, but know little about. They are in an industry known for its lack of innovation, and brute-force approach to getting things done.
But the leadership team at Skanska is proving that anyone can apply innovation for high rates of return. They
- understood that industry trends were soft, and they needed to change if they wanted to thrive.
- recognized that the best ideas for innovation would not come from customers, but rather from scanning the horizon for new ideas and then figuring out how to implement themselves
- weren't afraid to try doing something new. Even if the customer wasn't asking for it
- created a dedicated team (and it didn't have to be large) operating in white space, focused on identifying innovations, reviewing them, funding them and bringing in outside resources to help the projects succeed
In addition to growing its traditional business, Skanska is now something of a tech company. It sells its Digital Resource stations, making money directly off its innovation. And its iSite Monitor for monitoring environmental conditions on sensitive products, and pushing results to Skanska project leaders as well as clients in real time with an app on their iPhones, is also now a commercial product.
So, what are you waiting on? You'll never grow, or make returns, like Apple if you don't start innovating. Take some lessons from Skanska and you just might be a lot more successful.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 18, 2012 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, Food and Drink, In the Rapids, In the Whirlpool, Innovation, Leadership, Lifecycle
Apple is launching the iPhone 5, and the market cap is hitting record highs. No wonder, what with pre-orders on the Apple site selling out in an hour, and over 2 million units being presold in the first 24 hours after announcement.
We care a lot about Apple, largely because the company has made us all so productive. Instead of chained to PCs with their weight and processor-centric architecture (not to mention problems crashing and corrupting files) while simultaneously carrying limited function cell phones, we all now feel easily interconnected 24×7 from lightweight, always-on smart devices. We feel more productive as we access our work colleagues, work tools, social media or favorite internet sites with ease. We are entertained by music, videos and games at our leisure. And we enjoy the benefits of rapid problem solving – everything from navigation to time management and enterprise demands – with easy to use apps utilizing cloud-based data.
In short, what was a tired, nearly bankrupt Macintosh company has become the leading marketer of innovation that makes our lives remarkably better. So we care – a lot – about the products Apple offers, how it sells them and how much they cost. We want to know how we can apply them to solve even more problems for ourselves, colleagues, customers and suppliers.
Amidst all this hoopla, as you figure out how fast you can buy an iPhone 5 and what to do with your older phone, you very likely forgot that Kraft will be splitting itself into 2 parts in about 2 weeks (October 1). And, most likely, you don't really care.
And you can't imagine why I would even compare Kraft with Apple.
Kraft was once an innovation leader. Velveeta, a much maligned product today, gave Americans a fast, easy solution to cheese sauces that were difficult to make. Instant Mac & Cheese was a meal-in-a-box for people on the run, and at a low budget. Cheeze Whiz offered a ready-to-eat spread for canape's. Individually wrapped American cheese slices solved the problem of sticky product for homemakers putting together lunch sandwiches for school children. Miracle Whip added spice to boring sandwiches. Philadelphia brand cream cheese was a tasty, less fattening alternative to butter while also a great product for sauces.
But, the world changed and these innovations have grown a lot less interesting. Frozen food replaced homemade sauces and boxed solutions. Simultaneously, cooking skills improved. Better options for appetizers emerged than stuffed celery or something on a cracker. School lunches changed, and sandwich alternatives flourished. Across Kraft's product lines, demand changed as new technologies were developed that better fit customers' needs leading to revenue stagnation, margin erosion and an increasing irrelevancy of Kraft in the marketplace – despite its enormous size.
Apple turned itself around by focusing on innovation, becoming the most valuable American publicly traded company. Kraft eschewed innovation for cost cutting, doing more of the same trying to defend its "core," leaving investors with virtually no returns. Meanwhile thousands of Kraft employees have lost their jobs, even though revenues per employee at Kraft are 1/6th those at Apple. And supplier margins are a never-ending cycle of forced reductions as Kraft tries to capture their margin for itself.

Chart Source: Yahoo Finance 18 September, 2012
Apple's value went up because it's revenues went up. In 2007 Apple had #24B in revenues, while Kraft was 150% bigger at $37B. Ending 2011 Apple's revenues, all from organic growth, were up 4x (400%) at $108B. But Kraft's 2011 revenues were only $54B, including roughly $10B of purchased revenues from its Cadbury acquisition, meaning comparative Kraft revenues were $44B; a growth of (ho-hum) 3.5%/year.
Lacking innovation Kraft could not grow the topline, and simply could not grow its value. And paying a premium price for someone else's revenues has led to…. splitting the company in 2 in only 2 years, mystifying everyone as to what sort of strategy the company ever had to grow!
