My last column focused on growth, and the risks inherent in a Growth stall. As I mentioned then, Apple will enter a Growth Stall if its revenue declines year-over-year in the current quarter. This forecasts Apple has only a 7% probability of consistently growing just 2%/year in the future.
This usually happens when a company falls into Defend & Extend (D&E) management. D&E management is when the bulk of management attention, and resources, flow into protecting the “core” business by seeking ways to use sustaining innovations (rather than disruptive innovations) to defend current customers and extend into new markets. Unfortunately, this rarely leads to high growth rates, and more often leads to compressed margins as growth stalls. Instead of working on breakout performance products, efforts are focused on ways to make new versions of old products that are marginally better, faster or cheaper.
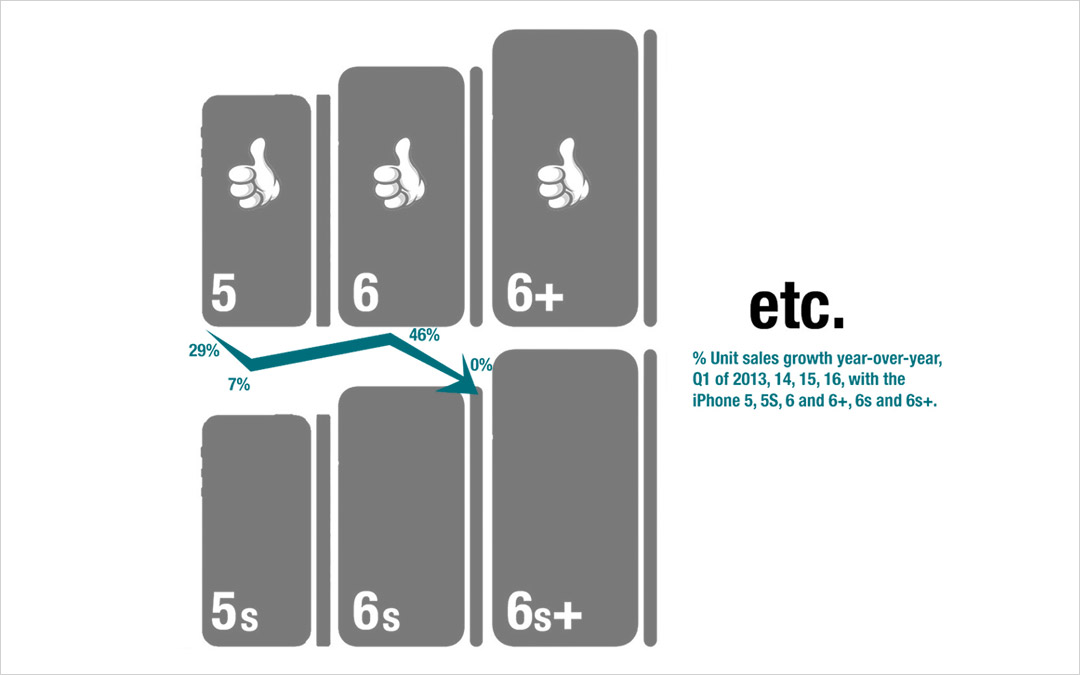 Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
Using the D&E lens, we can identify what looks like a sea change in Apple’s strategy.
For example, Apple’s CEO has trumpeted the company’s installed base of 1B iPhones, and stated they will be a future money maker. He bragged about the 20% growth in “services,” which are iPhone users taking advantage of Apple Music, iCloud storage, Apps and iTunes. This shows management’s desire to extend sales to its “installed base” with sustaining software innovations. Unfortunately, this 20% growth was a whopping $1.2B last quarter, which was 2.4% of revenues. Not nearly enough to make up for the decline in “core” iPhone, iPad or Mac sales of approximately $9.5B.
Apple has also been talking a lot about selling in China and India. Unfortunately, plans for selling in India were at least delayed, if not thwarted, by a decision on the part of India’s regulators to not allow Apple to sell low cost refurbished iPhones in the country. Fearing this was a cheap way to dispose of e-waste they are pushing Apple to develop a low-cost new iPhone for their market. Either tactic, selling the refurbished products or creating a cheaper version, are efforts at extending the “core” product sales at lower margins, in an effort to defend the historical iPhone business. Neither creates a superior product with new features, functions or benefits – but rather sustains traditional product sales.
Of even greater note was last week’s announcement that Apple inked a partnership with SAP to develop uses for iPhones and iPads built on the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platform. This announcement revealed that SAP would ask developers on its platform to program in Swift in order to support iOS devices, rather than having a PC-first mentality.
This announcement builds on last year’s similar announcement with IBM. Now 2 very large enterprise players are building applications on iOS devices. This extends the iPhone, a product long thought of as great for consumers, deeply into enterprise sales. A market long dominated by Microsoft. With these partnerships Apple is growing its developer community, while circumventing Microsoft’s long-held domain, promoting sales to companies as well as individuals.
And Apple has shown a willingness to help grow this market by introducing the iPhone 6se which is smaller and cheaper in order to obtain more traction with corporate buyers and corporate employees who have been iPhone resistant. This is a classic market extension intended to sustain sales with more applications while making no significant improvements in the “core” product itself.