But Kraft's new CEO is not deterred. In an Ad Age interview he promised to ramp up advertising while slashing more jobs to cut costs. As if somehow advertising Velveeta, Miracle Whip, Philadelphia and Mac & Cheese will reverse 30 years of market trends toward different products which better serve customer needs!
Apple spends nearly nothing on advertising. But it does spend on innovation. Innovation adds value. Advertising aging products that solve no new needs does not.
Unfortunately for employees, suppliers and shareholders we can expect Kraft to end up just like Hostess Brands, owner of Wonder Bread and Twinkies, which recently filed bankruptcy due to 40 years of sticking to its core business as the market shifted. Industry leaders know this, as they announced this week they are using Kraft's split to remove the company from the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Companies that innovate change markets and reap the rewards. By delivering on trends they excite customers who flock to their solutions. Companies that focus on defending and extending their past, especially in times of market shifts, end up failing. Failure may not happen overnight, but it is inevitable.
by Adam Hartung | Sep 10, 2012 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
It's been two very different stories for Amazon and Facebook this summer. Amazon's market cap has risen about 20%, while Facebook lost about 50% of its market value.

Chart source: Yahoo Finance
Why this has happened was somewhat encapsulated in each company's headlines last week.
Amazon announced it was releasing 2 new eReaders under the Paperwhite name requiring no external light source starting at $119. Additionally, Kindles for $69 will be available this week. These actions expand the market for eReaders, already dominated by Amazon, providing for additional growth and lowering a kaboom on the Barnes & Noble Nook which is partnered with Microsoft.
Offering more functionality and lower prices gives Amazon an even larger lead in the ereader market while simultaneously expanding demand for digital reading giving Amazon more strength versus traditional publishers and the printed book market. Despite a "nosebleed" high historical price/earnings multiple close to 300, investors, like customers, were charged up to see the opportunities for ongoing growth from new products.
On the other hand, Facebook spent last week explaining to investors a set of decisions being made to prop up the stock price. The CEO promised not to sell any stock for several months, and explained that the company would not sell more stock to cover taxes on stock-based compensation – even though that was the original plan. He even tried to promote the avoided transaction as some kind of stock buyback, although there was no stock buyback.
Facebook was focused on financial machinations – which have nothing to do with growing the company's revenues or profits. That the company avoided selling more stock at its deflated prices does help earnings per share, but what's more important is the fact that now $2B will be taken out of cash reserves to pay those taxes. $2B which won't be spent on new product development, or other activities oriented toward growth.
Although I am very bullish on Facebook, last week was not a good sign. A young CEO is clearly feeling heat over the stock value, even though he has control of the company regardless of share price. It gave the indication that he wanted to mollify investors rather than focus on producing better results – which is what Facebook has to do if it really wants to make investors happy. Rather than doing what he always promised to do, which was make the world's best network offering users the best experience, his attention was diverted to issues that have absolutely no long-term value, and in the short term reduce resources for fulfilling the long-term mission.
Given the choice between
- a company talking about how it plans to grow revenues and profits, and maintain market domination while outflanking the introduction of new Microsoft products, or
- a company apologetic about its IPO, fixated on its declining stock price and apparently diverting focus away from markets and solutions toward financial machinations
which would you choose? Both may have gone up in value last week – but clearly Mr. Bezos showed he was leading his company, while Mr. Zuckerberg came off looking like he was floundering.
As you look at the announcements from your company, over the last year and anticipate going forward, what do you see? Are there lots of announcements about new technology applications and product advancements that open new markets for growing revenue while warding off (and making outdated) competitors? Or is more time spent talking about layoffs, cost cutting efforts, price adjustments to maintain market share, stock buybacks intended to prop up the value, stock (or company) splits, asset (or division) sales, expense reductions, reorganizations or adjustments intended to improve earnings per share?
If its the former, congratulations! You're acting like Amazon. You're talking about how you are whupping competitors and creating growth for investors, employees and suppliers. But if it's the latter perhaps you understand why your equity value isn't rising, employees are disgruntled and suppliers are worried.
by Adam Hartung | Aug 29, 2012 | Current Affairs, Innovation, Leadership, Transparency, Travel, Web/Tech
Neil Armstrong, the first man to step on the moon died last Saturday. Overall, I was surprised at just how little attention this received. The Republican convention, Hurrican Isaac and many other issues dominated the news, even though Neil Armstrong represents something that had far more impact on our lives than this hurricane, or anyone attending this convention.
Neil Armstrong represents the adventurous spirit of an innovator willing to lead from the front. The advances in flight, and space travel, might have happened without him – or maybe not. Neil Armstrong was willing to see what could be done, willing to experiment and take chances, without being overly concerned about failure. Rather than worrying about what could go wrong, he was willing to see what could go right!
Most of us forget that it has been only 110 years since the Wright brothers made their 12 second, 120 foot flight at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Before that, flight had been impossible. Now, in such a short time, we have globalized travel. My father, born in 1912, lived in a world with no planes – or much need for one. I now live in Chicago largely because of O'Hare airport and its gateway (almost always in one leg) to any city. Flight has transformed everything about life, and the world owes a lot to Neil Armstrong for that change.
Neil Armstrong became a pilot at 15 and spent a lifetime pushing the envelope of flight. He not only flew planes, but he obtained an aeronautical engineering degree and used his experiences to help design better, more capable planes. His history of try, fail, test, improve, try, succeed is an example for all leaders:
- Firstly, know what you are talking about. Have the right education, obtain data and apply good analysis to everything you do. Don't operate just "from your gut," or on intuition, but rather know what you're talking about, and lead with knowledge.
- Second, don't be afraid to experiment, learn, improve and grow. Don't rest on what people have done, and proven, before. Don't accept limits just because that's how it was previously done. Constantly build upon the past to reach new heights. Just because it has not been done before does not mean it cannot be done.
Beyond his own leadership, Neil Armstrong is – for much of the world – the face of space travel. The first man on the moon. And that was only possible by being part of, and a leader in, NASA. And we could desperately use NASA today. It was, without a doubt, the most successful economic stimulus program in American history – even though politicians have been moving in the opposite direction for nearly 2 decades!
NASA offered Americans, and in fact the world, the opportunity to invest in science to see what could be done. By setting wildly unrealistic goals the organization was forced to constantly innovate. As a result NASA created and spun off more inventions creating more jobs than Eisenhower's interstate highway program and all other giant government programs combined.
NASA's heyday was from the John Kennedy challenge of 1961 through the lunar landing in 1969. Yet since 1976 alone there have been over 1,400 documented NASA inventions benefiting industry!! Not only did NASA's experiments in flight aid physical globalization, but it was NASA that developed wireless (satellite based) long-distance communications – which now gives us nearly free global voice and data connectivity. And the need to solve complex engineering problems pushed the computer race exponentially, giving us the digital technology now embedded in almost everything we do.
Consider these other NASA innovations that have driven economic growth:
- The microwave oven, and tasty, desirable frozen food used not only in homes but in countless restaurants
- Water filtration for cities and even your refrigerator reducing disease and illness
- High powered batteries – for everything from laptops to cordless tools to electric cars
- Cordless phones, which led to cell phones
- Ear thermometers (for those of us who remember using anal thermometers on sick babies this is a BIG deal)
- Non-destructive testing of rockets and other devices led to what are now medical CAT scanners and MRI machines
- Scratch resistant lenses now used in glasses, and invisible, easy to adjust braces at prices, adjusted for inflation, considered impossible 30 years ago
- Superior coatings for cookware, paints and just about everything
As the American economy sputters, southern Europe looks to drag down economic growth across the continent, and growth slows in China the need for economic stimulus has never been greater. But far too often politicians reach for outdated programs like highways, dams or other construction projects. And monetary stimulus, in the form of lower interest rates and easier money, almost always goes into asset intensive projects like factories – at a time when capacity utilization remains far from any peak. We keep spending, and making money cheap, but it doesn't matter.
We have transitioned from an industrial to an information economy. Effective economic stimulus in 2012 cannot happen by creating labor-intensive, or asset-intensive, programs. Rather it must create jobs built upon the kind of value-added work in today's economy – and that means knowledge-intensive work. Exactly the kind of work created by NASA, and all the subsidiary businesses born of the NASA innovations.
Nobody seems to care about going to space any more. And I must admit, it is not my dream. But in one of his last efforts to help America grow Neil Armstrong told a Congressional committee "It would be as if 16th century Monarchs proclaimed we need not go to the New World, we have already been there." He was so right. We have barely begun understanding the implications of growth created by exploring space. Only our imaginations are limited, not the opportunity.
What Neil Armstrong told us all, and practiced with his actions, was to never stop setting crazy goals. Even when the immediate benefit may be unclear. The journey of discovery unleashes opportunities which create their own benefits – for society, and for our economy. Losing Neil Armstrong is an enormous loss, because we need leaders like him now more than ever.
by Adam Hartung | Aug 15, 2012 | Current Affairs, In the Rapids, Leadership, Web/Tech
Forbes magazine labeled Groupon the world's fastest growing corporation. And that didn't hurt the company's valuation when it went public in November, 2011.
But after trading up for a couple of months, at the beginning of March Groupon turned down and has since lost 75% of its market capitalization. Groupon is now valued at about $3.6B – approaching half of what Google offered to pay for the company in 2011 before leadership decided to go public.