And Apple’s CEO has said he intends to make more acquisitions – which will surely be done to shore up weaknesses in existing products and extend into new markets. Although Apple has over $200M of cash it can use for acquisitions, unfortunately this tactic can be a very difficult way to actually find new growth. Each would be targeted at some sort of market extension, but like Beats the impact can be hard to find.
Remember, after all revenue gains and losses were summed, Apple’s revenue fell $7.6B last quarter. Let’s look at some favorite analyst acquisition targets to explain:
- Box could be a great acquisition to help bring more enterprise developers to Apple. Box is widely used by enterprises today, and would help grow where iCloud is weak. IBM has already partnered with Box, and is working on applications in areas like financial services. Box is valued at $1.45B, so easily affordable. But it also has only $300M of annual revenue. Clearly Apple would have to unleash an enormous development program to have Box make any meaningful impact in a company with over $500B of revenue. Something akin of Instagram’s growth for Facebook would be required. But where Instagram made Facebook a pic (versus words) site, it is unclear what major change Box would bring to Apple’s product lines.
- Fitbit is considered a good buy in order to put some glamour and growth onto iWatch. Of course, iWatch already had first year sales that exceeded iPhone sales in its first year. But Apple is now so big that all numbers have to be much bigger in order to make any difference. With a valuation of $3.7B Apple could easily afford FitBit. But FitBit has only $1.9B revenue. Given that they are different technologies, it is unclear how FitBit drives iWatch growth in any meaningful way – even if Apple converted 100% of Fitbit users to the iWatch. There would need to be a “killer app” in development at FitBit that would drive $10B-$20B additional annual revenue very quickly for it to have any meaningful impact on Apple.
- GoPro is seen as a way to kick up Apple’s photography capabilities in order to make the iPhone more valuable – or perhaps developing product extensions to drive greater revenue. At a $1.45B valuation, again easily affordable. But with only $1.6B revenue there’s just not much oomph to the Apple top line. Even maximum Apple Store distribution would probably not make an enormous impact. It would take finding some new markets in industry (enterprise) to build on things like IoT to make this a growth engine – but nobody has said GoPro or Apple have any innovations in that direction. And when Amazon tried to build on fancy photography capability with its FirePhone the product was a flop.
- Tesla is seen as the savior for the Apple Car – even though nobody really knows what the latter is supposed to be. Never mind the actual business proposition, some just think Elon Musk is the perfect replacement for the late Steve Jobs. After all the excitement for its products, Tesla is valued at only $28.4B, so again easily affordable by Apple. And the thinking is that Apple would have plenty of cash to invest in much faster growth — although Apple doesn’t invest in manufacturing and has been the king of outsourcing when it comes to actually making its products. But unfortunately, Tesla has only $4B revenue – so even a rapid doubling of Tesla shipments would yield a mere 1.6% increase in Apple’s revenues.
- In a spree, Apple could buy all 4 companies! Current market value is $35B, so even including a market premium $55B-$60B should bring in the lot. There would still be plenty of cash in the bank for growth. But, realize this would add only $8B of annual revenue to the current run rate – barely 25% of what was needed to cover the gap last quarter – and less than 2% incremental growth to the new lower run rate (that magic growth percentage to pull out of a Growth Stall mentioned earlier in this column.)
Such acquisitions would also be problematic because all have P/E (price/earnings) ratios far higher than Apple’s 10.4. FitBit is 24, GoPro is 43, and both Box and Tesla are infinite because they lose money. So all would have a negative impact on earnings per share, which theoretically should lower Apple’s P/E even more.
Acquisitions get the blood pumping for investment bankers and media folks alike – but, truthfully, it is very hard to see an acquisition path that solves Apple’s revenue problem.
All of Apple’s efforts big efforts today are around sustaining innovations to defend & extend current products. No longer do we hear about gee whiz innovations, nor do we hear about growth in market changing products like iBeacons or ApplePay. Today’s discussions are how to rejuvenate sales of products that are several versions old. This may work. Sales may recover via growth in India, or a big pick-up in enterprise as people leave their PCs behind. It could happen, and Apple could avoid its Growth Stall.
But investors have the right to be concerned. Apple can grow by defending and extending the iPhone market only so long. This strategy will certainly affect future margins as prices, on average, decline. In short, investors need to know what will be Apple’s next “big thing,” and when it is likely to emerge. It will take something quite significant for Apple to maintain it’s revenue, and profit, growth.
The good news is that Apple does sell for a lowly P/E of 10 today. That is incredibly low for a company as profitable as Apple, with such a large installed base and so many market extensions – even if its growth has stalled. Even if Apple is caught in the Innovator’s Dilemma (i.e. Clayton Christensen) and shifting its strategy to defending and extending, it is very lowly valued. So the stock could continue to perform well. It just may never reach the P/E of 15 or 20 that is common for its industry peers, and investors envisioned 2 or 3 years ago. Unless there is some new, disruptive innovation in the pipeline not yet revealed to investors.

Trackbacks/Pingbacks