And nobody, absolutely nobody, can be happy about that.
Groupon pioneered the use of digital coupons in a way that created an explosive new market for local business. Paper coupon use had been declining for years. But when Groupon made it possible for on-line individuals to achieve deep discounts on products in local stores using emailed coupons masses of people started buying. From nothing in June, 2009, by June, 2010 revenues grew to an astonishing $100M. Then, between June, 2010 and June, 2011 revenues exploded 10-fold, reaching the magical $1B. Forbes was not wrong – as this was an astonishing growth accomplishment.
Google, Yahoo, Amazon and other suitors quickly recognized that this was not a fad – but a true growth market:
- People like deals, and coupons could be successful when updated to modern technology
- Local programs were extremely hard for internet-wide companies like Google, and Groupon had "cracked the code" for acquiring local-market customers
- Some Groupon programs had simply astounding results – far exceeding the offerer's expectations. The downside was the businessess complained about how much the discounts cost them as success exceeded expectations. The upside was it demonstrated the business had remarkable reach and success.
- As mobile use grows Groupon can interact with location apps like Foursquare to allow local merchants to target local customers for rapid sales. Combine that with Twitter distribution and you could have extremely effective local store targeted marketing programs – previously unavailable on the web.
- Groupon reached a scale allowing it to potentially work with national consumer goods companies like PepsiCo or P&G and their local retailers on new product launches or market specific sales programs, something not previously done via digital networks.
Ah, but problems have emerged at Groupon. Although none of them really change the above items:

Source: Business Insider August 13, 2012 Permission to reproduce: Jay Yarrow, Silicon Alley Insider Editor
This last point is extremely deadly. Groupon's growth rate has fallen from 1,000% to about 35%! Further, Groupon is dangerously close to a growth stall, which is 2 consecutive quarters of declining revenue. Only 7% of companies that incur a growth stall maintain a consistent growth rate of even 2%!! Groupon's value is completely based upon maintaining high growth. So regardless of anything else – including profitability – unless Groupon can find its growth mojo then investors are screwed!
Has the market for daily deals declined? Not according to Yelp and Amazon, which continue growing their markets. Consumers are still smarting from a bad economy, and love digital coupons. The problems at Groupon do not appear to be that the market is disappearing – but rather that management simply does not know what to do next.
Groupon was a rocket ship of growth, and founding CEO Andrew Mason deserves a lot of credit for building the sales machine that outperformed everyone else – including Google and Amazon. But the other side of his performance was complete inexperience in how to manage finances, operations or any other part of a large publicly traded corporation. Unprofessional analyst presentations, executive turnover, disrespectful comments to investors and chronic unprofitability all were acceptable if – and only if – he kept up that torrid growth pace. If he can't drive sales, what's the benefit of keeping him in the top job?
Groupon is a remarkable company, in a remarkable market. But it has incredibly tough competition. Seasoned tech investors know that as fast as Groupon sales went up, they can go down. With smart, well managed competitors in their markets there is no room for error – and no time. Groupon has to keep the growth going, or it will quickly be overwhelmed by bigger, smarter companies – remember Palm? RIM?
It's not too late for Groupon. It is #1 in its market. Groupon has the most users, the most customers and by far the most salespeople. Groupon has other products in the pipeline which solve new needs and can extend sales into other emerging market opportunities. But Groupon will not survive if it does not recapture growth – and it's time for a CEO with the experience to do just that. Mr. Mason does not appear to be the next Jeff Bezos or Steve Jobs, so Groupon's Board better go find one!
by Adam Hartung | Aug 9, 2012 | Current Affairs, Disruptions, In the Rapids, Innovation, Leadership, Web/Tech
Mark Zuckerberg was Time magazine's Person of the Year in December, 2010. He was given that honor because Facebook dominated the emerging social media marketplace, and social media had clearly begun changing how people do things. Despite his young age, Mr. Zuckerberg had created a phenomenon demonstrated by the hundreds of million new Facebook users.
But things have turned pretty rough for the young Mr. Zuckerberg.
- Facebook was pretty much forced, legally, to go public because it had accumulated so many shareholders. The stock hit the NASDAQ with much fanfare in May, 2012 – only to have gone pretty much straight down since. It now trades at about 50% of IPO pricing, and is under constant pressure from analysts who say it may still be overpriced.
- Facebook discovered perhaps 83million accounts were fake (about 9%) unleashing a torrent of discussion that perhaps the fake accounts was a much, much larger number.
- User growth has fallen to some 35% – which is much slower than initial investors hoped. Combined with concerns about fake accounts, there are people wondering if Facebook growth is stalling.
- Facebook has not grown revenues commensurate with user growth, and people are screaming that despite its widespread use Facebook doesn't know how to "monetize" its base into revenues and profits.
- Mobile use is growing much faster than laptop/PC use, and Facebook has not revealed any method to monetize its use on mobile devices – causing concerns that it has no plan to monetize all those users on smartphones and tablets and thus future revenues may decline.
- Zynga, a major web games supplier, announced weak earnings and said its growth was slowing – which affects Facebook because people play Zinga games on Facebook.
- GM, one of the 10 largest U.S. advertisers, publicly announced it was dropping Facebook advertising because executives believed it had insufficient return on investment. Investors now fret Facebook won't bring in major advertisers.
- Google keeps plugging away at competitive product Google+. And while Facebook disappointed investors with its earnings, much smaller competitor Linked-in announced revenues and earnings which exceeded expectations. Investors now worry about competitors dicing up the market and minimalizing Facebook's future growth.
Wow, this is enough to make 50-something CEOs of low-growth, non-tech companies jump with joy at the upending of the hoody-wearing 28 year old Facebook CEO. Zynga booted its Chief Operating Officer and has shaken up management, and not suprisingly, there are analysts now calling for Mr. Zuckerberg to step aside and install a new CEO.
Yet, Mr. Zuckerberg has been wildly successful. Much more than almost anyone else in American business today. He may well feel he needs no advice. But…. what do you suppose Steve Jobs would tell him to do?
Recall that Mr. Jobs was once the young head of Apple, only to be displaced by former Pepsi exec John Sculley — and run out of Apple. As everyone now famously knows, after a string of Apple CEOs led the company to the brink of disaster Mr. Jobs agreed to return and completely turned around Apple making it the most successful tech company of the last decade. Given what we've observed of Mr. Jobs career, and read in his biography, what advice might he give Mr. Zuckerberg?
- Don't give up your job. Not even partly. If you create a "shadow" or "co" CEO you'll be gone soon enough. Lead, quit or make the Board fire you. If you had the vision to take the company this far, why would you quit?
- Nothing is more important than product. Make Facebook's the best in the world. Nothing less will allow a tech company to survive, much less thrive. Don't become so involved with financials and analysts that you lose sight of your #1 job, which is to make the very, very best social media product in the world. Never stop improving and perfecting. If your product isn't obviously superior to other solutions you haven't accomplished your #1 priority.
- Be unique. Make sure your products fulfill needs no one else fulfills – at least not well. Meet unserved and underserved needs so that people talk about your product and what it does – not how much it costs. Make sure that Facebook has devoted, diehard customers that believe your products meet their needs so well they would not consider your competition.
- Don't ask customers what they want – give them what they need. Understand the trends and create future scenarios so you are constantly striving to create a better future, not just improve on history. Never look backward at what you've done, but instead always look forward at creating what noone else has ever done. Push your staff to create solutions that meet user needs so well that you can tell customers why they need your product in ways they never before considered.
- Turn your product releases into a show. Don't just run out new products willy-nilly, or on a random timeline. Make sure you bundle products together and make a big show of each release so you can describe the upgrades, benefits and superiority of what you offer for customers. People need to understand the trends you are meeting, and need to see the future scenario you are creating, and you have to tell them that story or they won't "get it."
- Price for profit. You run a business, not a hobby or not-for-profit society. If you do the product right you shouldn't even be talking about price – so price to make ridiculous margins by industry standards. At Apple, Next and Pixar the products were never the cheapest, but they accomplished what customers needed so well that we could price high enough to make margins that supported additional product development. And you can't remain the best solution if you don't have enough margin to keep developing future products.
- Don't expect products to sell themselves. Be the #1 passionate spokesperson for the elegance and superiority of your products. Never stop beating the drum for the unique capability and superiority of your product, in every meeting, all the time, never ending. People like to "revert to the mean" so you have to keep telling them that isn't good enough – and you have something far superior that will greatly improve their success.
- Never miss an opportunity to compare your products to competition and tell everyone why your products are far better. Don't disparage the competition, but constantly reinforce that you are first, you are ahead of everyone else, you are far better — and the best is yet to come! Competition is everywhere, and listen to the Andy Groves advice "only the paranoid survive." You aren't satisfied with what the competition offers, and customers should not be satisfied either. Every once in a while give people a small glimpse as to the radically different world you see in 3-5 years so they buy what you are selling in order to prepare for that future world.
- Identify key customers that need your solution and SELL THEM. Disney needed Pixar, so we made sure they knew it. Identify the customers who can gain the most from doing business with you and SELL THEM. Turn them into lead customers, obtain their testimonials and spread the word. If GM isn't your target, who is? Find them and sell them, then tell us all how you will build on those early accounts to eventually dominate the market – even displacing current solutions that are more popular. If GM is your target then make the changes you need to make so you can SELL THEM. Everyone wants to do business with a winner, so you must show you are a winner.
- Identify 5 of your competition's biggest customers (at Google, Yahoo, Linked-in, etc.) and make them yours. Demonstrate your solutions are superior with competitive wins.
- Hire someone who can talk to the financial community for you – and do it incredibly well. While you focus on future markets and solutions someone has to tell this story to the financial analysts in their lingo so they don't lose faith (and they are a sacrilegious lot who have no faith.) Keep Facebook out of the forecasting game, but you MUST create and maintain good communication with analysts so you need someone who can tell the story not only with products and case studies but numbers. Facebook is a disruptive innovation company, so someone has to explain why this will work. You blew the IPO road show horribly by showing up at meetings in a hoodie – so now you need to make amends by hiring someone who will give them faith that you know what you're doing and can make it happen.
These are my ideas for what Steve Jobs would tell Mark Zuckerberg. What are yours? What do you think the #1 CEO of the last decade would say to the young, embattled CEO as he faces his first test under fire leading a public company?
by Adam Hartung | Aug 9, 2012 | Current Affairs, Defend & Extend, In the Swamp, Leadership, Lock-in
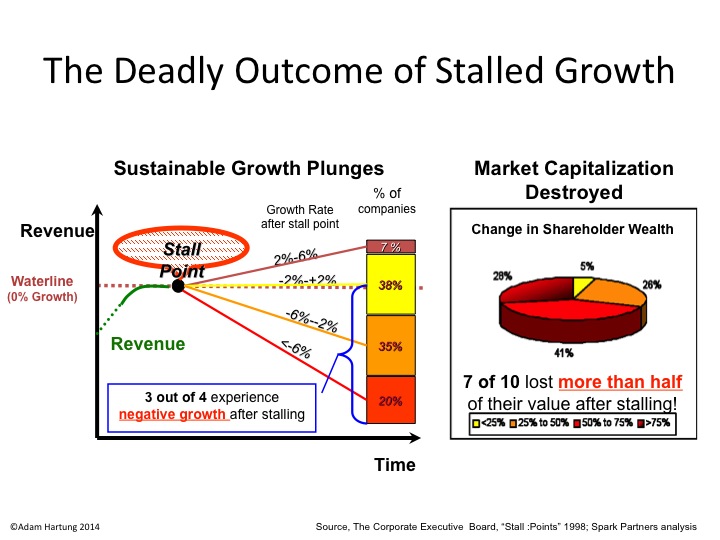
McDonald’s is in a Growth Stall. Even though the stock is less than 10% off its recent 52 week high (which is about the same high it’s had since the start of 2012,) the odds of McDonald’s equity going down are nearly 10x the odds of it achieving new highs.
A Growth Stall occurs when a company has 2 consecutive quarters of declining sales or earnings, or 2 consecutive quarters of lower sales or earnings than the previous year. And our research, in conjunction with The Conference Board, proved that when this happens the future becomes fairly easy to predict.
Growth Stalls are Deadly
When companies hit a growth Stall, 93% of the time they are unable to maintain even a 2% growth rate. 55% fall into a consistent revenue decline of more than 2%. 1 in 5 drop into a negative 6%/year revenue slide. 69% of Growth Stalled companies will lose at least half their market capitalization in just a few years. 95% will lose more than 25% of their market value.
Back in February, McDonalds sales in USA stores open at least 13 months fell 1.4%. By May these same stores reported reported their 7th consecutive month (now more than 2 quarters) of declining revenues. And in July McDonald’s reported the worst sales decline in over a decade – with stores globally selling 2.5% less (USA stores were down 3.2% for the month.) McDonald’s leadership is now warning that annual sales will be weaker than forecast – and could well be a reported decline.
While McDonald’s has been saying that Asian store revenue growth had offset the USA declines, we now can see that the USA drop is the key signal of a stall. There was no specific program in Asia to indicate that offshore revenues could create a renewed uptick in USA sales. Now with offshore sales plummeting we can see that McDonald’s American performance is the lead indicator of a company with serious performance issues.
Growth Stalls are a great forecasting tool because they indicate when a company has become “out of step” with its marketplace. While management, and in fact many analysts, will claim that this performance deficit is a short term aberration which will be repaired in coming months, historical evidence — and a plethora of case stories – tell us that in fact by the time a Growth Stall shows itself (especially in a company as large as McDonald’s) the situation is far more dire (and systemic) than management would like investors to believe.
Something fundamental has happened in the marketplace, and company leadership is busy trying to defend its historical business in the face of a major change that is pulling customers toward substitute solutions. Frequently this defend & extend approach exacerbates the problems as retrenchment efforts further hurt revenues.
McDonald’s has reached this inflection point as the result of a long string of leadership decisions which have worked to submarine long-term value.
Back in 2006 McDonald’s sold its fast growing Chipotle chain in order to raise additional funds to close some McDonald’s stores, and undertake an overhaul of the supply chain as well as many remaining stores. This one-time event was initially good for McDonald’s, but it hurt shareholders by letting go of an enormously successful revenue growth machine.
Since that sale Chipotle has outperformed McDonalds by 3x, and it was clear in 2011 that investors were better off with the faster growing Chipotle than the operationally focused McDonald’s. Desperate for revenues as its products lagged changing customer tastes, by December, 2012 McDonald’s was urging franchisees to stay open on Christmas Day in order to add just a bit more to the top line. However, such operational tactics cannot overcome a product line that is fat-and-carb-heavy and off current customer food trends, and by this July was ranked the worst burger in the marketplace. Meanwhile McDonald’s customer service this June ranked dead last in the industry. All telltale signs of the problems creating the emergent Growth Stall.
Meanwhile, McDonald’s is facing a significant attack on its business model as trends turn toward higher minimum wages. By August, 2013 the first signs of the trend were clear – and the impact on McDonald’s long-term fortunes were put in question. By February, 2014 the trend was accelerating, yet McDonald’s continued ignoring the situation. And this month the issue has become a front-and-center problem for McDonald’s investors as the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) has said it will not separate McDonald’s from its franchisees in pay and hours disputes – something which opens McDonald’s deep pockets to litigants looking to build on the living wage trend.
The McDonald’s CEO is somewhat “under seige” due to the poor revenue and earnings reports. Yet, the company continues to ascribe its Growth Stall to short-term problems such as a meat processing scandal in China. But this inverts the real situation. Such scandals are not the cause of current poor results. Rather, they are the outcome of actions taken to meet goals set by leadership pushing too hard, trying to achieve too much, by defending and extending an outdated success formula desperately in need of change to meet new competitive market conditions.
Application of Growth Stall analysis has historically been very valuable. In May, 2009 I reported on the Growth Stall at Motorola which threatened to dramatically lower company value. Subsequently Motorola spun off its money losing phone business, sold other assets and businesses, and is now a very small remnant of the business prior to its Growth Stall; which was brought on by an overwhelming market shift to smartphones from 2-way radios and traditional cell phones.
In February, 2008 a Growth Stall at General Electric indicated the company would struggle to reach historical performance for long-term investors. The stock peaked at $57.80 in 2000, then at $41.40 in July, 2007. By January, 2009 (post Stall) the company had crashed to only $10, and even recent higher valuations ($28 in 10/2013) are still far from the all-time highs – or even highs in the last decade.
In May, 2008 the Growth Stall at AIG portended big problems for the Dow Jones Industrial (DJIA) giant as financial markets continued to shift radically and quickly. By the end of 2008 AIG stock cratered and the company was forced to wipe out shareholders completely in a government-backed restructuring.
Perhaps the most compelling case has been Microsoft. By February, 2010 a Growth Stall was impending (and confirmed by May, 2011) warning of big changes for the tech giant. Mobile device sales exploded, sending Apple and Google stocks soaring, while Microsoft’s primary, core market for PCs (and software for PCs) has fallen into decline. Windows 8 subsequently had a tepid market acceptance, and gained no traction in mobile devices, causing Microsoft to write-off its investment in the Surface tablet. Recent announcements about enormous lay-offs, with vast cuts in the acquired Nokia handheld unit, do not bode well for long-term revenue growth at the decaying (yet cash rich) giant.
As the Dow has surged to record highs, it has lifted all boats. Including those companies which are showing serious problems. It is easy to look at the ubiquity of McDonald’s stores and expect the chain to remain forever dominant. But, the company is facing serious strategic problems with its products, service and business model which leadership has shown no sign of addressing. The recent Growth Stall serves as a key long-term indicator that McDonald’s is facing serious problems which will most likely seriously jeopardize investors’ (as well as employees’, suppliers’ and supporting communities’) potential returns.
by Adam Hartung | Jul 31, 2012 | Current Affairs, In the Whirlpool, Leadership, Lock-in
In a fascinating move this week, Best Buy's septuagenarion founder (who is no longer part of the company) has started calling company execs and offering them jobs – at Best Buy! Apparently he hopes to engage a private equity firm to take over Best Buy, and he wants to keep some of the exec team, while replacing others. Even more fascinating is that at last some of the execs are taking his calls, and agreeing to his "job offer." Clearly these folks have lost faith in Best Buy's future.
This happens one day after the Board of Directors fired the CEO at Supervalu, parent company of such large grocery chains as Albertson's, Jewel-Osco, ACME, Shaw's and Star Markets. Apparently this pleased most everyone, since the company has lost 85% of its equity value since he was brought in from Wal-Mart while simultaneously killing bonuses and even free employee coffee. Even though just last week he was paid a retention bonus by the same Board to remain in his job!
And even thought the Chairman at Wal-Mart was clearly in the thick of bribing Mexican officials to open stores south of the border, there is no sign of any changes expected in Wal-Mart's leadership team.
What is sparking such bizarre behavior in retail? Quite simply, industry leadership that is so stuck in the past it has no idea how to grow or make money in a dramatically changed marketplace. They keep trying to do more of the same, while growth goes elsewhere.
Everyone, and I mean everyone, outside of retail knows that the game has changed – permanently. Since 2000 on-line sales of everything, and I mean everything, has increased. Sure, there were some collosal flops in early on-line retail (remember Pets.com?) But every year sales of products on-line increase at double digit rates. It's rare to walk through a store – and I mean any store – and not see at least one customer comparison shopping the product on the shelf with an on-line vendor.
What 15 years ago was a niche seller of non-stock books, Amazon.com, has become the industry vanguard selling everything from apple juice to zombie memorabilia. Even though most industry analysts don't clump it as a direct competitor to Best Buy, Sears, and Wal-Mart – holding it aside in its own "internet retail" category – everyone knows Amazon is growing and changing shopping habits, and reducing demand in traditional stores.
The signs of this shift are everywhere. From the complete collapse of Circuit City and Sharper Image to the flat sales, reduced number of U.S. outlets and falling per-store numbers at Wal-Mart.
Across America drivers are accustomed to seeing retail outlets boarded up, and strip malls full of empty window space. You don't have to be a fancy analyst to notice how many malls would be knocked down entirely if they weren't being converted to low-cost office space for lawyers, tax preparers, dentists, veterinarians and emergency clinics – demonstrably non-retail businesses. Or to recognize an old Sears or superstore location converted into an evangelical nondenominational church.
For example, in the collar counties around Chicago vacant retail space has accumulated to over 3million square feet – a 45% increase since 2007. In that local market retail rents have fallen to $16.76 per foot, down 29% in the last four years. And this is typical of just about everywhere. America simply has a LOT more retail space than it needs – and will need for the foreseeable future. Demand for traditional retail is going down, not up, and that is a permanent change.
It is not impossible to make money in retail. But you can't do it the way it was done in the past. The answer isn't as simple as "location, location, location;" or even inventory. As the new, and struggling, CEO at JC Penney has learned the hard way, it's not about "every day low price." Or even low price at all, as the former WalMart exec just fired at Supervalu learned – along with all their employees.
Today traditional retail store success requires you have unique products, unique merchandising, sales assistance that meets immediacy needs, strong trend connectivity and effective pricing. Just look at IKEA, Lululemon, Sephora, Whole Foods, Trader Joe's and PetSmart – for example.
Of course there will be grocery stores. Traditional retail will not disappear. But that doesn't mean it will be profitable. And trying to chase profits by constantly beating down costs gets you – well – Circuit City, Toys R Us, Drug Emporium, Pay N Save, Crazy Eddie, Egghead Software, Bradlee's, Korvette's, TG&Y, Wickes, Skagg's, Payless Cashways, Musicland — and Supervalu. There is more to business than price, something the vast, vast majority of retailers keep forgetting.
Fifty years ago if you wanted a TV you went to a television store where they not only sold you a TV, they repaired it! You selected from tube-based machines made by Zenith, RCA, Philco and Magnavox. The TV shop owner made some money on the TV, but he also made money on the service. And if you wanted a washer or refrigerator you went to an "appliance store" for the same reason. But the world changed, and the need for those stores disappeared. Almost none changed to what people wanted – they simply failed.
Now the world has changed again. The customer value proposition in retail is shifting from location and inventory to information. And it is extremely hard to have salespeople – or shelf tags – with comparable information to a web page, which have not only product and price info but competitive comparisons on everything. There simply isn't enough profit in a TV, stereo, PC, CD or DVD to cover the overhead of salespeople, check-out clerks, on-hand inventory and the building.
And that's why Best Buy had to shutter 50 stores in March. On its way to the same ending as Polk Brothers, Grant's Appliance and Circuit City.
Don't expect a 70 year old retailer to understand what retail markets will look like in 2020. Or anyone trained in traditional retail at Wal-Mart. Or anyone who thinks they can save a traditional "retail brand" like Sears. The world has already shifted – and those are stories from last decade (or long before.)
If you are interested in retail go where the growth is – and that is all about on-line leadership. Sell Best Buy and put your money in Amazon. You'll sleep better.


